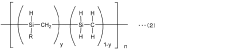How To Use Composite Fillers To Improve Thermal Conductivity Of Module Substrates
SEP 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Composite Fillers Technology Background and Objectives
The evolution of electronic modules has been marked by continuous miniaturization and increased power density, creating significant thermal management challenges. Historically, thermal management in electronic substrates relied primarily on metallic materials like aluminum and copper due to their excellent thermal conductivity. However, these materials present limitations in terms of weight, cost, and integration capabilities, driving the industry toward composite solutions since the early 2000s.
Composite fillers represent a revolutionary approach to enhancing thermal conductivity in module substrates while maintaining or improving other critical properties. These fillers consist of thermally conductive particles dispersed within a matrix material, creating a composite system that can be tailored to specific application requirements. The development of these materials has accelerated significantly over the past decade, with research focusing on optimizing filler type, concentration, size distribution, and interface characteristics.
The primary objective of composite filler technology is to achieve thermal conductivity values approaching those of metallic materials while maintaining the processing advantages, weight benefits, and cost-effectiveness of polymer-based substrates. Current research aims to surpass the 10 W/m·K threshold for polymer composites, a significant improvement over the 0.2-0.5 W/m·K typical of unfilled polymers, while remaining well below the 200-400 W/m·K of pure metals.
Industry trends indicate a growing demand for thermally conductive composites across multiple sectors, including automotive electronics, consumer electronics, LED lighting, and power electronics. The global market for thermally conductive plastics, estimated at $1.2 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of approximately 11.5%.
Technical evolution in this field has progressed through several distinct phases: initial exploration of micro-scale metallic and ceramic fillers (2000-2010), development of hybrid filler systems combining particles of different shapes and sizes (2010-2015), and the current focus on nanoscale fillers and three-dimensional conductive networks (2015-present). Each phase has contributed to significant improvements in thermal performance while addressing challenges related to electrical conductivity, mechanical properties, and processability.
The ultimate goal of composite filler technology development is to create substrate materials that offer an optimal balance of thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, mechanical strength, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. This requires a multidisciplinary approach combining materials science, thermal engineering, and manufacturing process optimization to develop next-generation substrate solutions capable of meeting the increasingly demanding requirements of advanced electronic modules.
Composite fillers represent a revolutionary approach to enhancing thermal conductivity in module substrates while maintaining or improving other critical properties. These fillers consist of thermally conductive particles dispersed within a matrix material, creating a composite system that can be tailored to specific application requirements. The development of these materials has accelerated significantly over the past decade, with research focusing on optimizing filler type, concentration, size distribution, and interface characteristics.
The primary objective of composite filler technology is to achieve thermal conductivity values approaching those of metallic materials while maintaining the processing advantages, weight benefits, and cost-effectiveness of polymer-based substrates. Current research aims to surpass the 10 W/m·K threshold for polymer composites, a significant improvement over the 0.2-0.5 W/m·K typical of unfilled polymers, while remaining well below the 200-400 W/m·K of pure metals.
Industry trends indicate a growing demand for thermally conductive composites across multiple sectors, including automotive electronics, consumer electronics, LED lighting, and power electronics. The global market for thermally conductive plastics, estimated at $1.2 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2027, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of approximately 11.5%.
Technical evolution in this field has progressed through several distinct phases: initial exploration of micro-scale metallic and ceramic fillers (2000-2010), development of hybrid filler systems combining particles of different shapes and sizes (2010-2015), and the current focus on nanoscale fillers and three-dimensional conductive networks (2015-present). Each phase has contributed to significant improvements in thermal performance while addressing challenges related to electrical conductivity, mechanical properties, and processability.
The ultimate goal of composite filler technology development is to create substrate materials that offer an optimal balance of thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, mechanical strength, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. This requires a multidisciplinary approach combining materials science, thermal engineering, and manufacturing process optimization to develop next-generation substrate solutions capable of meeting the increasingly demanding requirements of advanced electronic modules.
Market Demand Analysis for Thermally Conductive Substrates
The global market for thermally conductive substrates is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for high-performance electronic devices across multiple industries. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for this market is projected to exceed 6% through 2028, with particularly strong demand emerging from electric vehicle manufacturing, 5G infrastructure deployment, and advanced computing applications.
Electronic device miniaturization continues to intensify thermal management challenges, creating substantial market pull for innovative substrate solutions. As power densities increase and component sizes decrease, conventional substrate materials are reaching their thermal performance limits. This technological bottleneck has created a significant opportunity for composite filler-enhanced substrates that can provide superior thermal conductivity without compromising other essential properties.
The automotive electronics sector represents one of the fastest-growing market segments, with thermal management becoming critical for electric vehicle battery systems, power electronics, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These applications require substrates capable of efficiently dissipating heat while maintaining reliability under harsh operating conditions, driving demand for composite-enhanced solutions.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are similarly seeking advanced thermal management solutions to address heat dissipation in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The trend toward thinner, more powerful devices has created acute thermal challenges that conventional substrates cannot adequately address, opening opportunities for composite-enhanced alternatives.
Industrial and power electronics represent another substantial market segment, with applications in renewable energy systems, industrial automation, and power distribution requiring increasingly efficient thermal management solutions. These applications often operate in demanding environments and at high power levels, necessitating substrates with exceptional thermal performance.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market for thermally conductive substrates, accounting for over 60% of global demand. This concentration reflects the region's manufacturing strength in electronics and automotive sectors. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with particularly strong growth in applications requiring high reliability and performance.
Customer requirements are evolving beyond simple thermal conductivity metrics to include considerations such as coefficient of thermal expansion matching, mechanical strength, weight reduction, and environmental sustainability. This evolution is driving demand for customized composite solutions that can be tailored to specific application requirements rather than one-size-fits-all approaches.
The market shows increasing willingness to adopt premium-priced substrate solutions when clear performance advantages and total cost of ownership benefits can be demonstrated, creating opportunities for innovative composite filler technologies that deliver superior thermal management capabilities.
Electronic device miniaturization continues to intensify thermal management challenges, creating substantial market pull for innovative substrate solutions. As power densities increase and component sizes decrease, conventional substrate materials are reaching their thermal performance limits. This technological bottleneck has created a significant opportunity for composite filler-enhanced substrates that can provide superior thermal conductivity without compromising other essential properties.
The automotive electronics sector represents one of the fastest-growing market segments, with thermal management becoming critical for electric vehicle battery systems, power electronics, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These applications require substrates capable of efficiently dissipating heat while maintaining reliability under harsh operating conditions, driving demand for composite-enhanced solutions.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are similarly seeking advanced thermal management solutions to address heat dissipation in smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The trend toward thinner, more powerful devices has created acute thermal challenges that conventional substrates cannot adequately address, opening opportunities for composite-enhanced alternatives.
Industrial and power electronics represent another substantial market segment, with applications in renewable energy systems, industrial automation, and power distribution requiring increasingly efficient thermal management solutions. These applications often operate in demanding environments and at high power levels, necessitating substrates with exceptional thermal performance.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the market for thermally conductive substrates, accounting for over 60% of global demand. This concentration reflects the region's manufacturing strength in electronics and automotive sectors. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, with particularly strong growth in applications requiring high reliability and performance.
Customer requirements are evolving beyond simple thermal conductivity metrics to include considerations such as coefficient of thermal expansion matching, mechanical strength, weight reduction, and environmental sustainability. This evolution is driving demand for customized composite solutions that can be tailored to specific application requirements rather than one-size-fits-all approaches.
The market shows increasing willingness to adopt premium-priced substrate solutions when clear performance advantages and total cost of ownership benefits can be demonstrated, creating opportunities for innovative composite filler technologies that deliver superior thermal management capabilities.
Current Status and Challenges in Thermal Management
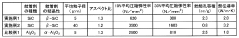
The thermal management landscape for electronic module substrates has evolved significantly over the past decade, with increasing power densities and miniaturization driving demand for enhanced thermal conductivity solutions. Currently, conventional substrate materials like FR-4 (0.3 W/mK) and aluminum (150-200 W/mK) are widely used but increasingly insufficient for advanced applications. High-performance ceramics such as aluminum nitride (170-230 W/mK) and silicon carbide (120-270 W/mK) offer superior thermal properties but at prohibitively high costs for many applications.
Composite fillers represent a promising approach to enhance thermal conductivity while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Market leaders have achieved thermal conductivities of 5-30 W/mK in polymer composites through strategic filler incorporation, but significant challenges remain in reaching higher conductivity values without compromising other material properties.
The primary technical challenge lies in the thermal interface resistance between fillers and matrix materials. This resistance creates bottlenecks in heat transfer pathways, significantly reducing the effective thermal conductivity of the composite. Research indicates that even with high loading (>60 vol%) of thermally conductive fillers, the composite conductivity often reaches only 10-15% of theoretical maximum values due to these interface effects.
Another critical challenge is maintaining processability at high filler loadings. As filler content increases to improve thermal conductivity, viscosity rises exponentially, making conventional manufacturing processes difficult or impossible. This creates a practical upper limit for filler content that constrains thermal performance improvement.
Filler geometry and orientation present additional complexities. Studies show that high-aspect-ratio fillers like carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets can form more effective thermal networks, but controlling their orientation during processing remains difficult. Random orientation typically yields isotropic but suboptimal thermal conductivity, while achieving directional thermal properties requires specialized processing techniques not readily available in mass production.
Geographical distribution of thermal management technology development shows concentration in East Asia (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan), North America, and Western Europe. Japan leads in ceramic-based solutions, while the United States demonstrates strength in polymer composite innovations and carbon-based fillers.
Recent advancements in surface functionalization of fillers have shown promise in reducing interface resistance, with research groups reporting 30-50% improvements in effective thermal conductivity through chemical treatments that enhance filler-matrix compatibility. However, scaling these treatments to industrial production remains challenging due to cost and processing complexity.
Composite fillers represent a promising approach to enhance thermal conductivity while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Market leaders have achieved thermal conductivities of 5-30 W/mK in polymer composites through strategic filler incorporation, but significant challenges remain in reaching higher conductivity values without compromising other material properties.
The primary technical challenge lies in the thermal interface resistance between fillers and matrix materials. This resistance creates bottlenecks in heat transfer pathways, significantly reducing the effective thermal conductivity of the composite. Research indicates that even with high loading (>60 vol%) of thermally conductive fillers, the composite conductivity often reaches only 10-15% of theoretical maximum values due to these interface effects.
Another critical challenge is maintaining processability at high filler loadings. As filler content increases to improve thermal conductivity, viscosity rises exponentially, making conventional manufacturing processes difficult or impossible. This creates a practical upper limit for filler content that constrains thermal performance improvement.
Filler geometry and orientation present additional complexities. Studies show that high-aspect-ratio fillers like carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets can form more effective thermal networks, but controlling their orientation during processing remains difficult. Random orientation typically yields isotropic but suboptimal thermal conductivity, while achieving directional thermal properties requires specialized processing techniques not readily available in mass production.
Geographical distribution of thermal management technology development shows concentration in East Asia (Japan, South Korea, Taiwan), North America, and Western Europe. Japan leads in ceramic-based solutions, while the United States demonstrates strength in polymer composite innovations and carbon-based fillers.
Recent advancements in surface functionalization of fillers have shown promise in reducing interface resistance, with research groups reporting 30-50% improvements in effective thermal conductivity through chemical treatments that enhance filler-matrix compatibility. However, scaling these treatments to industrial production remains challenging due to cost and processing complexity.
Current Composite Filler Solutions for Module Substrates
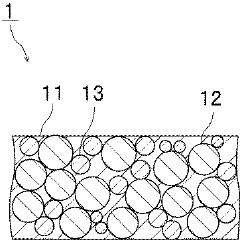
01 Carbon-based fillers for enhanced thermal conductivity
Carbon-based materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, and graphite are widely used as fillers in composite materials to significantly enhance thermal conductivity. These materials offer excellent heat transfer properties due to their unique molecular structure and high intrinsic thermal conductivity. When properly dispersed in polymer matrices, carbon-based fillers create effective thermal pathways, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation such as electronics packaging and thermal interface materials.- Carbon-based fillers for enhanced thermal conductivity: Carbon-based materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, and graphite are widely used as fillers in composite materials to significantly enhance thermal conductivity. These materials offer excellent heat transfer properties due to their unique molecular structure and high intrinsic thermal conductivity. When properly dispersed in polymer matrices, they create effective thermal pathways that allow for efficient heat dissipation, making them ideal for applications requiring thermal management.
- Ceramic and metal oxide fillers for thermal applications: Ceramic and metal oxide fillers, including aluminum oxide, boron nitride, silicon carbide, and aluminum nitride, are incorporated into composite materials to improve thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical insulation properties. These fillers provide a balance of thermal performance and other desirable characteristics such as low coefficient of thermal expansion and high temperature stability, making them suitable for electronics packaging, thermal interface materials, and other heat management applications.
- Hybrid filler systems for synergistic thermal effects: Hybrid filler systems combine multiple types of thermally conductive materials to achieve synergistic effects that exceed the performance of single-filler systems. By strategically combining fillers of different sizes, shapes, and thermal properties (such as micro and nano-sized particles), these composites create more efficient thermal networks within the matrix. This approach allows for optimization of filler loading levels while maintaining processability and mechanical properties of the composite.
- Surface modification of fillers for improved matrix compatibility: Surface modification techniques are applied to thermal conductive fillers to improve their compatibility with polymer matrices and enhance the filler-matrix interface. These treatments reduce interfacial thermal resistance and improve dispersion quality, leading to better thermal conductivity in the final composite. Common modification methods include silane coupling agents, functional group grafting, and polymer coating, which help prevent filler agglomeration and improve overall composite performance.
- Processing techniques for optimizing thermal conductivity in composites: Advanced processing techniques play a crucial role in optimizing the thermal conductivity of composite materials. Methods such as alignment of anisotropic fillers, controlled filler orientation, specialized mixing protocols, and innovative curing processes can significantly enhance thermal pathways within composites. These techniques focus on creating continuous thermal networks, minimizing interfacial thermal resistance, and achieving optimal filler distribution throughout the matrix to maximize heat transfer efficiency.
02 Ceramic and metal oxide fillers for thermal management
Ceramic and metal oxide fillers, including aluminum oxide, boron nitride, silicon carbide, and aluminum nitride, are incorporated into composite materials to improve thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical insulation properties. These fillers offer good thermal stability at high temperatures and can be surface-treated to enhance compatibility with various matrix materials. The particle size, shape, and distribution of these ceramic fillers significantly impact the resulting thermal conductivity of the composite material.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hybrid filler systems for synergistic thermal effects
Hybrid filler systems combine different types of thermally conductive materials to achieve synergistic effects that exceed the performance of single-filler systems. These combinations often include mixtures of micro and nano-sized particles or different material classes such as ceramics with metallic or carbon-based fillers. The synergistic effect occurs through the formation of more efficient thermal networks within the composite, where smaller particles fill gaps between larger ones, creating continuous pathways for heat transfer.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surface modification of fillers for improved matrix compatibility
Surface modification techniques are applied to composite fillers to improve their compatibility with polymer matrices and enhance the thermal conductivity of the resulting composites. These modifications include silane coupling agents, surfactants, and functional group attachments that reduce interfacial thermal resistance between the filler and matrix. Improved dispersion and stronger interfacial bonding lead to more efficient thermal conduction pathways throughout the composite material, resulting in higher overall thermal conductivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for optimized filler distribution
Advanced processing techniques are crucial for optimizing the distribution and orientation of thermally conductive fillers within composite materials. Methods such as three-dimensional printing, alignment in electromagnetic fields, and specialized mixing protocols can create preferential pathways for heat conduction. The processing approach significantly influences the percolation threshold of fillers and can enable the achievement of high thermal conductivity at lower filler loadings, maintaining better mechanical properties and processability of the composite material.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Composite Materials
The thermal conductivity enhancement of module substrates using composite fillers is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing demand for high-performance electronic components. The global market for thermally conductive materials is projected to reach significant scale as electronics miniaturization continues. From a technological maturity perspective, major players are at different development stages. Industry leaders like Siemens AG, Robert Bosch, and General Electric are advancing commercial applications, while Laird Technologies and Rogers Corp. specialize in thermal management solutions. Research institutions including CNRS, AIT Austrian Institute, and various Chinese universities are developing next-generation composite fillers. Japanese corporations such as Sekisui Chemical, JNC Corp., and Nitto Denko are contributing specialized materials expertise, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established industrial players and emerging research-driven innovations.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed sophisticated thermal management solutions for automotive and industrial electronics using advanced composite fillers in module substrates. Their proprietary technology utilizes a hierarchical filler approach combining hexagonal boron nitride platelets (h-BN) with spherical aluminum oxide particles to create three-dimensional thermal networks within polymer matrices. This structure achieves thermal conductivity values of 4-6 W/mK while maintaining electrical isolation properties. Bosch's manufacturing process employs a patented extrusion technique that aligns the anisotropic h-BN particles in preferred orientations, creating enhanced thermal pathways in critical directions. Their materials incorporate proprietary coupling agents that improve the filler-matrix interface, reducing phonon scattering and enhancing overall thermal transfer efficiency. Bosch has also pioneered hybrid organic-inorganic composite systems that combine the processability of polymers with the thermal performance of ceramics, resulting in cost-effective solutions for high-volume automotive applications requiring reliable thermal management under extreme operating conditions.
Strengths: Extensive automotive qualification testing ensures reliability; optimized for mass production environments; excellent thermal cycling resistance. Weaknesses: Moderate thermal conductivity compared to pure ceramic solutions; limited flexibility in some formulations; requires specific processing parameters for optimal performance.
General Electric Company
Technical Solution: General Electric has pioneered advanced thermal management solutions for module substrates through their proprietary ceramic-polymer composite technology. Their approach utilizes a multi-scale filler strategy incorporating both micro and nano-sized particles of aluminum nitride, boron nitride, and synthetic diamond in a specialized polymer matrix. GE's patented manufacturing process employs acoustic mixing technology to achieve uniform filler dispersion at loadings exceeding 70% by volume while maintaining processability. Their thermal interface materials achieve conductivity values of 6-8 W/mK while preserving mechanical flexibility. GE has also developed a novel surface functionalization technique for ceramic fillers that creates covalent bonds with the polymer matrix, reducing interfacial thermal resistance by approximately 40%. Their latest innovation involves 3D-printable thermally conductive composites with aligned filler orientations that create preferential heat dissipation pathways, enabling customized thermal management solutions for complex module geometries.
Strengths: Comprehensive materials science capabilities; extensive testing facilities for thermal performance validation; strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing processes increase production costs; some formulations have limited environmental stability; requires specialized application techniques.
Critical Technologies in Thermal Interface Materials
Composite filler and thermosetting material
PatentInactiveJP2017128475A
Innovation
- A composite filler comprising boron nitride particles bonded by a silicon carbide binder, with specific properties such as aspect ratio, particle size, and compression modulus, is developed to improve thermal conductivity.
Substrate for power electronic module comprising organic-inorganic composite
PatentActiveKR1020220075852A
Innovation
- A substrate composed of an organic-inorganic composite with two or more types of ceramic fillers having different particle sizes dispersed in a curable resin, which enhances thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, and reduces thermal expansion mismatch.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The integration of composite fillers to enhance thermal conductivity in module substrates presents significant environmental and sustainability considerations that must be addressed throughout the product lifecycle. The production of high thermal conductivity fillers such as boron nitride, aluminum oxide, and graphene often involves energy-intensive processes that contribute to carbon emissions. Manufacturing methods for these materials typically require high temperatures and specialized equipment, resulting in substantial energy consumption and associated environmental impacts.
Material sourcing represents another critical environmental concern. Many high-performance fillers rely on rare or difficult-to-extract raw materials, potentially leading to habitat disruption, soil degradation, and water pollution in mining regions. The sustainability of supply chains becomes increasingly important as demand for these specialized materials grows across multiple industries.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Composite substrates with multiple integrated materials can be difficult to recycle effectively, potentially increasing electronic waste. However, innovations in design for disassembly and advanced recycling technologies are emerging to address these concerns. Closed-loop systems that recover valuable fillers from discarded substrates show particular promise for reducing environmental footprint.
The operational benefits of thermally enhanced substrates must be weighed against their production impacts. Improved thermal conductivity typically extends device lifespan by preventing heat-related failures, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation. Additionally, more efficient thermal management can lower energy consumption during device operation, offering significant lifetime environmental benefits that may offset initial production impacts.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and similar regulations globally limit the use of certain materials in electronic components. Forward-thinking manufacturers are proactively developing composite fillers that not only deliver superior thermal performance but also comply with current and anticipated environmental regulations.
Bio-based alternatives represent an emerging frontier in sustainable composite fillers. Research into cellulose nanofibers, lignin-derived carbons, and other renewable materials shows promise for creating environmentally friendly thermal management solutions. Though currently less thermally efficient than conventional options, these materials offer significantly reduced environmental impacts and may become increasingly viable as technology advances.
Material sourcing represents another critical environmental concern. Many high-performance fillers rely on rare or difficult-to-extract raw materials, potentially leading to habitat disruption, soil degradation, and water pollution in mining regions. The sustainability of supply chains becomes increasingly important as demand for these specialized materials grows across multiple industries.
End-of-life management presents both challenges and opportunities. Composite substrates with multiple integrated materials can be difficult to recycle effectively, potentially increasing electronic waste. However, innovations in design for disassembly and advanced recycling technologies are emerging to address these concerns. Closed-loop systems that recover valuable fillers from discarded substrates show particular promise for reducing environmental footprint.
The operational benefits of thermally enhanced substrates must be weighed against their production impacts. Improved thermal conductivity typically extends device lifespan by preventing heat-related failures, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated waste generation. Additionally, more efficient thermal management can lower energy consumption during device operation, offering significant lifetime environmental benefits that may offset initial production impacts.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly emphasizing sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. The European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and similar regulations globally limit the use of certain materials in electronic components. Forward-thinking manufacturers are proactively developing composite fillers that not only deliver superior thermal performance but also comply with current and anticipated environmental regulations.
Bio-based alternatives represent an emerging frontier in sustainable composite fillers. Research into cellulose nanofibers, lignin-derived carbons, and other renewable materials shows promise for creating environmentally friendly thermal management solutions. Though currently less thermally efficient than conventional options, these materials offer significantly reduced environmental impacts and may become increasingly viable as technology advances.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability of manufacturing processes for composite fillers in module substrates presents both opportunities and challenges for industry adoption. Current production methods for thermally conductive composites typically involve multi-step processes including material preparation, mixing, molding, and curing. These processes must be carefully optimized when transitioning from laboratory scale to mass production to maintain consistent thermal performance while managing costs.
For high-volume manufacturing, continuous processing techniques such as extrusion compounding and injection molding offer significant advantages over batch processes. These methods can reduce production time by up to 60% compared to traditional techniques while maintaining uniform filler distribution. However, the capital investment for such equipment ranges from $500,000 to several million dollars, creating a significant barrier to entry for smaller manufacturers.
Material costs represent another critical consideration. Premium thermal fillers such as boron nitride and synthetic diamond can cost between $80-500 per kilogram, substantially higher than conventional polymer materials at $2-5 per kilogram. This cost differential necessitates careful optimization of filler loading to balance thermal performance with economic viability. Analysis indicates that increasing filler content beyond 40-50% by volume often yields diminishing thermal conductivity improvements while dramatically increasing material costs and processing difficulties.
Energy consumption during manufacturing also impacts overall cost structures. High-temperature processing required for certain ceramic-based composites can consume 2-3 times more energy than conventional polymer processing. Implementation of heat recovery systems and process optimization can reduce this energy penalty by 25-30%, improving cost-effectiveness for large-scale operations.
Quality control represents a significant cost factor, particularly for applications requiring consistent thermal performance. Advanced testing equipment for thermal conductivity measurement can cost $50,000-150,000, with ongoing calibration and maintenance expenses. Manufacturers must implement statistical process control methods to ensure consistent filler distribution and orientation throughout production runs.
Supply chain considerations further influence manufacturing scalability. Certain high-performance fillers face supply constraints or geopolitical risks, potentially causing price volatility. Developing secondary supplier relationships and exploring alternative filler combinations can mitigate these risks but requires additional R&D investment. Companies that establish vertical integration by securing raw material sources may achieve 15-20% cost advantages over competitors relying entirely on external suppliers.
For high-volume manufacturing, continuous processing techniques such as extrusion compounding and injection molding offer significant advantages over batch processes. These methods can reduce production time by up to 60% compared to traditional techniques while maintaining uniform filler distribution. However, the capital investment for such equipment ranges from $500,000 to several million dollars, creating a significant barrier to entry for smaller manufacturers.
Material costs represent another critical consideration. Premium thermal fillers such as boron nitride and synthetic diamond can cost between $80-500 per kilogram, substantially higher than conventional polymer materials at $2-5 per kilogram. This cost differential necessitates careful optimization of filler loading to balance thermal performance with economic viability. Analysis indicates that increasing filler content beyond 40-50% by volume often yields diminishing thermal conductivity improvements while dramatically increasing material costs and processing difficulties.
Energy consumption during manufacturing also impacts overall cost structures. High-temperature processing required for certain ceramic-based composites can consume 2-3 times more energy than conventional polymer processing. Implementation of heat recovery systems and process optimization can reduce this energy penalty by 25-30%, improving cost-effectiveness for large-scale operations.
Quality control represents a significant cost factor, particularly for applications requiring consistent thermal performance. Advanced testing equipment for thermal conductivity measurement can cost $50,000-150,000, with ongoing calibration and maintenance expenses. Manufacturers must implement statistical process control methods to ensure consistent filler distribution and orientation throughout production runs.
Supply chain considerations further influence manufacturing scalability. Certain high-performance fillers face supply constraints or geopolitical risks, potentially causing price volatility. Developing secondary supplier relationships and exploring alternative filler combinations can mitigate these risks but requires additional R&D investment. Companies that establish vertical integration by securing raw material sources may achieve 15-20% cost advantages over competitors relying entirely on external suppliers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!