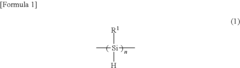
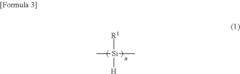
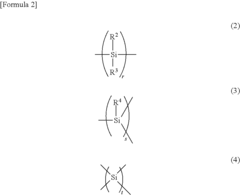Optimizing Industrial Processes with Polysilane
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Technology Evolution and Objectives
Polysilane technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the 1980s. Initially developed as a potential photoresist material for semiconductor manufacturing, polysilanes have since found applications in various industrial processes due to their unique electronic and optical properties. The technology's progression has been marked by advancements in synthesis methods, structural control, and understanding of structure-property relationships.
Early research focused on the synthesis of high molecular weight polysilanes through Wurtz-type coupling reactions. This laid the foundation for exploring their potential in optoelectronic applications. As the field matured, researchers developed more sophisticated synthesis techniques, including living anionic polymerization and ring-opening polymerization, enabling better control over molecular weight and polydispersity.
The discovery of σ-conjugation in polysilanes in the late 1980s sparked intense interest in their electronic properties. This led to investigations into their potential as conductive materials and precursors for silicon carbide ceramics. Concurrently, the photosensitivity of polysilanes was explored for applications in photolithography and as photoinitiators in various polymerization processes.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing industrial processes using polysilanes. Objectives in this area include enhancing the efficiency of photovoltaic cells, improving the performance of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and developing novel catalysts for chemical transformations. Researchers are also exploring the use of polysilanes in energy storage devices and as precursors for advanced ceramic materials.
Current technological goals involve overcoming challenges related to the stability and processability of polysilanes. Efforts are being made to develop polysilanes with improved thermal and oxidative stability, as well as enhanced solubility in common organic solvents. Another important objective is to fine-tune the electronic properties of polysilanes through structural modifications, enabling their use in a wider range of electronic and optoelectronic applications.
The integration of polysilanes into existing industrial processes is a key focus area. Researchers are working on developing scalable production methods and exploring ways to incorporate polysilanes into composite materials for enhanced performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging the unique properties of polysilanes for environmental applications, such as water purification and pollutant degradation.
As the field continues to evolve, future objectives include the development of stimuli-responsive polysilanes for smart materials and the exploration of their potential in emerging technologies like quantum computing and flexible electronics. The ongoing research aims to unlock the full potential of polysilanes in optimizing industrial processes across various sectors, from electronics to energy and environmental technologies.
Early research focused on the synthesis of high molecular weight polysilanes through Wurtz-type coupling reactions. This laid the foundation for exploring their potential in optoelectronic applications. As the field matured, researchers developed more sophisticated synthesis techniques, including living anionic polymerization and ring-opening polymerization, enabling better control over molecular weight and polydispersity.
The discovery of σ-conjugation in polysilanes in the late 1980s sparked intense interest in their electronic properties. This led to investigations into their potential as conductive materials and precursors for silicon carbide ceramics. Concurrently, the photosensitivity of polysilanes was explored for applications in photolithography and as photoinitiators in various polymerization processes.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards optimizing industrial processes using polysilanes. Objectives in this area include enhancing the efficiency of photovoltaic cells, improving the performance of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and developing novel catalysts for chemical transformations. Researchers are also exploring the use of polysilanes in energy storage devices and as precursors for advanced ceramic materials.
Current technological goals involve overcoming challenges related to the stability and processability of polysilanes. Efforts are being made to develop polysilanes with improved thermal and oxidative stability, as well as enhanced solubility in common organic solvents. Another important objective is to fine-tune the electronic properties of polysilanes through structural modifications, enabling their use in a wider range of electronic and optoelectronic applications.
The integration of polysilanes into existing industrial processes is a key focus area. Researchers are working on developing scalable production methods and exploring ways to incorporate polysilanes into composite materials for enhanced performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging the unique properties of polysilanes for environmental applications, such as water purification and pollutant degradation.
As the field continues to evolve, future objectives include the development of stimuli-responsive polysilanes for smart materials and the exploration of their potential in emerging technologies like quantum computing and flexible electronics. The ongoing research aims to unlock the full potential of polysilanes in optimizing industrial processes across various sectors, from electronics to energy and environmental technologies.
Industrial Demand for Polysilane-Based Process Optimization
The industrial demand for polysilane-based process optimization has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by the increasing need for more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes. Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, have shown remarkable potential in enhancing various industrial applications, particularly in the fields of electronics, photovoltaics, and advanced materials production.
In the electronics industry, polysilanes have garnered significant attention for their unique optoelectronic properties. Manufacturers are exploring the use of polysilanes in the production of thin-film transistors, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and other electronic components. The demand for polysilane-based solutions in this sector is expected to rise as companies seek to improve device performance and reduce production costs.
The photovoltaic industry has also shown a keen interest in polysilane-based process optimization. Polysilanes have demonstrated potential as precursors for the production of high-quality silicon films used in solar cells. This application has led to increased demand from solar panel manufacturers looking to enhance the efficiency and reduce the cost of their products.
In the field of advanced materials, polysilanes are being investigated for their ability to improve the properties of various composites and coatings. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction are exploring polysilane-based solutions to develop lighter, stronger, and more durable materials. This trend is expected to drive further demand for polysilane-based process optimization in the coming years.
The chemical industry has also recognized the potential of polysilanes in catalysis and as precursors for the synthesis of novel materials. This has led to increased research and development efforts aimed at optimizing polysilane-based processes for large-scale chemical production.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices has contributed to the rising demand for polysilane-based solutions. Polysilanes offer the potential for more environmentally friendly production processes, aligning with the global push towards greener industrial practices.
As industries continue to seek ways to improve their processes and products, the demand for polysilane-based optimization is expected to expand into new sectors. This trend is likely to drive further innovation in polysilane chemistry and its applications, opening up new opportunities for industrial optimization across various fields.
In the electronics industry, polysilanes have garnered significant attention for their unique optoelectronic properties. Manufacturers are exploring the use of polysilanes in the production of thin-film transistors, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and other electronic components. The demand for polysilane-based solutions in this sector is expected to rise as companies seek to improve device performance and reduce production costs.
The photovoltaic industry has also shown a keen interest in polysilane-based process optimization. Polysilanes have demonstrated potential as precursors for the production of high-quality silicon films used in solar cells. This application has led to increased demand from solar panel manufacturers looking to enhance the efficiency and reduce the cost of their products.
In the field of advanced materials, polysilanes are being investigated for their ability to improve the properties of various composites and coatings. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction are exploring polysilane-based solutions to develop lighter, stronger, and more durable materials. This trend is expected to drive further demand for polysilane-based process optimization in the coming years.
The chemical industry has also recognized the potential of polysilanes in catalysis and as precursors for the synthesis of novel materials. This has led to increased research and development efforts aimed at optimizing polysilane-based processes for large-scale chemical production.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices has contributed to the rising demand for polysilane-based solutions. Polysilanes offer the potential for more environmentally friendly production processes, aligning with the global push towards greener industrial practices.
As industries continue to seek ways to improve their processes and products, the demand for polysilane-based optimization is expected to expand into new sectors. This trend is likely to drive further innovation in polysilane chemistry and its applications, opening up new opportunities for industrial optimization across various fields.
Current Polysilane Applications and Challenges
Polysilanes have emerged as versatile materials with a wide range of applications in industrial processes. Currently, these silicon-based polymers are utilized in various sectors, including electronics, photonics, and materials science. In the electronics industry, polysilanes serve as precursors for silicon carbide production, which is crucial for high-power electronic devices. Their unique optical properties make them valuable in photonic applications, such as photoresists for lithography and as active layers in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
Despite their potential, the widespread adoption of polysilanes in industrial processes faces several challenges. One significant hurdle is the complexity and cost associated with their synthesis. Traditional methods often involve the use of expensive catalysts and harsh reaction conditions, limiting large-scale production. Additionally, the stability of polysilanes under various environmental conditions remains a concern, as some types are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, potentially affecting their long-term performance in industrial applications.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of polysilane molecular weight and polydispersity, which directly impacts their properties and performance in specific applications. Achieving consistent and reproducible results in polysilane synthesis is crucial for their integration into industrial processes but remains a significant technical challenge. Furthermore, the development of polysilanes with tailored properties for specific industrial applications requires extensive research and development efforts.
In the field of photonics, while polysilanes show promise as photoresists, their sensitivity and resolution still lag behind some conventional materials. Improving these characteristics is essential for their adoption in advanced lithography processes used in semiconductor manufacturing. Similarly, in the context of OLEDs, enhancing the efficiency and stability of polysilane-based devices is necessary to compete with established technologies.
The environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane production and use in industrial processes also present challenges. As with many synthetic polymers, concerns about biodegradability and potential long-term environmental effects need to be addressed. Developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods and exploring the recyclability of polysilane-based materials are important areas of ongoing research.
Despite these challenges, the unique properties of polysilanes continue to drive research and development efforts. Recent advancements in synthesis techniques, such as the development of more efficient catalysts and milder reaction conditions, are gradually addressing some of the production-related challenges. Additionally, the exploration of novel applications, such as in energy storage devices and as precursors for advanced ceramics, is expanding the potential industrial uses of polysilanes.
Despite their potential, the widespread adoption of polysilanes in industrial processes faces several challenges. One significant hurdle is the complexity and cost associated with their synthesis. Traditional methods often involve the use of expensive catalysts and harsh reaction conditions, limiting large-scale production. Additionally, the stability of polysilanes under various environmental conditions remains a concern, as some types are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, potentially affecting their long-term performance in industrial applications.
Another challenge lies in the precise control of polysilane molecular weight and polydispersity, which directly impacts their properties and performance in specific applications. Achieving consistent and reproducible results in polysilane synthesis is crucial for their integration into industrial processes but remains a significant technical challenge. Furthermore, the development of polysilanes with tailored properties for specific industrial applications requires extensive research and development efforts.
In the field of photonics, while polysilanes show promise as photoresists, their sensitivity and resolution still lag behind some conventional materials. Improving these characteristics is essential for their adoption in advanced lithography processes used in semiconductor manufacturing. Similarly, in the context of OLEDs, enhancing the efficiency and stability of polysilane-based devices is necessary to compete with established technologies.
The environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane production and use in industrial processes also present challenges. As with many synthetic polymers, concerns about biodegradability and potential long-term environmental effects need to be addressed. Developing more environmentally friendly synthesis methods and exploring the recyclability of polysilane-based materials are important areas of ongoing research.
Despite these challenges, the unique properties of polysilanes continue to drive research and development efforts. Recent advancements in synthesis techniques, such as the development of more efficient catalysts and milder reaction conditions, are gradually addressing some of the production-related challenges. Additionally, the exploration of novel applications, such as in energy storage devices and as precursors for advanced ceramics, is expanding the potential industrial uses of polysilanes.
Existing Polysilane-Based Industrial Solutions
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have a backbone consisting of silicon atoms and can be modified with different substituents. They possess interesting optical and electronic properties, making them suitable for various applications in materials science and electronics.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates and may offer benefits such as improved durability, optical properties, or electronic characteristics. The formulation and application methods of polysilane-based coatings are crucial for their performance.
- Polysilanes in photoresist applications: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations for semiconductor manufacturing. Their unique properties make them suitable for lithography processes, allowing for the creation of fine patterns on substrates. The development of polysilane-based photoresists involves optimizing their photosensitivity and resolution capabilities.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This involves adding specific chemical groups or combining polysilanes with other materials to create hybrid structures. These modifications can lead to improved performance in various applications.
- Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Polysilanes are employed in the fabrication of electronic and optoelectronic devices. Their unique electronic structure and charge transport properties make them suitable for applications such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), solar cells, and transistors. The integration of polysilanes into these devices requires careful consideration of their electronic and optical characteristics.
02 Applications in photoresists and lithography
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations and lithographic processes. Their photosensitivity and ability to undergo photochemical reactions make them valuable in the production of microelectronic devices and semiconductor manufacturing. They can be used as positive or negative photoresists, offering high resolution and good etching resistance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilane-based coatings and films
Polysilanes are employed in the development of coatings and thin films. These materials can be applied to various substrates to impart specific properties such as improved adhesion, chemical resistance, or optical characteristics. The films can be formed through spin-coating, dip-coating, or other deposition techniques.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and modification of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This includes the incorporation of various organic groups, metal atoms, or other elements into the polymer structure. Such modifications can lead to improved thermal stability, conductivity, or compatibility with other materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in optoelectronic applications
Polysilanes find applications in optoelectronic devices due to their unique electronic and optical properties. They can be used in the fabrication of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other optoelectronic components. The σ-conjugation along the silicon backbone contributes to their interesting electronic behavior.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Industry
The optimization of industrial processes with polysilane is in an emerging phase, characterized by growing market potential and ongoing technological advancements. The global market for polysilane-based solutions is expanding, driven by increasing demand for high-performance materials in various industries. Companies like Wacker Chemie AG, Evonik Operations GmbH, and Dow Silicones Corp. are at the forefront of polysilane technology development, leveraging their expertise in specialty chemicals. The technology's maturity is progressing, with research institutions such as Japan Science & Technology Agency and Kanazawa University contributing to fundamental advancements. However, the field remains dynamic, with opportunities for innovation and market penetration across different industrial applications.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane-based solutions for optimizing industrial processes. Their approach involves using high-purity polysilanes as precursors for silicon-based materials, enabling the production of ultra-thin films and coatings with enhanced properties[1]. The company has implemented a novel synthesis method that allows for precise control over the molecular weight and structure of polysilanes, resulting in improved performance in various applications[2]. Wacker's polysilane technology has been successfully applied in the semiconductor industry, where it has demonstrated significant improvements in the efficiency of photoresist materials used in lithography processes[3]. Additionally, they have explored the use of polysilanes as additives in polymer composites, enhancing thermal stability and mechanical properties in industrial components[4].
Strengths: High-purity precursors, precise molecular control, and proven applications in semiconductors. Weaknesses: Potentially high production costs and limited scalability for some applications.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik Operations GmbH has developed innovative polysilane-based solutions for industrial process optimization. Their approach focuses on utilizing polysilanes as precursors for silicon carbide (SiC) production, which has significant applications in high-temperature and high-wear environments[1]. Evonik's proprietary synthesis method allows for the creation of tailored polysilanes with specific molecular structures, enabling the production of SiC with controlled properties[2]. The company has successfully implemented this technology in the manufacturing of advanced ceramics, where polysilane-derived SiC components have shown superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to traditional materials[3]. Furthermore, Evonik has explored the use of polysilanes in the development of novel coating technologies, providing enhanced protection against corrosion and wear in industrial equipment[4].
Strengths: Tailored polysilane synthesis, advanced SiC production, and improved material properties. Weaknesses: Potentially high initial investment costs and limited applications outside of specialized industries.
Innovative Polysilane Synthesis Techniques
Polysilanes of medium chain length and a method for the production of same
PatentWO2012001180A1
Innovation
- A method for producing medium-chain polysilanes with direct Si-Si bonds, using plasma-assisted synthesis and specific reaction conditions to achieve polysilanes with controlled chain lengths, solubility, and purity, allowing for efficient deposition of silicon and minimizing contamination.
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Usage
The environmental impact of polysilane usage in industrial processes is a critical consideration as the material gains prominence in various applications. Polysilanes, being silicon-based polymers, offer unique properties that can enhance industrial efficiency. However, their production, use, and disposal have potential environmental implications that must be carefully evaluated.
The manufacturing process of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This raises concerns about carbon emissions and the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Efforts to optimize production techniques and implement cleaner technologies are ongoing to mitigate these environmental risks.
During the usage phase, polysilanes demonstrate promising environmental benefits in certain applications. For instance, when used in photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing, they can lead to more efficient processes, reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Similarly, their application in solar cell production can contribute to the advancement of renewable energy technologies, indirectly supporting environmental sustainability.
However, the long-term environmental fate of polysilanes remains a subject of ongoing research. Their degradation products and potential accumulation in ecosystems need to be thoroughly investigated to ensure they do not pose risks to wildlife or human health. Studies have shown that some polysilanes can break down into silica-based compounds, which are generally considered environmentally benign.
Waste management and disposal of polysilane-containing products present another environmental challenge. Proper recycling and disposal methods must be developed to prevent these materials from entering landfills or natural environments. The silicon content in polysilanes offers potential for recovery and reuse, which could contribute to a more circular economy approach in industrial processes.
Water pollution is another concern associated with polysilane usage. Effluents from industrial processes utilizing polysilanes must be carefully treated to remove any residual compounds or breakdown products before release into water bodies. Advanced water treatment technologies and strict regulatory compliance are essential to minimize aquatic ecosystem impacts.
As the adoption of polysilanes in industrial processes grows, life cycle assessments (LCAs) become crucial tools for evaluating their overall environmental impact. These assessments consider all stages from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing a comprehensive view of the environmental footprint associated with polysilane usage.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer potential benefits for optimizing industrial processes, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. Continued research, development of sustainable production methods, and implementation of responsible use and disposal practices are essential to ensure that the advantages of polysilane usage do not come at the cost of environmental degradation.
The manufacturing process of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. This raises concerns about carbon emissions and the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Efforts to optimize production techniques and implement cleaner technologies are ongoing to mitigate these environmental risks.
During the usage phase, polysilanes demonstrate promising environmental benefits in certain applications. For instance, when used in photoresists for semiconductor manufacturing, they can lead to more efficient processes, reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Similarly, their application in solar cell production can contribute to the advancement of renewable energy technologies, indirectly supporting environmental sustainability.
However, the long-term environmental fate of polysilanes remains a subject of ongoing research. Their degradation products and potential accumulation in ecosystems need to be thoroughly investigated to ensure they do not pose risks to wildlife or human health. Studies have shown that some polysilanes can break down into silica-based compounds, which are generally considered environmentally benign.
Waste management and disposal of polysilane-containing products present another environmental challenge. Proper recycling and disposal methods must be developed to prevent these materials from entering landfills or natural environments. The silicon content in polysilanes offers potential for recovery and reuse, which could contribute to a more circular economy approach in industrial processes.
Water pollution is another concern associated with polysilane usage. Effluents from industrial processes utilizing polysilanes must be carefully treated to remove any residual compounds or breakdown products before release into water bodies. Advanced water treatment technologies and strict regulatory compliance are essential to minimize aquatic ecosystem impacts.
As the adoption of polysilanes in industrial processes grows, life cycle assessments (LCAs) become crucial tools for evaluating their overall environmental impact. These assessments consider all stages from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing a comprehensive view of the environmental footprint associated with polysilane usage.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer potential benefits for optimizing industrial processes, their environmental impact must be carefully managed. Continued research, development of sustainable production methods, and implementation of responsible use and disposal practices are essential to ensure that the advantages of polysilane usage do not come at the cost of environmental degradation.
Polysilane Safety and Handling Protocols
Polysilane safety and handling protocols are critical aspects of optimizing industrial processes involving these versatile materials. Due to the reactive nature of polysilanes, proper safety measures and handling procedures must be implemented to ensure worker safety and process efficiency. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential when working with polysilanes, including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate respiratory protection. Proper ventilation systems should be in place to minimize exposure to potentially harmful vapors or dust particles.
Storage and transportation of polysilanes require careful consideration. These materials should be kept in tightly sealed containers in cool, dry areas away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or ignition. Incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizers or acids, must be stored separately to prevent unwanted reactions. When transporting polysilanes, use appropriate packaging and labeling in compliance with relevant regulations for hazardous materials.
Handling procedures for polysilanes should include measures to prevent static electricity buildup, as some polysilanes can be sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Grounding and bonding of equipment and containers is essential during transfer operations. Additionally, inert gas blanketing may be necessary for certain polysilane formulations to prevent unwanted reactions with atmospheric moisture or oxygen.
Emergency response protocols are crucial in the event of spills or accidental releases. Spill control kits should be readily available, and personnel must be trained in proper containment and cleanup procedures. In case of fire, appropriate extinguishing agents should be used, as water may be ineffective or even dangerous for some polysilane formulations.
Regular safety training and refresher courses should be provided to all personnel working with polysilanes. This training should cover proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the interpretation of safety data sheets (SDS). Implementing a robust safety culture and encouraging open communication about potential hazards can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and improve overall process safety.
Waste management is another critical aspect of polysilane handling protocols. Proper disposal methods must be employed to prevent environmental contamination and comply with local regulations. This may include specialized treatment processes or the use of licensed hazardous waste disposal facilities.
By adhering to these comprehensive safety and handling protocols, industrial processes involving polysilanes can be optimized for both efficiency and safety. Regular review and updating of these procedures ensure that they remain effective as technology and best practices evolve in the field of polysilane applications.
Storage and transportation of polysilanes require careful consideration. These materials should be kept in tightly sealed containers in cool, dry areas away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or ignition. Incompatible materials, such as strong oxidizers or acids, must be stored separately to prevent unwanted reactions. When transporting polysilanes, use appropriate packaging and labeling in compliance with relevant regulations for hazardous materials.
Handling procedures for polysilanes should include measures to prevent static electricity buildup, as some polysilanes can be sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Grounding and bonding of equipment and containers is essential during transfer operations. Additionally, inert gas blanketing may be necessary for certain polysilane formulations to prevent unwanted reactions with atmospheric moisture or oxygen.
Emergency response protocols are crucial in the event of spills or accidental releases. Spill control kits should be readily available, and personnel must be trained in proper containment and cleanup procedures. In case of fire, appropriate extinguishing agents should be used, as water may be ineffective or even dangerous for some polysilane formulations.
Regular safety training and refresher courses should be provided to all personnel working with polysilanes. This training should cover proper handling techniques, emergency procedures, and the interpretation of safety data sheets (SDS). Implementing a robust safety culture and encouraging open communication about potential hazards can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and improve overall process safety.
Waste management is another critical aspect of polysilane handling protocols. Proper disposal methods must be employed to prevent environmental contamination and comply with local regulations. This may include specialized treatment processes or the use of licensed hazardous waste disposal facilities.
By adhering to these comprehensive safety and handling protocols, industrial processes involving polysilanes can be optimized for both efficiency and safety. Regular review and updating of these procedures ensure that they remain effective as technology and best practices evolve in the field of polysilane applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!