Standards compliance challenges for gate valves in international markets
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Gate Valve Standards Evolution and Objectives
Gate valves have been a critical component in fluid control systems for over a century, with their evolution closely tied to industrial development and safety standards. The journey of gate valve standards began in the early 20th century, primarily driven by the need for consistency in manufacturing and performance across various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
Initially, standards were largely regional or industry-specific, leading to challenges in international trade and compatibility. The American Petroleum Institute (API) introduced some of the earliest comprehensive standards for gate valves in the 1920s, focusing on oil and gas applications. These standards laid the groundwork for future developments, addressing issues such as material specifications, pressure ratings, and testing procedures.
As global trade expanded in the post-World War II era, the need for international standardization became apparent. This led to the formation of organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1947, which began to develop globally recognized standards for various industrial components, including gate valves.
The evolution of gate valve standards has been marked by a continuous drive towards greater safety, reliability, and efficiency. Key milestones include the introduction of fugitive emissions standards in the 1990s, addressing environmental concerns, and the development of fire-safe designs to enhance safety in high-risk environments.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards harmonization of standards across different regions and industries. This trend aims to reduce trade barriers, improve interoperability, and streamline manufacturing processes. However, it also presents challenges as different regions may have varying priorities and regulatory frameworks.
The primary objectives of modern gate valve standards are multifaceted. They aim to ensure consistent quality and performance across different manufacturers and applications, enhance safety in various operating conditions, and promote sustainability through improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, these standards seek to facilitate innovation by providing a framework that allows for technological advancements while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
Another key objective is to address the challenges posed by emerging technologies and new industrial applications. This includes developing standards for smart valves with integrated sensors and control systems, as well as addressing the unique requirements of renewable energy sectors such as hydrogen infrastructure.
Looking forward, the evolution of gate valve standards is expected to continue, with a focus on digitalization, advanced materials, and enhanced testing methodologies. The goal is to create a robust, flexible framework that can adapt to changing technological landscapes while ensuring the highest levels of safety, reliability, and performance in an increasingly globalized market.
Initially, standards were largely regional or industry-specific, leading to challenges in international trade and compatibility. The American Petroleum Institute (API) introduced some of the earliest comprehensive standards for gate valves in the 1920s, focusing on oil and gas applications. These standards laid the groundwork for future developments, addressing issues such as material specifications, pressure ratings, and testing procedures.
As global trade expanded in the post-World War II era, the need for international standardization became apparent. This led to the formation of organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1947, which began to develop globally recognized standards for various industrial components, including gate valves.
The evolution of gate valve standards has been marked by a continuous drive towards greater safety, reliability, and efficiency. Key milestones include the introduction of fugitive emissions standards in the 1990s, addressing environmental concerns, and the development of fire-safe designs to enhance safety in high-risk environments.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards harmonization of standards across different regions and industries. This trend aims to reduce trade barriers, improve interoperability, and streamline manufacturing processes. However, it also presents challenges as different regions may have varying priorities and regulatory frameworks.
The primary objectives of modern gate valve standards are multifaceted. They aim to ensure consistent quality and performance across different manufacturers and applications, enhance safety in various operating conditions, and promote sustainability through improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, these standards seek to facilitate innovation by providing a framework that allows for technological advancements while maintaining compatibility with existing systems.
Another key objective is to address the challenges posed by emerging technologies and new industrial applications. This includes developing standards for smart valves with integrated sensors and control systems, as well as addressing the unique requirements of renewable energy sectors such as hydrogen infrastructure.
Looking forward, the evolution of gate valve standards is expected to continue, with a focus on digitalization, advanced materials, and enhanced testing methodologies. The goal is to create a robust, flexible framework that can adapt to changing technological landscapes while ensuring the highest levels of safety, reliability, and performance in an increasingly globalized market.
Global Market Demand Analysis for Compliant Gate Valves
The global market for compliant gate valves is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing industrialization, urbanization, and stringent regulatory standards across various sectors. The demand for gate valves that meet international compliance standards is particularly strong in industries such as oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, power generation, and chemical processing.
In the oil and gas sector, the need for compliant gate valves is paramount due to the high-pressure and high-temperature environments in which they operate. The industry's focus on safety and environmental protection has led to a surge in demand for valves that meet or exceed international standards such as API 6D, ISO 10423, and ASME B16.34. This trend is especially pronounced in regions with mature oil and gas markets, including North America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe.
The water and wastewater treatment industry is another key driver of demand for compliant gate valves. As governments worldwide invest in improving water infrastructure and implementing more stringent water quality regulations, the need for reliable and standards-compliant valves has increased. Standards such as AWWA C509 and EN 1074 are becoming increasingly important in this sector, particularly in developing countries where water infrastructure is expanding rapidly.
In the power generation sector, the shift towards cleaner energy sources and the modernization of existing power plants have created a substantial market for compliant gate valves. Nuclear power plants, in particular, require valves that meet the highest safety standards, such as those set by the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
The chemical processing industry is also a significant consumer of compliant gate valves, driven by the need for corrosion-resistant and leak-proof valves that can handle a wide range of chemicals. Standards such as ANSI/ASME B16.34 and API 600 are crucial in this sector, with a growing emphasis on valves that can withstand aggressive media and extreme operating conditions.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for compliant gate valves, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily driven by replacement demand and upgrades to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
The market is also seeing a shift towards smart and automated valve systems, which offer improved monitoring and control capabilities. This trend is creating new opportunities for valve manufacturers to integrate compliance features with advanced technologies, further driving market growth.
In the oil and gas sector, the need for compliant gate valves is paramount due to the high-pressure and high-temperature environments in which they operate. The industry's focus on safety and environmental protection has led to a surge in demand for valves that meet or exceed international standards such as API 6D, ISO 10423, and ASME B16.34. This trend is especially pronounced in regions with mature oil and gas markets, including North America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe.
The water and wastewater treatment industry is another key driver of demand for compliant gate valves. As governments worldwide invest in improving water infrastructure and implementing more stringent water quality regulations, the need for reliable and standards-compliant valves has increased. Standards such as AWWA C509 and EN 1074 are becoming increasingly important in this sector, particularly in developing countries where water infrastructure is expanding rapidly.
In the power generation sector, the shift towards cleaner energy sources and the modernization of existing power plants have created a substantial market for compliant gate valves. Nuclear power plants, in particular, require valves that meet the highest safety standards, such as those set by the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
The chemical processing industry is also a significant consumer of compliant gate valves, driven by the need for corrosion-resistant and leak-proof valves that can handle a wide range of chemicals. Standards such as ANSI/ASME B16.34 and API 600 are crucial in this sector, with a growing emphasis on valves that can withstand aggressive media and extreme operating conditions.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in demand for compliant gate valves, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily driven by replacement demand and upgrades to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
The market is also seeing a shift towards smart and automated valve systems, which offer improved monitoring and control capabilities. This trend is creating new opportunities for valve manufacturers to integrate compliance features with advanced technologies, further driving market growth.
Current Challenges in International Standards Compliance
Gate valves play a crucial role in various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing. As global trade continues to expand, manufacturers face significant challenges in ensuring their products comply with diverse international standards. These standards are designed to guarantee safety, reliability, and performance across different markets, but they often vary considerably between regions and countries.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of global harmonization in standards for gate valves. While efforts have been made to create unified standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), many countries still maintain their own specific requirements. This fragmentation leads to increased complexity and costs for manufacturers who must adapt their products to meet multiple standards simultaneously.
Material selection and certification pose another significant hurdle. Different markets may require specific materials or have stringent requirements for material traceability and documentation. For instance, the European Union's Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) mandates specific material certifications, while the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may have different requirements for oil and gas applications. Manufacturers must navigate these varying demands while ensuring their products maintain consistent quality and performance.
Testing and validation procedures also differ across international markets. While some regions may accept self-certification, others require third-party testing and validation. The costs and time associated with these processes can be substantial, particularly for smaller manufacturers looking to expand their global presence. Additionally, the interpretation and application of standards can vary between certification bodies, leading to inconsistencies and potential delays in product approval.
The rapid pace of technological advancement presents another challenge. As new materials and manufacturing techniques emerge, standards struggle to keep pace. This lag can create uncertainty for manufacturers investing in innovative solutions, as they may not align with existing compliance frameworks. Balancing innovation with compliance becomes a delicate act, requiring careful consideration of long-term market trends and regulatory developments.
Regulatory changes and updates to standards further complicate compliance efforts. Manufacturers must stay informed about evolving requirements across multiple jurisdictions, which can be resource-intensive. Failure to adapt to these changes promptly can result in market access barriers or costly product recalls. The need for continuous monitoring and adaptation places a significant burden on companies, particularly those with limited regulatory affairs resources.
Language barriers and cultural differences also contribute to compliance challenges. Interpreting standards accurately across different languages and understanding the nuances of local regulatory environments require specialized expertise. Misinterpretations can lead to non-compliance issues, highlighting the importance of clear communication and local market knowledge in navigating international standards.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of global harmonization in standards for gate valves. While efforts have been made to create unified standards, such as those developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), many countries still maintain their own specific requirements. This fragmentation leads to increased complexity and costs for manufacturers who must adapt their products to meet multiple standards simultaneously.
Material selection and certification pose another significant hurdle. Different markets may require specific materials or have stringent requirements for material traceability and documentation. For instance, the European Union's Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) mandates specific material certifications, while the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may have different requirements for oil and gas applications. Manufacturers must navigate these varying demands while ensuring their products maintain consistent quality and performance.
Testing and validation procedures also differ across international markets. While some regions may accept self-certification, others require third-party testing and validation. The costs and time associated with these processes can be substantial, particularly for smaller manufacturers looking to expand their global presence. Additionally, the interpretation and application of standards can vary between certification bodies, leading to inconsistencies and potential delays in product approval.
The rapid pace of technological advancement presents another challenge. As new materials and manufacturing techniques emerge, standards struggle to keep pace. This lag can create uncertainty for manufacturers investing in innovative solutions, as they may not align with existing compliance frameworks. Balancing innovation with compliance becomes a delicate act, requiring careful consideration of long-term market trends and regulatory developments.
Regulatory changes and updates to standards further complicate compliance efforts. Manufacturers must stay informed about evolving requirements across multiple jurisdictions, which can be resource-intensive. Failure to adapt to these changes promptly can result in market access barriers or costly product recalls. The need for continuous monitoring and adaptation places a significant burden on companies, particularly those with limited regulatory affairs resources.
Language barriers and cultural differences also contribute to compliance challenges. Interpreting standards accurately across different languages and understanding the nuances of local regulatory environments require specialized expertise. Misinterpretations can lead to non-compliance issues, highlighting the importance of clear communication and local market knowledge in navigating international standards.
Existing Solutions for Standards Compliance
01 Compliance management systems for gate valves
Automated systems for managing and ensuring compliance of gate valves with industry standards. These systems can track, monitor, and report on various compliance aspects, including design specifications, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures.- Compliance management systems for gate valves: Automated systems for managing and ensuring compliance of gate valves with industry standards. These systems can track regulatory requirements, perform audits, and generate compliance reports to ensure gate valves meet necessary standards and specifications.
- Quality control and testing procedures: Implementation of rigorous quality control and testing procedures to ensure gate valves meet required standards. This includes automated testing systems, inspection protocols, and documentation processes to verify compliance with industry regulations and specifications.
- Standards-based design and manufacturing: Incorporation of industry standards into the design and manufacturing processes of gate valves. This involves using standardized components, materials, and manufacturing techniques to ensure consistency and compliance with relevant regulations and specifications.
- Certification and documentation management: Systems and methods for managing certifications and documentation related to gate valve standards compliance. This includes digital platforms for storing, updating, and retrieving compliance-related documents, as well as tools for generating and maintaining certification records.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement: Implementation of continuous monitoring and improvement processes to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving standards. This involves real-time data collection, analysis of performance metrics, and feedback systems to identify and address potential compliance issues in gate valve production and operation.
02 Standards-based validation and verification
Methods and tools for validating and verifying gate valve designs and performance against established standards. This includes simulation software, testing protocols, and documentation processes to ensure compliance with relevant industry norms and regulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automated compliance reporting and documentation
Systems for generating automated compliance reports and maintaining documentation for gate valves. These solutions streamline the process of demonstrating adherence to standards, facilitating audits, and managing regulatory submissions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of standards in design and manufacturing processes
Approaches for incorporating compliance requirements directly into the design and manufacturing processes for gate valves. This ensures that standards are considered from the outset, reducing the need for post-production modifications and improving overall compliance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Continuous monitoring and updating of compliance status
Systems for real-time monitoring of gate valve compliance status and automatic updating based on changes in standards or regulations. These solutions help maintain ongoing compliance and quickly adapt to evolving industry requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Gate Valve Manufacturing and Certification
The standards compliance landscape for gate valves in international markets is characterized by a complex and evolving competitive environment. The industry is in a mature stage, with established players like NOV, Inc., Halliburton Energy Services, and Baker Hughes Co. dominating the market. However, emerging companies from China, such as Beijing Aerospace Petrochemical Tech Equipment Eng Co., Ltd. and Sinopec Engineering, Inc., are increasingly challenging this dominance. The global gate valve market size is substantial, driven by growing demand in oil and gas, power generation, and water treatment sectors. Technological maturity varies, with leading companies like Cameron International Corp. and ULVAC, Inc. pushing innovation in valve design and materials to meet stringent international standards and improve performance in diverse operating conditions.
NOV, Inc.
Technical Solution: NOV has developed advanced gate valve technologies to meet international standards compliance challenges. Their GateVision™ system incorporates smart sensors and real-time monitoring capabilities to ensure valves operate within specified parameters across diverse global markets[1]. The company's TruGate™ valves feature a patented seat design that enhances sealing performance and longevity, meeting stringent fugitive emissions requirements in various regions[2]. NOV also employs advanced materials and coatings, such as their DuraGate™ technology, which provides superior corrosion and erosion resistance to comply with NACE standards worldwide[3].
Strengths: Global presence, innovative technologies, and comprehensive testing facilities. Weaknesses: Higher initial costs and potential complexity in implementation for some markets.
Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: Halliburton addresses international standards compliance for gate valves through their Advantage™ line. These valves incorporate a unique bi-directional sealing mechanism that meets API 6A and 6D specifications for both upstream and downstream applications[4]. The company's H2S-resistant materials and designs comply with NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 standards, ensuring suitability for sour service environments globally[5]. Halliburton's ValveWatch™ monitoring system provides real-time data on valve performance, helping operators maintain compliance with local regulations and industry best practices across different regions[6].
Strengths: Extensive global experience, comprehensive product range, and strong after-sales support. Weaknesses: Potential for higher costs in some markets and occasional supply chain challenges.
Core Innovations in Gate Valve Design for Compliance
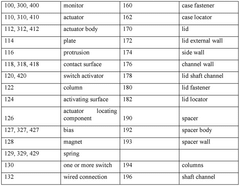
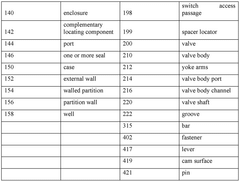
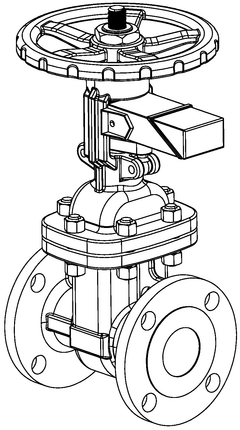
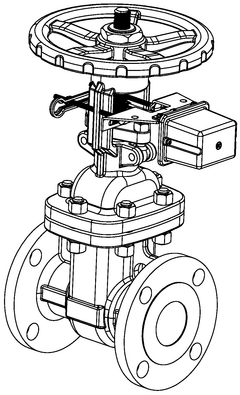
Gate valve monitor
PatentWO2024216343A1
Innovation
- A gate valve monitor with an actuator and switch accommodated within an enclosure, allowing the gate valve shaft to pass through, which operates to trigger the switch without external modifications, providing enhanced tamper protection and eliminating false alarms by being fully enclosed within the valve body, thus preventing unauthorized access and tampering.
Low pressure stem gas seal
PatentWO2005106302A1
Innovation
- A backup stem seal design featuring metal-to-metal contact with radially or sloping surfaces and a retaining groove for a seal ring, which helps maintain the seal's position and integrity even under fluid flow, using materials like Teflon® with PEEK, and allowing for minor surface misalignment compensation.
Regulatory Framework for Gate Valve Certification
The regulatory framework for gate valve certification in international markets is a complex and multifaceted system designed to ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of these critical components across various industries. This framework encompasses a wide range of standards, regulations, and certification processes that manufacturers must navigate to bring their products to global markets.
At the core of this framework are international standards organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Petroleum Institute (API). These bodies develop and maintain comprehensive standards that define the design, manufacturing, testing, and performance requirements for gate valves. Key standards include ISO 10434 for bolted bonnet steel gate valves and API 600 for steel gate valves, flanged and butt-welding ends.
National and regional regulatory bodies also play a crucial role in shaping the certification landscape. In the European Union, the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) sets out essential safety requirements for pressure equipment, including gate valves. The directive mandates CE marking for products that meet these requirements. Similarly, in North America, organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) establish codes and standards that influence gate valve certification.
The certification process typically involves rigorous testing and inspection procedures to verify compliance with relevant standards. This may include hydrostatic shell tests, seat leakage tests, and material composition analysis. Third-party certification bodies, such as TÜV, DNV GL, and Lloyd's Register, often conduct these assessments and issue certificates of conformity.
Industry-specific regulations further complicate the certification landscape. For instance, gate valves used in the oil and gas sector must often meet additional requirements set by organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) or the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP). Similarly, valves intended for use in nuclear power plants are subject to stringent regulations enforced by bodies such as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) or the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Manufacturers seeking to enter international markets must also contend with varying national standards and regulations. Countries like China, Russia, and India have their own certification requirements, which may necessitate additional testing or documentation. This diversity of standards can create significant challenges for manufacturers, requiring them to navigate a complex web of overlapping and sometimes conflicting requirements.
The regulatory framework for gate valve certification is not static but evolves in response to technological advancements, safety concerns, and changing industry needs. This dynamic nature requires manufacturers to stay informed about updates to standards and regulations, and to continuously adapt their products and processes to maintain compliance.
At the core of this framework are international standards organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Petroleum Institute (API). These bodies develop and maintain comprehensive standards that define the design, manufacturing, testing, and performance requirements for gate valves. Key standards include ISO 10434 for bolted bonnet steel gate valves and API 600 for steel gate valves, flanged and butt-welding ends.
National and regional regulatory bodies also play a crucial role in shaping the certification landscape. In the European Union, the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) sets out essential safety requirements for pressure equipment, including gate valves. The directive mandates CE marking for products that meet these requirements. Similarly, in North America, organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) establish codes and standards that influence gate valve certification.
The certification process typically involves rigorous testing and inspection procedures to verify compliance with relevant standards. This may include hydrostatic shell tests, seat leakage tests, and material composition analysis. Third-party certification bodies, such as TÜV, DNV GL, and Lloyd's Register, often conduct these assessments and issue certificates of conformity.
Industry-specific regulations further complicate the certification landscape. For instance, gate valves used in the oil and gas sector must often meet additional requirements set by organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) or the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP). Similarly, valves intended for use in nuclear power plants are subject to stringent regulations enforced by bodies such as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) or the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Manufacturers seeking to enter international markets must also contend with varying national standards and regulations. Countries like China, Russia, and India have their own certification requirements, which may necessitate additional testing or documentation. This diversity of standards can create significant challenges for manufacturers, requiring them to navigate a complex web of overlapping and sometimes conflicting requirements.
The regulatory framework for gate valve certification is not static but evolves in response to technological advancements, safety concerns, and changing industry needs. This dynamic nature requires manufacturers to stay informed about updates to standards and regulations, and to continuously adapt their products and processes to maintain compliance.
Economic Impact of Standards Compliance on Manufacturers
The economic impact of standards compliance on gate valve manufacturers is significant and multifaceted. Compliance with international standards is crucial for manufacturers to access global markets and maintain competitiveness. However, the process of achieving and maintaining compliance can be costly and time-consuming.
Manufacturers must invest heavily in research and development to ensure their products meet the stringent requirements of various international standards. This often involves redesigning existing products or developing new ones, which can lead to increased production costs. Additionally, manufacturers may need to upgrade their manufacturing facilities and processes to meet the quality control requirements specified in these standards.
The certification process itself is another major expense for manufacturers. Third-party testing and certification can be costly, especially when multiple certifications are required for different markets. Ongoing compliance also necessitates regular audits and re-certifications, adding to the long-term financial burden.
Despite these costs, compliance with international standards can provide significant economic benefits. It opens up new market opportunities, allowing manufacturers to expand their customer base globally. Compliant products are often perceived as higher quality, which can justify premium pricing and lead to increased revenue.
Standards compliance can also lead to operational efficiencies. By adhering to standardized processes and specifications, manufacturers can streamline their production, reduce waste, and improve overall product quality. This can result in cost savings in the long run and enhance the company's reputation.
Furthermore, compliance can serve as a competitive advantage. In markets where standards are strictly enforced, non-compliant manufacturers may be excluded entirely. Compliant manufacturers can leverage their certification status in marketing efforts, differentiating themselves from competitors and potentially capturing a larger market share.
However, the economic impact is not uniform across all manufacturers. Larger companies with greater resources may find it easier to absorb the costs of compliance and capitalize on the benefits. Smaller manufacturers, on the other hand, may struggle with the initial investment required, potentially leading to market consolidation.
In conclusion, while standards compliance presents significant upfront costs and ongoing expenses for gate valve manufacturers, it also offers substantial economic benefits through market access, operational improvements, and competitive advantages. The overall economic impact depends on the manufacturer's size, resources, and ability to leverage compliance for strategic growth.
Manufacturers must invest heavily in research and development to ensure their products meet the stringent requirements of various international standards. This often involves redesigning existing products or developing new ones, which can lead to increased production costs. Additionally, manufacturers may need to upgrade their manufacturing facilities and processes to meet the quality control requirements specified in these standards.
The certification process itself is another major expense for manufacturers. Third-party testing and certification can be costly, especially when multiple certifications are required for different markets. Ongoing compliance also necessitates regular audits and re-certifications, adding to the long-term financial burden.
Despite these costs, compliance with international standards can provide significant economic benefits. It opens up new market opportunities, allowing manufacturers to expand their customer base globally. Compliant products are often perceived as higher quality, which can justify premium pricing and lead to increased revenue.
Standards compliance can also lead to operational efficiencies. By adhering to standardized processes and specifications, manufacturers can streamline their production, reduce waste, and improve overall product quality. This can result in cost savings in the long run and enhance the company's reputation.
Furthermore, compliance can serve as a competitive advantage. In markets where standards are strictly enforced, non-compliant manufacturers may be excluded entirely. Compliant manufacturers can leverage their certification status in marketing efforts, differentiating themselves from competitors and potentially capturing a larger market share.
However, the economic impact is not uniform across all manufacturers. Larger companies with greater resources may find it easier to absorb the costs of compliance and capitalize on the benefits. Smaller manufacturers, on the other hand, may struggle with the initial investment required, potentially leading to market consolidation.
In conclusion, while standards compliance presents significant upfront costs and ongoing expenses for gate valve manufacturers, it also offers substantial economic benefits through market access, operational improvements, and competitive advantages. The overall economic impact depends on the manufacturer's size, resources, and ability to leverage compliance for strategic growth.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!