Regulatory Perspectives on Shape Memory Alloys in Medical Treatments
SEP 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
SMA Medical Applications Background and Objectives
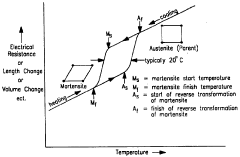
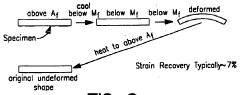
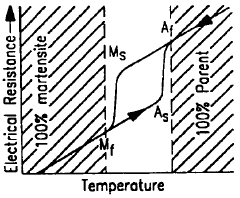
Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) have emerged as revolutionary materials in the medical field since their discovery in the 1960s. These unique metallic compounds possess the remarkable ability to "remember" and return to their original shape when subjected to specific temperature changes or mechanical stresses. The most widely utilized SMA in medical applications is Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, which has transformed numerous medical treatment approaches due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties that closely mimic human tissues.
The evolution of SMA technology in medicine has followed a trajectory of increasing sophistication and application breadth. Initially limited to orthodontic wires and simple surgical instruments, SMAs now feature prominently in cardiovascular stents, orthopedic implants, neurosurgical devices, and minimally invasive surgical tools. This technological progression has been driven by advances in material science, manufacturing techniques, and a deeper understanding of the unique metallurgical properties of these alloys.
Regulatory frameworks governing SMAs in medical treatments have similarly evolved, reflecting the growing complexity of applications and heightened awareness of patient safety considerations. Early regulatory approaches treated SMAs as conventional metallic implants, but contemporary regulatory perspectives recognize their unique characteristics and potential risks, particularly regarding nickel sensitivity, fatigue behavior, and long-term biocompatibility.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively analyze the current regulatory landscape surrounding SMAs in medical treatments across major global markets. We aim to identify regulatory trends, challenges, and inconsistencies that may impact the development, approval, and commercialization of SMA-based medical devices and treatments.
Additionally, this report seeks to evaluate how regulatory requirements for SMAs have adapted to technological advancements and emerging clinical applications. By examining case studies of successful regulatory approvals and notable regulatory hurdles, we intend to provide insights into effective compliance strategies and potential regulatory evolution pathways.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore the intersection between material science innovations in SMAs and corresponding regulatory considerations, particularly focusing on how novel alloy compositions, processing techniques, and surface modifications might influence regulatory perspectives and requirements. Understanding this relationship is crucial for anticipating future regulatory developments and informing strategic R&D investments in this rapidly advancing field.
The evolution of SMA technology in medicine has followed a trajectory of increasing sophistication and application breadth. Initially limited to orthodontic wires and simple surgical instruments, SMAs now feature prominently in cardiovascular stents, orthopedic implants, neurosurgical devices, and minimally invasive surgical tools. This technological progression has been driven by advances in material science, manufacturing techniques, and a deeper understanding of the unique metallurgical properties of these alloys.
Regulatory frameworks governing SMAs in medical treatments have similarly evolved, reflecting the growing complexity of applications and heightened awareness of patient safety considerations. Early regulatory approaches treated SMAs as conventional metallic implants, but contemporary regulatory perspectives recognize their unique characteristics and potential risks, particularly regarding nickel sensitivity, fatigue behavior, and long-term biocompatibility.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to comprehensively analyze the current regulatory landscape surrounding SMAs in medical treatments across major global markets. We aim to identify regulatory trends, challenges, and inconsistencies that may impact the development, approval, and commercialization of SMA-based medical devices and treatments.
Additionally, this report seeks to evaluate how regulatory requirements for SMAs have adapted to technological advancements and emerging clinical applications. By examining case studies of successful regulatory approvals and notable regulatory hurdles, we intend to provide insights into effective compliance strategies and potential regulatory evolution pathways.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore the intersection between material science innovations in SMAs and corresponding regulatory considerations, particularly focusing on how novel alloy compositions, processing techniques, and surface modifications might influence regulatory perspectives and requirements. Understanding this relationship is crucial for anticipating future regulatory developments and informing strategic R&D investments in this rapidly advancing field.
Market Analysis for SMA-Based Medical Devices
The global market for Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) medical devices has experienced significant growth over the past decade, with a current market valuation exceeding $12 billion. This growth trajectory is expected to continue at a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% through 2028, driven primarily by increasing applications in minimally invasive surgeries and personalized medical treatments.
Cardiovascular applications represent the largest segment of the SMA medical device market, accounting for approximately 35% of total revenue. Stents and guidewires utilizing nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy) dominate this segment due to their superior biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Orthopedic applications follow closely at 28% market share, with dental applications representing 15% of the market.
North America currently leads the global market with 42% share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 22%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.5% annually, primarily due to expanding healthcare infrastructure in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of advanced medical technologies.
The competitive landscape features both established medical device manufacturers and specialized SMA technology companies. Major players include Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott Laboratories, collectively controlling approximately 45% of the market. These companies have established robust regulatory compliance frameworks and extensive distribution networks, creating significant barriers to entry for new competitors.
Consumer demand patterns indicate a strong preference for devices that reduce recovery time and minimize surgical trauma. This trend aligns perfectly with SMA-based devices, which can be deployed in compressed forms and activated within the body. Patient-reported outcomes show 30% faster recovery times with SMA-based interventions compared to traditional surgical approaches.
Reimbursement policies significantly impact market adoption rates across different regions. In countries with favorable reimbursement structures for minimally invasive procedures, SMA device penetration rates are typically 2-3 times higher than in markets with restrictive policies. This correlation highlights the importance of regulatory and insurance frameworks in determining market potential.
Pricing analysis reveals that while SMA-based devices command a premium of 15-25% over conventional alternatives, the total treatment cost often proves lower when accounting for reduced hospitalization time and fewer complications. This value proposition has been instrumental in driving adoption despite initial higher device costs.
Cardiovascular applications represent the largest segment of the SMA medical device market, accounting for approximately 35% of total revenue. Stents and guidewires utilizing nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy) dominate this segment due to their superior biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Orthopedic applications follow closely at 28% market share, with dental applications representing 15% of the market.
North America currently leads the global market with 42% share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 22%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.5% annually, primarily due to expanding healthcare infrastructure in China and India, coupled with increasing adoption of advanced medical technologies.
The competitive landscape features both established medical device manufacturers and specialized SMA technology companies. Major players include Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott Laboratories, collectively controlling approximately 45% of the market. These companies have established robust regulatory compliance frameworks and extensive distribution networks, creating significant barriers to entry for new competitors.
Consumer demand patterns indicate a strong preference for devices that reduce recovery time and minimize surgical trauma. This trend aligns perfectly with SMA-based devices, which can be deployed in compressed forms and activated within the body. Patient-reported outcomes show 30% faster recovery times with SMA-based interventions compared to traditional surgical approaches.
Reimbursement policies significantly impact market adoption rates across different regions. In countries with favorable reimbursement structures for minimally invasive procedures, SMA device penetration rates are typically 2-3 times higher than in markets with restrictive policies. This correlation highlights the importance of regulatory and insurance frameworks in determining market potential.
Pricing analysis reveals that while SMA-based devices command a premium of 15-25% over conventional alternatives, the total treatment cost often proves lower when accounting for reduced hospitalization time and fewer complications. This value proposition has been instrumental in driving adoption despite initial higher device costs.
Current SMA Technology Landscape and Barriers
Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) have established a significant presence in the medical device industry, with Nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy) dominating the landscape. Currently, SMAs are widely utilized in cardiovascular stents, orthodontic archwires, orthopedic implants, and minimally invasive surgical instruments. The global medical SMA market is estimated at approximately $12 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 8-10%, indicating robust industry adoption.
Despite widespread implementation, the regulatory landscape for SMAs presents substantial challenges. The FDA classifies most SMA-based medical devices as Class II or III, requiring rigorous premarket approval processes. European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) similarly imposes strict requirements, particularly regarding nickel leaching concerns and long-term biocompatibility. These regulatory frameworks create significant barriers to market entry, with approval timelines often extending 3-5 years for novel SMA applications.
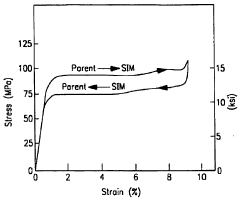
Technical limitations further constrain SMA implementation in medical treatments. Current manufacturing processes struggle with precise control of transformation temperatures across complex geometries, resulting in performance variability that complicates regulatory approval. Material fatigue remains a critical concern, particularly for applications requiring repeated actuation cycles, such as artificial heart valves or dynamic orthopedic implants.
Biocompatibility issues represent another significant barrier. While Nitinol has demonstrated acceptable biocompatibility in many applications, concerns persist regarding nickel hypersensitivity, which affects approximately 10-15% of the population. Alternative SMA compositions, such as copper-based or iron-based alloys, have shown promise in laboratory settings but face substantial regulatory hurdles due to limited clinical data and unresolved toxicity concerns.
The geographical distribution of SMA technology development shows concentration in North America, Europe, and Japan, with emerging research centers in China and South Korea. This distribution creates regulatory complexity as manufacturers must navigate multiple approval pathways across different jurisdictions, each with unique requirements for SMA-based medical devices.
Cost factors present additional barriers, with specialized SMA manufacturing requiring significant capital investment. The complex processing requirements and stringent quality control measures necessary to meet regulatory standards drive production costs substantially higher than conventional medical-grade materials, limiting adoption in cost-sensitive healthcare markets and applications.
Despite widespread implementation, the regulatory landscape for SMAs presents substantial challenges. The FDA classifies most SMA-based medical devices as Class II or III, requiring rigorous premarket approval processes. European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) similarly imposes strict requirements, particularly regarding nickel leaching concerns and long-term biocompatibility. These regulatory frameworks create significant barriers to market entry, with approval timelines often extending 3-5 years for novel SMA applications.
Technical limitations further constrain SMA implementation in medical treatments. Current manufacturing processes struggle with precise control of transformation temperatures across complex geometries, resulting in performance variability that complicates regulatory approval. Material fatigue remains a critical concern, particularly for applications requiring repeated actuation cycles, such as artificial heart valves or dynamic orthopedic implants.
Biocompatibility issues represent another significant barrier. While Nitinol has demonstrated acceptable biocompatibility in many applications, concerns persist regarding nickel hypersensitivity, which affects approximately 10-15% of the population. Alternative SMA compositions, such as copper-based or iron-based alloys, have shown promise in laboratory settings but face substantial regulatory hurdles due to limited clinical data and unresolved toxicity concerns.
The geographical distribution of SMA technology development shows concentration in North America, Europe, and Japan, with emerging research centers in China and South Korea. This distribution creates regulatory complexity as manufacturers must navigate multiple approval pathways across different jurisdictions, each with unique requirements for SMA-based medical devices.
Cost factors present additional barriers, with specialized SMA manufacturing requiring significant capital investment. The complex processing requirements and stringent quality control measures necessary to meet regulatory standards drive production costs substantially higher than conventional medical-grade materials, limiting adoption in cost-sensitive healthcare markets and applications.
Existing SMA Solutions in Medical Treatments
01 Composition and manufacturing of shape memory alloys
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) can be manufactured with specific compositions to achieve desired transformation temperatures and mechanical properties. The manufacturing processes include melting, casting, and thermomechanical treatments that influence the microstructure and functional properties of the alloys. These processes are critical for controlling the shape memory effect and superelasticity characteristics that make these materials valuable for various applications.- Composition and manufacturing of shape memory alloys: Shape memory alloys (SMAs) can be manufactured with specific compositions to achieve desired transformation temperatures and mechanical properties. These alloys typically contain nickel-titanium (Nitinol) or copper-based compositions. The manufacturing process involves precise control of melting, casting, and heat treatment to ensure the shape memory effect is properly developed. Advanced processing techniques can enhance the functional properties of these alloys, including their ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated above their transformation temperature.
- Applications in medical devices and implants: Shape memory alloys are widely used in medical applications due to their biocompatibility and unique mechanical properties. These materials are particularly valuable for minimally invasive surgical devices, stents, orthodontic wires, and other implantable devices. The superelasticity of these alloys allows medical devices to be compressed for insertion and then expand to their functional shape once deployed in the body. Their ability to maintain constant force over a range of deformations makes them ideal for applications requiring gentle but persistent pressure on biological tissues.
- Actuators and mechanical systems using shape memory alloys: Shape memory alloys are employed as actuators in various mechanical systems due to their ability to generate significant force and displacement when heated. These actuators can replace conventional motors and pneumatic systems in applications requiring compact design and silent operation. The thermomechanical response of shape memory alloys allows them to convert thermal energy directly into mechanical work. These materials are used in automotive, aerospace, and robotics applications where traditional actuators may be too bulky or complex.
- Heat treatment and processing techniques for shape memory alloys: Specific heat treatment processes are crucial for optimizing the performance of shape memory alloys. These processes include annealing, aging, and quenching treatments that control the microstructure and transformation characteristics of the alloy. The temperature, duration, and cooling rate during heat treatment significantly affect the shape memory effect and superelastic properties. Advanced processing techniques such as thermomechanical training can enhance the functional stability and fatigue resistance of these materials, extending their operational lifespan in demanding applications.
- Novel shape memory alloy compositions and high-performance variants: Research has led to the development of novel shape memory alloy compositions with enhanced properties such as higher transformation temperatures, improved corrosion resistance, and greater fatigue life. These include high-temperature shape memory alloys that can operate in extreme environments, magnetic shape memory alloys that respond to magnetic fields, and multi-component alloys with tailored characteristics. Advancements in material science have enabled the creation of shape memory alloys with faster response times, larger recoverable strains, and better functional stability under cyclic loading conditions.
02 Applications in medical devices and implants
Shape memory alloys are extensively used in medical applications due to their biocompatibility and unique mechanical properties. These alloys are employed in stents, orthodontic wires, surgical instruments, and implantable devices. The ability of SMAs to recover their original shape when heated above their transformation temperature makes them ideal for minimally invasive procedures where devices need to deploy after insertion into the body.Expand Specific Solutions03 Actuators and mechanical systems
Shape memory alloys are utilized as actuators in various mechanical systems due to their ability to generate significant force during shape recovery. These actuators can be designed to respond to temperature changes, making them suitable for applications in automotive, aerospace, and robotics industries. SMA-based actuators offer advantages such as silent operation, compact design, and high power-to-weight ratio compared to conventional electromagnetic actuators.Expand Specific Solutions04 Heat treatment and processing techniques
Heat treatment processes are crucial for optimizing the properties of shape memory alloys. These techniques include annealing, aging, and quenching, which affect the transformation temperatures and mechanical behavior of the alloys. Proper heat treatment can enhance the shape memory effect, improve fatigue resistance, and adjust the hysteresis characteristics of the material, making it more suitable for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and emerging technologies
Shape memory alloys are finding new applications in emerging technologies such as smart textiles, self-healing structures, and energy harvesting devices. Research is focused on developing new alloy compositions with enhanced properties, including wider transformation temperature ranges, improved fatigue resistance, and greater recoverable strain. These innovations are expanding the potential uses of SMAs in fields such as civil engineering, consumer electronics, and environmental monitoring systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Analysis
The regulatory landscape for Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) in medical treatments is evolving within a maturing industry characterized by significant growth potential. The global SMA medical device market is estimated at $12-15 billion annually, with 8-10% projected growth through 2028. Leading companies like Medtronic, W.L. Gore & Associates, and Shape Memory Medical are driving innovation with FDA-cleared SMA devices, while academic institutions including MIT, Johns Hopkins, and Texas A&M provide crucial research support. The technology has reached commercial viability for certain applications but remains in developmental stages for others, with regulatory frameworks varying significantly between regions. Companies must navigate complex approval pathways that balance innovation with patient safety requirements across cardiovascular, orthopedic, and neurological applications.
Medtronic, Inc.
Technical Solution: Medtronic has developed comprehensive regulatory compliance strategies for their shape memory alloy (SMA) medical devices, particularly focusing on nitinol-based implants. Their approach includes extensive biocompatibility testing protocols that address FDA and international regulatory concerns about nickel leaching and tissue response[1]. Medtronic's regulatory pathway involves a multi-phase clinical trial design specifically adapted for SMA devices, with particular attention to long-term implant stability and fatigue resistance. They've pioneered standardized testing methodologies for superelastic nitinol components that have been incorporated into FDA guidance documents[3]. Their regulatory strategy includes post-market surveillance systems specifically designed to track the unique failure modes and long-term performance of SMA implants, with specialized adverse event reporting categories for shape-recovery related incidents[5]. Medtronic has also developed specialized manufacturing process validation protocols that satisfy regulatory requirements for consistent phase transformation temperatures across production lots.
Strengths: Extensive experience navigating FDA approval pathways for nitinol devices; established relationships with regulatory bodies; comprehensive internal testing capabilities for SMA materials. Weaknesses: Regulatory approach may be overly conservative, potentially slowing innovation; heavy focus on nitinol may limit expertise with newer SMA compositions that could face different regulatory challenges.
SAES Getters SpA
Technical Solution: SAES Getters has developed a comprehensive regulatory strategy for their high-purity nitinol materials used in medical devices, focusing on material consistency and purity as key regulatory considerations. Their approach includes specialized testing protocols that address regulatory concerns about nickel leaching and biocompatibility of nitinol alloys[3]. The company has pioneered advanced surface treatment technologies that improve the corrosion resistance of nitinol components, with corresponding regulatory documentation demonstrating enhanced safety profiles. Their regulatory pathway emphasizes material characterization techniques that verify consistent transformation temperatures and mechanical properties across production lots, addressing FDA concerns about batch-to-batch variability in SMA materials[6]. SAES has developed specialized regulatory documentation packages for material suppliers that support their medical device customers' regulatory submissions, including detailed information on manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Their approach includes collaborative regulatory strategies with device manufacturers, providing specialized testing data and documentation to support various regulatory approval pathways for nitinol-containing medical devices across global markets.
Strengths: Deep expertise in material science aspects of regulatory compliance; established relationships with device manufacturers; advanced testing capabilities for material properties and purity. Weaknesses: As a material supplier rather than device manufacturer, limited direct experience with clinical trial requirements; regulatory approach heavily focused on nitinol rather than newer SMA compositions.
Critical Patents and Technical Literature Review
Medical instruments and devices and parts thereof using shape memory alloys
PatentInactiveAU774230B2
Innovation
- A nickel-titanium shape memory alloy with a higher than equiatomic Ni/Ti ratio, subjected to high-temperature solution treatment, water quenching, and aging, exhibits pseudoelastic behavior and excellent forming characteristics, allowing for strain recovery over a broader temperature range without cold working, reducing the risk of cracking and kinking.
Medical Devices Utilizing Modified Shape Memory Alloy
PatentInactiveUS20080058859A1
Innovation
- The development of medical devices with portions having different recovery forces by selectively altering the recovery force characteristics through techniques like direct heating, laser treatment, mechanical cycling, or ion treatment, allowing for softer or stiffer sections in specific areas to reduce trauma during deployment and interaction with tissues.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape for Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) in medical applications is governed by stringent frameworks established by international regulatory bodies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies SMA-based medical devices primarily under Class II and Class III categories, requiring either 510(k) clearance or Premarket Approval (PMA). The regulatory pathway depends on the intended use, implantation duration, and risk profile of the device. Notably, devices incorporating Nitinol, the most common SMA in medical applications, must demonstrate biocompatibility according to ISO 10993 standards.
European regulation follows the Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745), which replaced the Medical Device Directive in 2021, imposing more rigorous clinical evidence requirements for SMA-based devices. The MDR introduces Unique Device Identification (UDI) systems and enhanced post-market surveillance obligations, significantly impacting manufacturers of SMA devices. Additionally, the classification rules under the MDR may categorize certain SMA implants in higher risk classes compared to previous frameworks.
Compliance with these regulations necessitates comprehensive documentation of material properties, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. Manufacturers must implement robust Quality Management Systems (QMS) that adhere to ISO 13485 standards. For SMA materials specifically, ASTM F2063 provides standard specifications for wrought nickel-titanium shape memory alloys for medical devices and surgical implants, serving as a critical reference for regulatory compliance.
Risk management represents another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for SMA devices. Manufacturers must conduct thorough risk analyses following ISO 14971 guidelines, addressing potential failure modes specific to SMAs, such as fatigue resistance, corrosion behavior, and transformation temperature stability in physiological environments. The risk assessment must consider the unique properties of SMAs, including superelasticity and shape memory effect, which may introduce novel failure mechanisms not present in conventional medical materials.
Post-market surveillance requirements have become increasingly stringent, particularly for implantable SMA devices. Manufacturers must implement systems to collect and analyze real-world performance data, adverse events, and long-term outcomes. This information feeds back into the risk management process and may trigger design modifications or additional testing requirements. The regulatory emphasis on lifecycle management means that compliance is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing process throughout the product lifecycle.
International harmonization efforts, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes across multiple jurisdictions. However, significant regional variations persist in the regulatory approach to novel materials like SMAs, creating challenges for global market access. Manufacturers must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes while addressing emerging concerns about long-term biocompatibility and potential for metal ion release from SMA implants.
European regulation follows the Medical Device Regulation (MDR 2017/745), which replaced the Medical Device Directive in 2021, imposing more rigorous clinical evidence requirements for SMA-based devices. The MDR introduces Unique Device Identification (UDI) systems and enhanced post-market surveillance obligations, significantly impacting manufacturers of SMA devices. Additionally, the classification rules under the MDR may categorize certain SMA implants in higher risk classes compared to previous frameworks.
Compliance with these regulations necessitates comprehensive documentation of material properties, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. Manufacturers must implement robust Quality Management Systems (QMS) that adhere to ISO 13485 standards. For SMA materials specifically, ASTM F2063 provides standard specifications for wrought nickel-titanium shape memory alloys for medical devices and surgical implants, serving as a critical reference for regulatory compliance.
Risk management represents another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for SMA devices. Manufacturers must conduct thorough risk analyses following ISO 14971 guidelines, addressing potential failure modes specific to SMAs, such as fatigue resistance, corrosion behavior, and transformation temperature stability in physiological environments. The risk assessment must consider the unique properties of SMAs, including superelasticity and shape memory effect, which may introduce novel failure mechanisms not present in conventional medical materials.
Post-market surveillance requirements have become increasingly stringent, particularly for implantable SMA devices. Manufacturers must implement systems to collect and analyze real-world performance data, adverse events, and long-term outcomes. This information feeds back into the risk management process and may trigger design modifications or additional testing requirements. The regulatory emphasis on lifecycle management means that compliance is not a one-time achievement but an ongoing process throughout the product lifecycle.
International harmonization efforts, such as the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), aim to streamline regulatory processes across multiple jurisdictions. However, significant regional variations persist in the regulatory approach to novel materials like SMAs, creating challenges for global market access. Manufacturers must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes while addressing emerging concerns about long-term biocompatibility and potential for metal ion release from SMA implants.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Biocompatibility remains a paramount concern for shape memory alloys (SMAs) in medical applications, with nickel-titanium (Nitinol) being the most widely utilized SMA in medical devices. Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA and European Medicines Agency, have established stringent guidelines for evaluating the biocompatibility of these materials. The assessment typically follows ISO 10993 standards, which mandate comprehensive testing for cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, systemic toxicity, and genotoxicity.
The primary safety concern with Nitinol stems from its nickel content, which can potentially cause allergic reactions in approximately 10-15% of the population. Regulatory frameworks require manufacturers to demonstrate that nickel leaching remains below established thresholds throughout the device's lifecycle. Surface treatments such as electropolishing, passivation, and specialized coatings have become standard industry practices to minimize ion release and enhance biocompatibility profiles.
Long-term implantation safety represents another critical regulatory consideration. Medical devices incorporating SMAs must undergo rigorous fatigue testing to simulate physiological conditions over extended periods. Regulatory agencies typically require data demonstrating mechanical integrity for the expected device lifespan, which may range from several years to decades depending on the application. This includes evaluation under various stress conditions, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive environments mimicking biological systems.
The manufacturing process for SMA medical devices faces strict regulatory scrutiny due to its direct impact on material properties and safety. Regulatory bodies mandate detailed documentation of manufacturing protocols, quality control measures, and validation procedures. Any process changes require revalidation and potentially additional biocompatibility testing, reflecting the regulatory emphasis on manufacturing consistency as a safety determinant.
Recent regulatory developments have focused on the potential for nanoparticle release from SMA surfaces during wear or corrosion processes. Emerging research suggests these particles may exhibit different toxicological profiles compared to bulk materials. Consequently, regulatory agencies increasingly request characterization of potential particulate release and associated biological responses, particularly for high-wear applications like orthopedic implants or cardiovascular devices experiencing continuous mechanical stress.
Regulatory perspectives also encompass risk-benefit assessments that consider the unique advantages SMAs offer against potential safety concerns. For critical applications where alternative materials cannot provide comparable therapeutic benefits, regulatory bodies may accept higher theoretical risks provided they are well-characterized and mitigated through appropriate design features, patient selection criteria, and post-market surveillance protocols.
The primary safety concern with Nitinol stems from its nickel content, which can potentially cause allergic reactions in approximately 10-15% of the population. Regulatory frameworks require manufacturers to demonstrate that nickel leaching remains below established thresholds throughout the device's lifecycle. Surface treatments such as electropolishing, passivation, and specialized coatings have become standard industry practices to minimize ion release and enhance biocompatibility profiles.
Long-term implantation safety represents another critical regulatory consideration. Medical devices incorporating SMAs must undergo rigorous fatigue testing to simulate physiological conditions over extended periods. Regulatory agencies typically require data demonstrating mechanical integrity for the expected device lifespan, which may range from several years to decades depending on the application. This includes evaluation under various stress conditions, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive environments mimicking biological systems.
The manufacturing process for SMA medical devices faces strict regulatory scrutiny due to its direct impact on material properties and safety. Regulatory bodies mandate detailed documentation of manufacturing protocols, quality control measures, and validation procedures. Any process changes require revalidation and potentially additional biocompatibility testing, reflecting the regulatory emphasis on manufacturing consistency as a safety determinant.
Recent regulatory developments have focused on the potential for nanoparticle release from SMA surfaces during wear or corrosion processes. Emerging research suggests these particles may exhibit different toxicological profiles compared to bulk materials. Consequently, regulatory agencies increasingly request characterization of potential particulate release and associated biological responses, particularly for high-wear applications like orthopedic implants or cardiovascular devices experiencing continuous mechanical stress.
Regulatory perspectives also encompass risk-benefit assessments that consider the unique advantages SMAs offer against potential safety concerns. For critical applications where alternative materials cannot provide comparable therapeutic benefits, regulatory bodies may accept higher theoretical risks provided they are well-characterized and mitigated through appropriate design features, patient selection criteria, and post-market surveillance protocols.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!