How To Minimize Thermal Losses In TEG System Installation Best Practices
SEP 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
TEG Thermal Efficiency Background and Objectives
Thermoelectric generators (TEGs) have emerged as a promising technology for energy harvesting, converting waste heat directly into electrical energy through the Seebeck effect. The evolution of TEG technology dates back to the early 19th century with the discovery of thermoelectric phenomena, but significant practical applications only materialized in the mid-20th century, primarily in specialized fields like space exploration and remote power generation.
The technological trajectory of TEGs has been characterized by incremental improvements in material science, manufacturing techniques, and system integration. Early TEG systems exhibited conversion efficiencies of merely 2-3%, limiting their widespread adoption. However, recent advancements in semiconductor materials, particularly skutterudites, half-Heusler alloys, and nanostructured materials, have pushed theoretical efficiency boundaries toward 15-20%, though practical systems typically achieve 5-8% efficiency.
A critical challenge in TEG implementation remains thermal management—specifically minimizing heat losses that directly impact system performance. Thermal losses occur through various mechanisms including radiation, convection, conduction through support structures, and parasitic heat flows. These losses significantly reduce the temperature gradient across thermoelectric modules, which is the primary driver of power generation in TEG systems.
The technical objectives for advancing TEG installation practices focus on maximizing the temperature differential between hot and cold sides while minimizing unintended thermal pathways. This includes developing optimal thermal interface materials, designing efficient heat exchangers, implementing strategic insulation techniques, and creating installation methodologies that maintain system integrity under thermal cycling conditions.
Industry benchmarks indicate that well-designed TEG systems can capture up to 80% of available thermal energy for conversion purposes, with the remaining 20% lost through various inefficiencies. However, suboptimal installation practices frequently result in systems operating at 40-60% of their theoretical capacity, representing a substantial performance gap that can be addressed through improved installation protocols.
The economic implications of thermal efficiency improvements are substantial. Analysis suggests that each percentage point improvement in thermal efficiency typically translates to a 3-5% increase in power output, directly affecting return on investment calculations. For industrial waste heat recovery applications, this can mean the difference between economically viable and non-viable implementations.
As global emphasis on energy efficiency and carbon reduction intensifies, optimizing TEG thermal performance through superior installation practices represents a significant opportunity to expand the practical application range of this technology across sectors including automotive, industrial manufacturing, and distributed power generation.
The technological trajectory of TEGs has been characterized by incremental improvements in material science, manufacturing techniques, and system integration. Early TEG systems exhibited conversion efficiencies of merely 2-3%, limiting their widespread adoption. However, recent advancements in semiconductor materials, particularly skutterudites, half-Heusler alloys, and nanostructured materials, have pushed theoretical efficiency boundaries toward 15-20%, though practical systems typically achieve 5-8% efficiency.
A critical challenge in TEG implementation remains thermal management—specifically minimizing heat losses that directly impact system performance. Thermal losses occur through various mechanisms including radiation, convection, conduction through support structures, and parasitic heat flows. These losses significantly reduce the temperature gradient across thermoelectric modules, which is the primary driver of power generation in TEG systems.
The technical objectives for advancing TEG installation practices focus on maximizing the temperature differential between hot and cold sides while minimizing unintended thermal pathways. This includes developing optimal thermal interface materials, designing efficient heat exchangers, implementing strategic insulation techniques, and creating installation methodologies that maintain system integrity under thermal cycling conditions.
Industry benchmarks indicate that well-designed TEG systems can capture up to 80% of available thermal energy for conversion purposes, with the remaining 20% lost through various inefficiencies. However, suboptimal installation practices frequently result in systems operating at 40-60% of their theoretical capacity, representing a substantial performance gap that can be addressed through improved installation protocols.
The economic implications of thermal efficiency improvements are substantial. Analysis suggests that each percentage point improvement in thermal efficiency typically translates to a 3-5% increase in power output, directly affecting return on investment calculations. For industrial waste heat recovery applications, this can mean the difference between economically viable and non-viable implementations.
As global emphasis on energy efficiency and carbon reduction intensifies, optimizing TEG thermal performance through superior installation practices represents a significant opportunity to expand the practical application range of this technology across sectors including automotive, industrial manufacturing, and distributed power generation.
Market Analysis for High-Efficiency TEG Systems
The global market for high-efficiency Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for waste heat recovery solutions across multiple industries. The TEG market was valued at approximately $460 million in 2022 and is projected to reach $720 million by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.4%. This growth trajectory is supported by the rising focus on energy efficiency and sustainable practices across industrial sectors.
The automotive industry represents the largest market segment for TEG systems, accounting for nearly 35% of the total market share. Major automotive manufacturers are increasingly incorporating TEG technology to recover waste heat from exhaust systems, improving fuel efficiency by 2-5% depending on driving conditions and system integration. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent emission regulations such as Europe and North America.
Industrial manufacturing constitutes the second-largest market segment at approximately 28% of the market share. Process industries with high-temperature operations, including steel, glass, and cement manufacturing, present substantial opportunities for TEG implementation. These industries typically generate significant waste heat that can be effectively converted to usable electricity through properly installed TEG systems.
The aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as high-value niche markets for TEG technology, with applications in remote power generation for satellites, unmanned vehicles, and military equipment. Though smaller in volume, these applications command premium pricing due to their specialized requirements and critical operational environments.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 32% share, followed closely by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 27%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, coupled with increasing energy efficiency regulations.
Consumer demand is increasingly shifting toward TEG systems with higher conversion efficiencies and lower installation complexities. Market research indicates that systems demonstrating thermal efficiency improvements of even 2-3% command price premiums of 15-20% over standard offerings, highlighting the economic value of minimizing thermal losses during installation.
The competitive landscape features established players like Gentherm, Laird Thermal Systems, and Ferrotec, alongside emerging technology companies focused on innovative installation techniques and materials that minimize thermal interface losses. Market consolidation is expected as larger energy management companies acquire specialized TEG technology providers to expand their waste heat recovery portfolios.
The automotive industry represents the largest market segment for TEG systems, accounting for nearly 35% of the total market share. Major automotive manufacturers are increasingly incorporating TEG technology to recover waste heat from exhaust systems, improving fuel efficiency by 2-5% depending on driving conditions and system integration. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent emission regulations such as Europe and North America.
Industrial manufacturing constitutes the second-largest market segment at approximately 28% of the market share. Process industries with high-temperature operations, including steel, glass, and cement manufacturing, present substantial opportunities for TEG implementation. These industries typically generate significant waste heat that can be effectively converted to usable electricity through properly installed TEG systems.
The aerospace and defense sectors are emerging as high-value niche markets for TEG technology, with applications in remote power generation for satellites, unmanned vehicles, and military equipment. Though smaller in volume, these applications command premium pricing due to their specialized requirements and critical operational environments.
Geographically, North America leads the market with approximately 32% share, followed closely by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 27%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the next five years, driven by rapid industrialization in China and India, coupled with increasing energy efficiency regulations.
Consumer demand is increasingly shifting toward TEG systems with higher conversion efficiencies and lower installation complexities. Market research indicates that systems demonstrating thermal efficiency improvements of even 2-3% command price premiums of 15-20% over standard offerings, highlighting the economic value of minimizing thermal losses during installation.
The competitive landscape features established players like Gentherm, Laird Thermal Systems, and Ferrotec, alongside emerging technology companies focused on innovative installation techniques and materials that minimize thermal interface losses. Market consolidation is expected as larger energy management companies acquire specialized TEG technology providers to expand their waste heat recovery portfolios.
Current Challenges in TEG Thermal Management
Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) systems face significant thermal management challenges that directly impact their efficiency and performance. The primary issue stems from the inherent low conversion efficiency of TEG modules, typically ranging between 3-8% in commercial applications. This means that over 90% of thermal energy is lost rather than converted to electricity, creating substantial heat dissipation requirements.
Heat transfer interface problems represent a major challenge in TEG installations. Imperfect thermal contact between TEG modules and heat sources/sinks creates thermal resistance that impedes efficient heat flow. Microscopic air gaps, surface roughness, and material expansion differences all contribute to these interface losses, which can reduce system efficiency by 15-30% in poorly designed installations.
Temperature gradient stability presents another critical challenge. TEG systems require consistent temperature differentials to generate power effectively. However, many industrial applications feature fluctuating heat sources or varying ambient conditions that destabilize these gradients. Without proper thermal management strategies, these fluctuations can lead to thermal cycling stress and reduced power output.
Thermal bypass and parasitic heat flows significantly undermine TEG performance. In complex installations, heat often finds alternative pathways around TEG modules rather than flowing through them. These unintended heat flows can account for up to 40% of thermal losses in poorly designed systems, effectively short-circuiting the thermal energy that could otherwise generate electricity.
Material limitations further complicate thermal management. Current heat exchanger materials must balance thermal conductivity, cost, weight, and corrosion resistance. Many high-performance materials with excellent thermal properties (like copper or silver) face practical limitations in harsh environments or cost constraints in large-scale applications.
System integration challenges arise when incorporating TEGs into existing industrial processes or equipment. The physical space requirements, mounting considerations, and need to minimize disruption to primary processes often force compromises in thermal design that reduce overall efficiency.
Scaling issues become apparent in larger TEG installations, where uniform heat distribution across multiple modules proves difficult. Hot spots and uneven temperature distributions lead to electrical mismatches between modules, reducing overall system output below theoretical capabilities.
These thermal management challenges collectively represent the primary technical barriers to wider TEG adoption, with research indicating that addressing these issues could potentially double the effective efficiency of many TEG installations in practical applications.
Heat transfer interface problems represent a major challenge in TEG installations. Imperfect thermal contact between TEG modules and heat sources/sinks creates thermal resistance that impedes efficient heat flow. Microscopic air gaps, surface roughness, and material expansion differences all contribute to these interface losses, which can reduce system efficiency by 15-30% in poorly designed installations.
Temperature gradient stability presents another critical challenge. TEG systems require consistent temperature differentials to generate power effectively. However, many industrial applications feature fluctuating heat sources or varying ambient conditions that destabilize these gradients. Without proper thermal management strategies, these fluctuations can lead to thermal cycling stress and reduced power output.
Thermal bypass and parasitic heat flows significantly undermine TEG performance. In complex installations, heat often finds alternative pathways around TEG modules rather than flowing through them. These unintended heat flows can account for up to 40% of thermal losses in poorly designed systems, effectively short-circuiting the thermal energy that could otherwise generate electricity.
Material limitations further complicate thermal management. Current heat exchanger materials must balance thermal conductivity, cost, weight, and corrosion resistance. Many high-performance materials with excellent thermal properties (like copper or silver) face practical limitations in harsh environments or cost constraints in large-scale applications.
System integration challenges arise when incorporating TEGs into existing industrial processes or equipment. The physical space requirements, mounting considerations, and need to minimize disruption to primary processes often force compromises in thermal design that reduce overall efficiency.
Scaling issues become apparent in larger TEG installations, where uniform heat distribution across multiple modules proves difficult. Hot spots and uneven temperature distributions lead to electrical mismatches between modules, reducing overall system output below theoretical capabilities.
These thermal management challenges collectively represent the primary technical barriers to wider TEG adoption, with research indicating that addressing these issues could potentially double the effective efficiency of many TEG installations in practical applications.
Best Practices for TEG System Installation
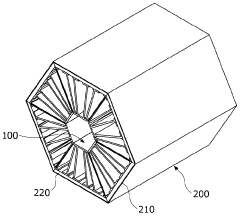
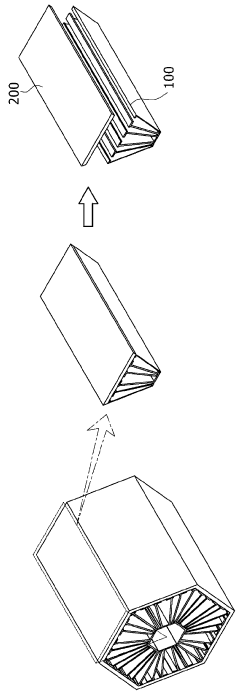
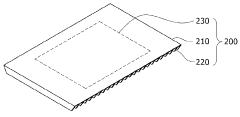
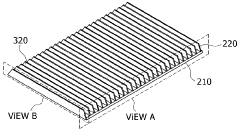
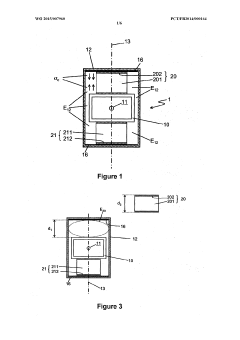
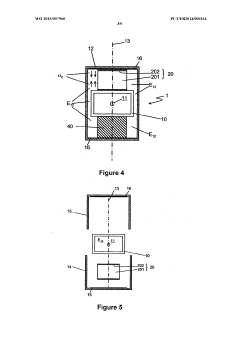
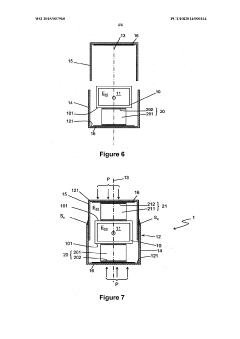
01 Heat dissipation and thermal management in TEG systems
Effective heat dissipation and thermal management are crucial for minimizing thermal losses in thermoelectric generator systems. Various techniques such as advanced heat sink designs, cooling mechanisms, and thermal interface materials are employed to optimize heat transfer and reduce thermal resistance at interfaces. Proper thermal management ensures that temperature gradients are maintained efficiently across the thermoelectric elements, maximizing power generation while minimizing energy losses to the environment.- Heat dissipation and thermal management in TEG systems: Effective heat dissipation and thermal management are crucial for minimizing thermal losses in thermoelectric generator systems. Various techniques such as heat sinks, cooling systems, and optimized heat exchanger designs can be employed to manage excess heat and improve thermal efficiency. Proper thermal interfaces between components help reduce contact resistance and ensure efficient heat transfer throughout the system, ultimately increasing the temperature gradient across the thermoelectric elements and improving overall system performance.
- Insulation and thermal barrier technologies: Advanced insulation and thermal barrier technologies play a significant role in reducing unwanted heat losses in TEG systems. These technologies include specialized insulating materials, vacuum-sealed enclosures, and multi-layer thermal barriers that help maintain the temperature differential across thermoelectric modules. By minimizing parasitic heat flows and thermal bypassing, these solutions ensure that more thermal energy is directed through the thermoelectric elements rather than being lost to the surrounding environment, thereby improving conversion efficiency.
- Structural design optimization for thermal efficiency: The structural design of TEG systems significantly impacts thermal losses. Optimized geometries, component arrangements, and flow patterns can minimize thermal resistance and maximize heat transfer to the thermoelectric elements. Advanced designs incorporate features such as flow channels, heat spreaders, and strategic placement of thermoelectric modules to ensure uniform temperature distribution. Computational fluid dynamics and thermal modeling are often used to identify and eliminate thermal bottlenecks, resulting in more efficient energy conversion and reduced thermal losses.
- Material selection and interface engineering: The selection of materials with appropriate thermal conductivity properties and effective interface engineering are essential for minimizing thermal losses in TEG systems. High-performance thermal interface materials, specialized bonding techniques, and surface treatments can reduce contact resistance between components. Advanced thermoelectric materials with optimized figure of merit (ZT) values help maximize the conversion of thermal energy to electrical energy. Composite materials and nano-engineered interfaces can further enhance thermal management by directing heat flow paths and reducing parasitic thermal losses.
- Waste heat recovery and system integration: Innovative approaches to waste heat recovery and system integration can significantly reduce thermal losses in TEG applications. These include cascaded TEG systems that utilize multiple stages of thermoelectric modules to capture heat at different temperature ranges, hybrid systems that combine TEGs with other energy conversion technologies, and integrated cooling solutions that repurpose waste heat. By capturing and utilizing heat that would otherwise be lost, these approaches improve overall system efficiency and maximize the useful energy output from available thermal resources.
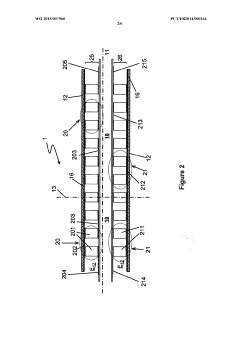
02 Insulation techniques to reduce thermal bypass
Thermal bypass losses occur when heat flows around the thermoelectric elements rather than through them, reducing the temperature gradient and system efficiency. Advanced insulation materials and designs are implemented to minimize these losses. Techniques include vacuum insulation, aerogel barriers, multi-layer insulation systems, and strategic placement of thermal breaks. These approaches help contain heat within the intended thermal pathway, ensuring more heat energy is converted to electricity rather than being lost to the surroundings.Expand Specific Solutions03 Contact resistance reduction methods
Contact resistance at interfaces between thermoelectric materials and heat exchangers represents a significant source of thermal losses in TEG systems. Various methods are employed to minimize these losses, including improved bonding techniques, specialized interface materials, surface treatment processes, and pressure-optimized connections. Reducing contact resistance ensures more efficient heat transfer to and from the thermoelectric elements, improving overall system performance and power output.Expand Specific Solutions04 Geometric optimization of TEG components
The geometric design of thermoelectric generator components significantly impacts thermal losses. Optimization techniques include adjusting the aspect ratio of thermoelectric elements, optimizing heat exchanger fin designs, creating specialized flow channels for heat transfer fluids, and implementing segmented or cascaded structures. These geometric optimizations help to maximize temperature gradients across the thermoelectric materials while minimizing parasitic heat losses, resulting in improved conversion efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Waste heat recovery and recycling systems
Advanced waste heat recovery and recycling systems are implemented to capture and utilize thermal energy that would otherwise be lost in TEG operations. These systems include heat recuperators, regenerative heat exchangers, thermal energy storage components, and cascaded TEG arrangements. By recapturing waste heat and redirecting it back into the system, overall thermal efficiency is improved, and the net thermal losses are significantly reduced, leading to higher power output from the same heat input.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Competitors in TEG Industry
The thermoelectric generator (TEG) system market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across automotive, industrial, and energy sectors. The global market size is estimated to be expanding at a CAGR of 8-10%, driven by waste heat recovery applications and energy efficiency initiatives. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovations in material science and system integration. Leading players include automotive manufacturers like BMW and Jaguar Land Rover focusing on vehicle efficiency; technology corporations such as Toshiba, TSMC, and LG Electronics developing semiconductor-based solutions; and specialized companies like Gentherm and Phononic pioneering advanced TEG applications. Energy giants including State Grid of China and Saudi Aramco are exploring large-scale implementations, while research institutions like IMEC and Shanghai Polytechnic University are advancing fundamental technologies to improve thermal efficiency and minimize losses.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has engineered a comprehensive TEG thermal loss minimization system centered around their patented "ThermoSeal" technology. This approach utilizes precision-manufactured heat exchangers with optimized flow geometries that maximize heat transfer efficiency while minimizing pressure drops. Their installation methodology incorporates thermal expansion-compensating mounting systems that maintain consistent contact pressure across thermal interfaces despite temperature fluctuations. Bosch's solution includes specialized thermal interface materials with phase-change properties that fill microscopic air gaps and reduce thermal contact resistance by up to 85% compared to conventional materials. The system employs modular design principles with standardized connection interfaces, allowing for simplified installation while maintaining thermal integrity. Additionally, Bosch has developed advanced thermal insulation composites that incorporate aerogel technology with reflective barriers to minimize both conductive and radiative heat losses in the system periphery.
Strengths: Highly engineered system components with tight manufacturing tolerances ensuring consistent performance; extensive field testing in automotive applications has validated long-term reliability. Weaknesses: System optimization requires detailed thermal modeling specific to each application; higher initial investment compared to basic installation methods.
Eberspächer Exhaust Technology GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Eberspächer has developed a specialized TEG installation system focused on exhaust heat recovery applications. Their approach centers on their proprietary "ThermoConnect" technology that addresses thermal losses through precision-engineered heat exchanger geometries optimized via computational fluid dynamics. The system incorporates segmented heat exchangers with turbulence-inducing features that enhance heat transfer coefficients while minimizing pressure drops. Eberspächer's installation methodology employs specialized high-temperature gaskets with embedded metal matrices that maintain thermal conductivity while preventing exhaust gas leakage. Their solution includes modular insulation packages with multi-layer ceramic fiber composites that can withstand temperatures exceeding 800°C while providing effective thermal isolation. Additionally, Eberspächer has pioneered adaptive mounting systems that accommodate thermal expansion differences between components, maintaining optimal thermal interfaces throughout wide temperature ranges experienced in exhaust applications.
Strengths: Exceptional expertise in high-temperature applications specific to exhaust heat recovery; solutions designed to withstand harsh operating environments including thermal cycling and vibration. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on automotive and industrial exhaust applications; solutions may require adaptation for other TEG deployment scenarios.
Key Thermal Interface Materials and Innovations
Thermoelectric generator, manufacturing method therefor, and thermoelectric generating apparatus equipped therewith
PatentWO2023243816A1
Innovation
- The thermoelectric generator incorporates a heat dissipation fin and an air distribution fin with an air flow path, where high-temperature air is distributed across the thermoelectric element through an air distribution unit, enhancing heat transfer and reducing temperature differences by separating the air flow path into distinct inlet and discharge areas.
Thermoelectric generator
PatentWO2015007960A1
Innovation
- A thermoelectric generator design featuring compressively stressed thermocouples between ducts with a unique arrangement of heat sources and fluid circulation, including a vacuum-sealed internal space with inert gas to minimize thermal resistances and mechanical deformations, and using materials with different thermoelectric properties for efficient energy conversion.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Thermoelectric Generator (TEG) systems represent a significant opportunity for sustainable energy generation by converting waste heat into usable electricity. The environmental implications of TEG installations extend far beyond their immediate energy production capabilities, encompassing their entire lifecycle from manufacturing to decommissioning.
The primary environmental benefit of properly installed TEG systems is their ability to capture waste heat that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. By minimizing thermal losses through proper installation practices, these systems can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of industrial processes, power generation facilities, and even residential applications. Each percentage point improvement in thermal efficiency translates directly to reduced fossil fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Material selection for TEG systems carries substantial environmental considerations. Traditional semiconductor materials used in thermoelectric modules often include bismuth telluride, lead telluride, and other compounds containing rare or toxic elements. Sustainable installation practices should prioritize modules manufactured with reduced toxic content and improved recyclability. Additionally, thermal interface materials and insulation components should be selected not only for their thermal performance but also for their environmental impact, favoring those with lower embodied carbon and minimal end-of-life disposal concerns.
The installation process itself presents opportunities for environmental optimization. Energy-efficient manufacturing techniques for system components, reduced transportation emissions through local sourcing, and minimized construction waste all contribute to a more sustainable TEG deployment. Installation teams should implement waste management protocols specific to the materials involved, particularly when handling potentially hazardous components like certain thermal interface materials or cleaning agents.
Long-term sustainability considerations must address the entire operational lifespan of TEG systems. Designs that facilitate easy maintenance, component replacement, and eventual recycling significantly reduce the lifetime environmental impact. Monitoring systems that detect efficiency degradation allow for timely interventions, preventing the wasted energy associated with underperforming installations. Furthermore, end-of-life planning should be incorporated into initial system designs, with clear protocols for the safe decommissioning and recycling of components.
Water usage represents another critical environmental factor in TEG installations, particularly in cooling systems for the cold side of thermoelectric modules. Water-efficient cooling designs, closed-loop systems, and alternative cooling methods can substantially reduce the water footprint of these installations, an increasingly important consideration in water-stressed regions.
The primary environmental benefit of properly installed TEG systems is their ability to capture waste heat that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. By minimizing thermal losses through proper installation practices, these systems can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of industrial processes, power generation facilities, and even residential applications. Each percentage point improvement in thermal efficiency translates directly to reduced fossil fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Material selection for TEG systems carries substantial environmental considerations. Traditional semiconductor materials used in thermoelectric modules often include bismuth telluride, lead telluride, and other compounds containing rare or toxic elements. Sustainable installation practices should prioritize modules manufactured with reduced toxic content and improved recyclability. Additionally, thermal interface materials and insulation components should be selected not only for their thermal performance but also for their environmental impact, favoring those with lower embodied carbon and minimal end-of-life disposal concerns.
The installation process itself presents opportunities for environmental optimization. Energy-efficient manufacturing techniques for system components, reduced transportation emissions through local sourcing, and minimized construction waste all contribute to a more sustainable TEG deployment. Installation teams should implement waste management protocols specific to the materials involved, particularly when handling potentially hazardous components like certain thermal interface materials or cleaning agents.
Long-term sustainability considerations must address the entire operational lifespan of TEG systems. Designs that facilitate easy maintenance, component replacement, and eventual recycling significantly reduce the lifetime environmental impact. Monitoring systems that detect efficiency degradation allow for timely interventions, preventing the wasted energy associated with underperforming installations. Furthermore, end-of-life planning should be incorporated into initial system designs, with clear protocols for the safe decommissioning and recycling of components.
Water usage represents another critical environmental factor in TEG installations, particularly in cooling systems for the cold side of thermoelectric modules. Water-efficient cooling designs, closed-loop systems, and alternative cooling methods can substantially reduce the water footprint of these installations, an increasingly important consideration in water-stressed regions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Advanced Thermal Solutions
When evaluating advanced thermal solutions for TEG (Thermoelectric Generator) systems, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis reveals significant economic implications across implementation phases. Initial investment costs for premium thermal management solutions typically range from 15-30% higher than standard installations, representing a substantial upfront premium for high-performance insulation materials, specialized heat sinks, and advanced thermal interface materials.
However, these elevated initial expenditures must be evaluated against long-term operational benefits. Enhanced thermal solutions demonstrably improve TEG conversion efficiency by 8-12% on average, directly translating to increased power output over the system lifetime. This efficiency gain creates a positive return trajectory, with most premium installations reaching break-even points within 2-4 years depending on application scale and operational conditions.
Maintenance economics further strengthen the case for advanced thermal solutions. Systems with optimized thermal management demonstrate 30-40% reduction in thermal stress-related failures, extending mean time between maintenance interventions by approximately 1.5-2 times compared to standard installations. This translates to reduced downtime costs and lower lifetime maintenance expenditures, factors often undervalued in initial procurement decisions.
Energy recapture represents another significant economic benefit. Advanced thermal solutions incorporating regenerative heat exchangers and multi-stage heat recovery systems can reclaim 15-25% of otherwise wasted thermal energy, creating secondary efficiency gains beyond primary TEG conversion. These systems effectively lower the net energy cost per operational hour, improving overall system economics.
Installation complexity presents a countervailing cost factor. Advanced thermal solutions typically require 25-40% more installation time and specialized expertise, increasing initial deployment costs. This complexity premium must be factored into project timelines and budgets, particularly for retrofit applications in existing infrastructure.
Scalability economics reveal that thermal solution costs do not scale linearly with system size. Larger TEG installations (>50kW) achieve significantly better cost-performance ratios for advanced thermal solutions, with per-watt implementation costs decreasing by approximately 30-45% compared to small-scale systems. This creates a compelling economic case for thermal optimization in industrial-scale applications where waste heat volumes are substantial.
However, these elevated initial expenditures must be evaluated against long-term operational benefits. Enhanced thermal solutions demonstrably improve TEG conversion efficiency by 8-12% on average, directly translating to increased power output over the system lifetime. This efficiency gain creates a positive return trajectory, with most premium installations reaching break-even points within 2-4 years depending on application scale and operational conditions.
Maintenance economics further strengthen the case for advanced thermal solutions. Systems with optimized thermal management demonstrate 30-40% reduction in thermal stress-related failures, extending mean time between maintenance interventions by approximately 1.5-2 times compared to standard installations. This translates to reduced downtime costs and lower lifetime maintenance expenditures, factors often undervalued in initial procurement decisions.
Energy recapture represents another significant economic benefit. Advanced thermal solutions incorporating regenerative heat exchangers and multi-stage heat recovery systems can reclaim 15-25% of otherwise wasted thermal energy, creating secondary efficiency gains beyond primary TEG conversion. These systems effectively lower the net energy cost per operational hour, improving overall system economics.
Installation complexity presents a countervailing cost factor. Advanced thermal solutions typically require 25-40% more installation time and specialized expertise, increasing initial deployment costs. This complexity premium must be factored into project timelines and budgets, particularly for retrofit applications in existing infrastructure.
Scalability economics reveal that thermal solution costs do not scale linearly with system size. Larger TEG installations (>50kW) achieve significantly better cost-performance ratios for advanced thermal solutions, with per-watt implementation costs decreasing by approximately 30-45% compared to small-scale systems. This creates a compelling economic case for thermal optimization in industrial-scale applications where waste heat volumes are substantial.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!