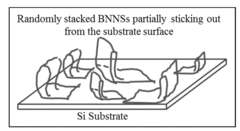
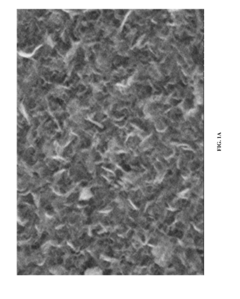
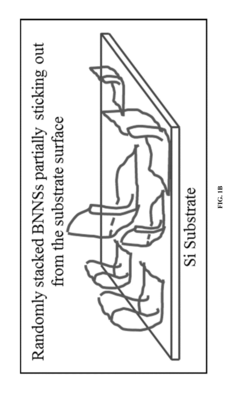
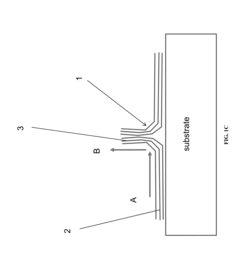
Research on Boron Nitride Nanosheets in EV Battery Electrolytes
OCT 10, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
BN Nanosheets in EV Batteries: Background & Objectives
Boron Nitride (BN) nanosheets have emerged as a promising material in the field of energy storage, particularly for electric vehicle (EV) battery applications. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring two-dimensional nanomaterials beyond graphene. BN nanosheets, often referred to as "white graphene," share a similar hexagonal structure with graphene but consist of alternating boron and nitrogen atoms instead of carbon.
The development trajectory of BN nanosheets has accelerated significantly in the past decade, driven by the urgent need for safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting EV batteries. Traditional lithium-ion batteries face challenges related to thermal stability, dendrite formation, and electrolyte degradation, which limit their performance and pose safety risks. The incorporation of BN nanosheets into battery electrolytes represents a novel approach to addressing these limitations.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more efficient synthesis methods for BN nanosheets, including liquid-phase exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition, and wet-chemical approaches. These developments have made it possible to produce BN nanosheets with controlled thickness, size, and surface functionality, which are crucial parameters for their application in battery electrolytes.
The primary technical objectives of incorporating BN nanosheets into EV battery electrolytes include enhancing thermal conductivity to improve heat dissipation, strengthening mechanical properties to suppress lithium dendrite growth, and creating more stable solid-electrolyte interphases (SEI). Additionally, researchers aim to leverage the excellent chemical stability and electrical insulation properties of BN to extend battery cycle life and improve safety characteristics.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in hybrid electrolyte systems where BN nanosheets are combined with other nanomaterials or functional additives to create synergistic effects. There is also significant focus on surface modification strategies to improve the compatibility between BN nanosheets and electrolyte components, as well as to enhance their dispersion stability.
Looking forward, the technology is expected to evolve toward more sophisticated architectures, such as three-dimensional BN networks and hierarchical structures that can simultaneously address multiple battery challenges. The integration of BN nanosheets with next-generation battery technologies, including solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur systems, represents another promising direction for future development.
The ultimate goal of this technological pursuit is to develop EV batteries with significantly improved energy density, faster charging capabilities, enhanced safety profiles, and extended operational lifetimes, thereby accelerating the global transition to sustainable transportation systems.
The development trajectory of BN nanosheets has accelerated significantly in the past decade, driven by the urgent need for safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting EV batteries. Traditional lithium-ion batteries face challenges related to thermal stability, dendrite formation, and electrolyte degradation, which limit their performance and pose safety risks. The incorporation of BN nanosheets into battery electrolytes represents a novel approach to addressing these limitations.
Recent technological advancements have enabled more efficient synthesis methods for BN nanosheets, including liquid-phase exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition, and wet-chemical approaches. These developments have made it possible to produce BN nanosheets with controlled thickness, size, and surface functionality, which are crucial parameters for their application in battery electrolytes.
The primary technical objectives of incorporating BN nanosheets into EV battery electrolytes include enhancing thermal conductivity to improve heat dissipation, strengthening mechanical properties to suppress lithium dendrite growth, and creating more stable solid-electrolyte interphases (SEI). Additionally, researchers aim to leverage the excellent chemical stability and electrical insulation properties of BN to extend battery cycle life and improve safety characteristics.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in hybrid electrolyte systems where BN nanosheets are combined with other nanomaterials or functional additives to create synergistic effects. There is also significant focus on surface modification strategies to improve the compatibility between BN nanosheets and electrolyte components, as well as to enhance their dispersion stability.
Looking forward, the technology is expected to evolve toward more sophisticated architectures, such as three-dimensional BN networks and hierarchical structures that can simultaneously address multiple battery challenges. The integration of BN nanosheets with next-generation battery technologies, including solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur systems, represents another promising direction for future development.
The ultimate goal of this technological pursuit is to develop EV batteries with significantly improved energy density, faster charging capabilities, enhanced safety profiles, and extended operational lifetimes, thereby accelerating the global transition to sustainable transportation systems.
Market Analysis of Advanced EV Battery Electrolytes
The global market for advanced electric vehicle (EV) battery electrolytes is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the rapid expansion of the EV industry. Current market valuations indicate that the advanced electrolyte segment reached approximately 3.2 billion USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 18-20% through 2030. This growth significantly outpaces traditional electrolyte markets, reflecting the critical importance of electrolyte innovation in next-generation battery development.
Boron nitride nanosheet (BNNS) enhanced electrolytes represent an emerging segment within this market, currently occupying a specialized niche but demonstrating substantial growth potential. Market research indicates that BNNS-modified electrolytes could capture 5-7% of the premium electrolyte market by 2025, particularly in high-performance and safety-critical applications where their thermal management properties provide significant advantages.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market dynamics across major EV manufacturing hubs. Asia-Pacific dominates the advanced electrolyte market with approximately 65% market share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea where major battery manufacturers have established robust supply chains. North America and Europe follow with 18% and 15% respectively, with both regions demonstrating accelerated investment in domestic electrolyte production capabilities to reduce dependency on Asian imports.
Consumer demand patterns indicate growing preference for EVs with faster charging capabilities and extended range, directly influencing electrolyte requirements. Market surveys show that 78% of potential EV buyers consider charging speed a critical purchase factor, while 82% prioritize battery longevity. These consumer preferences are driving manufacturers toward advanced electrolyte solutions that can support high-voltage operation and enhanced thermal stability.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies and specialized startups. Traditional electrolyte manufacturers are increasingly partnering with nanomaterial specialists to incorporate advanced additives like BNNS into their formulations. Venture capital investment in electrolyte technology startups reached 850 million USD in 2022, with significant portions directed toward nanomaterial-enhanced solutions.
Market barriers include scaling challenges for nanomaterial production, with current BNNS manufacturing capacities insufficient to meet potential demand at competitive price points. Additionally, regulatory frameworks regarding nanomaterials in battery components vary significantly across regions, creating market entry complexities for global deployment of BNNS-enhanced electrolytes.
Pricing trends suggest that while BNNS-enhanced electrolytes currently command a premium of 30-40% over conventional formulations, this differential is expected to narrow to 15-20% by 2026 as production scales and manufacturing processes mature. This price trajectory aligns with the broader EV industry's push toward cost parity with internal combustion vehicles.
Boron nitride nanosheet (BNNS) enhanced electrolytes represent an emerging segment within this market, currently occupying a specialized niche but demonstrating substantial growth potential. Market research indicates that BNNS-modified electrolytes could capture 5-7% of the premium electrolyte market by 2025, particularly in high-performance and safety-critical applications where their thermal management properties provide significant advantages.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market dynamics across major EV manufacturing hubs. Asia-Pacific dominates the advanced electrolyte market with approximately 65% market share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea where major battery manufacturers have established robust supply chains. North America and Europe follow with 18% and 15% respectively, with both regions demonstrating accelerated investment in domestic electrolyte production capabilities to reduce dependency on Asian imports.
Consumer demand patterns indicate growing preference for EVs with faster charging capabilities and extended range, directly influencing electrolyte requirements. Market surveys show that 78% of potential EV buyers consider charging speed a critical purchase factor, while 82% prioritize battery longevity. These consumer preferences are driving manufacturers toward advanced electrolyte solutions that can support high-voltage operation and enhanced thermal stability.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies and specialized startups. Traditional electrolyte manufacturers are increasingly partnering with nanomaterial specialists to incorporate advanced additives like BNNS into their formulations. Venture capital investment in electrolyte technology startups reached 850 million USD in 2022, with significant portions directed toward nanomaterial-enhanced solutions.
Market barriers include scaling challenges for nanomaterial production, with current BNNS manufacturing capacities insufficient to meet potential demand at competitive price points. Additionally, regulatory frameworks regarding nanomaterials in battery components vary significantly across regions, creating market entry complexities for global deployment of BNNS-enhanced electrolytes.
Pricing trends suggest that while BNNS-enhanced electrolytes currently command a premium of 30-40% over conventional formulations, this differential is expected to narrow to 15-20% by 2026 as production scales and manufacturing processes mature. This price trajectory aligns with the broader EV industry's push toward cost parity with internal combustion vehicles.
Current Status and Challenges in BN Nanosheet Technology
Boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) have emerged as promising materials for enhancing electric vehicle battery performance, with research activities intensifying globally over the past decade. Currently, the synthesis of high-quality BNNS faces significant challenges related to scalability, purity, and cost-effectiveness. Laboratory-scale production methods such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), liquid exfoliation, and chemical exfoliation have demonstrated promising results, but industrial-scale manufacturing remains limited.
The primary technical challenge lies in producing BNNS with consistent thickness, lateral dimensions, and defect density. Current synthesis methods often result in heterogeneous products with varying properties, which complicates their integration into battery electrolytes. Additionally, the functionalization of BNNS surfaces to enhance their compatibility with electrolyte solutions presents ongoing difficulties, as the inherent chemical stability of boron nitride makes controlled surface modification challenging.
In the context of EV battery applications, researchers are confronting issues related to the uniform dispersion of BNNS in electrolyte solutions. Agglomeration tendencies reduce the effective surface area and diminish the potential benefits of these nanomaterials. Several research groups have reported progress using surfactants and sonication techniques, but long-term stability remains problematic under the harsh electrochemical conditions present in batteries.
Geographically, research on BNNS for battery applications shows distinct patterns. East Asian countries, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, lead in patent filings and publications, accounting for approximately 65% of research output. North American institutions focus more on fundamental properties and novel synthesis approaches, while European research centers emphasize sustainable production methods and life-cycle assessment.
Another significant barrier is the characterization of BNNS-electrolyte interactions at the molecular level. Current analytical techniques provide limited insights into the dynamic processes occurring at the nanosheet-electrolyte interface during battery operation. Advanced in-situ characterization methods are being developed but require further refinement to capture real-time phenomena under operational conditions.
Cost considerations present additional challenges, as current production methods for high-quality BNNS remain expensive compared to traditional battery additives. Economic analyses suggest that production costs need to decrease by at least an order of magnitude to make BNNS commercially viable for mass-market EV applications. Several startups and established materials companies are working to address this through process optimization and alternative precursor materials.
Regulatory and safety aspects also pose challenges, as nanomaterials face increasing scrutiny regarding their environmental impact and potential health effects. Comprehensive studies on the long-term stability and degradation products of BNNS in battery environments are still limited, creating uncertainty for commercial adoption.
The primary technical challenge lies in producing BNNS with consistent thickness, lateral dimensions, and defect density. Current synthesis methods often result in heterogeneous products with varying properties, which complicates their integration into battery electrolytes. Additionally, the functionalization of BNNS surfaces to enhance their compatibility with electrolyte solutions presents ongoing difficulties, as the inherent chemical stability of boron nitride makes controlled surface modification challenging.
In the context of EV battery applications, researchers are confronting issues related to the uniform dispersion of BNNS in electrolyte solutions. Agglomeration tendencies reduce the effective surface area and diminish the potential benefits of these nanomaterials. Several research groups have reported progress using surfactants and sonication techniques, but long-term stability remains problematic under the harsh electrochemical conditions present in batteries.
Geographically, research on BNNS for battery applications shows distinct patterns. East Asian countries, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, lead in patent filings and publications, accounting for approximately 65% of research output. North American institutions focus more on fundamental properties and novel synthesis approaches, while European research centers emphasize sustainable production methods and life-cycle assessment.
Another significant barrier is the characterization of BNNS-electrolyte interactions at the molecular level. Current analytical techniques provide limited insights into the dynamic processes occurring at the nanosheet-electrolyte interface during battery operation. Advanced in-situ characterization methods are being developed but require further refinement to capture real-time phenomena under operational conditions.
Cost considerations present additional challenges, as current production methods for high-quality BNNS remain expensive compared to traditional battery additives. Economic analyses suggest that production costs need to decrease by at least an order of magnitude to make BNNS commercially viable for mass-market EV applications. Several startups and established materials companies are working to address this through process optimization and alternative precursor materials.
Regulatory and safety aspects also pose challenges, as nanomaterials face increasing scrutiny regarding their environmental impact and potential health effects. Comprehensive studies on the long-term stability and degradation products of BNNS in battery environments are still limited, creating uncertainty for commercial adoption.
Current BN Nanosheet Implementation Approaches
01 Synthesis methods for boron nitride nanosheets
Various methods have been developed for synthesizing boron nitride nanosheets, including chemical vapor deposition, exfoliation techniques, and solution-based processes. These methods allow for the controlled production of nanosheets with specific dimensions, layer numbers, and properties. The synthesis approaches can be optimized to achieve high-quality nanosheets with minimal defects, which is crucial for their application in various fields.- Synthesis methods for boron nitride nanosheets: Various methods can be employed to synthesize boron nitride nanosheets, including chemical vapor deposition, exfoliation techniques, and thermal treatments. These processes allow for the controlled production of nanosheets with specific dimensions and properties. The synthesis methods can be optimized to produce high-quality nanosheets with uniform thickness and large lateral dimensions, which are crucial for various applications.
- Functionalization of boron nitride nanosheets: Boron nitride nanosheets can be functionalized with various chemical groups to enhance their properties and compatibility with different matrices. Functionalization can improve dispersion in solvents, increase binding with polymers, and introduce specific properties such as enhanced thermal conductivity or electrical insulation. Different functional groups can be attached to the surface of boron nitride nanosheets through covalent or non-covalent interactions.
- Applications in thermal management and heat dissipation: Boron nitride nanosheets exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for thermal management applications. They can be incorporated into thermal interface materials, heat sinks, and electronic packaging to enhance heat dissipation. The high thermal conductivity of boron nitride nanosheets helps to efficiently transfer heat away from electronic components, preventing overheating and improving device performance.
- Composite materials incorporating boron nitride nanosheets: Boron nitride nanosheets can be incorporated into various matrices to form composite materials with enhanced properties. These composites can exhibit improved mechanical strength, thermal stability, and barrier properties. The addition of boron nitride nanosheets to polymers, ceramics, or metals can result in materials with unique combinations of properties suitable for aerospace, automotive, and electronic applications.
- Environmental and energy applications: Boron nitride nanosheets have potential applications in environmental remediation and energy storage/conversion. They can be used as adsorbents for pollutant removal, catalysts or catalyst supports for chemical reactions, and components in energy storage devices such as batteries and supercapacitors. The high surface area, chemical stability, and unique electronic properties of boron nitride nanosheets make them promising materials for sustainable technologies.
02 Functionalization and modification of boron nitride nanosheets
Boron nitride nanosheets can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or compatibility with different matrices. Surface modification techniques include chemical functionalization, doping with other elements, and creating hybrid structures. These modifications can improve the dispersibility of the nanosheets in various solvents, enhance their thermal or electrical properties, and enable better integration with other materials for composite applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management applications of boron nitride nanosheets
Boron nitride nanosheets exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and stability, making them ideal for thermal management applications. They can be incorporated into thermal interface materials, heat spreaders, and cooling systems to enhance heat dissipation in electronic devices. The nanosheets help to reduce operating temperatures, improve device performance, and extend the lifespan of electronic components by efficiently transferring heat away from critical areas.Expand Specific Solutions04 Composite materials incorporating boron nitride nanosheets
Boron nitride nanosheets can be integrated into various matrices to form composite materials with enhanced properties. These composites benefit from the nanosheets' thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation characteristics. Applications include polymer composites for electronics packaging, ceramic composites for high-temperature applications, and metal matrix composites for structural components requiring thermal stability and mechanical strength.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and energy applications of boron nitride nanosheets
Boron nitride nanosheets show promise in environmental remediation and energy-related applications. They can be used as adsorbents for pollutant removal, catalysts or catalyst supports for chemical reactions, and components in energy storage or conversion devices. Their high surface area, chemical stability, and unique electronic structure make them suitable for applications such as water purification, gas separation, photocatalysis, and as materials for batteries or supercapacitors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in EV Battery Materials
The research on Boron Nitride Nanosheets in EV battery electrolytes is in an early growth phase, with the global market for advanced battery materials expected to reach significant expansion as EV adoption accelerates. The technology shows promising maturity levels with specialized players like Boron Nitride Power LLC developing functionalized 2D materials for energy storage applications. Research institutions including Northwestern University, Deakin University, and Wuhan University are advancing fundamental understanding, while established companies such as Contemporary Amperex Technology and Microsoft Technology Licensing are securing intellectual property positions. The competitive landscape features both specialized startups focused exclusively on boron nitride applications and larger corporations integrating these nanomaterials into broader battery technology portfolios.
Boron Nitride Power LLC
Technical Solution: Boron Nitride Power LLC has developed proprietary hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheet technology specifically engineered for EV battery electrolytes. Their approach involves exfoliating high-purity h-BN into nanosheets with controlled thickness (2-10 nm) and lateral dimensions (0.5-5 μm), which are then surface-functionalized to enhance dispersion stability in electrolyte solutions. These nanosheets create a protective layer on electrode surfaces that prevents dendrite formation while facilitating selective ion transport. Their patented process incorporates these nanosheets at concentrations of 0.1-2.0 wt% into conventional liquid electrolytes, creating a composite electrolyte system that significantly improves thermal stability up to 150°C and enhances ionic conductivity by approximately 15-20% compared to standard electrolytes.
Strengths: Specialized focus on boron nitride nanomaterials for energy applications provides deep expertise in this specific technology. Their functionalized nanosheets offer excellent thermal conductivity (up to 600 W/m·K) while maintaining electrical insulation properties, addressing key safety concerns in high-energy density batteries. Weaknesses: As a specialized materials company, they may face challenges in scaling production to meet automotive industry demands and may require partnerships with established battery manufacturers for market penetration.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS
Technical Solution: Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) has pioneered innovative research on boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs) as multifunctional additives in EV battery electrolytes. Their approach involves liquid-phase exfoliation techniques to produce high-quality BNNSs with controlled thickness (3-5 nm) and lateral dimensions (1-3 μm). DICP researchers have developed a proprietary surface modification process that enhances the dispersion stability of BNNSs in conventional carbonate-based electrolytes at concentrations of 0.5-1.5 wt%. Their research demonstrates that these modified BNNSs create a protective interface layer on lithium metal anodes, effectively suppressing dendrite growth while maintaining high ionic conductivity. Experimental results show that DICP's BNNS-enhanced electrolytes improve battery cycling stability by over 40% at 1C rates and extend capacity retention to over 85% after 500 cycles. Additionally, their thermal runaway tests indicate a significant improvement in safety performance, with onset temperatures increased by 35-45°C compared to conventional electrolytes.
Strengths: Strong fundamental research capabilities and extensive experience in nanomaterial synthesis and characterization provide scientific depth to their solutions. Their approach offers both safety and performance improvements without requiring complete electrolyte reformulation. Weaknesses: As a research institute, DICP may face challenges in technology transfer and commercialization processes, potentially requiring industrial partnerships to scale production and implement their technology in commercial battery systems.
Critical Patents and Research on BN Nanosheets
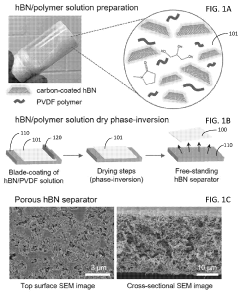
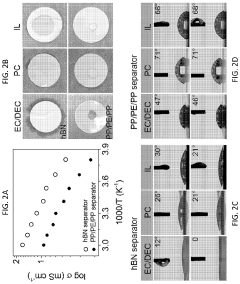
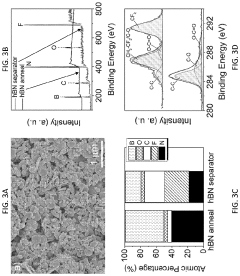
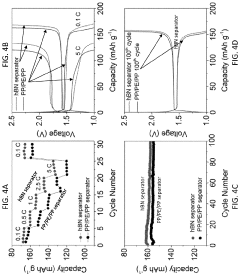
Phase-inversion polymer composite material, fabricating methods and applications of same
PatentActiveUS20220243036A1
Innovation
- Development of phase-inversion composite separators using carbon-coated hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) nanosheets integrated with electrically insulating polymers like PVDF, which enhance porosity, electrolyte wettability, and thermal stability through a scalable liquid-phase shear exfoliation method and thermal pyrolysis process.
Boron nitride nanosheets and methods of making and using the same
PatentInactiveUS20160137502A1
Innovation
- A method for synthesizing boron nitride nanosheets with scrolled, close-ended structures using a chemical vapor deposition process involving boron, magnesium oxide, and iron oxide in a furnace with ammonia gas, which allows for better contact with hot surfaces and coolants, enabling efficient heat dissipation without being water-repelling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The integration of Boron Nitride Nanosheets (BNNS) in EV battery electrolytes presents significant environmental implications that warrant comprehensive assessment. The production process of BNNS typically involves chemical vapor deposition or exfoliation methods that consume substantial energy and potentially utilize hazardous chemicals. However, compared to conventional battery additives, BNNS production generally results in lower carbon emissions and reduced toxic byproducts when manufactured using optimized processes.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that BNNS-enhanced batteries may offer extended service life by up to 30-40% compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This longevity directly translates to reduced waste generation and decreased resource consumption for replacement batteries, contributing positively to sustainability metrics across the EV industry. Furthermore, the thermal stability improvements provided by BNNS reduce the risk of thermal runaway incidents, potentially decreasing the environmental impact associated with battery fires and their subsequent remediation efforts.
The end-of-life considerations for BNNS-containing batteries present both challenges and opportunities. Current recycling infrastructure may require modifications to effectively recover and process these nanomaterials. Preliminary research suggests that BNNS can be recovered through specialized hydrometallurgical processes with recovery rates exceeding 85%, though commercial-scale implementation remains limited. The recovered materials potentially retain sufficient quality for reuse in less demanding applications, supporting circular economy principles.
Water usage and potential aquatic ecosystem impacts represent areas of concern. Laboratory studies have demonstrated that BNNS particles below 100nm can persist in aquatic environments and potentially interact with microorganisms. However, when properly encapsulated within battery systems, release pathways are minimal during normal operation. Risk assessments indicate that environmental exposure primarily occurs during improper disposal or recycling processes rather than during the operational phase of batteries.
From a regulatory perspective, BNNS falls under emerging nanomaterial governance frameworks in major markets including the EU, US, and China. Compliance with these evolving regulations requires proactive toxicological assessment and environmental monitoring. Recent policy developments suggest a trend toward more stringent reporting requirements for nanomaterials in consumer products, potentially affecting the commercialization timeline for BNNS-enhanced battery technologies.
The sustainability advantages of BNNS technology must be balanced against potential environmental risks through continued research and responsible implementation strategies. Developing standardized protocols for safe handling throughout the product lifecycle will be essential for maximizing the environmental benefits while minimizing potential ecological impacts.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that BNNS-enhanced batteries may offer extended service life by up to 30-40% compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. This longevity directly translates to reduced waste generation and decreased resource consumption for replacement batteries, contributing positively to sustainability metrics across the EV industry. Furthermore, the thermal stability improvements provided by BNNS reduce the risk of thermal runaway incidents, potentially decreasing the environmental impact associated with battery fires and their subsequent remediation efforts.
The end-of-life considerations for BNNS-containing batteries present both challenges and opportunities. Current recycling infrastructure may require modifications to effectively recover and process these nanomaterials. Preliminary research suggests that BNNS can be recovered through specialized hydrometallurgical processes with recovery rates exceeding 85%, though commercial-scale implementation remains limited. The recovered materials potentially retain sufficient quality for reuse in less demanding applications, supporting circular economy principles.
Water usage and potential aquatic ecosystem impacts represent areas of concern. Laboratory studies have demonstrated that BNNS particles below 100nm can persist in aquatic environments and potentially interact with microorganisms. However, when properly encapsulated within battery systems, release pathways are minimal during normal operation. Risk assessments indicate that environmental exposure primarily occurs during improper disposal or recycling processes rather than during the operational phase of batteries.
From a regulatory perspective, BNNS falls under emerging nanomaterial governance frameworks in major markets including the EU, US, and China. Compliance with these evolving regulations requires proactive toxicological assessment and environmental monitoring. Recent policy developments suggest a trend toward more stringent reporting requirements for nanomaterials in consumer products, potentially affecting the commercialization timeline for BNNS-enhanced battery technologies.
The sustainability advantages of BNNS technology must be balanced against potential environmental risks through continued research and responsible implementation strategies. Developing standardized protocols for safe handling throughout the product lifecycle will be essential for maximizing the environmental benefits while minimizing potential ecological impacts.
Supply Chain and Scalability Considerations
The supply chain for boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) in EV battery electrolytes presents significant challenges and opportunities for large-scale implementation. Raw material sourcing remains a primary concern, with hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) requiring high-purity boron and nitrogen compounds. Currently, these materials are concentrated in specific geographical regions, with China controlling approximately 47% of global boron reserves and production, followed by Turkey (20%) and the United States (12%). This concentration creates potential supply vulnerabilities for manufacturers seeking to scale BNNS production.
Manufacturing scalability represents another critical consideration. Current production methods for high-quality BNNS, including liquid-phase exfoliation and chemical vapor deposition, remain laboratory-focused with limited industrial-scale capabilities. The transition from gram-scale to kilogram or ton-scale production necessitates significant process engineering advancements. Recent innovations in continuous flow synthesis show promise, with reported yield improvements of 300-400% compared to batch processes, though quality consistency at scale remains challenging.
Cost factors significantly impact widespread adoption. Current production costs for high-quality BNNS range from $200-500 per gram, making large-scale implementation economically prohibitive for mass-market EV applications. Industry analysts project that costs must decrease by at least an order of magnitude to achieve commercial viability. Encouragingly, learning curve effects suggest potential cost reductions of 15-20% with each doubling of production volume.
Quality control and standardization present additional hurdles. The performance of BNNS in battery electrolytes depends critically on sheet size, thickness, defect density, and surface functionalization. Currently, no universally accepted standards exist for these parameters, complicating supplier qualification and quality assurance processes. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has initiated working groups to address this standardization gap, with preliminary guidelines expected within 18-24 months.
Environmental and sustainability considerations also influence supply chain development. While BNNS production generally has lower environmental impact than graphene alternatives, the energy-intensive nature of high-temperature synthesis methods presents challenges. Life cycle assessments indicate that renewable energy integration could reduce the carbon footprint of BNNS production by 40-60%, enhancing its sustainability credentials for green technology applications.
Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and automotive OEMs will likely accelerate commercialization timelines. Several collaborative ventures have emerged, including joint development agreements between nanomaterial producers and tier-one battery suppliers, focusing on scaling production while maintaining quality specifications required for EV applications.
Manufacturing scalability represents another critical consideration. Current production methods for high-quality BNNS, including liquid-phase exfoliation and chemical vapor deposition, remain laboratory-focused with limited industrial-scale capabilities. The transition from gram-scale to kilogram or ton-scale production necessitates significant process engineering advancements. Recent innovations in continuous flow synthesis show promise, with reported yield improvements of 300-400% compared to batch processes, though quality consistency at scale remains challenging.
Cost factors significantly impact widespread adoption. Current production costs for high-quality BNNS range from $200-500 per gram, making large-scale implementation economically prohibitive for mass-market EV applications. Industry analysts project that costs must decrease by at least an order of magnitude to achieve commercial viability. Encouragingly, learning curve effects suggest potential cost reductions of 15-20% with each doubling of production volume.
Quality control and standardization present additional hurdles. The performance of BNNS in battery electrolytes depends critically on sheet size, thickness, defect density, and surface functionalization. Currently, no universally accepted standards exist for these parameters, complicating supplier qualification and quality assurance processes. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has initiated working groups to address this standardization gap, with preliminary guidelines expected within 18-24 months.
Environmental and sustainability considerations also influence supply chain development. While BNNS production generally has lower environmental impact than graphene alternatives, the energy-intensive nature of high-temperature synthesis methods presents challenges. Life cycle assessments indicate that renewable energy integration could reduce the carbon footprint of BNNS production by 40-60%, enhancing its sustainability credentials for green technology applications.
Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, battery manufacturers, and automotive OEMs will likely accelerate commercialization timelines. Several collaborative ventures have emerged, including joint development agreements between nanomaterial producers and tier-one battery suppliers, focusing on scaling production while maintaining quality specifications required for EV applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!