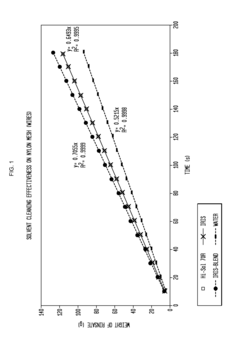
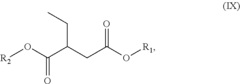
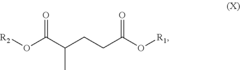
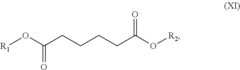
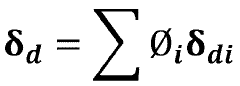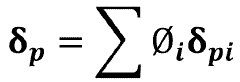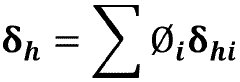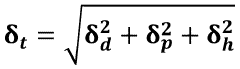Analysis of Biomass-Derived Solvent Efficacy in Industrial Cleaning
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvent Development Background and Objectives
The evolution of industrial cleaning solvents has historically been dominated by petroleum-based products, which have demonstrated high efficacy but pose significant environmental and health concerns. Since the 1970s, increasing awareness of these issues has driven research toward more sustainable alternatives. Biomass-derived solvents represent a promising frontier in this transition, utilizing renewable resources such as agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops as feedstock for solvent production.
The development of biomass-derived solvents has accelerated significantly over the past decade, propelled by stricter environmental regulations, corporate sustainability initiatives, and consumer demand for greener products. Notable milestones include the commercial introduction of bio-based esters in the early 2000s, followed by more sophisticated bio-derived terpenes and furans in the 2010s, demonstrating the industry's progressive technical capabilities.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward multi-functional biomass solvents that combine cleaning efficacy with additional benefits such as antimicrobial properties or enhanced material compatibility. Research is increasingly focused on developing solvents with targeted performance characteristics for specific industrial applications, moving beyond simple drop-in replacements for conventional products.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of various biomass-derived solvents in industrial cleaning applications across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, food processing, healthcare, and electronics. This assessment aims to identify which bio-solvents offer performance comparable to or exceeding traditional petroleum-based products while providing improved environmental and safety profiles.
Secondary objectives include mapping the relationship between biomass feedstock characteristics and resulting solvent properties, identifying optimal processing technologies for different biomass sources, and determining cost-effective scaling pathways to enhance commercial viability. The research also seeks to establish standardized testing protocols for evaluating biomass solvent performance, addressing a significant gap in current industry practices.
Long-term goals of biomass solvent development extend beyond direct substitution of petroleum-based products to creating entirely new cleaning paradigms that leverage the unique properties of bio-derived compounds. This includes exploring synergistic formulations that combine multiple biomass-derived components to achieve enhanced performance characteristics and developing closed-loop systems where spent cleaning solvents can be regenerated or biodegraded without environmental harm.
Through this comprehensive approach to biomass solvent research and development, we aim to accelerate the transition toward more sustainable industrial cleaning practices while maintaining or improving the performance standards that modern manufacturing and maintenance operations require.
The development of biomass-derived solvents has accelerated significantly over the past decade, propelled by stricter environmental regulations, corporate sustainability initiatives, and consumer demand for greener products. Notable milestones include the commercial introduction of bio-based esters in the early 2000s, followed by more sophisticated bio-derived terpenes and furans in the 2010s, demonstrating the industry's progressive technical capabilities.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward multi-functional biomass solvents that combine cleaning efficacy with additional benefits such as antimicrobial properties or enhanced material compatibility. Research is increasingly focused on developing solvents with targeted performance characteristics for specific industrial applications, moving beyond simple drop-in replacements for conventional products.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of various biomass-derived solvents in industrial cleaning applications across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, food processing, healthcare, and electronics. This assessment aims to identify which bio-solvents offer performance comparable to or exceeding traditional petroleum-based products while providing improved environmental and safety profiles.
Secondary objectives include mapping the relationship between biomass feedstock characteristics and resulting solvent properties, identifying optimal processing technologies for different biomass sources, and determining cost-effective scaling pathways to enhance commercial viability. The research also seeks to establish standardized testing protocols for evaluating biomass solvent performance, addressing a significant gap in current industry practices.
Long-term goals of biomass solvent development extend beyond direct substitution of petroleum-based products to creating entirely new cleaning paradigms that leverage the unique properties of bio-derived compounds. This includes exploring synergistic formulations that combine multiple biomass-derived components to achieve enhanced performance characteristics and developing closed-loop systems where spent cleaning solvents can be regenerated or biodegraded without environmental harm.
Through this comprehensive approach to biomass solvent research and development, we aim to accelerate the transition toward more sustainable industrial cleaning practices while maintaining or improving the performance standards that modern manufacturing and maintenance operations require.
Industrial Cleaning Market Demand Analysis
The global industrial cleaning market has experienced significant growth in recent years, with a market value reaching $50.2 billion in 2022 and projected to expand at a CAGR of 5.7% through 2030. This growth is primarily driven by stringent regulatory frameworks concerning workplace safety, environmental protection, and increasing awareness about hygiene standards across manufacturing facilities.
The demand for industrial cleaning solutions spans various sectors including manufacturing, healthcare, food processing, automotive, and electronics. Among these, the manufacturing sector accounts for approximately 32% of the total market share, followed by healthcare at 24% and food processing at 18%. These industries require specialized cleaning agents that effectively remove contaminants without damaging equipment or leaving harmful residues.
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent, particularly in North America and Europe, pushing industries to adopt greener cleaning alternatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and the EPA's Safer Choice program in the United States have significantly influenced market dynamics, creating a substantial demand for bio-based cleaning solvents. This regulatory pressure has accelerated the transition from traditional petroleum-based solvents to biomass-derived alternatives.
Consumer preferences are also shifting toward sustainable products, with 78% of industrial procurement managers indicating a willingness to pay premium prices for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. This trend is particularly pronounced in food processing and pharmaceutical industries, where end-product safety is paramount and residual chemical contamination poses significant risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further amplified the demand for industrial cleaning products, with heightened focus on disinfection and sanitation protocols. This has created a new market segment specifically for antimicrobial cleaning solutions, which is expected to grow at 7.3% annually through 2028.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the industrial cleaning market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the fastest growth is projected in emerging economies of Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of international manufacturing standards are driving demand for advanced cleaning solutions.
The biomass-derived solvent segment specifically is experiencing accelerated growth within the broader industrial cleaning market, with current market penetration at approximately 12%. Industry experts project this segment to grow at twice the rate of conventional cleaning solvents over the next five years, indicating substantial market potential for innovations in this space.
The demand for industrial cleaning solutions spans various sectors including manufacturing, healthcare, food processing, automotive, and electronics. Among these, the manufacturing sector accounts for approximately 32% of the total market share, followed by healthcare at 24% and food processing at 18%. These industries require specialized cleaning agents that effectively remove contaminants without damaging equipment or leaving harmful residues.
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent, particularly in North America and Europe, pushing industries to adopt greener cleaning alternatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and the EPA's Safer Choice program in the United States have significantly influenced market dynamics, creating a substantial demand for bio-based cleaning solvents. This regulatory pressure has accelerated the transition from traditional petroleum-based solvents to biomass-derived alternatives.
Consumer preferences are also shifting toward sustainable products, with 78% of industrial procurement managers indicating a willingness to pay premium prices for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. This trend is particularly pronounced in food processing and pharmaceutical industries, where end-product safety is paramount and residual chemical contamination poses significant risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further amplified the demand for industrial cleaning products, with heightened focus on disinfection and sanitation protocols. This has created a new market segment specifically for antimicrobial cleaning solutions, which is expected to grow at 7.3% annually through 2028.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the industrial cleaning market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the fastest growth is projected in emerging economies of Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of international manufacturing standards are driving demand for advanced cleaning solutions.
The biomass-derived solvent segment specifically is experiencing accelerated growth within the broader industrial cleaning market, with current market penetration at approximately 12%. Industry experts project this segment to grow at twice the rate of conventional cleaning solvents over the next five years, indicating substantial market potential for innovations in this space.
Current Status and Challenges in Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based solvents have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional petroleum-derived solvents in industrial cleaning applications. Currently, the global market for bio-based solvents is experiencing steady growth, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8-10%. This growth is primarily driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer demand for sustainable products, and corporate sustainability initiatives across various industries.
The most developed bio-based solvents in the market include d-limonene (derived from citrus peels), ethyl lactate (from fermentation of carbohydrates), methyl soyate (from soybean oil), and various terpenes extracted from pine trees and other plant materials. These solvents have demonstrated efficacy in removing greases, oils, adhesives, and other contaminants in industrial settings, sometimes matching or exceeding the performance of traditional petroleum-based solvents.
Despite promising developments, bio-based solvents face significant technical challenges. Consistency in performance remains a major hurdle, as the chemical composition of biomass feedstocks can vary based on growing conditions, harvesting time, and processing methods. This variability affects solvent properties and cleaning efficacy, making standardization difficult for industrial applications that require precise specifications.
Cost competitiveness presents another substantial challenge. Production costs for bio-based solvents typically exceed those of conventional solvents by 20-50%, primarily due to feedstock costs, complex processing requirements, and smaller production scales. This price premium limits widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive industrial sectors where cleaning solvents represent a significant operational expense.
Stability issues also plague many bio-based solvents. Some exhibit limited shelf life due to oxidation, polymerization, or degradation under standard storage conditions. Additionally, certain bio-based solvents demonstrate reduced efficacy at extreme temperatures or pH levels commonly encountered in industrial cleaning processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in bio-based solvent development and adoption, with established regulatory frameworks supporting their use. The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly emerging as a significant market, driven by industrial growth and increasing environmental awareness, particularly in Japan, South Korea, and China.
Research institutions and companies worldwide are addressing these challenges through various approaches. Current research focuses on developing more efficient extraction and conversion technologies, identifying novel biomass feedstocks with more consistent properties, and creating solvent formulations that combine bio-based components with stabilizers or performance enhancers to meet industrial requirements.
Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with policies in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia increasingly favoring bio-based alternatives through restrictions on conventional solvents, tax incentives, and green procurement policies. However, the lack of global harmonization in standards and definitions for bio-based products creates market fragmentation and compliance challenges for manufacturers.
The most developed bio-based solvents in the market include d-limonene (derived from citrus peels), ethyl lactate (from fermentation of carbohydrates), methyl soyate (from soybean oil), and various terpenes extracted from pine trees and other plant materials. These solvents have demonstrated efficacy in removing greases, oils, adhesives, and other contaminants in industrial settings, sometimes matching or exceeding the performance of traditional petroleum-based solvents.
Despite promising developments, bio-based solvents face significant technical challenges. Consistency in performance remains a major hurdle, as the chemical composition of biomass feedstocks can vary based on growing conditions, harvesting time, and processing methods. This variability affects solvent properties and cleaning efficacy, making standardization difficult for industrial applications that require precise specifications.
Cost competitiveness presents another substantial challenge. Production costs for bio-based solvents typically exceed those of conventional solvents by 20-50%, primarily due to feedstock costs, complex processing requirements, and smaller production scales. This price premium limits widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive industrial sectors where cleaning solvents represent a significant operational expense.
Stability issues also plague many bio-based solvents. Some exhibit limited shelf life due to oxidation, polymerization, or degradation under standard storage conditions. Additionally, certain bio-based solvents demonstrate reduced efficacy at extreme temperatures or pH levels commonly encountered in industrial cleaning processes.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead in bio-based solvent development and adoption, with established regulatory frameworks supporting their use. The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly emerging as a significant market, driven by industrial growth and increasing environmental awareness, particularly in Japan, South Korea, and China.
Research institutions and companies worldwide are addressing these challenges through various approaches. Current research focuses on developing more efficient extraction and conversion technologies, identifying novel biomass feedstocks with more consistent properties, and creating solvent formulations that combine bio-based components with stabilizers or performance enhancers to meet industrial requirements.
Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with policies in the EU, North America, and parts of Asia increasingly favoring bio-based alternatives through restrictions on conventional solvents, tax incentives, and green procurement policies. However, the lack of global harmonization in standards and definitions for bio-based products creates market fragmentation and compliance challenges for manufacturers.
Current Biomass Solvent Formulations and Applications
01 Efficacy of biomass-derived solvents in extraction processes
Biomass-derived solvents demonstrate high efficacy in various extraction processes, particularly for separating valuable compounds from natural materials. These green solvents offer comparable or superior extraction efficiency compared to traditional petroleum-based solvents while reducing environmental impact. Their selective dissolution properties enable effective separation of target compounds, making them suitable for applications in pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries.- Biomass-derived solvents for extraction processes: Biomass-derived solvents have demonstrated high efficacy in various extraction processes. These green solvents, produced from renewable resources, can effectively extract valuable compounds from natural materials while reducing environmental impact. Their extraction efficiency is comparable or superior to conventional petroleum-based solvents in many applications, particularly for polar compounds. The use of these solvents also addresses sustainability concerns by reducing dependence on fossil resources.
- Biomass-derived solvents in cleaning applications: Biomass-derived solvents show remarkable efficacy in cleaning applications across various industries. These bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum solvents demonstrate excellent degreasing properties and ability to dissolve diverse contaminants. Their low toxicity and biodegradability make them particularly suitable for environmentally sensitive cleaning applications. The solvents can be formulated to target specific cleaning challenges while maintaining performance comparable to conventional options.
- Production methods for biomass-derived solvents: Various efficient production methods have been developed for biomass-derived solvents, enhancing their commercial viability. These processes include fermentation, catalytic conversion, and thermochemical treatments of biomass feedstocks. Advanced catalytic systems enable selective transformation of biomass components into high-quality solvents with tailored properties. Optimization of these production methods has improved yields and reduced costs, making biomass-derived solvents increasingly competitive with petroleum-based alternatives.
- Performance characteristics of biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents exhibit diverse performance characteristics that determine their efficacy in various applications. These include polarity, volatility, solvation power, and stability under different conditions. Many bio-based solvents demonstrate excellent dissolution capabilities for specific solutes, sometimes outperforming conventional solvents. Their physical properties can be tuned through molecular design and formulation to optimize performance for targeted applications while maintaining their environmental benefits.
- Biomass-derived solvents in fuel applications: Biomass-derived solvents show promising efficacy as components in fuel formulations. These bio-based additives can enhance fuel properties, improve combustion efficiency, and reduce emissions. When incorporated into conventional fuels, they can help meet renewable content requirements while maintaining or improving performance. Some biomass-derived solvents also demonstrate potential as standalone fuels or major fuel components, offering pathways to more sustainable transportation and energy systems.
02 Performance of biomass-derived solvents in cleaning applications
Biomass-derived solvents show excellent efficacy as cleaning agents across various industrial and consumer applications. These bio-based alternatives effectively dissolve oils, greases, and other contaminants while being less toxic and more biodegradable than conventional petroleum-based solvents. Their cleaning performance is comparable to traditional solvents, with the added benefits of reduced VOC emissions and improved worker safety profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biomass-derived solvents as effective reaction media
Biomass-derived solvents serve as effective reaction media for various chemical transformations. These bio-based solvents can enhance reaction rates, improve selectivity, and facilitate product separation in organic synthesis processes. Their unique properties, including polarity, hydrogen bonding capability, and miscibility characteristics, make them suitable alternatives to conventional petroleum-derived solvents in catalytic reactions, polymerizations, and other chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production methods affecting efficacy of biomass-derived solvents
The production methods significantly impact the efficacy of biomass-derived solvents. Advanced conversion technologies, including catalytic processes, fermentation, and thermochemical treatments, can enhance the purity and performance characteristics of these solvents. Optimized production pathways lead to biomass-derived solvents with improved solubility parameters, stability, and functional properties, making them more effective in their intended applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulation strategies to enhance biomass-derived solvent efficacy
Various formulation strategies can enhance the efficacy of biomass-derived solvents. These include creating solvent blends that combine complementary properties of different bio-based solvents, incorporating additives to improve specific performance characteristics, and developing co-solvent systems that optimize dissolution power. Such formulation approaches can overcome limitations of individual biomass-derived solvents and expand their application range across industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Biomass-Derived Solvents
The biomass-derived solvent market for industrial cleaning is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by sustainability trends. The market is expanding as industries seek eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based solvents, with projections showing significant growth potential. Leading players include established chemical companies like BASF, Ecolab, Henkel, and Unilever, alongside biotechnology innovators such as Novozymes and Realco SA who are leveraging enzymatic approaches. The technology is approaching maturity with commercial applications already available, though ongoing research at institutions like MIT and University of California indicates continued innovation. Companies are focusing on improving efficacy, cost-competitiveness, and application-specific formulations to capture market share in this evolving green chemistry sector.
Novozymes A/S
Technical Solution: Novozymes has developed an innovative enzymatic platform called "BioSolv" that enables the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into highly effective industrial cleaning solvents. Their technology utilizes specialized enzyme cocktails to break down complex plant materials into simpler compounds with excellent solvent properties. The process specifically targets the production of lactate esters and furan derivatives that demonstrate superior degreasing capabilities compared to traditional petroleum-based solvents. Novozymes' approach incorporates a cascade enzymatic process that can be tuned to produce solvents with specific properties tailored to different industrial cleaning challenges. Their biomass-derived solvents have shown particular efficacy in removing protein-based soils in food processing equipment, with documented cleaning efficiency improvements of up to 35% compared to conventional methods. The company has also developed specialized enzyme stabilization technologies that allow their biomass processing systems to operate effectively across a wide range of pH and temperature conditions, increasing the versatility of their solvent production platform.
Strengths: World-leading expertise in industrial enzymes; established bioprocessing infrastructure; strong intellectual property position in enzymatic biomass conversion. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional chemical processes; enzyme sensitivity to certain process conditions limiting some applications; longer lead times for production scale-up.
Ecolab USA, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ecolab has developed a comprehensive biomass-derived solvent platform called "Biobased Solutions" specifically for industrial cleaning applications. Their technology utilizes solvents derived from agricultural waste streams, particularly corn and soybean oil processing byproducts. These solvents undergo proprietary enzymatic modification processes to enhance their cleaning efficacy while maintaining biodegradability. Ecolab's approach incorporates green chemistry principles to create formulations that match or exceed petroleum-based alternatives in performance metrics. Their solutions have demonstrated particular effectiveness in removing stubborn hydrocarbon soils and adhesives in food processing equipment, with documented reduction in cleaning time by approximately 25% compared to conventional methods. The company has also developed specialized biomass-derived surfactant systems that work synergistically with these solvents to enhance their cleaning power across various pH ranges and water hardness conditions.
Strengths: Extensive distribution network and customer relationships in industrial cleaning sector; proven track record of formulation expertise; comprehensive testing capabilities for performance validation. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents; performance limitations in certain high-temperature industrial applications; requires specialized handling protocols.
Technical Analysis of High-Performance Bio-Solvents
Industrial cleaning compositions and methods for using same
PatentInactiveUS20130157917A1
Innovation
- A cleaning composition comprising a blend of dibasic esters, biodiesel components, and optional additives such as surfactants and water, which is non-toxic, non-flammable, biodegradable, and has low VOC content, effectively dissolves residual materials on papermaking equipment without disrupting the papermaking process.
Eco-friendly industrial cleaning composition
PatentWO2024025115A1
Innovation
- A combination of a carbonate-based solvent with a carbonate ester group and a glycol ether-based solvent, optimized to achieve a specific solubility parameter range, is used to create an eco-friendly industrial cleaning composition that effectively removes oils, including those in water-dispersed or water-dissolved states, while avoiding the use of restricted substances.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of biomass-derived solvents in industrial cleaning applications reveals significant advantages over conventional petroleum-based alternatives. Life cycle analyses demonstrate that these bio-solvents typically produce 30-65% lower greenhouse gas emissions across their production, use, and disposal phases. This reduction stems primarily from the renewable nature of biomass feedstocks, which create a more closed carbon cycle compared to fossil-derived solvents that release previously sequestered carbon.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture. While some biomass-derived solvents require substantial irrigation during feedstock cultivation, advanced production methods utilizing agricultural waste streams and drought-resistant crops have reduced water footprints by approximately 40% in recent implementations. Industrial facilities transitioning to these optimized bio-solvents report water usage reductions between 15-25% in cleaning operations due to improved formulations requiring less rinse water.
Biodegradability testing confirms that most biomass-derived solvents decompose 3-5 times faster than their petroleum counterparts when released into the environment. This characteristic substantially reduces persistent environmental contamination risks in cases of accidental spills or improper disposal. Ecotoxicity studies indicate 50-80% lower aquatic toxicity levels for most bio-solvents, though certain formulations derived from specific biomass sources may contain naturally occurring compounds requiring additional refinement to achieve optimal environmental safety profiles.
The sustainability assessment extends beyond environmental metrics to encompass social and economic dimensions. From a resource security perspective, biomass-derived solvents offer significant advantages through geographical diversification of production capabilities. Unlike petroleum-based solvents concentrated in specific regions, biomass feedstocks can be cultivated across diverse climates, enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing geopolitical vulnerabilities.
Circular economy principles are increasingly integrated into biomass solvent production systems. Advanced biorefinery approaches now achieve 85-95% material utilization efficiency by extracting multiple value streams from single biomass sources. These integrated systems produce not only industrial solvents but also co-products for food, pharmaceutical, and material applications, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. This holistic approach transforms what was previously considered waste into valuable inputs, creating closed-loop systems that significantly enhance the overall sustainability profile of biomass-derived industrial cleaning solutions.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture. While some biomass-derived solvents require substantial irrigation during feedstock cultivation, advanced production methods utilizing agricultural waste streams and drought-resistant crops have reduced water footprints by approximately 40% in recent implementations. Industrial facilities transitioning to these optimized bio-solvents report water usage reductions between 15-25% in cleaning operations due to improved formulations requiring less rinse water.
Biodegradability testing confirms that most biomass-derived solvents decompose 3-5 times faster than their petroleum counterparts when released into the environment. This characteristic substantially reduces persistent environmental contamination risks in cases of accidental spills or improper disposal. Ecotoxicity studies indicate 50-80% lower aquatic toxicity levels for most bio-solvents, though certain formulations derived from specific biomass sources may contain naturally occurring compounds requiring additional refinement to achieve optimal environmental safety profiles.
The sustainability assessment extends beyond environmental metrics to encompass social and economic dimensions. From a resource security perspective, biomass-derived solvents offer significant advantages through geographical diversification of production capabilities. Unlike petroleum-based solvents concentrated in specific regions, biomass feedstocks can be cultivated across diverse climates, enhancing supply chain resilience and reducing geopolitical vulnerabilities.
Circular economy principles are increasingly integrated into biomass solvent production systems. Advanced biorefinery approaches now achieve 85-95% material utilization efficiency by extracting multiple value streams from single biomass sources. These integrated systems produce not only industrial solvents but also co-products for food, pharmaceutical, and material applications, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. This holistic approach transforms what was previously considered waste into valuable inputs, creating closed-loop systems that significantly enhance the overall sustainability profile of biomass-derived industrial cleaning solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Industrial Bio-based Chemicals
The regulatory landscape for bio-based chemicals in industrial applications has evolved significantly over the past decade, reflecting growing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives. At the international level, frameworks such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation have established comprehensive requirements for chemical substances, including those derived from biomass. These regulations mandate thorough safety assessments, documentation of environmental impacts, and transparent communication throughout supply chains.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees biomass-derived solvents through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which was substantially modernized in 2016 to enhance chemical safety evaluations. The EPA's Safer Choice program specifically recognizes environmentally preferable cleaning products, providing a pathway for biomass-derived solvents to gain market recognition for their reduced environmental footprint.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate lifecycle assessment methodologies to evaluate the true environmental impact of bio-based chemicals. This approach considers factors beyond just biodegradability, examining carbon footprint, water usage, land use changes, and potential competition with food production. For biomass-derived solvents used in industrial cleaning, these assessments are particularly relevant as they help quantify the actual sustainability benefits compared to petroleum-based alternatives.
Industry-specific regulations also impact the adoption of biomass-derived solvents. In food processing facilities, for instance, cleaning agents must comply with FDA regulations regarding food contact surfaces. Similarly, healthcare settings have stringent disinfection requirements that any alternative solvent must satisfy, regardless of its bio-based credentials.
Voluntary certification schemes have emerged as important market drivers, complementing mandatory regulations. Programs such as the USDA BioPreferred program, EU Ecolabel, and various industry-specific green certifications provide frameworks for verifying and communicating the environmental attributes of biomass-derived cleaning products. These schemes often require minimum bio-based content percentages and performance standards that match or exceed conventional products.
Global harmonization of these regulatory frameworks remains a challenge, with significant variations in requirements across different regions. This regulatory fragmentation creates compliance complexities for manufacturers of biomass-derived solvents seeking to enter multiple markets. However, international initiatives like the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) are working toward greater alignment of chemical management policies worldwide.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees biomass-derived solvents through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which was substantially modernized in 2016 to enhance chemical safety evaluations. The EPA's Safer Choice program specifically recognizes environmentally preferable cleaning products, providing a pathway for biomass-derived solvents to gain market recognition for their reduced environmental footprint.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate lifecycle assessment methodologies to evaluate the true environmental impact of bio-based chemicals. This approach considers factors beyond just biodegradability, examining carbon footprint, water usage, land use changes, and potential competition with food production. For biomass-derived solvents used in industrial cleaning, these assessments are particularly relevant as they help quantify the actual sustainability benefits compared to petroleum-based alternatives.
Industry-specific regulations also impact the adoption of biomass-derived solvents. In food processing facilities, for instance, cleaning agents must comply with FDA regulations regarding food contact surfaces. Similarly, healthcare settings have stringent disinfection requirements that any alternative solvent must satisfy, regardless of its bio-based credentials.
Voluntary certification schemes have emerged as important market drivers, complementing mandatory regulations. Programs such as the USDA BioPreferred program, EU Ecolabel, and various industry-specific green certifications provide frameworks for verifying and communicating the environmental attributes of biomass-derived cleaning products. These schemes often require minimum bio-based content percentages and performance standards that match or exceed conventional products.
Global harmonization of these regulatory frameworks remains a challenge, with significant variations in requirements across different regions. This regulatory fragmentation creates compliance complexities for manufacturers of biomass-derived solvents seeking to enter multiple markets. However, international initiatives like the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) are working toward greater alignment of chemical management policies worldwide.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!