Catalytic Efficiency of Biomass-Derived Solvents in Hydrocarbon Processing
OCT 23, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass-Derived Solvents Evolution and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents, marking a significant shift in the chemical processing industry over the past three decades. The evolution of these solvents began in the early 1990s with simple bio-alcohols like ethanol and progressed to more complex structures such as glycerol derivatives, terpenes, and cyclic carbonates by the 2010s. This transition has been driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and the growing emphasis on circular economy principles.
The development trajectory of biomass-derived solvents has been characterized by three distinct phases. The initial phase focused on direct extraction from biomass sources, yielding limited efficiency and application scope. The second phase, spanning from 2000 to 2015, saw significant advancements in chemical modification techniques, enabling the production of solvents with tailored properties. The current phase, beginning around 2016, emphasizes catalytic transformation pathways that enhance both yield and selectivity while reducing energy requirements.
In the context of hydrocarbon processing, biomass-derived solvents have demonstrated promising potential for replacing traditional solvents in extraction, separation, and reaction media applications. Their unique properties, including high polarity, biodegradability, and tunable solvent parameters, offer advantages in selective dissolution and phase separation processes critical to hydrocarbon refining and upgrading.
Recent technological breakthroughs have particularly focused on improving the catalytic efficiency of these bio-solvents in hydrocarbon processing. Notable innovations include the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES) derived from biomass components, which exhibit exceptional catalytic properties for hydrogenation and oxidation reactions. Additionally, lignin-derived aromatic solvents have shown remarkable stability under high-temperature processing conditions typical in hydrocarbon transformations.
The primary objectives for advancing biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing include enhancing catalytic activity, improving thermal and chemical stability, reducing production costs, and expanding the feedstock base beyond food crops to lignocellulosic materials and waste streams. Specifically, research aims to develop solvents that can facilitate selective C-C bond cleavage in heavy hydrocarbons, enable low-temperature desulfurization processes, and promote efficient hydrogen transfer reactions.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward multi-functional biomass-derived solvents that simultaneously serve as reaction media, catalysts, and stabilizing agents. This integration of functions represents a paradigm shift in solvent technology, potentially revolutionizing hydrocarbon processing by significantly reducing energy requirements and process complexity while enhancing product selectivity and yield.
The development trajectory of biomass-derived solvents has been characterized by three distinct phases. The initial phase focused on direct extraction from biomass sources, yielding limited efficiency and application scope. The second phase, spanning from 2000 to 2015, saw significant advancements in chemical modification techniques, enabling the production of solvents with tailored properties. The current phase, beginning around 2016, emphasizes catalytic transformation pathways that enhance both yield and selectivity while reducing energy requirements.
In the context of hydrocarbon processing, biomass-derived solvents have demonstrated promising potential for replacing traditional solvents in extraction, separation, and reaction media applications. Their unique properties, including high polarity, biodegradability, and tunable solvent parameters, offer advantages in selective dissolution and phase separation processes critical to hydrocarbon refining and upgrading.
Recent technological breakthroughs have particularly focused on improving the catalytic efficiency of these bio-solvents in hydrocarbon processing. Notable innovations include the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES) derived from biomass components, which exhibit exceptional catalytic properties for hydrogenation and oxidation reactions. Additionally, lignin-derived aromatic solvents have shown remarkable stability under high-temperature processing conditions typical in hydrocarbon transformations.
The primary objectives for advancing biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing include enhancing catalytic activity, improving thermal and chemical stability, reducing production costs, and expanding the feedstock base beyond food crops to lignocellulosic materials and waste streams. Specifically, research aims to develop solvents that can facilitate selective C-C bond cleavage in heavy hydrocarbons, enable low-temperature desulfurization processes, and promote efficient hydrogen transfer reactions.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward multi-functional biomass-derived solvents that simultaneously serve as reaction media, catalysts, and stabilizing agents. This integration of functions represents a paradigm shift in solvent technology, potentially revolutionizing hydrocarbon processing by significantly reducing energy requirements and process complexity while enhancing product selectivity and yield.
Market Analysis for Green Hydrocarbon Processing
The global market for green hydrocarbon processing has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations, corporate sustainability goals, and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. The integration of biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing represents a pivotal shift toward sustainable practices in the traditionally carbon-intensive petrochemical industry.
Market valuation studies indicate that the green hydrocarbon processing sector is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8.7% between 2020 and 2025. This growth trajectory is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as the European Union, where the European Green Deal has accelerated adoption of sustainable processing technologies.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring products manufactured using environmentally responsible methods. A recent industry survey revealed that 67% of consumers across major markets are willing to pay premium prices for products produced using green processing technologies. This consumer sentiment has created a strong market pull for innovations in catalytic efficiency using biomass-derived solvents.
The industrial application landscape shows varied adoption rates across different sectors. Specialty chemicals manufacturers have emerged as early adopters, implementing biomass-derived solvent technologies to reduce their carbon footprint while simultaneously improving process efficiency. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, driven by both sustainability goals and the potential for enhanced selectivity in complex synthesis pathways.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America currently leads in research and development investments in this field, while Asia-Pacific demonstrates the fastest growth rate in commercial applications. China's recent five-year plan specifically highlights green hydrocarbon processing as a strategic industrial development area, allocating substantial resources toward domestic technology advancement.
Market barriers include the higher initial cost of implementing biomass-derived solvent systems compared to conventional processes, technical challenges in scaling up laboratory successes to industrial production, and supply chain uncertainties for consistent biomass feedstock. However, these barriers are gradually diminishing as technology matures and economies of scale begin to take effect.
Future market projections suggest that as catalytic efficiency continues to improve and production costs decrease, biomass-derived solvents will capture an increasing share of the hydrocarbon processing market. Industry analysts predict that by 2030, green processing technologies could represent up to 30% of the total hydrocarbon processing market, with biomass-derived solvents playing a central role in this transformation.
Market valuation studies indicate that the green hydrocarbon processing sector is expanding at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 8.7% between 2020 and 2025. This growth trajectory is particularly pronounced in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as the European Union, where the European Green Deal has accelerated adoption of sustainable processing technologies.
Consumer preferences are increasingly favoring products manufactured using environmentally responsible methods. A recent industry survey revealed that 67% of consumers across major markets are willing to pay premium prices for products produced using green processing technologies. This consumer sentiment has created a strong market pull for innovations in catalytic efficiency using biomass-derived solvents.
The industrial application landscape shows varied adoption rates across different sectors. Specialty chemicals manufacturers have emerged as early adopters, implementing biomass-derived solvent technologies to reduce their carbon footprint while simultaneously improving process efficiency. The pharmaceutical industry follows closely, driven by both sustainability goals and the potential for enhanced selectivity in complex synthesis pathways.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America currently leads in research and development investments in this field, while Asia-Pacific demonstrates the fastest growth rate in commercial applications. China's recent five-year plan specifically highlights green hydrocarbon processing as a strategic industrial development area, allocating substantial resources toward domestic technology advancement.
Market barriers include the higher initial cost of implementing biomass-derived solvent systems compared to conventional processes, technical challenges in scaling up laboratory successes to industrial production, and supply chain uncertainties for consistent biomass feedstock. However, these barriers are gradually diminishing as technology matures and economies of scale begin to take effect.
Future market projections suggest that as catalytic efficiency continues to improve and production costs decrease, biomass-derived solvents will capture an increasing share of the hydrocarbon processing market. Industry analysts predict that by 2030, green processing technologies could represent up to 30% of the total hydrocarbon processing market, with biomass-derived solvents playing a central role in this transformation.
Current Catalytic Technologies and Barriers
Current catalytic technologies for biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing primarily rely on heterogeneous catalysis systems. Metal-based catalysts, particularly those containing platinum, palladium, ruthenium, and nickel, have demonstrated significant activity in converting biomass-derived compounds into valuable hydrocarbon products. These catalysts typically operate through hydrogenation, dehydration, and C-C coupling mechanisms to transform oxygenated biomass derivatives into hydrocarbon-compatible molecules.
Zeolite-based catalysts represent another major category, offering shape selectivity and tunable acidity that proves advantageous for specific biomass conversion pathways. HZSM-5, H-Beta, and H-Y zeolites have shown particular promise in deoxygenation reactions critical for upgrading biomass-derived solvents to hydrocarbon-compatible intermediates. Their microporous structure provides unique reaction environments that can enhance selectivity toward desired products.
Bifunctional catalysts combining metallic and acidic sites have emerged as particularly effective for cascade reactions in biomass processing. These systems enable one-pot transformations that reduce separation steps and improve overall process efficiency. Recent advances in catalyst design have focused on controlling the proximity between different active sites to optimize reaction pathways.
Despite these technological advances, several significant barriers impede widespread implementation. Catalyst deactivation remains a primary challenge, with carbon deposition (coking) and metal sintering occurring rapidly under typical processing conditions. Biomass-derived feedstocks often contain impurities such as alkali metals, nitrogen compounds, and sulfur species that can permanently poison catalyst active sites, necessitating frequent regeneration or replacement.
Water tolerance presents another major hurdle, as biomass processing inherently involves aqueous environments that can compromise catalyst stability and selectivity. Many conventional catalysts exhibit diminished performance in the presence of water, limiting their practical application in biomass conversion systems without extensive feedstock pretreatment.
Selectivity control represents a persistent challenge due to the complex, multifunctional nature of biomass-derived molecules. Current catalytic systems often produce broad product distributions rather than targeted compounds, reducing process efficiency and complicating downstream separation. The oxygen-rich nature of biomass derivatives requires multiple deoxygenation steps that must be carefully orchestrated to maintain carbon efficiency.
Economic barriers further complicate technology adoption, as catalyst costs—particularly for precious metal systems—can be prohibitive for large-scale implementation. Additionally, catalyst regeneration processes often consume significant energy and may not fully restore initial activity, impacting long-term economic viability of these technologies in competitive hydrocarbon markets.
Zeolite-based catalysts represent another major category, offering shape selectivity and tunable acidity that proves advantageous for specific biomass conversion pathways. HZSM-5, H-Beta, and H-Y zeolites have shown particular promise in deoxygenation reactions critical for upgrading biomass-derived solvents to hydrocarbon-compatible intermediates. Their microporous structure provides unique reaction environments that can enhance selectivity toward desired products.
Bifunctional catalysts combining metallic and acidic sites have emerged as particularly effective for cascade reactions in biomass processing. These systems enable one-pot transformations that reduce separation steps and improve overall process efficiency. Recent advances in catalyst design have focused on controlling the proximity between different active sites to optimize reaction pathways.
Despite these technological advances, several significant barriers impede widespread implementation. Catalyst deactivation remains a primary challenge, with carbon deposition (coking) and metal sintering occurring rapidly under typical processing conditions. Biomass-derived feedstocks often contain impurities such as alkali metals, nitrogen compounds, and sulfur species that can permanently poison catalyst active sites, necessitating frequent regeneration or replacement.
Water tolerance presents another major hurdle, as biomass processing inherently involves aqueous environments that can compromise catalyst stability and selectivity. Many conventional catalysts exhibit diminished performance in the presence of water, limiting their practical application in biomass conversion systems without extensive feedstock pretreatment.
Selectivity control represents a persistent challenge due to the complex, multifunctional nature of biomass-derived molecules. Current catalytic systems often produce broad product distributions rather than targeted compounds, reducing process efficiency and complicating downstream separation. The oxygen-rich nature of biomass derivatives requires multiple deoxygenation steps that must be carefully orchestrated to maintain carbon efficiency.
Economic barriers further complicate technology adoption, as catalyst costs—particularly for precious metal systems—can be prohibitive for large-scale implementation. Additionally, catalyst regeneration processes often consume significant energy and may not fully restore initial activity, impacting long-term economic viability of these technologies in competitive hydrocarbon markets.
Established Catalytic Systems Using Bio-Solvents
01 Biomass-derived solvents for enhanced catalytic reactions
Solvents derived from biomass can significantly enhance catalytic reactions by providing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly medium. These solvents often have unique properties that can improve reaction rates, selectivity, and yield compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents. The polar nature of many biomass-derived solvents can stabilize transition states and intermediates in catalytic processes, leading to improved efficiency in various chemical transformations.- Biomass-derived solvents for enhanced catalytic reactions: Solvents derived from biomass can significantly enhance catalytic efficiency in various chemical reactions. These green solvents provide better reaction environments compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents, leading to improved reaction rates and selectivity. The unique properties of biomass-derived solvents, such as polarity and hydrogen-bonding capabilities, can stabilize transition states and facilitate more efficient catalytic pathways.
- Lignin-based solvents for catalytic biomass conversion: Lignin, a major component of lignocellulosic biomass, can be transformed into effective solvents for catalytic processes. These lignin-derived solvents demonstrate exceptional performance in biomass conversion reactions, particularly in depolymerization and upgrading processes. Their aromatic structure provides favorable interactions with catalysts and substrates, enhancing mass transfer and improving overall catalytic efficiency in biomass valorization reactions.
- Bio-derived polar aprotic solvents in catalysis: Polar aprotic solvents derived from renewable resources show remarkable performance in catalytic systems. These solvents, including derivatives of glycerol, organic acids, and furans, can dissolve a wide range of catalysts and reactants while providing a suitable environment for efficient catalytic reactions. Their unique solvation properties can enhance catalyst stability, accessibility, and activity, leading to improved reaction outcomes and reduced energy requirements.
- Tunable biomass-derived solvent systems for catalyst optimization: Engineered solvent systems derived from biomass components offer tunable properties that can be optimized for specific catalytic applications. By adjusting the composition and structure of these bio-derived solvents, researchers can create tailored reaction environments that maximize catalyst performance. These customizable solvent systems allow for precise control over parameters such as polarity, hydrogen bonding capacity, and viscosity, enabling enhanced catalytic efficiency across diverse reaction types.
- Biomass-derived solvent effects on metal catalyst performance: Solvents obtained from biomass resources have demonstrated significant effects on the performance of metal catalysts. These bio-derived solvents can influence catalyst dispersion, prevent aggregation, and modify electronic properties of metal active sites. The interaction between biomass-derived solvents and metal catalysts can lead to enhanced activity, improved selectivity, and extended catalyst lifetime, making catalytic processes more efficient and sustainable.
02 Green solvent systems for catalyst optimization
Green solvent systems derived from renewable resources can be tailored to optimize catalyst performance. These systems often feature reduced toxicity, lower volatility, and better biodegradability compared to traditional solvents. By carefully selecting biomass-derived solvents with specific properties such as polarity, hydrogen-bonding capability, and viscosity, catalytic efficiency can be significantly improved. These solvent systems can also enable catalyst recycling and reduce energy requirements in separation processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lignocellulosic biomass conversion using specialized catalysts
Specialized catalysts can efficiently convert lignocellulosic biomass into valuable solvents and chemicals. These catalytic processes often involve the breakdown of complex biomass structures through hydrolysis, dehydration, or oxidation reactions. By employing tailored catalysts such as metal oxides, supported metals, or acid catalysts, the conversion efficiency can be significantly improved. The resulting biomass-derived solvents can then be used in subsequent catalytic processes, creating a sustainable cycle of biomass utilization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ionic liquids from biomass for catalytic applications
Ionic liquids synthesized from biomass components offer unique advantages as reaction media for catalytic processes. These designer solvents feature negligible vapor pressure, high thermal stability, and tunable physicochemical properties. When used as solvents in catalytic reactions, they can enhance catalyst stability, improve substrate solubility, and facilitate product separation. The ionic nature of these solvents can also provide additional activation of substrates or stabilization of transition states, leading to improved catalytic efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Catalyst design for biomass-derived solvent production
Advanced catalyst design is crucial for the efficient production of biomass-derived solvents. Heterogeneous catalysts with carefully engineered surface properties, pore structures, and active sites can selectively convert biomass feedstocks into targeted solvent molecules. Factors such as metal particle size, support acidity, and bimetallic compositions significantly influence catalytic performance. Novel approaches including catalyst immobilization, hierarchical structures, and in-situ regeneration techniques have been developed to overcome challenges related to catalyst deactivation and product selectivity in biomass conversion processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Bio-Solvent Catalysis
The catalytic efficiency of biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing is emerging as a strategic frontier in sustainable energy, currently in the early growth phase with increasing market adoption. The global market is expanding rapidly, driven by environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals, with projections suggesting significant growth over the next decade. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players like Virent, Shell, and ExxonMobil demonstrate advanced capabilities in biomass conversion technologies, while research institutions such as RTI International and Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation contribute fundamental innovations. Chinese entities including Sinopec Research Institute and Southeast University are making significant advances, particularly in process optimization. Collaborations between industry leaders and research organizations are accelerating commercialization pathways for these promising green solvent technologies.
Virent, Inc.
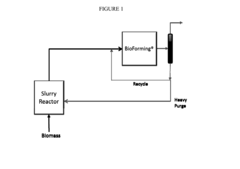
Technical Solution: Virent has developed the BioForming® process, a catalytic technology that converts plant-based sugars into hydrocarbon molecules identical to those produced from petroleum. Their patented catalytic process uses biomass-derived solvents in combination with proprietary catalysts to produce drop-in renewable fuels and chemicals. The technology employs aqueous phase reforming (APR) followed by catalytic condensation and hydrotreating steps. Virent's process can utilize a variety of feedstocks including corn starch, sugarcane, and cellulosic biomass. Their catalytic system operates at moderate temperatures (175-300°C) and pressures (10-90 bar), achieving high carbon efficiency with minimal hydrogen input requirements. The company has demonstrated commercial viability through partnerships with major corporations like Shell and Coca-Cola.
Strengths: Produces true "drop-in" hydrocarbons chemically identical to petroleum-derived counterparts; flexible feedstock capabilities; lower energy requirements compared to thermochemical processes. Weaknesses: Complex multi-step process requiring precise catalyst management; potential catalyst deactivation issues in the presence of certain biomass impurities; relatively high capital costs for commercial-scale implementation.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
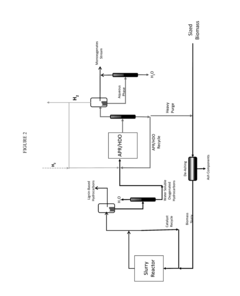
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an integrated biomass-to-liquid (BTL) platform utilizing biomass-derived solvents for efficient hydrocarbon processing. Their technology employs a two-stage catalytic system: first converting lignocellulosic biomass to bio-oil through solvolysis in gamma-valerolactone (GVL) or other biomass-derived solvents, followed by catalytic upgrading using proprietary zeolite-based catalysts. The process operates at temperatures between 180-350°C and moderate pressures, achieving conversion efficiencies of up to 85%. Sinopec has implemented pilot-scale facilities processing 100-500 kg/day of biomass feedstock. Their catalytic systems incorporate modified metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and hierarchical zeolites to enhance selectivity toward targeted hydrocarbon fractions. The company has also developed specialized catalyst regeneration protocols to address deactivation issues from biomass contaminants.
Strengths: Extensive refining infrastructure that can be leveraged for bio-based processing; strong R&D capabilities with significant financial resources; established distribution networks for end products. Weaknesses: Primary focus remains on traditional petroleum refining; biomass technologies still in development/pilot phase; potential challenges in scaling up biomass-derived solvent production to meet large-scale needs.
Key Innovations in Biomass-Derived Catalytic Media
Process of producing liquid fuels from coal using biomass-derived solvents
PatentActiveCA2998874C
Innovation
- A process using biomass-derived solvents as hydrogen-donor agents to facilitate coal liquefaction, which includes preparing biomass-derived coal solvents, dissolving coal in these solvents, and subjecting the resulting syncrude to hydrotreatment/hydrogenation to produce distillate fuels, thereby reducing capital and operating costs and greenhouse gas emissions without the need for carbon capture and storage.
Solvolysis of biomass using solvent from a bioreforming process
PatentActiveUS20170058370A1
Innovation
- A method involving catalytically reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon with hydrogen in the presence of a deoxygenation catalyst to produce a biomass processing solvent, which is then used to deconstruct biomass at specific temperatures and pressures to produce a biomass hydrolysate containing soluble derivatives and carbohydrates.
Sustainability Metrics and Life Cycle Assessment
The sustainability assessment of biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing requires comprehensive metrics and life cycle analysis to determine their true environmental impact. Traditional petroleum-based solvents have established environmental footprints, while biomass alternatives present both opportunities and challenges in sustainability evaluation.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodologies applied to biomass-derived solvents must account for feedstock cultivation, processing, utilization in hydrocarbon reactions, and end-of-life management. Current LCA frameworks reveal that these bio-solvents often demonstrate reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional alternatives, with studies indicating potential reductions of 30-70% depending on feedstock source and processing methods.
Carbon footprint analysis represents a critical sustainability metric, encompassing emissions from land use change, agricultural practices, solvent synthesis, and application in catalytic processes. Research indicates that solvents derived from agricultural residues typically offer superior carbon profiles compared to those requiring dedicated biomass cultivation, which may involve land conversion impacts.
Water consumption metrics reveal complex trade-offs in biomass solvent production. While petroleum-based solvents require significant water for extraction and refining, biomass alternatives may demand substantial irrigation during feedstock growth. Advanced water recycling technologies in bio-refineries have demonstrated potential water use reductions of 40-60% in recent pilot studies.
Energy return on investment (EROI) calculations for biomass-derived solvents show varying results based on processing efficiency. Current technologies achieve EROI ratios between 2:1 and 5:1, compared to 8:1 for conventional petroleum solvents. However, emerging catalytic processes for biomass conversion show promise for improving these ratios significantly.
Toxicity profiles and biodegradability metrics indicate substantial advantages for biomass-derived solvents. Studies demonstrate that many bio-solvents exhibit reduced aquatic toxicity and faster environmental degradation rates, with some achieving complete biodegradation within 14-28 days versus months or years for petroleum alternatives.
Economic sustainability metrics reveal current challenges in cost competitiveness. Production costs for biomass-derived solvents typically exceed conventional alternatives by 20-50%, though this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements and economies of scale. Integration of externality costs through carbon pricing mechanisms would significantly improve comparative economic sustainability metrics.
Standardization of sustainability metrics remains an ongoing challenge, with various competing frameworks employed across the industry. The development of harmonized assessment protocols specific to biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing would enable more accurate comparisons and guide future research priorities toward truly sustainable catalytic systems.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodologies applied to biomass-derived solvents must account for feedstock cultivation, processing, utilization in hydrocarbon reactions, and end-of-life management. Current LCA frameworks reveal that these bio-solvents often demonstrate reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional alternatives, with studies indicating potential reductions of 30-70% depending on feedstock source and processing methods.
Carbon footprint analysis represents a critical sustainability metric, encompassing emissions from land use change, agricultural practices, solvent synthesis, and application in catalytic processes. Research indicates that solvents derived from agricultural residues typically offer superior carbon profiles compared to those requiring dedicated biomass cultivation, which may involve land conversion impacts.
Water consumption metrics reveal complex trade-offs in biomass solvent production. While petroleum-based solvents require significant water for extraction and refining, biomass alternatives may demand substantial irrigation during feedstock growth. Advanced water recycling technologies in bio-refineries have demonstrated potential water use reductions of 40-60% in recent pilot studies.
Energy return on investment (EROI) calculations for biomass-derived solvents show varying results based on processing efficiency. Current technologies achieve EROI ratios between 2:1 and 5:1, compared to 8:1 for conventional petroleum solvents. However, emerging catalytic processes for biomass conversion show promise for improving these ratios significantly.
Toxicity profiles and biodegradability metrics indicate substantial advantages for biomass-derived solvents. Studies demonstrate that many bio-solvents exhibit reduced aquatic toxicity and faster environmental degradation rates, with some achieving complete biodegradation within 14-28 days versus months or years for petroleum alternatives.
Economic sustainability metrics reveal current challenges in cost competitiveness. Production costs for biomass-derived solvents typically exceed conventional alternatives by 20-50%, though this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements and economies of scale. Integration of externality costs through carbon pricing mechanisms would significantly improve comparative economic sustainability metrics.
Standardization of sustainability metrics remains an ongoing challenge, with various competing frameworks employed across the industry. The development of harmonized assessment protocols specific to biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing would enable more accurate comparisons and guide future research priorities toward truly sustainable catalytic systems.
Regulatory Framework for Bio-Based Processing
The regulatory landscape governing biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing is complex and evolving rapidly as governments worldwide seek to balance environmental protection with industrial innovation. Current regulations primarily focus on three key areas: emissions standards, waste management, and product certification requirements. The European Union leads with its Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II), which mandates sustainability criteria for bio-based products and establishes greenhouse gas emission reduction thresholds that biomass-derived solvents must meet to qualify for regulatory incentives.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates biomass-derived solvents through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. The RFS specifically incentivizes the development and use of advanced biofuels and bio-based chemicals, providing a regulatory pathway for biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing applications. Additionally, the USDA BioPreferred program offers certification for bio-based products, creating market advantages for compliant technologies.
Asian markets present a diverse regulatory environment. China's 14th Five-Year Plan emphasizes green chemistry and circular economy principles, introducing stricter environmental regulations that favor biomass-derived alternatives. Japan's Biomass Industrialization Strategy similarly promotes bio-based chemicals through tax incentives and subsidies for research and development.
Regulatory compliance costs represent a significant consideration for industrial adoption of biomass-derived solvents. Companies must navigate certification processes, emissions monitoring, and reporting requirements that vary by jurisdiction. However, these costs are increasingly offset by penalties associated with conventional petrochemical processes, as carbon pricing mechanisms and pollution taxes become more widespread globally.
Industry standards development is occurring in parallel with regulatory frameworks. Organizations such as ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are developing specific standards for bio-based solvents, addressing performance metrics, sustainability assessment methodologies, and quality control parameters. These standards facilitate market acceptance and regulatory compliance while ensuring consistent performance across applications.
Looking forward, regulatory trends indicate increasing stringency in environmental requirements coupled with expanded incentive programs for sustainable alternatives. The European Green Deal and similar initiatives worldwide suggest that regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve favorably for biomass-derived solvents. Companies investing in this technology can anticipate a regulatory environment that increasingly penalizes fossil-based alternatives while rewarding bio-based innovation through preferential treatment in government procurement, tax benefits, and expedited approval processes.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates biomass-derived solvents through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. The RFS specifically incentivizes the development and use of advanced biofuels and bio-based chemicals, providing a regulatory pathway for biomass-derived solvents in hydrocarbon processing applications. Additionally, the USDA BioPreferred program offers certification for bio-based products, creating market advantages for compliant technologies.
Asian markets present a diverse regulatory environment. China's 14th Five-Year Plan emphasizes green chemistry and circular economy principles, introducing stricter environmental regulations that favor biomass-derived alternatives. Japan's Biomass Industrialization Strategy similarly promotes bio-based chemicals through tax incentives and subsidies for research and development.
Regulatory compliance costs represent a significant consideration for industrial adoption of biomass-derived solvents. Companies must navigate certification processes, emissions monitoring, and reporting requirements that vary by jurisdiction. However, these costs are increasingly offset by penalties associated with conventional petrochemical processes, as carbon pricing mechanisms and pollution taxes become more widespread globally.
Industry standards development is occurring in parallel with regulatory frameworks. Organizations such as ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are developing specific standards for bio-based solvents, addressing performance metrics, sustainability assessment methodologies, and quality control parameters. These standards facilitate market acceptance and regulatory compliance while ensuring consistent performance across applications.
Looking forward, regulatory trends indicate increasing stringency in environmental requirements coupled with expanded incentive programs for sustainable alternatives. The European Green Deal and similar initiatives worldwide suggest that regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve favorably for biomass-derived solvents. Companies investing in this technology can anticipate a regulatory environment that increasingly penalizes fossil-based alternatives while rewarding bio-based innovation through preferential treatment in government procurement, tax benefits, and expedited approval processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!