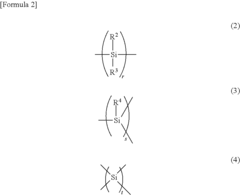How Polysilane Unlocks Evolving Communication Technologies?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution
Polysilanes have undergone a remarkable evolution since their initial discovery in the mid-20th century. These silicon-based polymers, characterized by their unique Si-Si backbone structure, have transitioned from laboratory curiosities to promising materials for advanced communication technologies.
The journey of polysilanes began with the synthesis of simple linear structures, primarily explored for their photochemical properties. As research progressed, scientists developed more complex architectures, including branched and cyclic polysilanes, expanding the potential applications of these materials.
A significant milestone in polysilane evolution was the discovery of their semiconducting properties in the 1980s. This breakthrough opened up new avenues for their use in electronic and optoelectronic devices, laying the groundwork for their potential in communication technologies.
The 1990s and early 2000s saw intensive research into improving the synthesis and processing of polysilanes. Scientists focused on enhancing their molecular weight, stability, and processability, crucial factors for practical applications. This period also witnessed the development of novel copolymers and hybrid materials, combining polysilanes with other organic or inorganic components to tailor their properties.
Recent advancements have centered on exploiting the unique electronic and optical properties of polysilanes for communication applications. Their high charge carrier mobility and tunable bandgap make them attractive candidates for next-generation semiconductor devices. Researchers have made significant progress in incorporating polysilanes into organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and field-effect transistors.
The evolution of polysilanes has also been marked by the exploration of their potential in photonics and optical communication. Their strong UV absorption and emission properties have led to investigations into their use as photoresists in lithography and as active materials in optical waveguides and switches.
As we move into the era of 5G and beyond, polysilanes are poised to play a crucial role in enabling high-speed, high-bandwidth communication technologies. Their ability to be processed into thin films and their compatibility with flexible substrates make them promising candidates for wearable and flexible communication devices.
The ongoing evolution of polysilanes continues to unlock new possibilities in communication technologies, driven by advancements in synthesis, processing, and device integration. As research progresses, these versatile materials are expected to contribute significantly to the development of faster, more efficient, and more flexible communication systems in the coming years.
The journey of polysilanes began with the synthesis of simple linear structures, primarily explored for their photochemical properties. As research progressed, scientists developed more complex architectures, including branched and cyclic polysilanes, expanding the potential applications of these materials.
A significant milestone in polysilane evolution was the discovery of their semiconducting properties in the 1980s. This breakthrough opened up new avenues for their use in electronic and optoelectronic devices, laying the groundwork for their potential in communication technologies.
The 1990s and early 2000s saw intensive research into improving the synthesis and processing of polysilanes. Scientists focused on enhancing their molecular weight, stability, and processability, crucial factors for practical applications. This period also witnessed the development of novel copolymers and hybrid materials, combining polysilanes with other organic or inorganic components to tailor their properties.
Recent advancements have centered on exploiting the unique electronic and optical properties of polysilanes for communication applications. Their high charge carrier mobility and tunable bandgap make them attractive candidates for next-generation semiconductor devices. Researchers have made significant progress in incorporating polysilanes into organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and field-effect transistors.
The evolution of polysilanes has also been marked by the exploration of their potential in photonics and optical communication. Their strong UV absorption and emission properties have led to investigations into their use as photoresists in lithography and as active materials in optical waveguides and switches.
As we move into the era of 5G and beyond, polysilanes are poised to play a crucial role in enabling high-speed, high-bandwidth communication technologies. Their ability to be processed into thin films and their compatibility with flexible substrates make them promising candidates for wearable and flexible communication devices.
The ongoing evolution of polysilanes continues to unlock new possibilities in communication technologies, driven by advancements in synthesis, processing, and device integration. As research progresses, these versatile materials are expected to contribute significantly to the development of faster, more efficient, and more flexible communication systems in the coming years.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-based technologies in evolving communication systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for faster, more efficient, and more reliable data transmission. As global data consumption continues to surge, traditional communication technologies are reaching their limits, creating a pressing demand for innovative solutions.
Polysilane, with its unique electronic and optical properties, is emerging as a promising material for next-generation communication technologies. Its potential applications span across various sectors of the communication industry, including high-speed optical interconnects, advanced photonic devices, and novel semiconductor materials for 5G and beyond.
In the optical communication sector, the demand for polysilane-based components is particularly strong. As data centers and cloud computing facilities expand, there is a growing need for high-performance optical interconnects that can handle massive data throughput with minimal latency. Polysilane's ability to efficiently transmit and modulate light signals makes it an attractive candidate for these applications.
The telecommunications industry is another key driver of polysilane demand. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the anticipated transition to 6G in the coming years, there is a substantial market for materials that can support higher frequency bands and improved signal processing. Polysilane's potential in developing high-frequency electronic components and advanced antennas aligns well with these industry requirements.
Consumer electronics represent another significant market for polysilane-based communication technologies. As smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices become increasingly sophisticated, there is a growing demand for materials that can enhance wireless communication capabilities while maintaining energy efficiency. Polysilane's properties make it a promising candidate for developing compact, high-performance antennas and other communication components in consumer devices.
The automotive sector is also emerging as a potential market for polysilane technologies, particularly in the context of connected and autonomous vehicles. These vehicles require advanced communication systems for vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure connectivity, creating opportunities for polysilane-based solutions in automotive radar systems and high-bandwidth data links.
While the market potential for polysilane in communication technologies is substantial, it is important to note that the technology is still in its early stages of commercialization. As research and development efforts continue to advance, and as manufacturing processes become more refined and cost-effective, the market demand is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
Polysilane, with its unique electronic and optical properties, is emerging as a promising material for next-generation communication technologies. Its potential applications span across various sectors of the communication industry, including high-speed optical interconnects, advanced photonic devices, and novel semiconductor materials for 5G and beyond.
In the optical communication sector, the demand for polysilane-based components is particularly strong. As data centers and cloud computing facilities expand, there is a growing need for high-performance optical interconnects that can handle massive data throughput with minimal latency. Polysilane's ability to efficiently transmit and modulate light signals makes it an attractive candidate for these applications.
The telecommunications industry is another key driver of polysilane demand. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the anticipated transition to 6G in the coming years, there is a substantial market for materials that can support higher frequency bands and improved signal processing. Polysilane's potential in developing high-frequency electronic components and advanced antennas aligns well with these industry requirements.
Consumer electronics represent another significant market for polysilane-based communication technologies. As smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices become increasingly sophisticated, there is a growing demand for materials that can enhance wireless communication capabilities while maintaining energy efficiency. Polysilane's properties make it a promising candidate for developing compact, high-performance antennas and other communication components in consumer devices.
The automotive sector is also emerging as a potential market for polysilane technologies, particularly in the context of connected and autonomous vehicles. These vehicles require advanced communication systems for vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure connectivity, creating opportunities for polysilane-based solutions in automotive radar systems and high-bandwidth data links.
While the market potential for polysilane in communication technologies is substantial, it is important to note that the technology is still in its early stages of commercialization. As research and development efforts continue to advance, and as manufacturing processes become more refined and cost-effective, the market demand is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
Polysilane technology, while promising for evolving communication technologies, faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of polysilane materials under various environmental conditions. These materials are known to be sensitive to light, heat, and oxygen, which can lead to degradation and loss of their unique electronic properties over time. This instability poses a significant hurdle for their integration into long-lasting and reliable communication devices.
Another critical challenge lies in the synthesis and processing of high-quality polysilane materials at scale. Current manufacturing methods often result in polymers with varying chain lengths and molecular weights, which can lead to inconsistent performance in electronic applications. Developing precise control over the polymerization process and achieving uniform molecular structures remains a key area of focus for researchers and engineers in this field.
The integration of polysilane materials with existing semiconductor technologies presents another set of challenges. While polysilanes show promise as alternatives to traditional silicon-based semiconductors, their compatibility with current manufacturing processes and device architectures is not yet fully established. This integration gap necessitates significant research and development efforts to create seamless interfaces between polysilane components and conventional electronic systems.
Furthermore, the electrical and optical properties of polysilanes, while promising, still require optimization for specific communication applications. Enhancing charge carrier mobility, improving light emission efficiency, and tailoring band gaps to desired specifications are ongoing areas of research. These improvements are crucial for realizing the full potential of polysilanes in high-speed data transmission and optoelectronic devices.
The cost-effectiveness of polysilane-based technologies compared to existing solutions is another hurdle that needs to be overcome. Current production methods and material costs may not yet be competitive with well-established technologies, potentially limiting their adoption in cost-sensitive markets. Developing more efficient and economical manufacturing processes is essential for making polysilane-based communication technologies commercially viable.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance of polysilane materials in real-world communication systems remain to be fully demonstrated. Extensive testing under various operational conditions and over extended periods is necessary to ensure that polysilane-based devices can meet the rigorous standards required for modern communication infrastructure. This includes assessing their resistance to environmental factors, electromagnetic interference, and long-term operational stress.
Another critical challenge lies in the synthesis and processing of high-quality polysilane materials at scale. Current manufacturing methods often result in polymers with varying chain lengths and molecular weights, which can lead to inconsistent performance in electronic applications. Developing precise control over the polymerization process and achieving uniform molecular structures remains a key area of focus for researchers and engineers in this field.
The integration of polysilane materials with existing semiconductor technologies presents another set of challenges. While polysilanes show promise as alternatives to traditional silicon-based semiconductors, their compatibility with current manufacturing processes and device architectures is not yet fully established. This integration gap necessitates significant research and development efforts to create seamless interfaces between polysilane components and conventional electronic systems.
Furthermore, the electrical and optical properties of polysilanes, while promising, still require optimization for specific communication applications. Enhancing charge carrier mobility, improving light emission efficiency, and tailoring band gaps to desired specifications are ongoing areas of research. These improvements are crucial for realizing the full potential of polysilanes in high-speed data transmission and optoelectronic devices.
The cost-effectiveness of polysilane-based technologies compared to existing solutions is another hurdle that needs to be overcome. Current production methods and material costs may not yet be competitive with well-established technologies, potentially limiting their adoption in cost-sensitive markets. Developing more efficient and economical manufacturing processes is essential for making polysilane-based communication technologies commercially viable.
Lastly, the long-term reliability and performance of polysilane materials in real-world communication systems remain to be fully demonstrated. Extensive testing under various operational conditions and over extended periods is necessary to ensure that polysilane-based devices can meet the rigorous standards required for modern communication infrastructure. This includes assessing their resistance to environmental factors, electromagnetic interference, and long-term operational stress.
Current Solutions
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
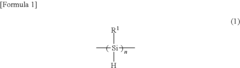
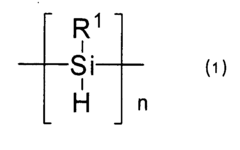
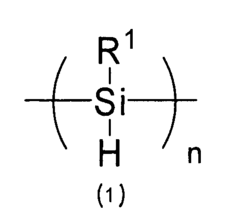
Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These materials exhibit high thermal stability and can be used in various applications such as photoresists and precursors for silicon carbide.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates and may offer benefits such as improved adhesion, thermal stability, or optical properties. The composition and processing of polysilane-based coatings can be optimized for different applications.
- Polysilanes in photoresist applications: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations for semiconductor manufacturing. Their unique properties make them suitable for lithography processes, allowing for the creation of fine patterns on substrates. The photosensitivity and etch resistance of polysilanes can be tailored for specific lithographic requirements.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This may involve the incorporation of various side groups or the creation of copolymers. These modifications can lead to improved solubility, processability, or specific optical and electronic properties.
- Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Polysilanes are employed in the development of electronic and optoelectronic devices. Their unique electronic structure and charge transport properties make them suitable for applications such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and transistors. The design and synthesis of polysilanes can be optimized for specific device requirements.
02 Polysilane-based coatings and films
Polysilanes can be used to create thin films and coatings with specific properties. These films can be applied through various methods such as spin-coating or vapor deposition. The resulting coatings exhibit properties like high refractive index, UV resistance, and improved adhesion to substrates.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilane applications in electronics
Polysilanes have found applications in electronic devices due to their unique electronic properties. They can be used as charge transport materials in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photoconductors in electrophotography, and as active layers in field-effect transistors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and modification of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This can involve the incorporation of various organic groups, crosslinking, or copolymerization with other monomers. Such modifications can lead to improved thermal stability, solubility, or specific optical properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane-based composites and hybrid materials
Polysilanes can be combined with other materials to create composites or hybrid materials with enhanced properties. These can include polysilane-based nanocomposites, organic-inorganic hybrid materials, or polysilane-modified ceramics. Such materials often exhibit improved mechanical, thermal, or optical properties compared to their individual components.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The polysilane technology market is in an early growth stage, with increasing interest from various industries due to its potential in evolving communication technologies. The market size is expanding, driven by applications in electronics, photonics, and advanced materials. While the technology is still developing, several key players are actively involved in research and development. Companies like JSR Corp., Nippon Soda Co., Ltd., and Wacker Chemie AG are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing to advance polysilane applications. Academic institutions such as the University of Rennes and research organizations like the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique are contributing to the fundamental understanding and potential applications of polysilanes, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia in this emerging field.
JSR Corp.
Technical Solution: JSR Corporation has focused on developing polysilane-based materials for next-generation communication technologies. Their research includes the creation of polysilane-containing photoresists for advanced lithography processes in semiconductor manufacturing[4]. These materials offer high resolution and sensitivity, enabling the production of smaller and more densely packed integrated circuits for communication devices. JSR has also explored the use of polysilanes in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic photovoltaics, which could lead to more energy-efficient displays and power sources for communication devices[5]. Furthermore, they have investigated polysilane-based nanocomposites for electromagnetic shielding in high-frequency communication systems[6].
Strengths: Advanced lithography applications, potential for energy-efficient devices, electromagnetic shielding capabilities. Weaknesses: May face competition from alternative materials in some applications, potential for higher material costs.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane materials for evolving communication technologies. Their approach involves synthesizing high-purity polysilanes with controlled molecular weight and structure. These materials exhibit excellent optical and electronic properties, making them suitable for photonic and optoelectronic applications[1]. Wacker's polysilanes demonstrate high photosensitivity and can be used in photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the production of smaller and more efficient communication devices[2]. Additionally, they have explored the use of polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide (SiC) production, which is crucial for high-power, high-frequency communication systems[3].
Strengths: High-purity synthesis, controlled properties, versatile applications in photonics and electronics. Weaknesses: Potential high production costs, limited scalability for some specialized applications.
Key Innovations
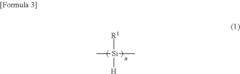
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding polysilane technology and its applications in communication technologies is a complex and evolving landscape. As polysilane continues to unlock new possibilities in the field of communications, regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the need to establish appropriate guidelines and standards.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC) play crucial roles in setting global standards for emerging communication technologies. These bodies are actively monitoring the development of polysilane-based technologies and considering their potential impact on existing regulatory frameworks.
National regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in Europe, are also closely examining the implications of polysilane technology. These agencies are responsible for allocating spectrum, ensuring interoperability, and maintaining safety standards for communication devices and infrastructure.
One of the key regulatory challenges surrounding polysilane technology is the need to balance innovation with safety and security concerns. As polysilane enables the development of more advanced and miniaturized communication devices, regulators must ensure that these devices meet stringent electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and radiation safety standards.
Another important aspect of the regulatory framework is the management of intellectual property rights related to polysilane technology. Patent offices and regulatory bodies are working to establish clear guidelines for the protection and licensing of polysilane-based innovations, which is crucial for fostering continued research and development in this field.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the adoption of polysilane technology. As the production and disposal of electronic devices become increasingly scrutinized, regulators are developing guidelines for the sustainable manufacturing and recycling of polysilane-based components.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in polysilane applications presents a challenge for regulatory bodies, which must strive to keep their frameworks up-to-date and relevant. This has led to the adoption of more flexible and adaptive regulatory approaches, such as regulatory sandboxes and technology-neutral policies, which allow for the testing and implementation of new technologies within controlled environments.
As polysilane technology continues to evolve, international cooperation and harmonization of regulatory standards will be crucial. This will help ensure a consistent approach to safety, interoperability, and market access across different regions, facilitating the global adoption of polysilane-based communication technologies.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC) play crucial roles in setting global standards for emerging communication technologies. These bodies are actively monitoring the development of polysilane-based technologies and considering their potential impact on existing regulatory frameworks.
National regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in Europe, are also closely examining the implications of polysilane technology. These agencies are responsible for allocating spectrum, ensuring interoperability, and maintaining safety standards for communication devices and infrastructure.
One of the key regulatory challenges surrounding polysilane technology is the need to balance innovation with safety and security concerns. As polysilane enables the development of more advanced and miniaturized communication devices, regulators must ensure that these devices meet stringent electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and radiation safety standards.
Another important aspect of the regulatory framework is the management of intellectual property rights related to polysilane technology. Patent offices and regulatory bodies are working to establish clear guidelines for the protection and licensing of polysilane-based innovations, which is crucial for fostering continued research and development in this field.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the adoption of polysilane technology. As the production and disposal of electronic devices become increasingly scrutinized, regulators are developing guidelines for the sustainable manufacturing and recycling of polysilane-based components.
The rapid pace of technological advancement in polysilane applications presents a challenge for regulatory bodies, which must strive to keep their frameworks up-to-date and relevant. This has led to the adoption of more flexible and adaptive regulatory approaches, such as regulatory sandboxes and technology-neutral policies, which allow for the testing and implementation of new technologies within controlled environments.
As polysilane technology continues to evolve, international cooperation and harmonization of regulatory standards will be crucial. This will help ensure a consistent approach to safety, interoperability, and market access across different regions, facilitating the global adoption of polysilane-based communication technologies.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of polysilane in evolving communication technologies is a critical aspect to consider as these materials gain prominence in the industry. Polysilanes, being silicon-based polymers, offer unique properties that make them attractive for various applications in communication technologies. However, their production, use, and disposal have both positive and negative environmental implications.
From a positive perspective, polysilanes have the potential to contribute to more energy-efficient communication devices. Their unique electronic properties allow for the development of more efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photovoltaic cells, which can lead to reduced energy consumption in communication systems. This efficiency gain can translate into lower carbon emissions associated with the operation of communication networks and devices.
Furthermore, polysilanes can be used in the fabrication of thin-film transistors and other electronic components, potentially reducing the amount of material needed in device manufacturing. This reduction in material usage can lead to a decrease in resource extraction and associated environmental impacts.
However, the production of polysilanes involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive processes. The synthesis of these materials often requires the use of organic solvents and catalysts, which can have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed. Additionally, the production of high-purity silicon, a key component in polysilanes, is an energy-intensive process that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
The disposal of polysilane-containing devices at the end of their life cycle also presents environmental challenges. While silicon-based materials are generally considered less toxic than some other electronic components, improper disposal can still lead to soil and water contamination. The recycling of polysilane-based materials is an area that requires further development to minimize environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
As communication technologies continue to evolve, the demand for polysilanes is likely to increase. This growth necessitates a comprehensive approach to mitigate potential environmental risks. Research into more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, such as green chemistry approaches and the use of renewable resources, is crucial. Additionally, the development of efficient recycling and disposal methods for polysilane-containing devices will be essential to minimize long-term environmental impacts.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer promising advancements in communication technologies, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of improved device performance and energy efficiency against the potential environmental risks associated with production and disposal is crucial for sustainable technological progress.
From a positive perspective, polysilanes have the potential to contribute to more energy-efficient communication devices. Their unique electronic properties allow for the development of more efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photovoltaic cells, which can lead to reduced energy consumption in communication systems. This efficiency gain can translate into lower carbon emissions associated with the operation of communication networks and devices.
Furthermore, polysilanes can be used in the fabrication of thin-film transistors and other electronic components, potentially reducing the amount of material needed in device manufacturing. This reduction in material usage can lead to a decrease in resource extraction and associated environmental impacts.
However, the production of polysilanes involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive processes. The synthesis of these materials often requires the use of organic solvents and catalysts, which can have negative environmental impacts if not properly managed. Additionally, the production of high-purity silicon, a key component in polysilanes, is an energy-intensive process that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
The disposal of polysilane-containing devices at the end of their life cycle also presents environmental challenges. While silicon-based materials are generally considered less toxic than some other electronic components, improper disposal can still lead to soil and water contamination. The recycling of polysilane-based materials is an area that requires further development to minimize environmental impact and promote circular economy principles.
As communication technologies continue to evolve, the demand for polysilanes is likely to increase. This growth necessitates a comprehensive approach to mitigate potential environmental risks. Research into more environmentally friendly synthesis methods, such as green chemistry approaches and the use of renewable resources, is crucial. Additionally, the development of efficient recycling and disposal methods for polysilane-containing devices will be essential to minimize long-term environmental impacts.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer promising advancements in communication technologies, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of improved device performance and energy efficiency against the potential environmental risks associated with production and disposal is crucial for sustainable technological progress.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!