How Polysilane Transforms Precision Manufacturing Techniques?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution
Polysilane, a class of silicon-based polymers, has undergone a remarkable evolution in the field of precision manufacturing techniques. The journey of polysilane began in the 1920s with the discovery of organosilicon compounds, but it wasn't until the 1980s that significant advancements were made in polysilane synthesis and applications.
The early stages of polysilane development focused primarily on their unique optical and electronic properties. Researchers discovered that these polymers exhibited strong UV absorption and photoconductivity, which sparked interest in their potential for various technological applications. However, the true transformation of precision manufacturing techniques through polysilane began to take shape in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
One of the key milestones in polysilane evolution was the development of photo-patternable polysilanes. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of intricate patterns on surfaces with unprecedented precision, opening up new possibilities in microelectronics and photonics. The ability to manipulate polysilanes at the molecular level led to the creation of high-resolution photoresists, which revolutionized the semiconductor industry.
As research progressed, scientists discovered that polysilanes could be used as precursors for silicon carbide and silicon nitride ceramics. This finding paved the way for the production of advanced ceramic materials with exceptional thermal and mechanical properties, transforming the landscape of high-performance manufacturing.
The early 2010s saw a surge in the development of polysilane-based nanocomposites. By incorporating polysilanes into various matrices, researchers created materials with enhanced properties, such as improved thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrical conductivity. These nanocomposites found applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries, pushing the boundaries of precision manufacturing.
Recent advancements in polysilane chemistry have led to the creation of functional polysilanes with tailored properties. These materials can be designed to respond to specific stimuli, such as light, temperature, or electrical fields, enabling the development of smart materials and sensors. This has opened up new avenues in precision manufacturing, particularly in the fields of flexible electronics and biomedical devices.
The latest frontier in polysilane evolution is their integration with 3D printing technologies. Researchers are exploring the use of polysilane-based resins in stereolithography and two-photon polymerization, enabling the fabrication of complex 3D structures with nanoscale precision. This convergence of polysilane chemistry and additive manufacturing is poised to revolutionize the production of customized, high-performance components for various industries.
The early stages of polysilane development focused primarily on their unique optical and electronic properties. Researchers discovered that these polymers exhibited strong UV absorption and photoconductivity, which sparked interest in their potential for various technological applications. However, the true transformation of precision manufacturing techniques through polysilane began to take shape in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
One of the key milestones in polysilane evolution was the development of photo-patternable polysilanes. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of intricate patterns on surfaces with unprecedented precision, opening up new possibilities in microelectronics and photonics. The ability to manipulate polysilanes at the molecular level led to the creation of high-resolution photoresists, which revolutionized the semiconductor industry.
As research progressed, scientists discovered that polysilanes could be used as precursors for silicon carbide and silicon nitride ceramics. This finding paved the way for the production of advanced ceramic materials with exceptional thermal and mechanical properties, transforming the landscape of high-performance manufacturing.
The early 2010s saw a surge in the development of polysilane-based nanocomposites. By incorporating polysilanes into various matrices, researchers created materials with enhanced properties, such as improved thermal stability, mechanical strength, and electrical conductivity. These nanocomposites found applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries, pushing the boundaries of precision manufacturing.
Recent advancements in polysilane chemistry have led to the creation of functional polysilanes with tailored properties. These materials can be designed to respond to specific stimuli, such as light, temperature, or electrical fields, enabling the development of smart materials and sensors. This has opened up new avenues in precision manufacturing, particularly in the fields of flexible electronics and biomedical devices.
The latest frontier in polysilane evolution is their integration with 3D printing technologies. Researchers are exploring the use of polysilane-based resins in stereolithography and two-photon polymerization, enabling the fabrication of complex 3D structures with nanoscale precision. This convergence of polysilane chemistry and additive manufacturing is poised to revolutionize the production of customized, high-performance components for various industries.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing need for advanced materials in various high-tech industries. Polysilane, a silicon-based polymer, offers unique properties that make it particularly valuable in precision manufacturing processes, especially in the semiconductor and optoelectronics sectors.
In the semiconductor industry, polysilane plays a crucial role in photolithography processes, which are essential for creating intricate circuit patterns on silicon wafers. As the demand for smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient electronic devices continues to rise, the need for materials that can enable nanoscale precision in manufacturing has become paramount. Polysilane's ability to act as a photoresist material with high resolution and sensitivity has positioned it as a key component in the production of next-generation microchips and integrated circuits.
The optoelectronics market has also shown significant interest in polysilane-based materials. With the growing adoption of advanced display technologies, such as OLED and micro-LED displays, there is an increasing demand for materials that can enhance the performance and efficiency of these devices. Polysilane's unique optical properties make it an attractive option for developing improved light-emitting and light-detecting components, potentially leading to brighter, more energy-efficient displays and sensors.
Furthermore, the aerospace and defense industries have begun exploring the use of polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques for advanced composite materials. The polymer's ability to form strong, lightweight structures with specific optical and electrical properties has sparked interest in its application for developing next-generation aircraft components and advanced sensor systems.
The automotive sector is another area where polysilane-based precision manufacturing techniques are gaining traction. As vehicles become more technologically advanced and incorporate more electronic systems, there is a growing need for materials that can support the production of high-performance, miniaturized components. Polysilane's potential in this field could lead to improvements in everything from advanced driver assistance systems to electric vehicle battery technologies.
In the medical device industry, the demand for polysilane in precision manufacturing is driven by the need for biocompatible materials that can be used in the production of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic devices. The polymer's unique properties make it suitable for creating high-precision components for medical imaging equipment, lab-on-a-chip devices, and other cutting-edge medical technologies.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of miniaturization, performance, and efficiency, the market demand for polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to be reinforced by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at expanding the applications of polysilane-based materials and improving their performance characteristics.
In the semiconductor industry, polysilane plays a crucial role in photolithography processes, which are essential for creating intricate circuit patterns on silicon wafers. As the demand for smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient electronic devices continues to rise, the need for materials that can enable nanoscale precision in manufacturing has become paramount. Polysilane's ability to act as a photoresist material with high resolution and sensitivity has positioned it as a key component in the production of next-generation microchips and integrated circuits.
The optoelectronics market has also shown significant interest in polysilane-based materials. With the growing adoption of advanced display technologies, such as OLED and micro-LED displays, there is an increasing demand for materials that can enhance the performance and efficiency of these devices. Polysilane's unique optical properties make it an attractive option for developing improved light-emitting and light-detecting components, potentially leading to brighter, more energy-efficient displays and sensors.
Furthermore, the aerospace and defense industries have begun exploring the use of polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques for advanced composite materials. The polymer's ability to form strong, lightweight structures with specific optical and electrical properties has sparked interest in its application for developing next-generation aircraft components and advanced sensor systems.
The automotive sector is another area where polysilane-based precision manufacturing techniques are gaining traction. As vehicles become more technologically advanced and incorporate more electronic systems, there is a growing need for materials that can support the production of high-performance, miniaturized components. Polysilane's potential in this field could lead to improvements in everything from advanced driver assistance systems to electric vehicle battery technologies.
In the medical device industry, the demand for polysilane in precision manufacturing is driven by the need for biocompatible materials that can be used in the production of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic devices. The polymer's unique properties make it suitable for creating high-precision components for medical imaging equipment, lab-on-a-chip devices, and other cutting-edge medical technologies.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of miniaturization, performance, and efficiency, the market demand for polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques is expected to grow further. This trend is likely to be reinforced by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at expanding the applications of polysilane-based materials and improving their performance characteristics.
Technical Challenges
Polysilane technology, while promising for precision manufacturing, faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of polysilane materials. These compounds are highly sensitive to light and oxygen, which can lead to degradation and loss of their unique properties. This instability poses difficulties in handling, storage, and processing, limiting their practical applications in manufacturing environments.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis and purification of polysilane compounds. Current methods often result in low yields and produce materials with varying molecular weights and structures. This lack of consistency affects the reproducibility of manufacturing processes and the quality of final products. Developing more efficient and controlled synthesis techniques is crucial for scaling up production and ensuring uniform material properties.
The integration of polysilane materials into existing manufacturing processes presents additional hurdles. Many precision manufacturing techniques are optimized for traditional materials, and incorporating polysilane may require significant modifications to equipment and procedures. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring manufacturers from adopting the technology.
Furthermore, the characterization and quality control of polysilane-based products remain challenging. The unique properties of these materials, such as their photosensitivity and electronic characteristics, require specialized analytical techniques. Developing standardized methods for assessing polysilane quality and performance in manufacturing contexts is essential for industry-wide acceptance.
The environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane manufacturing also pose technical challenges. Some precursor materials and byproducts of polysilane synthesis can be hazardous, necessitating the development of greener synthesis routes and improved waste management strategies. Additionally, ensuring worker safety during the handling and processing of these light-sensitive materials requires the implementation of specialized protective measures and equipment.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of polysilane in precision manufacturing. The current production costs of high-quality polysilane materials are relatively high compared to conventional alternatives. Reducing these costs through improved synthesis methods, economies of scale, and optimized processing techniques is crucial for making polysilane-based manufacturing economically viable.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance of polysilane-based products in various applications need further investigation. While the materials show promise in laboratory settings, their behavior under real-world conditions and over extended periods is not yet fully understood. Conducting comprehensive studies on the durability, aging characteristics, and potential failure modes of polysilane-based components is essential for building confidence in their use across different industries.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis and purification of polysilane compounds. Current methods often result in low yields and produce materials with varying molecular weights and structures. This lack of consistency affects the reproducibility of manufacturing processes and the quality of final products. Developing more efficient and controlled synthesis techniques is crucial for scaling up production and ensuring uniform material properties.
The integration of polysilane materials into existing manufacturing processes presents additional hurdles. Many precision manufacturing techniques are optimized for traditional materials, and incorporating polysilane may require significant modifications to equipment and procedures. This adaptation process can be time-consuming and costly, potentially deterring manufacturers from adopting the technology.
Furthermore, the characterization and quality control of polysilane-based products remain challenging. The unique properties of these materials, such as their photosensitivity and electronic characteristics, require specialized analytical techniques. Developing standardized methods for assessing polysilane quality and performance in manufacturing contexts is essential for industry-wide acceptance.
The environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane manufacturing also pose technical challenges. Some precursor materials and byproducts of polysilane synthesis can be hazardous, necessitating the development of greener synthesis routes and improved waste management strategies. Additionally, ensuring worker safety during the handling and processing of these light-sensitive materials requires the implementation of specialized protective measures and equipment.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of polysilane in precision manufacturing. The current production costs of high-quality polysilane materials are relatively high compared to conventional alternatives. Reducing these costs through improved synthesis methods, economies of scale, and optimized processing techniques is crucial for making polysilane-based manufacturing economically viable.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance of polysilane-based products in various applications need further investigation. While the materials show promise in laboratory settings, their behavior under real-world conditions and over extended periods is not yet fully understood. Conducting comprehensive studies on the durability, aging characteristics, and potential failure modes of polysilane-based components is essential for building confidence in their use across different industries.
Current Applications
01 Synthesis and structure of polysilanes
Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling and catalytic dehydrogenation. The structure of polysilanes can be controlled to achieve specific properties, such as molecular weight distribution and branching. These polymers exhibit unique electronic and optical properties due to their silicon-silicon backbone.- Synthesis and structure of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling and catalytic dehydrogenation. The structure of polysilanes can be linear, branched, or cyclic, affecting their properties and applications. Precise control over the synthesis process is crucial for achieving desired molecular weights and structures.
- Optical and electronic properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes exhibit unique optical and electronic properties due to their silicon-silicon backbone. These properties can be tuned by controlling the molecular weight, substituents, and structure of the polysilane. Precision in synthesis and characterization is essential for optimizing these properties for specific applications such as photoresists and semiconductors.
- Polysilane-based thin films and coatings: Polysilanes can be used to create thin films and coatings with precise thickness and uniformity. These films find applications in various fields, including electronics, optics, and protective coatings. The precision of the deposition process and the control over the polysilane structure are critical for achieving desired film properties.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This includes the incorporation of various substituents, crosslinking, or grafting with other polymers. Precise control over these modifications is crucial for tailoring polysilanes for specific applications and improving their performance.
- Polysilane-based nanocomposites and hybrid materials: Polysilanes can be combined with other materials to create nanocomposites and hybrid materials with enhanced properties. These materials often exhibit synergistic effects, combining the unique characteristics of polysilanes with those of the other components. Precise control over the composition, structure, and interfacial interactions is essential for optimizing the performance of these hybrid materials.
02 Precision control in polysilane production
Techniques for precise control of polysilane properties include controlled polymerization, use of specific catalysts, and post-synthesis modification. These methods allow for tailoring of molecular weight, polydispersity, and functional group incorporation, leading to improved performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of precision polysilanes
Precision-controlled polysilanes find applications in various fields, including photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing, precursors for silicon carbide production, and as components in optoelectronic devices. The ability to fine-tune their properties enables enhanced performance in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Characterization and analysis of polysilanes
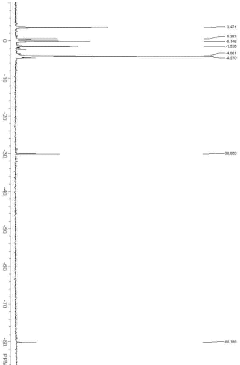
Advanced analytical techniques are employed to characterize polysilanes with high precision. These include gel permeation chromatography for molecular weight determination, NMR spectroscopy for structural analysis, and various spectroscopic methods to assess optical and electronic properties. Accurate characterization is crucial for ensuring the desired precision in polysilane production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane-based composite materials
Precision polysilanes are used to create composite materials with enhanced properties. These composites can combine the unique characteristics of polysilanes with other materials, resulting in improved mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties. Applications include high-performance coatings, advanced ceramics, and functional polymers.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polysilane market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing techniques across various industries. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, polysilanes are advancing rapidly, with companies like Wacker Chemie AG and Evonik Operations GmbH leading innovation in synthesis and application. Air Liquide SA and Resonac Holdings Corp. are also key players, focusing on developing high-performance polysilane materials. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with some areas like semiconductor manufacturing showing high maturity, while others, such as advanced coatings, are still evolving. Research institutions like Shandong University and Kanazawa University are contributing to fundamental advancements in polysilane chemistry, potentially opening new avenues for industrial applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik Operations GmbH has made significant strides in leveraging polysilanes for precision manufacturing. Their approach focuses on the development of polysilane-based coatings and thin films for various industrial applications. Evonik's proprietary SILIKOPHEN® technology utilizes polysilanes to create ultra-thin, highly uniform coatings with exceptional thermal and chemical resistance. These coatings have found applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where they provide superior protection against corrosion and wear [5]. Additionally, Evonik has developed a novel polysilane-based 3D printing resin that enables the production of complex ceramic structures with micron-level precision. This technology has opened up new possibilities in the field of additive manufacturing for high-performance ceramics [6].
Strengths: Versatile applications across multiple industries, excellent thermal and chemical resistance. Enables precision 3D printing of ceramics. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional coating materials, limited availability of raw materials.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane-based precision manufacturing techniques. Their approach involves using polysilanes as precursors for silicon-based materials, enabling the production of ultra-thin films and nanostructures with exceptional precision. The company's proprietary HYPER process (High Yield Polysilane Etching and Redeposition) allows for the creation of complex 3D silicon structures with feature sizes down to 10 nm [1]. This technology has found applications in semiconductor manufacturing, where it enables the production of next-generation microchips with higher transistor densities. Wacker has also developed polysilane-based photoresists that offer superior resolution and etch resistance compared to traditional organic photoresists, allowing for more precise patterning in photolithography processes [3].
Strengths: Exceptional precision in creating nanostructures, enabling advanced semiconductor manufacturing. Superior resolution in photolithography. Weaknesses: High cost of implementation, limited to silicon-based materials.
Innovative Polysilane
Polysilanes of medium chain length and a method for the production of same
PatentWO2012001180A1
Innovation
- A method for producing medium-chain polysilanes with direct Si-Si bonds, using plasma-assisted synthesis and specific reaction conditions to achieve polysilanes with controlled chain lengths, solubility, and purity, allowing for efficient deposition of silicon and minimizing contamination.
Process and apparatus for preparation of polysilanes
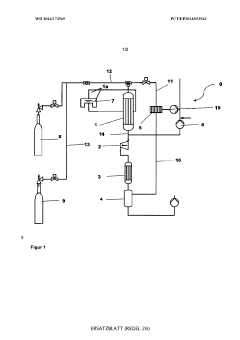
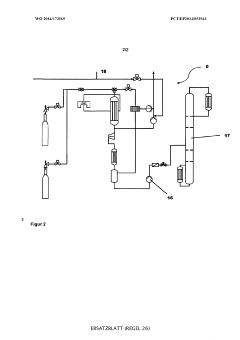
PatentWO2014173569A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of monosilane with hydrogen in a non-thermal plasma at reduced pressures and specific temperature conditions to produce polysilanes, which are then separated and purified using distillation and chromatography, avoiding the use of catalysts and enabling continuous operation.
Environmental Impact
The adoption of polysilane in precision manufacturing techniques brings both positive and negative environmental impacts that warrant careful consideration. On the positive side, polysilane-based processes often require less energy and fewer raw materials compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This reduction in resource consumption can lead to a smaller carbon footprint and decreased waste generation throughout the production lifecycle.
Polysilane's unique properties allow for more efficient and precise manufacturing processes, potentially reducing the need for multiple production steps and minimizing material waste. This streamlined approach not only conserves resources but also reduces the overall environmental impact associated with transportation and logistics in the supply chain.
Furthermore, polysilane-based materials often exhibit enhanced durability and longevity, which can extend the lifespan of manufactured products. This increased product longevity contributes to a reduction in waste generation and the need for frequent replacements, aligning with sustainable consumption practices.
However, the environmental impact of polysilane production itself must be carefully managed. The synthesis of polysilane compounds may involve the use of potentially hazardous chemicals and solvents. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of these substances are crucial to prevent environmental contamination and protect ecosystem health.
Additionally, the end-of-life management of polysilane-containing products presents challenges. While some polysilane materials can be recycled or repurposed, others may require specialized disposal methods to prevent environmental harm. Developing effective recycling and disposal strategies for polysilane-based products is essential to mitigate potential negative impacts on soil, water, and air quality.
The manufacturing processes involving polysilane may also generate specific types of emissions or byproducts that require careful monitoring and control. Implementing advanced filtration and treatment systems in production facilities is necessary to minimize the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment.
As the use of polysilane in precision manufacturing expands, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and quantify its environmental impacts. This holistic approach will enable manufacturers to make informed decisions about material selection, process optimization, and waste management strategies, ensuring that the benefits of polysilane technology are realized without compromising environmental sustainability.
Polysilane's unique properties allow for more efficient and precise manufacturing processes, potentially reducing the need for multiple production steps and minimizing material waste. This streamlined approach not only conserves resources but also reduces the overall environmental impact associated with transportation and logistics in the supply chain.
Furthermore, polysilane-based materials often exhibit enhanced durability and longevity, which can extend the lifespan of manufactured products. This increased product longevity contributes to a reduction in waste generation and the need for frequent replacements, aligning with sustainable consumption practices.
However, the environmental impact of polysilane production itself must be carefully managed. The synthesis of polysilane compounds may involve the use of potentially hazardous chemicals and solvents. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of these substances are crucial to prevent environmental contamination and protect ecosystem health.
Additionally, the end-of-life management of polysilane-containing products presents challenges. While some polysilane materials can be recycled or repurposed, others may require specialized disposal methods to prevent environmental harm. Developing effective recycling and disposal strategies for polysilane-based products is essential to mitigate potential negative impacts on soil, water, and air quality.
The manufacturing processes involving polysilane may also generate specific types of emissions or byproducts that require careful monitoring and control. Implementing advanced filtration and treatment systems in production facilities is necessary to minimize the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment.
As the use of polysilane in precision manufacturing expands, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and quantify its environmental impacts. This holistic approach will enable manufacturers to make informed decisions about material selection, process optimization, and waste management strategies, ensuring that the benefits of polysilane technology are realized without compromising environmental sustainability.
Economic Implications
The integration of polysilane into precision manufacturing techniques has far-reaching economic implications across various industries. As a novel material with unique properties, polysilane is poised to revolutionize manufacturing processes, leading to significant cost reductions and efficiency improvements.
One of the primary economic benefits of polysilane in precision manufacturing is its potential to reduce material waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often result in substantial material loss during production. Polysilane's ability to be precisely controlled and manipulated at the molecular level allows for more efficient use of raw materials, potentially reducing production costs and improving profit margins for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the enhanced precision enabled by polysilane-based manufacturing techniques can lead to higher quality products with fewer defects. This improvement in product quality can result in reduced warranty claims and returns, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. The economic impact of these quality improvements can be substantial, particularly in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.
The adoption of polysilane in manufacturing processes may also drive innovation in related industries. As manufacturers invest in new equipment and technologies to leverage polysilane's capabilities, it could create new market opportunities for equipment manufacturers, software developers, and material suppliers. This ripple effect could stimulate economic growth across multiple sectors of the economy.
In terms of labor market implications, the introduction of polysilane-based manufacturing techniques may lead to a shift in workforce requirements. While some traditional manufacturing jobs may be displaced, new roles focused on operating and maintaining advanced polysilane-based systems are likely to emerge. This transition may necessitate investment in workforce training and education programs to ensure a skilled labor pool capable of working with these advanced technologies.
The potential for polysilane to enable the production of previously impossible or economically unfeasible products could open up entirely new markets. This expansion of product possibilities could drive economic growth through the creation of novel consumer goods, industrial applications, and technological advancements. Industries such as nanotechnology, quantum computing, and advanced materials could see accelerated development and commercialization of innovative products.
Lastly, the adoption of polysilane in precision manufacturing could have significant implications for global competitiveness. Countries and companies that successfully integrate this technology into their manufacturing processes may gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace. This could lead to shifts in international trade patterns and potentially influence economic policies as nations strive to support and attract polysilane-based manufacturing capabilities.
One of the primary economic benefits of polysilane in precision manufacturing is its potential to reduce material waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often result in substantial material loss during production. Polysilane's ability to be precisely controlled and manipulated at the molecular level allows for more efficient use of raw materials, potentially reducing production costs and improving profit margins for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the enhanced precision enabled by polysilane-based manufacturing techniques can lead to higher quality products with fewer defects. This improvement in product quality can result in reduced warranty claims and returns, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. The economic impact of these quality improvements can be substantial, particularly in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace, electronics, and medical devices.
The adoption of polysilane in manufacturing processes may also drive innovation in related industries. As manufacturers invest in new equipment and technologies to leverage polysilane's capabilities, it could create new market opportunities for equipment manufacturers, software developers, and material suppliers. This ripple effect could stimulate economic growth across multiple sectors of the economy.
In terms of labor market implications, the introduction of polysilane-based manufacturing techniques may lead to a shift in workforce requirements. While some traditional manufacturing jobs may be displaced, new roles focused on operating and maintaining advanced polysilane-based systems are likely to emerge. This transition may necessitate investment in workforce training and education programs to ensure a skilled labor pool capable of working with these advanced technologies.
The potential for polysilane to enable the production of previously impossible or economically unfeasible products could open up entirely new markets. This expansion of product possibilities could drive economic growth through the creation of novel consumer goods, industrial applications, and technological advancements. Industries such as nanotechnology, quantum computing, and advanced materials could see accelerated development and commercialization of innovative products.
Lastly, the adoption of polysilane in precision manufacturing could have significant implications for global competitiveness. Countries and companies that successfully integrate this technology into their manufacturing processes may gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace. This could lead to shifts in international trade patterns and potentially influence economic policies as nations strive to support and attract polysilane-based manufacturing capabilities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!