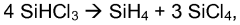How Polysilane Fuels Hybrid Manufacturing Processes?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane in Hybrid Manufacturing: Background and Objectives
Polysilane, a class of silicon-based polymers, has emerged as a promising material in the field of hybrid manufacturing processes. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers first synthesized and characterized polysilanes. Since then, the field has witnessed significant advancements, driven by the unique properties of these materials and their potential applications in various industries.
The technological trajectory of polysilanes in hybrid manufacturing has been shaped by the increasing demand for advanced materials with tailored properties. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for materials that can bridge the gap between traditional and emerging fabrication techniques. Polysilanes, with their versatile chemical structure and tunable properties, have positioned themselves as ideal candidates for this role.
One of the key trends in the evolution of polysilane technology is the development of hybrid manufacturing processes that combine additive and subtractive techniques. These processes leverage the photosensitive nature of polysilanes, allowing for precise patterning and structuring of materials at the micro and nanoscale. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards more flexible and efficient manufacturing methods in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and biomedical engineering.
The primary technological objectives in the field of polysilane-fueled hybrid manufacturing processes are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a focus on enhancing the processability of polysilanes to make them compatible with a wider range of manufacturing techniques. This includes improving their solubility, thermal stability, and mechanical properties to enable seamless integration into existing production lines.
Secondly, researchers aim to expand the functional capabilities of polysilane-based materials. This involves developing new polysilane derivatives with enhanced optical, electrical, or chemical properties that can be exploited in specific applications. For instance, the development of photopatternable polysilanes with improved resolution and sensitivity is crucial for advancing microfabrication techniques.
Another important objective is to optimize the interface between polysilanes and other materials in hybrid structures. This is essential for creating multi-functional components that combine the unique properties of polysilanes with those of other materials, such as metals, ceramics, or organic polymers. Achieving strong and stable interfaces is critical for the performance and reliability of hybrid manufactured products.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations in polysilane research. Efforts are being made to develop eco-friendly synthesis methods and explore biodegradable polysilane variants. This aligns with the broader trend towards green manufacturing and circular economy principles in the industry.
The technological trajectory of polysilanes in hybrid manufacturing has been shaped by the increasing demand for advanced materials with tailored properties. As manufacturing processes become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for materials that can bridge the gap between traditional and emerging fabrication techniques. Polysilanes, with their versatile chemical structure and tunable properties, have positioned themselves as ideal candidates for this role.
One of the key trends in the evolution of polysilane technology is the development of hybrid manufacturing processes that combine additive and subtractive techniques. These processes leverage the photosensitive nature of polysilanes, allowing for precise patterning and structuring of materials at the micro and nanoscale. This trend aligns with the broader movement towards more flexible and efficient manufacturing methods in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and biomedical engineering.
The primary technological objectives in the field of polysilane-fueled hybrid manufacturing processes are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a focus on enhancing the processability of polysilanes to make them compatible with a wider range of manufacturing techniques. This includes improving their solubility, thermal stability, and mechanical properties to enable seamless integration into existing production lines.
Secondly, researchers aim to expand the functional capabilities of polysilane-based materials. This involves developing new polysilane derivatives with enhanced optical, electrical, or chemical properties that can be exploited in specific applications. For instance, the development of photopatternable polysilanes with improved resolution and sensitivity is crucial for advancing microfabrication techniques.
Another important objective is to optimize the interface between polysilanes and other materials in hybrid structures. This is essential for creating multi-functional components that combine the unique properties of polysilanes with those of other materials, such as metals, ceramics, or organic polymers. Achieving strong and stable interfaces is critical for the performance and reliability of hybrid manufactured products.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations in polysilane research. Efforts are being made to develop eco-friendly synthesis methods and explore biodegradable polysilane variants. This aligns with the broader trend towards green manufacturing and circular economy principles in the industry.
Market Analysis for Polysilane-Based Hybrid Manufacturing
The market for polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced materials in various industries. Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, have emerged as versatile materials with unique properties that make them ideal for hybrid manufacturing applications. These applications span across multiple sectors, including electronics, aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
In the electronics industry, polysilanes are gaining traction due to their excellent photosensitivity and semiconductor properties. The market for polysilane-based electronic components is expected to grow as manufacturers seek more efficient and cost-effective materials for producing high-performance devices. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing, particularly for the production of lightweight components and advanced sensors.
The aerospace industry represents another significant market for polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing. The material's high thermal stability and resistance to extreme conditions make it suitable for producing components used in aircraft and spacecraft. As the space exploration and satellite industries continue to expand, the demand for polysilane-based materials is likely to increase.
In the healthcare sector, polysilanes are finding applications in the production of medical devices and drug delivery systems. The biocompatibility and controllable degradation properties of certain polysilane formulations make them attractive for use in implantable devices and tissue engineering scaffolds.
The global market for polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing is characterized by regional variations in adoption and growth rates. North America and Europe currently lead in terms of market share, owing to their well-established manufacturing sectors and strong focus on technological innovation. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key factors influencing market growth include ongoing research and development efforts to enhance the properties and applications of polysilanes, as well as the increasing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. The ability of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing to reduce material waste and energy consumption aligns well with global sustainability goals, further driving market expansion.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized equipment and expertise may hinder widespread adoption in some sectors. However, as the technology matures and becomes more accessible, these barriers are expected to diminish, leading to broader market penetration and increased opportunities for growth in polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes.
In the electronics industry, polysilanes are gaining traction due to their excellent photosensitivity and semiconductor properties. The market for polysilane-based electronic components is expected to grow as manufacturers seek more efficient and cost-effective materials for producing high-performance devices. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing, particularly for the production of lightweight components and advanced sensors.
The aerospace industry represents another significant market for polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing. The material's high thermal stability and resistance to extreme conditions make it suitable for producing components used in aircraft and spacecraft. As the space exploration and satellite industries continue to expand, the demand for polysilane-based materials is likely to increase.
In the healthcare sector, polysilanes are finding applications in the production of medical devices and drug delivery systems. The biocompatibility and controllable degradation properties of certain polysilane formulations make them attractive for use in implantable devices and tissue engineering scaffolds.
The global market for polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing is characterized by regional variations in adoption and growth rates. North America and Europe currently lead in terms of market share, owing to their well-established manufacturing sectors and strong focus on technological innovation. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies.
Key factors influencing market growth include ongoing research and development efforts to enhance the properties and applications of polysilanes, as well as the increasing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. The ability of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing to reduce material waste and energy consumption aligns well with global sustainability goals, further driving market expansion.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized equipment and expertise may hinder widespread adoption in some sectors. However, as the technology matures and becomes more accessible, these barriers are expected to diminish, leading to broader market penetration and increased opportunities for growth in polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes.
Current Challenges in Polysilane Hybrid Manufacturing
Polysilane hybrid manufacturing processes face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of integrating polysilane materials into existing manufacturing workflows. The unique properties of polysilanes, such as their sensitivity to light and temperature, require careful handling and precise control throughout the manufacturing process.
The stability of polysilane materials during processing remains a critical concern. These compounds can undergo undesired decomposition or cross-linking reactions when exposed to certain environmental conditions, leading to inconsistent product quality and reduced performance. Developing robust stabilization techniques and protective measures is essential to maintain the integrity of polysilanes throughout the hybrid manufacturing process.
Another challenge lies in achieving uniform dispersion and distribution of polysilane components within the hybrid material matrix. Inadequate dispersion can result in inhomogeneous properties and compromised performance of the final product. Researchers and manufacturers are actively exploring advanced mixing and dispersion techniques to address this issue and ensure consistent material properties across the manufactured components.
The scalability of polysilane hybrid manufacturing processes presents a significant hurdle for industrial applications. While laboratory-scale production has shown promising results, translating these processes to large-scale manufacturing environments poses technical and economic challenges. Optimizing process parameters, equipment design, and material handling systems for high-volume production remains an active area of research and development.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes is a concern for commercial viability. The synthesis and purification of high-quality polysilane precursors can be expensive, potentially limiting their adoption in price-sensitive industries. Efforts are underway to develop more efficient and economical production methods for polysilanes to make them more competitive with traditional manufacturing materials.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane hybrid manufacturing processes require careful attention. Some polysilane compounds may pose health and environmental risks if not properly handled or disposed of. Developing green synthesis routes, implementing effective waste management strategies, and ensuring worker safety throughout the manufacturing process are crucial challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable implementation of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing technologies.
The stability of polysilane materials during processing remains a critical concern. These compounds can undergo undesired decomposition or cross-linking reactions when exposed to certain environmental conditions, leading to inconsistent product quality and reduced performance. Developing robust stabilization techniques and protective measures is essential to maintain the integrity of polysilanes throughout the hybrid manufacturing process.
Another challenge lies in achieving uniform dispersion and distribution of polysilane components within the hybrid material matrix. Inadequate dispersion can result in inhomogeneous properties and compromised performance of the final product. Researchers and manufacturers are actively exploring advanced mixing and dispersion techniques to address this issue and ensure consistent material properties across the manufactured components.
The scalability of polysilane hybrid manufacturing processes presents a significant hurdle for industrial applications. While laboratory-scale production has shown promising results, translating these processes to large-scale manufacturing environments poses technical and economic challenges. Optimizing process parameters, equipment design, and material handling systems for high-volume production remains an active area of research and development.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes is a concern for commercial viability. The synthesis and purification of high-quality polysilane precursors can be expensive, potentially limiting their adoption in price-sensitive industries. Efforts are underway to develop more efficient and economical production methods for polysilanes to make them more competitive with traditional manufacturing materials.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane hybrid manufacturing processes require careful attention. Some polysilane compounds may pose health and environmental risks if not properly handled or disposed of. Developing green synthesis routes, implementing effective waste management strategies, and ensuring worker safety throughout the manufacturing process are crucial challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable implementation of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing technologies.
Existing Polysilane-Based Hybrid Manufacturing Solutions
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates to impart characteristics such as improved durability, optical properties, or electrical conductivity. The composition and processing of polysilane-based coatings can be optimized for different applications.
- Polysilanes in photoresist and lithography applications: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations and lithography processes. Their unique optical and electronic properties make them suitable for use in semiconductor manufacturing and other microfabrication techniques. The photosensitivity and etch resistance of polysilanes can be exploited in these applications.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This includes the incorporation of various side groups, crosslinking, or combining polysilanes with other materials to create hybrid structures. These modifications allow for the tailoring of polysilanes for specific applications.
- Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Polysilanes are employed in the development of electronic and optoelectronic devices. Their unique electronic structure and charge transport properties make them suitable for applications such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other semiconductor devices. The processing and integration of polysilanes into these devices are areas of ongoing research.
02 Polysilane-based coatings and films
Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates and may offer benefits such as improved durability, optical properties, or electronic characteristics. The formulation and application methods of polysilane coatings are crucial for their performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilanes in photoresist applications
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations for semiconductor manufacturing. Their unique properties make them suitable for lithography processes, allowing for the creation of fine patterns on substrates. The development of polysilane-based photoresists aims to improve resolution and sensitivity in microelectronics fabrication.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and modification of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This includes the addition of various side groups or the incorporation of other elements into the polymer backbone. These modifications allow for the tailoring of polysilanes for specific applications or to improve their compatibility with other materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in composite materials
Polysilanes are incorporated into composite materials to impart unique properties or enhance existing characteristics. These composites may combine polysilanes with other polymers, inorganic materials, or nanoparticles. The resulting materials can exhibit improved mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties, making them suitable for various advanced applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane and Hybrid Manufacturing Industry
The polysilane-fueled hybrid manufacturing processes market is in an early growth stage, characterized by increasing research and development activities. While the market size remains relatively small, it shows promising potential due to the unique properties of polysilanes in advanced manufacturing applications. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different companies. Key players like Wacker Chemie AG, Air Liquide SA, and Momentive Performance Materials, Inc. are at the forefront of polysilane development, leveraging their expertise in specialty chemicals and materials science. Other companies such as Evonik Operations GmbH and JSR Corp. are also making significant strides in this field, contributing to the overall advancement of polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing technologies.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane-based hybrid manufacturing processes. Their approach involves using polysilanes as precursors for silicon-based ceramics and composites. The company's proprietary SICATEC® technology utilizes polysilanes to create silicon carbide fibers and matrices for high-performance ceramic matrix composites (CMCs)[1]. This process allows for the production of complex-shaped components with excellent thermal and mechanical properties. Wacker has also pioneered the use of polysilanes in additive manufacturing, enabling the 3D printing of silicon-based ceramics with unprecedented precision and material properties[2]. Their hybrid manufacturing approach combines traditional ceramic processing techniques with polysilane chemistry to achieve unique material structures and performance characteristics.
Strengths: Proprietary technology for high-performance CMCs, expertise in polysilane chemistry, and integration with additive manufacturing. Weaknesses: High production costs and limited scalability for mass production.
Dow Silicones Corp.
Technical Solution: Dow Silicones Corp. has developed a hybrid manufacturing process that leverages polysilanes for advanced silicone materials production. Their approach involves using polysilanes as precursors for the synthesis of novel silicone polymers with enhanced properties. The company's proprietary SILASTIC™ technology incorporates polysilane-derived building blocks into silicone elastomers, resulting in improved thermal stability and mechanical strength[3]. Dow's hybrid process also enables the creation of silicone-organic copolymers with unique functionalities, such as self-healing properties and enhanced adhesion to various substrates[4]. By combining traditional silicone manufacturing techniques with polysilane chemistry, Dow has achieved breakthroughs in material performance for applications in electronics, automotive, and healthcare industries.
Strengths: Extensive expertise in silicone chemistry, wide range of applications, and established market presence. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns related to silicone production and limited biodegradability of end products.
Core Innovations in Polysilane Hybrid Manufacturing Processes
Process for preparing polysilanes
PatentInactiveEP0382651A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of silane monomers with sodium in a solvent mixture of toluene and dioxane, followed by filtration and sodium oxidation, which produces a low-viscosity, crosslinkable polysilane that can be easily transformed into silicon carbide with minimal mass loss and improved polydispersity.
Production of silanes by grinding silica grains mixed with a metal such as mg or al in a hydrogen atmosphere
PatentWO2011036389A1
Innovation
- A process involving the introduction of silica grains mixed with magnesium or aluminum into a ball mill reactor under a hydrogen atmosphere, where the silica is crushed by agitated refractory balls, generating silanes efficiently at reduced temperatures and pressures, followed by fractional distillation to separate monosilane from higher silanes.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane in Manufacturing
The environmental impact of polysilane in manufacturing processes is a critical consideration as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. Polysilane, a silicon-based polymer, has gained attention for its potential to fuel hybrid manufacturing processes, but its environmental footprint must be carefully evaluated.
Polysilane production typically involves energy-intensive processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. However, advancements in synthesis techniques have led to more efficient production methods, reducing the overall energy consumption. The use of renewable energy sources in polysilane manufacturing facilities can further mitigate these environmental concerns.
One of the key environmental benefits of polysilane in hybrid manufacturing is its potential to reduce material waste. Polysilane-based processes often allow for more precise control over material deposition, resulting in less excess material and fewer byproducts. This efficiency can lead to a significant reduction in raw material consumption and waste generation throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Water usage is another important environmental factor to consider. While some polysilane manufacturing processes require water for cooling or as a reaction medium, innovative closed-loop systems have been developed to minimize water consumption and promote recycling. These advancements help to reduce the overall water footprint of polysilane-fueled hybrid manufacturing.
The end-of-life considerations for polysilane-based products are also crucial. Research has shown that many polysilane compounds can be recycled or repurposed, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with disposal. However, the development of efficient recycling processes for polysilane-containing materials is still an area that requires further investigation and improvement.
Emissions from polysilane during manufacturing processes are generally low compared to traditional petrochemical-based materials. The silicon-based nature of polysilane often results in fewer volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, contributing to better air quality in manufacturing environments. Additionally, the potential for polysilane to enable room-temperature processing in some applications can lead to reduced energy consumption and associated emissions.
As the industry continues to explore the use of polysilane in hybrid manufacturing, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important. These comprehensive analyses help to quantify the environmental impacts across all stages of polysilane production, use, and disposal. Early LCA studies have shown promising results, indicating that polysilane-fueled processes may offer environmental advantages over traditional manufacturing methods in certain applications.
Polysilane production typically involves energy-intensive processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. However, advancements in synthesis techniques have led to more efficient production methods, reducing the overall energy consumption. The use of renewable energy sources in polysilane manufacturing facilities can further mitigate these environmental concerns.
One of the key environmental benefits of polysilane in hybrid manufacturing is its potential to reduce material waste. Polysilane-based processes often allow for more precise control over material deposition, resulting in less excess material and fewer byproducts. This efficiency can lead to a significant reduction in raw material consumption and waste generation throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Water usage is another important environmental factor to consider. While some polysilane manufacturing processes require water for cooling or as a reaction medium, innovative closed-loop systems have been developed to minimize water consumption and promote recycling. These advancements help to reduce the overall water footprint of polysilane-fueled hybrid manufacturing.
The end-of-life considerations for polysilane-based products are also crucial. Research has shown that many polysilane compounds can be recycled or repurposed, potentially reducing the environmental impact associated with disposal. However, the development of efficient recycling processes for polysilane-containing materials is still an area that requires further investigation and improvement.
Emissions from polysilane during manufacturing processes are generally low compared to traditional petrochemical-based materials. The silicon-based nature of polysilane often results in fewer volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, contributing to better air quality in manufacturing environments. Additionally, the potential for polysilane to enable room-temperature processing in some applications can lead to reduced energy consumption and associated emissions.
As the industry continues to explore the use of polysilane in hybrid manufacturing, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important. These comprehensive analyses help to quantify the environmental impacts across all stages of polysilane production, use, and disposal. Early LCA studies have shown promising results, indicating that polysilane-fueled processes may offer environmental advantages over traditional manufacturing methods in certain applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Polysilane Hybrid Manufacturing
The cost-benefit analysis of polysilane hybrid manufacturing reveals a complex interplay of economic factors and technological advantages. Initial investment costs for implementing polysilane-based processes can be substantial, primarily due to the need for specialized equipment and facilities. However, these upfront expenses are often offset by the long-term benefits and efficiency gains.
One of the primary advantages of polysilane hybrid manufacturing is its potential for significant cost reduction in material usage. Polysilanes, as precursors for various silicon-based materials, offer improved yield and reduced waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This efficiency translates into lower raw material costs and decreased environmental impact, both of which contribute positively to the overall cost-benefit equation.
Energy consumption is another critical factor in the analysis. Polysilane-based processes often require lower processing temperatures compared to conventional methods, leading to reduced energy costs. This energy efficiency not only lowers operational expenses but also aligns with sustainability goals, potentially offering additional benefits in terms of regulatory compliance and corporate social responsibility.
The versatility of polysilanes in hybrid manufacturing processes presents opportunities for product diversification and market expansion. By enabling the production of novel materials and components with enhanced properties, polysilane technology can open up new revenue streams and increase market share. This potential for innovation and product differentiation must be weighed against the research and development costs associated with bringing new polysilane-based products to market.
Quality improvements and reduced defect rates are significant benefits of polysilane hybrid manufacturing. The precise control over material properties at the molecular level leads to more consistent and higher-quality outputs. This improvement in quality can result in reduced warranty claims, increased customer satisfaction, and potentially higher profit margins for premium products.
However, the analysis must also consider potential challenges. The relative novelty of polysilane technology in some applications may lead to a learning curve and initial productivity losses. Additionally, the supply chain for polysilane precursors may be less established than for traditional materials, potentially leading to supply volatility and price fluctuations.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of adopting polysilane hybrid manufacturing can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of material efficiency, energy savings, product quality, and innovation potential often outweigh these expenses. Companies must carefully evaluate their specific manufacturing needs, market position, and long-term strategic goals to determine if the investment in polysilane technology aligns with their overall business objectives.
One of the primary advantages of polysilane hybrid manufacturing is its potential for significant cost reduction in material usage. Polysilanes, as precursors for various silicon-based materials, offer improved yield and reduced waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This efficiency translates into lower raw material costs and decreased environmental impact, both of which contribute positively to the overall cost-benefit equation.
Energy consumption is another critical factor in the analysis. Polysilane-based processes often require lower processing temperatures compared to conventional methods, leading to reduced energy costs. This energy efficiency not only lowers operational expenses but also aligns with sustainability goals, potentially offering additional benefits in terms of regulatory compliance and corporate social responsibility.
The versatility of polysilanes in hybrid manufacturing processes presents opportunities for product diversification and market expansion. By enabling the production of novel materials and components with enhanced properties, polysilane technology can open up new revenue streams and increase market share. This potential for innovation and product differentiation must be weighed against the research and development costs associated with bringing new polysilane-based products to market.
Quality improvements and reduced defect rates are significant benefits of polysilane hybrid manufacturing. The precise control over material properties at the molecular level leads to more consistent and higher-quality outputs. This improvement in quality can result in reduced warranty claims, increased customer satisfaction, and potentially higher profit margins for premium products.
However, the analysis must also consider potential challenges. The relative novelty of polysilane technology in some applications may lead to a learning curve and initial productivity losses. Additionally, the supply chain for polysilane precursors may be less established than for traditional materials, potentially leading to supply volatility and price fluctuations.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of adopting polysilane hybrid manufacturing can be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of material efficiency, energy savings, product quality, and innovation potential often outweigh these expenses. Companies must carefully evaluate their specific manufacturing needs, market position, and long-term strategic goals to determine if the investment in polysilane technology aligns with their overall business objectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!