Thermoelectric Module Packaging For Long-Term Thermal Cycling Reliability
SEP 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Thermoelectric Module Packaging Background and Objectives
Thermoelectric modules (TEMs) have evolved significantly since their inception in the mid-20th century, transitioning from laboratory curiosities to practical devices with applications spanning aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer electronics sectors. The fundamental principle of thermoelectric conversion, known as the Seebeck effect, was discovered in 1821, but practical implementation faced significant barriers until the development of semiconductor materials in the 1950s.
The evolution of TEM packaging technology has been driven by increasing demands for reliability under thermal cycling conditions. Early designs suffered from mechanical failures at interconnection points and degradation of thermoelectric materials when subjected to repeated temperature fluctuations. This limitation has historically restricted their deployment in applications requiring long operational lifetimes under variable thermal conditions.
Recent advancements in materials science and packaging techniques have improved reliability, but significant challenges persist. Current state-of-the-art TEMs typically demonstrate performance degradation after 10,000-30,000 thermal cycles, falling short of the requirements for many high-reliability applications that demand 100,000+ cycles over 10-15 year operational lifespans.
The primary objective of this technical research is to investigate and develop advanced packaging solutions for thermoelectric modules that can maintain performance integrity under extended thermal cycling conditions. Specifically, we aim to identify packaging architectures, materials, and manufacturing processes that can mitigate the primary failure mechanisms: thermal expansion mismatch, solder fatigue, and interconnect degradation.
Secondary objectives include quantifying the relationship between packaging design parameters and reliability metrics, establishing accelerated testing protocols that accurately predict long-term performance, and developing analytical models to optimize design trade-offs between thermal performance, electrical efficiency, mechanical robustness, and manufacturing cost.
The technological trajectory indicates growing interest in flexible and conformal TEM packaging to accommodate non-planar heat sources and sinks. Additionally, there is movement toward integrated packaging approaches that combine thermoelectric elements with heat exchangers and power conditioning electronics in unified modules, reducing system complexity and thermal interfaces.
This research aligns with broader industry trends toward energy harvesting from waste heat sources and the increasing electrification of transportation systems, both of which require highly reliable thermal management solutions. Success in this domain would enable expanded application of thermoelectric technology in environments previously considered too demanding for reliable operation.
The evolution of TEM packaging technology has been driven by increasing demands for reliability under thermal cycling conditions. Early designs suffered from mechanical failures at interconnection points and degradation of thermoelectric materials when subjected to repeated temperature fluctuations. This limitation has historically restricted their deployment in applications requiring long operational lifetimes under variable thermal conditions.
Recent advancements in materials science and packaging techniques have improved reliability, but significant challenges persist. Current state-of-the-art TEMs typically demonstrate performance degradation after 10,000-30,000 thermal cycles, falling short of the requirements for many high-reliability applications that demand 100,000+ cycles over 10-15 year operational lifespans.
The primary objective of this technical research is to investigate and develop advanced packaging solutions for thermoelectric modules that can maintain performance integrity under extended thermal cycling conditions. Specifically, we aim to identify packaging architectures, materials, and manufacturing processes that can mitigate the primary failure mechanisms: thermal expansion mismatch, solder fatigue, and interconnect degradation.
Secondary objectives include quantifying the relationship between packaging design parameters and reliability metrics, establishing accelerated testing protocols that accurately predict long-term performance, and developing analytical models to optimize design trade-offs between thermal performance, electrical efficiency, mechanical robustness, and manufacturing cost.
The technological trajectory indicates growing interest in flexible and conformal TEM packaging to accommodate non-planar heat sources and sinks. Additionally, there is movement toward integrated packaging approaches that combine thermoelectric elements with heat exchangers and power conditioning electronics in unified modules, reducing system complexity and thermal interfaces.
This research aligns with broader industry trends toward energy harvesting from waste heat sources and the increasing electrification of transportation systems, both of which require highly reliable thermal management solutions. Success in this domain would enable expanded application of thermoelectric technology in environments previously considered too demanding for reliable operation.
Market Demand Analysis for Reliable Thermoelectric Solutions
The global market for thermoelectric modules is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for reliable thermal management solutions across multiple industries. Current market valuations indicate the thermoelectric module market reached approximately 600 million USD in 2022, with projections suggesting growth to exceed 900 million USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of around 7.5% during this forecast period.
This growth is primarily fueled by expanding applications in automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors where thermal cycling reliability has become a critical performance parameter. In the automotive industry, thermoelectric generators for waste heat recovery and climate control systems require modules capable of withstanding thousands of thermal cycles under harsh operating conditions. Market research indicates that automotive applications alone account for nearly 25% of the total thermoelectric module market.
The telecommunications and data center sectors represent another significant market segment, where cooling solutions for high-density electronics demand reliable thermoelectric modules with extended operational lifespans. With data centers consuming approximately 1-2% of global electricity and growing, the need for efficient cooling technologies presents substantial market opportunities for reliable thermoelectric solutions.
Consumer demand trends show increasing preference for miniaturized, energy-efficient devices with longer warranties, directly translating to higher requirements for thermal cycling reliability in thermoelectric modules. Market surveys indicate that end-users are willing to pay premium prices for solutions demonstrating proven long-term reliability, with reliability ranking as the second most important purchasing factor after initial cost.
Medical and laboratory equipment represents another high-value market segment where precise temperature control and exceptional reliability are paramount. Applications such as PCR thermal cyclers, blood analyzers, and tissue storage systems require thermoelectric modules capable of maintaining performance through hundreds of thousands of thermal cycles without degradation.
Industry analysis reveals a significant gap between current packaging technologies and market requirements for thermal cycling reliability. While standard thermoelectric modules typically offer 200,000-300,000 cycles before performance degradation, emerging applications in aerospace, medical diagnostics, and industrial automation often require reliability exceeding 500,000 cycles under varying temperature differentials.
This reliability gap represents both a market challenge and opportunity, with surveys indicating that 68% of system designers cite packaging reliability as their primary concern when selecting thermoelectric solutions. Companies that can demonstrate superior thermal cycling performance through advanced packaging technologies stand to capture premium market segments and establish long-term competitive advantages.
This growth is primarily fueled by expanding applications in automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors where thermal cycling reliability has become a critical performance parameter. In the automotive industry, thermoelectric generators for waste heat recovery and climate control systems require modules capable of withstanding thousands of thermal cycles under harsh operating conditions. Market research indicates that automotive applications alone account for nearly 25% of the total thermoelectric module market.
The telecommunications and data center sectors represent another significant market segment, where cooling solutions for high-density electronics demand reliable thermoelectric modules with extended operational lifespans. With data centers consuming approximately 1-2% of global electricity and growing, the need for efficient cooling technologies presents substantial market opportunities for reliable thermoelectric solutions.
Consumer demand trends show increasing preference for miniaturized, energy-efficient devices with longer warranties, directly translating to higher requirements for thermal cycling reliability in thermoelectric modules. Market surveys indicate that end-users are willing to pay premium prices for solutions demonstrating proven long-term reliability, with reliability ranking as the second most important purchasing factor after initial cost.
Medical and laboratory equipment represents another high-value market segment where precise temperature control and exceptional reliability are paramount. Applications such as PCR thermal cyclers, blood analyzers, and tissue storage systems require thermoelectric modules capable of maintaining performance through hundreds of thousands of thermal cycles without degradation.
Industry analysis reveals a significant gap between current packaging technologies and market requirements for thermal cycling reliability. While standard thermoelectric modules typically offer 200,000-300,000 cycles before performance degradation, emerging applications in aerospace, medical diagnostics, and industrial automation often require reliability exceeding 500,000 cycles under varying temperature differentials.
This reliability gap represents both a market challenge and opportunity, with surveys indicating that 68% of system designers cite packaging reliability as their primary concern when selecting thermoelectric solutions. Companies that can demonstrate superior thermal cycling performance through advanced packaging technologies stand to capture premium market segments and establish long-term competitive advantages.
Current Challenges in Thermal Cycling Reliability
Thermoelectric modules (TEMs) face significant reliability challenges when subjected to thermal cycling conditions, particularly in long-term applications. The primary challenge stems from the inherent material mismatch between different components within the module. Bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric materials, copper conductors, ceramic substrates, and solder interconnections all possess different coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE), creating substantial thermomechanical stress during temperature fluctuations.
These stresses manifest most severely at interface regions, particularly at solder joints connecting thermoelectric elements to copper conductors. Repeated thermal cycling induces fatigue in these connections, leading to crack initiation and propagation. Once cracks form, electrical resistance increases, thermal transfer efficiency decreases, and module performance degrades progressively over time.
Current packaging technologies struggle to maintain hermetic sealing throughout extended thermal cycling. Environmental factors such as moisture ingress and oxidation accelerate degradation mechanisms when seals fail. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring thousands of thermal cycles over multi-year operational lifespans, such as in automotive waste heat recovery systems or space applications.
Another significant challenge is the trade-off between mechanical robustness and thermal performance. Traditional approaches to improve mechanical reliability often involve thicker solder layers or compliant interfaces, which inevitably increase thermal resistance and reduce overall system efficiency. This fundamental conflict between reliability and performance represents a critical engineering challenge.
The industry currently lacks standardized accelerated testing protocols specifically designed for thermoelectric modules under thermal cycling conditions. This hampers comparative evaluation of different packaging solutions and makes lifetime prediction models less reliable. Most existing reliability models are adapted from microelectronics packaging, which may not fully capture the unique thermomechanical behavior of thermoelectric systems.
Manufacturing consistency presents another obstacle, as minor variations in assembly processes can significantly impact long-term reliability. Parameters such as solder composition, reflow profiles, and surface preparation must be precisely controlled to ensure consistent performance across production batches. Current manufacturing techniques struggle to maintain this precision at scale.
Advanced computational modeling capabilities are needed but remain underdeveloped for thermoelectric applications. While finite element analysis tools exist, they often fail to accurately predict failure modes under complex thermal cycling conditions due to insufficient material property data and inadequate multi-physics coupling between thermal, electrical, and mechanical domains.
These stresses manifest most severely at interface regions, particularly at solder joints connecting thermoelectric elements to copper conductors. Repeated thermal cycling induces fatigue in these connections, leading to crack initiation and propagation. Once cracks form, electrical resistance increases, thermal transfer efficiency decreases, and module performance degrades progressively over time.
Current packaging technologies struggle to maintain hermetic sealing throughout extended thermal cycling. Environmental factors such as moisture ingress and oxidation accelerate degradation mechanisms when seals fail. This is particularly problematic in applications requiring thousands of thermal cycles over multi-year operational lifespans, such as in automotive waste heat recovery systems or space applications.
Another significant challenge is the trade-off between mechanical robustness and thermal performance. Traditional approaches to improve mechanical reliability often involve thicker solder layers or compliant interfaces, which inevitably increase thermal resistance and reduce overall system efficiency. This fundamental conflict between reliability and performance represents a critical engineering challenge.
The industry currently lacks standardized accelerated testing protocols specifically designed for thermoelectric modules under thermal cycling conditions. This hampers comparative evaluation of different packaging solutions and makes lifetime prediction models less reliable. Most existing reliability models are adapted from microelectronics packaging, which may not fully capture the unique thermomechanical behavior of thermoelectric systems.
Manufacturing consistency presents another obstacle, as minor variations in assembly processes can significantly impact long-term reliability. Parameters such as solder composition, reflow profiles, and surface preparation must be precisely controlled to ensure consistent performance across production batches. Current manufacturing techniques struggle to maintain this precision at scale.
Advanced computational modeling capabilities are needed but remain underdeveloped for thermoelectric applications. While finite element analysis tools exist, they often fail to accurately predict failure modes under complex thermal cycling conditions due to insufficient material property data and inadequate multi-physics coupling between thermal, electrical, and mechanical domains.
State-of-the-Art Packaging Solutions
01 Thermal interface materials for improved reliability
Specialized thermal interface materials are used between thermoelectric modules and heat exchangers to improve thermal cycling reliability. These materials, including thermal greases, phase change materials, and compliant thermal pads, help accommodate thermal expansion mismatches while maintaining effective heat transfer. The proper selection and application of these materials can significantly enhance the durability of thermoelectric modules under repeated thermal cycling conditions.- Thermal interface materials for improved reliability: Specialized thermal interface materials are used between thermoelectric modules and heat exchangers to improve thermal cycling reliability. These materials, including phase change materials, thermal greases, and compliant thermal pads, help accommodate thermal expansion mismatches between different components while maintaining effective heat transfer. The proper selection and application of these materials can significantly enhance the thermal cycling durability of thermoelectric module packages by reducing mechanical stress during temperature fluctuations.
- Structural design for thermal stress management: Advanced structural designs are implemented to manage thermal stress in thermoelectric module packaging. These designs include flexible interconnects, stress-relieving structures, and optimized geometry configurations that accommodate thermal expansion and contraction during cycling. By incorporating compliant mechanical structures and strategic component placement, these designs minimize stress concentration at critical interfaces, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and operational lifespan of thermoelectric modules under thermal cycling conditions.
- Encapsulation and sealing techniques: Effective encapsulation and sealing techniques protect thermoelectric modules from environmental factors that can accelerate degradation during thermal cycling. Hermetic sealing methods, moisture-resistant encapsulants, and specialized polymer coatings create protective barriers against humidity, oxidation, and contaminants. These techniques preserve the integrity of thermoelectric elements and electrical connections during repeated temperature changes, significantly improving long-term reliability and preventing performance deterioration in challenging operating environments.
- Advanced bonding and interconnection methods: Innovative bonding and interconnection methods enhance the reliability of thermoelectric modules during thermal cycling. Techniques such as transient liquid phase bonding, low-temperature sintering, and specialized soldering processes create robust connections between thermoelectric elements and substrates. These methods produce joints with improved mechanical strength and fatigue resistance, minimizing the risk of connection failures during repeated thermal expansion and contraction cycles, which are common failure points in thermoelectric module packages.
- Testing and qualification protocols: Comprehensive testing and qualification protocols are essential for evaluating and ensuring the thermal cycling reliability of thermoelectric module packages. These protocols include accelerated life testing, thermal shock testing, and performance monitoring under simulated operating conditions. Advanced analytical techniques such as infrared thermography, acoustic microscopy, and in-situ resistance monitoring help identify potential failure modes and validate design improvements, enabling the development of more reliable thermoelectric module packaging solutions for demanding applications.
02 Structural design for thermal stress management
Advanced structural designs are implemented to manage thermal stresses during cycling. These include flexible interconnects, stress-relieving geometries, and mechanically decoupled structures that allow for thermal expansion without creating damaging stresses. Some designs incorporate compliant members or floating connections that absorb dimensional changes during temperature fluctuations, thereby extending the operational lifetime of thermoelectric modules under thermal cycling conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Encapsulation and sealing techniques
Protective encapsulation and sealing methods are employed to shield thermoelectric modules from environmental factors that could accelerate degradation during thermal cycling. These techniques include hermetic sealing, polymer encapsulation, and specialized coating technologies that prevent moisture ingress and oxidation. The encapsulation materials are selected for their ability to withstand repeated temperature changes while maintaining their protective properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced bonding and interconnection methods
Innovative bonding and interconnection technologies are developed to enhance the reliability of thermoelectric modules during thermal cycling. These include low-temperature sintering, transient liquid phase bonding, and specialized soldering techniques with stress-accommodating properties. The connections are designed to maintain electrical and thermal conductivity while withstanding the mechanical stresses induced by repeated thermal expansion and contraction cycles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and qualification protocols
Comprehensive testing and qualification protocols are established to evaluate and predict the thermal cycling reliability of thermoelectric module packages. These include accelerated life testing, thermal shock testing, and real-time monitoring of electrical and thermal performance during cycling. Advanced analytical techniques such as finite element analysis and thermal imaging are used to identify potential failure modes and optimize package designs for enhanced reliability under varying thermal conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
Thermoelectric module packaging for long-term thermal cycling reliability is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing demand for reliable thermal management solutions across automotive, electronics, and energy sectors. The global market is projected to reach significant scale as applications in waste heat recovery and precision temperature control gain traction. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established players like LG Innotek, KELK Ltd., and Kyocera leading commercial development, while companies such as Hyundai Motor, DENSO, and MAHLE are advancing automotive-specific applications. Research institutions including University of Cambridge and AIST are pushing boundaries in material science and packaging techniques to address the critical challenge of maintaining performance integrity during repeated thermal cycling.
LG Innotek Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Innotek has developed a comprehensive thermoelectric module packaging solution focused on long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions. Their technology employs a multi-layer composite substrate structure with carefully matched thermal expansion coefficients to minimize mechanical stress during temperature fluctuations. The company utilizes advanced nano-metallization techniques to create robust electrical connections between thermoelectric elements and substrates, significantly reducing failure points during thermal cycling. LG's packaging incorporates specialized flexible bonding materials that accommodate thermal expansion while maintaining thermal conductivity pathways. Their modules feature a proprietary hermetic sealing system using high-temperature resistant polymers combined with inorganic barriers that prevent moisture penetration while allowing for thermal expansion movement. This integrated approach enables their modules to maintain consistent performance characteristics even after thousands of thermal cycles across industrial temperature ranges.
Strengths: Excellent thermal cycling endurance with minimal performance degradation; advanced nano-metallization creates highly reliable electrical connections; comprehensive moisture protection system extends operational life. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process increases production costs; slightly lower power density compared to less durable alternatives; requires specialized handling during system integration.
KELK Ltd.
Technical Solution: KELK Ltd. has developed advanced thermoelectric module packaging solutions specifically designed for long-term thermal cycling reliability. Their technology employs a proprietary multi-layer structure with specialized metallization and bonding techniques that significantly reduce thermal expansion mismatches between different materials. The company utilizes a combination of copper-based substrates with specialized diffusion barriers and stress-relieving intermediate layers to prevent delamination during thermal cycling. KELK's modules incorporate pre-stressed design elements that accommodate the differential expansion rates during temperature fluctuations, maintaining electrical connectivity and thermal performance over extended cycling periods. Their packaging technology includes hermetic sealing methods with specialized polymer encapsulants that resist moisture ingress while allowing for thermal expansion, significantly extending module lifespan in variable temperature environments.
Strengths: Superior thermal cycling endurance exceeding 100,000 cycles with minimal performance degradation; excellent resistance to thermal shock; proprietary bonding technology minimizes internal stresses. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to conventional packaging; requires specialized assembly processes; slightly lower power density due to stress-relieving design elements.
Key Patents and Technical Innovations
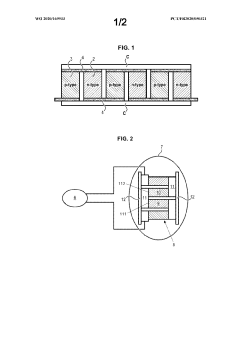
Thermoelectric supply module of a measurement device for a turbomachine
PatentWO2020169933A1
Innovation
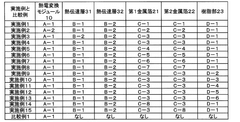
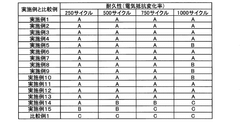
- A thermoelectric power supply module is designed with parallel support plates, n-type and p-type legs made of specific alloys (iron-silicon and manganese-silicon), and interconnection elements comprising solid solutions like TiMnSi2 and TiFeSi2, along with optional doping elements, to enhance mechanical coherence, chemical compatibility, and the formation of protective oxide layers.
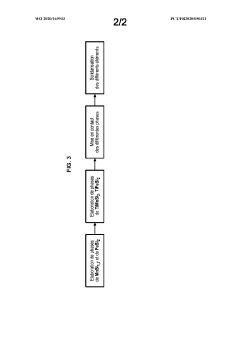
Thermoelectric conversion module package
PatentWO2017179735A1
Innovation
- A thermoelectric conversion module package design using metal foils covered by a resin, which thermally insulates the substrates and allows for airtight sealing of lead wires, maintaining temperature differences and reducing manufacturing complexity.
Materials Science Advancements for Thermal Interfaces
Recent advancements in materials science have significantly contributed to improving the reliability and performance of thermoelectric module packaging under thermal cycling conditions. The development of novel thermal interface materials (TIMs) has been particularly crucial in addressing the challenges of coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatches between different components, which often lead to mechanical stress and eventual failure during thermal cycling.
Nanostructured composite materials have emerged as promising candidates for thermal interfaces in thermoelectric modules. These materials combine high thermal conductivity with mechanical compliance, allowing them to maintain good thermal contact while accommodating dimensional changes during temperature fluctuations. Carbon-based materials, including graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs), have demonstrated exceptional thermal conductivity values exceeding 2000 W/m·K, significantly outperforming traditional metal-based interfaces.
Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporated into thermal interfaces represent another significant advancement. These materials undergo solid-liquid transitions at specific temperatures, enabling them to fill microscopic gaps at interfaces and maintain consistent thermal contact throughout thermal cycling. Recent formulations have achieved melting points tailored to specific operating temperature ranges while maintaining stability for thousands of cycles.
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) with engineered CTE values have been developed specifically for thermoelectric applications. By incorporating ceramic particles into metal matrices, researchers have created interfaces with CTEs that closely match those of both semiconductor thermoelectric materials and heat exchangers, minimizing thermomechanical stress during cycling. These MMCs maintain thermal conductivity values above 150 W/m·K while providing the necessary mechanical compliance.
Sintered silver and other nano-silver based joining technologies represent a significant breakthrough for high-temperature thermoelectric applications. These materials form strong metallurgical bonds without the reliability issues associated with traditional solders, maintaining integrity through thousands of thermal cycles between -40°C and 150°C. The porous microstructure of sintered silver accommodates strain during thermal cycling while providing excellent thermal pathways.
Polymer-based TIMs with engineered viscoelastic properties have also shown promise for long-term reliability. These materials incorporate thermally conductive fillers within elastomeric matrices that can absorb mechanical stress during thermal cycling. Recent formulations have achieved thermal conductivity values exceeding 5 W/m·K while maintaining compliance through thousands of thermal cycles, representing a tenfold improvement over materials available just a decade ago.
Nanostructured composite materials have emerged as promising candidates for thermal interfaces in thermoelectric modules. These materials combine high thermal conductivity with mechanical compliance, allowing them to maintain good thermal contact while accommodating dimensional changes during temperature fluctuations. Carbon-based materials, including graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs), have demonstrated exceptional thermal conductivity values exceeding 2000 W/m·K, significantly outperforming traditional metal-based interfaces.
Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporated into thermal interfaces represent another significant advancement. These materials undergo solid-liquid transitions at specific temperatures, enabling them to fill microscopic gaps at interfaces and maintain consistent thermal contact throughout thermal cycling. Recent formulations have achieved melting points tailored to specific operating temperature ranges while maintaining stability for thousands of cycles.
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) with engineered CTE values have been developed specifically for thermoelectric applications. By incorporating ceramic particles into metal matrices, researchers have created interfaces with CTEs that closely match those of both semiconductor thermoelectric materials and heat exchangers, minimizing thermomechanical stress during cycling. These MMCs maintain thermal conductivity values above 150 W/m·K while providing the necessary mechanical compliance.
Sintered silver and other nano-silver based joining technologies represent a significant breakthrough for high-temperature thermoelectric applications. These materials form strong metallurgical bonds without the reliability issues associated with traditional solders, maintaining integrity through thousands of thermal cycles between -40°C and 150°C. The porous microstructure of sintered silver accommodates strain during thermal cycling while providing excellent thermal pathways.
Polymer-based TIMs with engineered viscoelastic properties have also shown promise for long-term reliability. These materials incorporate thermally conductive fillers within elastomeric matrices that can absorb mechanical stress during thermal cycling. Recent formulations have achieved thermal conductivity values exceeding 5 W/m·K while maintaining compliance through thousands of thermal cycles, representing a tenfold improvement over materials available just a decade ago.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of thermoelectric module packaging extends beyond performance considerations to encompass sustainability across the entire product lifecycle. Traditional packaging materials often include lead-based solders and other hazardous substances that pose significant environmental risks during manufacturing, operation, and disposal phases. Recent regulatory frameworks such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives have accelerated the transition toward lead-free alternatives in thermoelectric packaging solutions.
Material selection for thermoelectric module packaging presents a critical sustainability challenge. While high-performance metals like copper and aluminum offer excellent thermal conductivity, their extraction and processing carry substantial carbon footprints. Emerging research focuses on developing bio-based polymers and composite materials that can provide adequate thermal performance while reducing environmental impact. These materials must balance thermal cycling reliability with ecological considerations throughout their lifecycle.
Energy consumption during manufacturing represents another significant environmental factor. Conventional thermoelectric module packaging processes often require high-temperature soldering and bonding operations that consume substantial energy. Advanced manufacturing techniques such as low-temperature sintering and cold welding are being explored to reduce energy requirements while maintaining or improving long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions.
End-of-life considerations for thermoelectric modules present unique challenges due to the heterogeneous material composition of packaging systems. Current recycling infrastructure struggles to efficiently separate and recover valuable materials from thermoelectric modules, resulting in significant material loss. Design for disassembly approaches are gaining traction, where packaging architectures incorporate features that facilitate material separation and recovery at end-of-life.
Carbon footprint analysis of thermoelectric module packaging reveals that operational efficiency improvements must be balanced against manufacturing impacts. While more sophisticated packaging may enhance thermal cycling reliability and extend service life, the additional materials and processing steps may increase initial environmental impact. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to optimize this balance, considering factors such as operational lifetime, energy efficiency gains, and material recoverability.
Water usage in manufacturing processes for thermoelectric packaging also warrants attention, particularly for cleaning operations and chemical treatments. Closed-loop water systems and waterless processing alternatives are being developed to minimize this environmental burden while maintaining the cleanliness standards necessary for reliable packaging performance under thermal cycling conditions.
Material selection for thermoelectric module packaging presents a critical sustainability challenge. While high-performance metals like copper and aluminum offer excellent thermal conductivity, their extraction and processing carry substantial carbon footprints. Emerging research focuses on developing bio-based polymers and composite materials that can provide adequate thermal performance while reducing environmental impact. These materials must balance thermal cycling reliability with ecological considerations throughout their lifecycle.
Energy consumption during manufacturing represents another significant environmental factor. Conventional thermoelectric module packaging processes often require high-temperature soldering and bonding operations that consume substantial energy. Advanced manufacturing techniques such as low-temperature sintering and cold welding are being explored to reduce energy requirements while maintaining or improving long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions.
End-of-life considerations for thermoelectric modules present unique challenges due to the heterogeneous material composition of packaging systems. Current recycling infrastructure struggles to efficiently separate and recover valuable materials from thermoelectric modules, resulting in significant material loss. Design for disassembly approaches are gaining traction, where packaging architectures incorporate features that facilitate material separation and recovery at end-of-life.
Carbon footprint analysis of thermoelectric module packaging reveals that operational efficiency improvements must be balanced against manufacturing impacts. While more sophisticated packaging may enhance thermal cycling reliability and extend service life, the additional materials and processing steps may increase initial environmental impact. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are increasingly being applied to optimize this balance, considering factors such as operational lifetime, energy efficiency gains, and material recoverability.
Water usage in manufacturing processes for thermoelectric packaging also warrants attention, particularly for cleaning operations and chemical treatments. Closed-loop water systems and waterless processing alternatives are being developed to minimize this environmental burden while maintaining the cleanliness standards necessary for reliable packaging performance under thermal cycling conditions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!