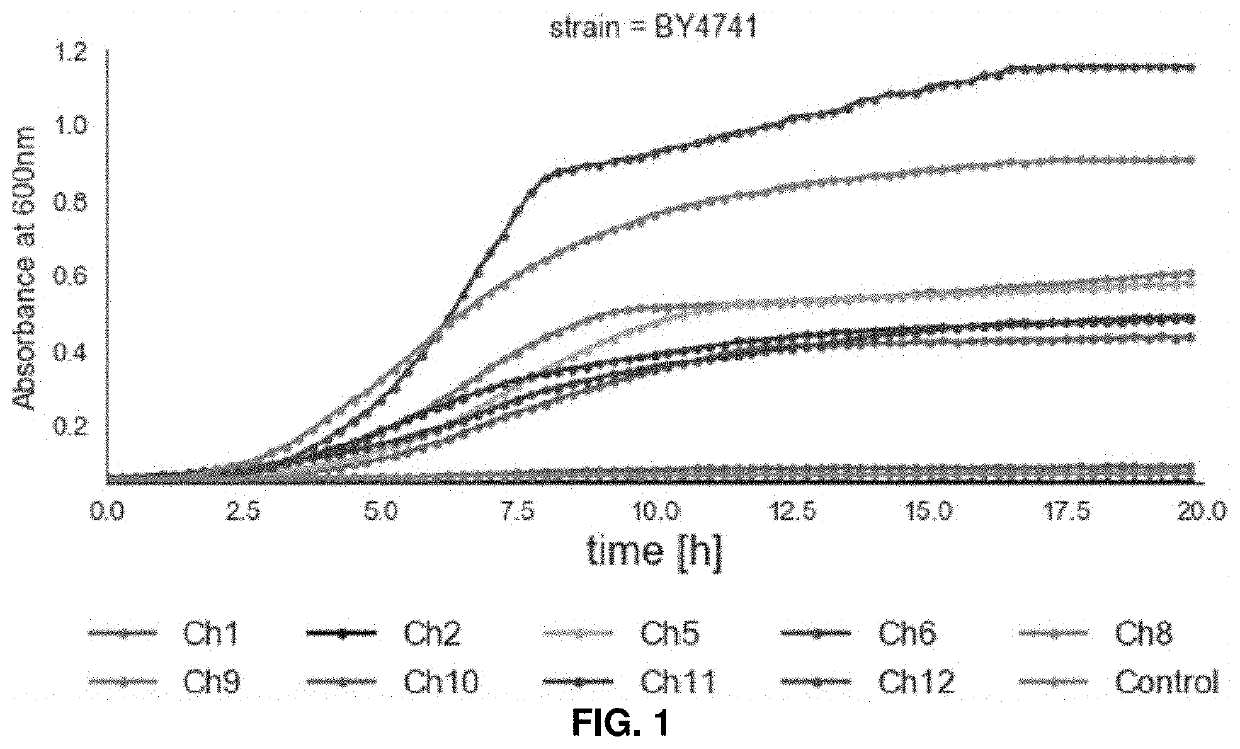
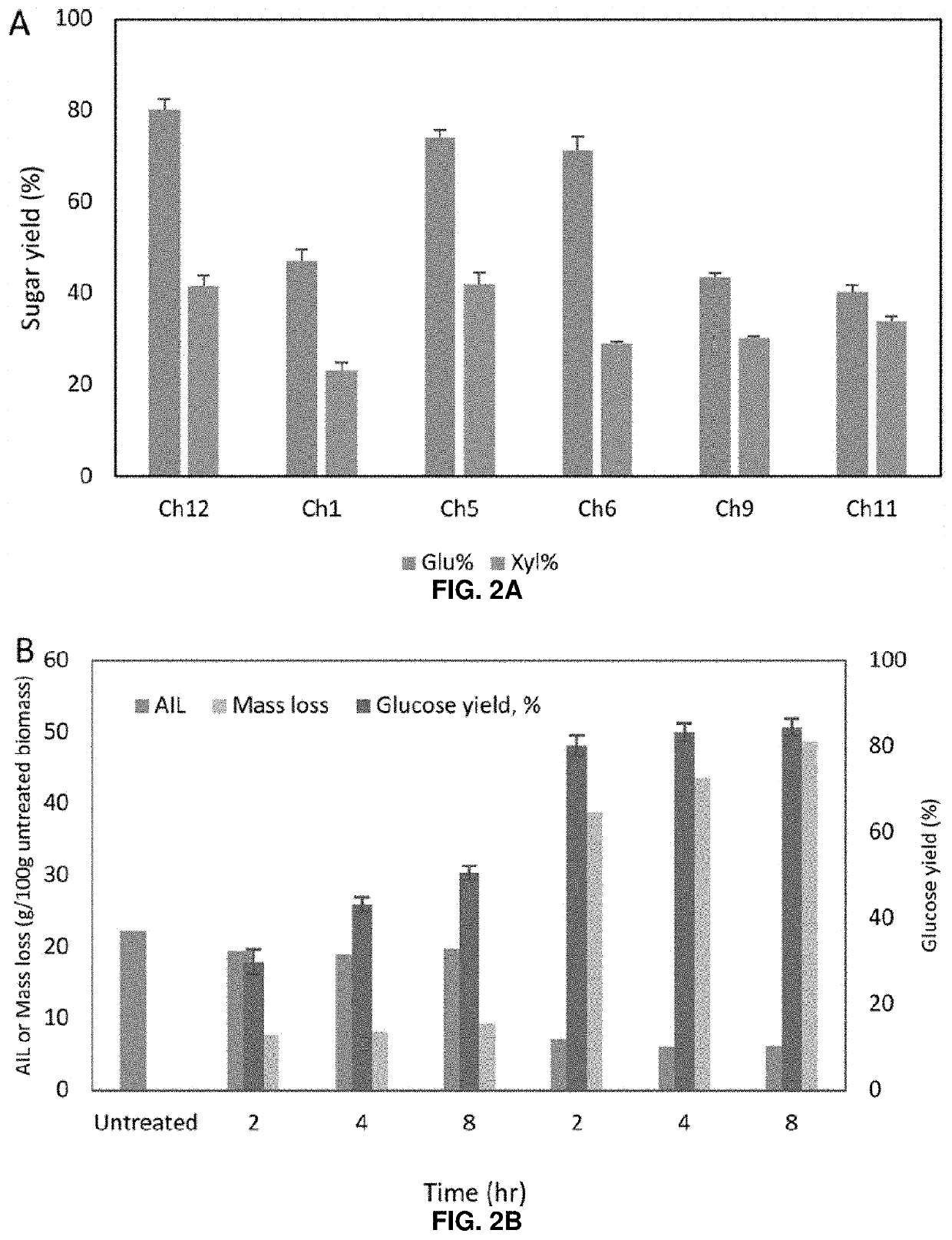
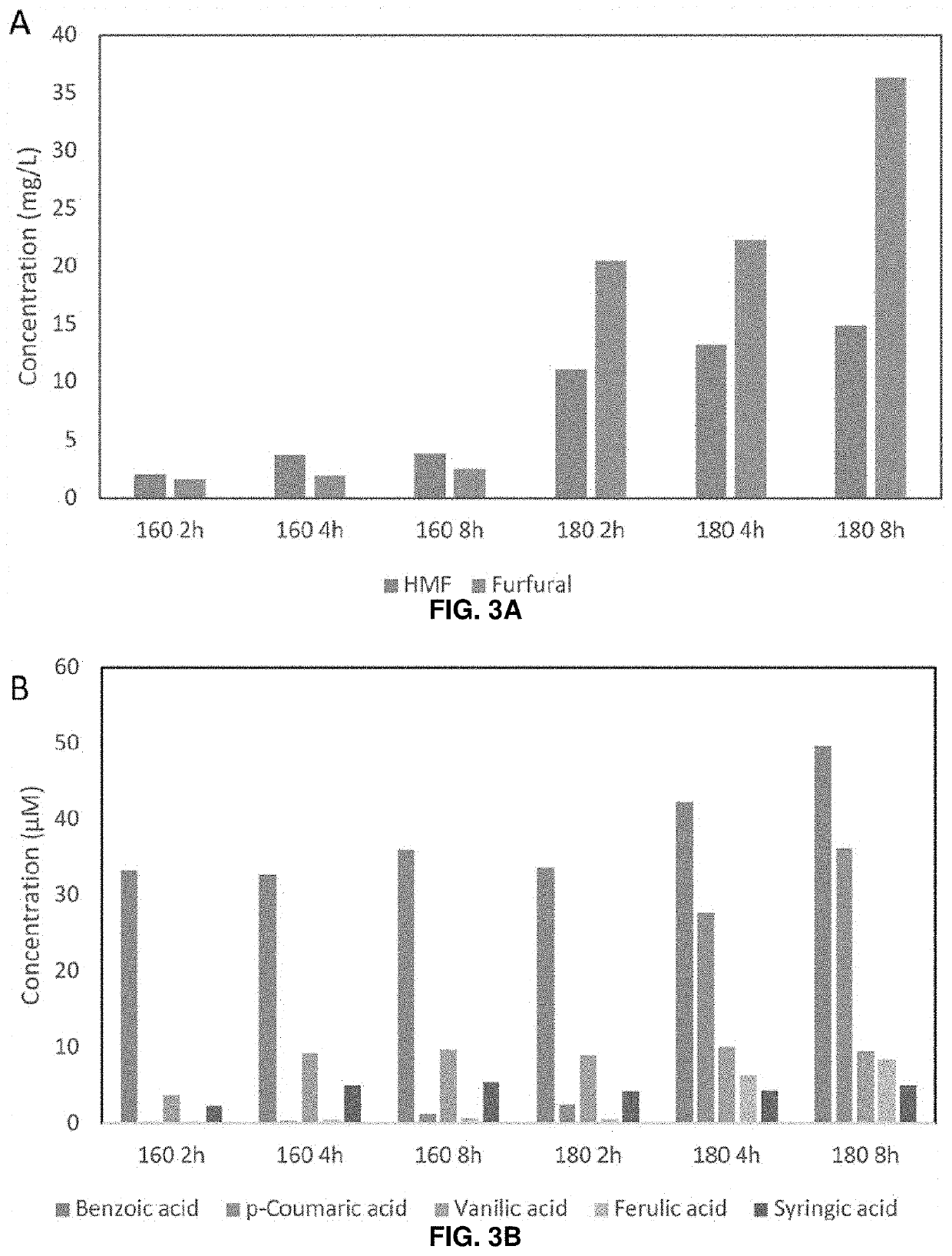
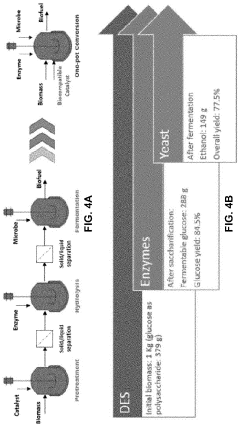
Regulatory Challenges for the Adoption of Biomass-Derived Solvents
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvents Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents over the past few decades. The evolution of these bio-based alternatives has been driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and the global push towards sustainable chemistry. Initially developed in the 1990s as simple replacements for toxic solvents, biomass-derived solvents have evolved significantly through continuous research and development efforts aimed at improving their performance, reducing production costs, and expanding their application scope.
The technological trajectory of biomass-derived solvents has seen remarkable advancements, moving from first-generation bio-alcohols to more sophisticated platforms including bio-esters, terpenes, furans, and cyrene derivatives. Each generation has addressed specific limitations of its predecessors, with recent innovations focusing on tailoring solvent properties for specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Current research trends indicate a shift towards developing integrated biorefinery concepts where biomass-derived solvents are produced as part of a broader portfolio of bio-based chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. Additionally, there is growing interest in designing solvents with enhanced biodegradability and reduced ecotoxicity profiles to meet increasingly stringent environmental standards globally.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the regulatory challenges impeding the widespread adoption of biomass-derived solvents across different industries and geographical regions. This includes identifying inconsistencies in regulatory frameworks, understanding approval processes for novel solvents, and evaluating how existing chemical management systems accommodate or hinder bio-based alternatives.
Furthermore, this research aims to establish a clear understanding of how regulatory hurdles interact with technical limitations, market dynamics, and consumer acceptance. By mapping these complex relationships, we seek to identify strategic intervention points where regulatory reforms could accelerate adoption without compromising safety or environmental protection standards.
The ultimate goal is to develop a roadmap for navigating the regulatory landscape that can guide industry stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers in creating a more conducive environment for biomass-derived solvent innovation and commercialization. This includes recommendations for harmonizing standards across jurisdictions, streamlining approval processes for bio-based chemicals, and developing appropriate risk assessment methodologies that accurately capture the unique characteristics and benefits of these sustainable alternatives.
The technological trajectory of biomass-derived solvents has seen remarkable advancements, moving from first-generation bio-alcohols to more sophisticated platforms including bio-esters, terpenes, furans, and cyrene derivatives. Each generation has addressed specific limitations of its predecessors, with recent innovations focusing on tailoring solvent properties for specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and advanced materials manufacturing.
Current research trends indicate a shift towards developing integrated biorefinery concepts where biomass-derived solvents are produced as part of a broader portfolio of bio-based chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. Additionally, there is growing interest in designing solvents with enhanced biodegradability and reduced ecotoxicity profiles to meet increasingly stringent environmental standards globally.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively analyze the regulatory challenges impeding the widespread adoption of biomass-derived solvents across different industries and geographical regions. This includes identifying inconsistencies in regulatory frameworks, understanding approval processes for novel solvents, and evaluating how existing chemical management systems accommodate or hinder bio-based alternatives.
Furthermore, this research aims to establish a clear understanding of how regulatory hurdles interact with technical limitations, market dynamics, and consumer acceptance. By mapping these complex relationships, we seek to identify strategic intervention points where regulatory reforms could accelerate adoption without compromising safety or environmental protection standards.
The ultimate goal is to develop a roadmap for navigating the regulatory landscape that can guide industry stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers in creating a more conducive environment for biomass-derived solvent innovation and commercialization. This includes recommendations for harmonizing standards across jurisdictions, streamlining approval processes for bio-based chemicals, and developing appropriate risk assessment methodologies that accurately capture the unique characteristics and benefits of these sustainable alternatives.
Market Demand Analysis for Green Solvents
The global market for green solvents has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures to reduce the use of conventional petroleum-based solvents. Biomass-derived solvents represent a promising segment within this market, offering renewable alternatives with potentially lower environmental impacts and reduced carbon footprints.
Current market analysis indicates that the global green solvents market was valued at approximately $4.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $6.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. Biomass-derived solvents specifically are gaining traction, with market share increasing from 23% to 28% over the past five years.
Key demand drivers include stringent environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and North America, where policies like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act have accelerated the transition away from conventional solvents. Consumer preferences are also shifting toward eco-friendly products, creating pull-through demand for green formulations across multiple industries.
Industrial sectors showing the strongest demand include paints and coatings (32% of market share), pharmaceuticals (24%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (11%). The paints and coatings sector remains the largest consumer of green solvents due to VOC emission regulations and growing consumer preference for low-odor, environmentally friendly products.
Regional analysis reveals Europe leading the market with 38% share, followed by North America (32%), Asia-Pacific (22%), and rest of the world (8%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.5% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental awareness, and tightening regulations in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Price sensitivity remains a significant market challenge, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding a 15-40% premium over conventional alternatives. This price differential has limited adoption in cost-sensitive applications and emerging markets. However, as production scales increase and technologies mature, this gap is gradually narrowing, with price premiums decreasing by approximately 3-5% annually over the past three years.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for biomass-derived solvents will continue to grow as regulatory pressures intensify and sustainability becomes increasingly central to corporate strategies. Industries with direct consumer exposure and those subject to strict environmental regulations are expected to lead adoption, with projected annual growth rates of 9-12% in these sectors through 2030.
Current market analysis indicates that the global green solvents market was valued at approximately $4.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $6.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. Biomass-derived solvents specifically are gaining traction, with market share increasing from 23% to 28% over the past five years.
Key demand drivers include stringent environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and North America, where policies like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act have accelerated the transition away from conventional solvents. Consumer preferences are also shifting toward eco-friendly products, creating pull-through demand for green formulations across multiple industries.
Industrial sectors showing the strongest demand include paints and coatings (32% of market share), pharmaceuticals (24%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (11%). The paints and coatings sector remains the largest consumer of green solvents due to VOC emission regulations and growing consumer preference for low-odor, environmentally friendly products.
Regional analysis reveals Europe leading the market with 38% share, followed by North America (32%), Asia-Pacific (22%), and rest of the world (8%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.5% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental awareness, and tightening regulations in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Price sensitivity remains a significant market challenge, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding a 15-40% premium over conventional alternatives. This price differential has limited adoption in cost-sensitive applications and emerging markets. However, as production scales increase and technologies mature, this gap is gradually narrowing, with price premiums decreasing by approximately 3-5% annually over the past three years.
Market forecasts suggest that demand for biomass-derived solvents will continue to grow as regulatory pressures intensify and sustainability becomes increasingly central to corporate strategies. Industries with direct consumer exposure and those subject to strict environmental regulations are expected to lead adoption, with projected annual growth rates of 9-12% in these sectors through 2030.
Regulatory Landscape and Technical Barriers
The regulatory landscape for biomass-derived solvents presents a complex web of international, national, and regional frameworks that significantly impact their commercial adoption. At the global level, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement provide overarching guidelines that encourage the transition to bio-based alternatives. However, these frameworks lack specific provisions for biomass-derived solvents, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and end-users.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires extensive safety data and registration for new chemical substances, including bio-based solvents. This process can cost between €50,000 and €150,000 per substance, creating a substantial barrier for small and medium enterprises developing innovative biomass-derived solvents. Additionally, the EU's Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) provides incentives for bio-based products but does not specifically address solvents.
The United States regulatory framework is fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) overseeing chemical substances under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), while the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates solvents used in food processing and pharmaceuticals. This dual-agency approach often results in conflicting requirements and extended approval timelines, sometimes exceeding 3-5 years for novel biomass-derived solvents.
Technical barriers compound these regulatory challenges. The variability in biomass feedstock composition creates inconsistencies in the final solvent properties, making it difficult to meet strict regulatory specifications. Current analytical methods, designed primarily for petroleum-based solvents, often lack the sensitivity to detect trace impurities specific to bio-based alternatives, resulting in regulatory non-compliance despite actual safety.
Scaling production from laboratory to industrial levels introduces additional regulatory hurdles. Processes that work efficiently at small scales may generate different impurity profiles at commercial volumes, necessitating repeated regulatory submissions and approvals. This scale-up challenge is particularly acute for lignocellulosic biomass-derived solvents, where the complex separation processes can introduce unexpected byproducts.
The lack of harmonized international standards specifically for biomass-derived solvents forces manufacturers to navigate disparate regulatory requirements across different markets. While organizations like ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have developed some relevant standards, these primarily focus on biofuels rather than bio-based solvents, creating a significant gap in the regulatory framework.
Addressing these regulatory and technical barriers requires coordinated efforts between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and research institutions to develop standardized testing protocols and streamlined approval processes specifically designed for biomass-derived solvents.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires extensive safety data and registration for new chemical substances, including bio-based solvents. This process can cost between €50,000 and €150,000 per substance, creating a substantial barrier for small and medium enterprises developing innovative biomass-derived solvents. Additionally, the EU's Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) provides incentives for bio-based products but does not specifically address solvents.
The United States regulatory framework is fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) overseeing chemical substances under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), while the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates solvents used in food processing and pharmaceuticals. This dual-agency approach often results in conflicting requirements and extended approval timelines, sometimes exceeding 3-5 years for novel biomass-derived solvents.
Technical barriers compound these regulatory challenges. The variability in biomass feedstock composition creates inconsistencies in the final solvent properties, making it difficult to meet strict regulatory specifications. Current analytical methods, designed primarily for petroleum-based solvents, often lack the sensitivity to detect trace impurities specific to bio-based alternatives, resulting in regulatory non-compliance despite actual safety.
Scaling production from laboratory to industrial levels introduces additional regulatory hurdles. Processes that work efficiently at small scales may generate different impurity profiles at commercial volumes, necessitating repeated regulatory submissions and approvals. This scale-up challenge is particularly acute for lignocellulosic biomass-derived solvents, where the complex separation processes can introduce unexpected byproducts.
The lack of harmonized international standards specifically for biomass-derived solvents forces manufacturers to navigate disparate regulatory requirements across different markets. While organizations like ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have developed some relevant standards, these primarily focus on biofuels rather than bio-based solvents, creating a significant gap in the regulatory framework.
Addressing these regulatory and technical barriers requires coordinated efforts between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and research institutions to develop standardized testing protocols and streamlined approval processes specifically designed for biomass-derived solvents.
Current Regulatory Compliance Solutions
01 Production of bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass
Methods for producing bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass through various conversion processes such as fermentation, hydrolysis, and chemical transformation. These processes convert biomass components like cellulose and hemicellulose into valuable solvents that can replace petroleum-derived alternatives. The resulting solvents offer environmental benefits including biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint while maintaining performance characteristics required for industrial applications.- Production of biomass-derived solvents from lignocellulosic materials: Lignocellulosic materials can be processed to produce various biomass-derived solvents through methods such as hydrolysis, fermentation, and chemical conversion. These processes typically involve breaking down cellulose and hemicellulose components into sugars, which are then further converted into solvents like ethanol, butanol, and acetone. These renewable solvents offer environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-based products while utilizing abundant agricultural and forestry residues.
- Green solvents derived from biomass for industrial applications: Biomass-derived green solvents are being developed for various industrial applications including cleaning, degreasing, paint formulation, and chemical processing. These solvents offer reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and lower environmental impact compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents. Examples include esters, alcohols, and terpenes derived from plant materials, which can effectively replace harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in many industrial processes.
- Biomass-derived solvents for pulp and paper processing: Solvents derived from biomass are being utilized in pulp and paper processing as environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional chemicals. These bio-based solvents can effectively dissolve lignin and separate cellulose fibers while reducing the environmental impact of paper production. The process often involves using organic acids, alcohols, or other compounds derived from renewable resources to replace conventional pulping chemicals, resulting in reduced emissions and waste.
- Biofuel production processes utilizing biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents play a crucial role in biofuel production processes, serving as reaction media, extraction agents, or as biofuels themselves. These solvents can enhance the efficiency of biomass conversion to biofuels by improving the dissolution of biomass components, facilitating reactions, and aiding in product separation. The use of bio-based solvents in biofuel production creates a more sustainable and circular production system where renewable resources are used throughout the process.
- Novel biomass-derived solvent formulations and synthesis methods: Research is advancing in the development of novel biomass-derived solvent formulations and improved synthesis methods. These innovations include new catalytic processes, hybrid solvent systems combining multiple bio-based components, and engineered microorganisms for more efficient fermentation-based production. The focus is on creating solvents with tailored properties for specific applications while maximizing yield from biomass feedstocks and minimizing energy consumption and waste generation during production.
02 Enzymatic and microbial conversion for biomass-derived solvent production
Utilization of enzymes and microorganisms to convert biomass into solvents through biological pathways. These bioprocesses employ specialized microbes or isolated enzymes to break down complex biomass structures and transform them into solvent molecules. The approach enables selective conversion under mild conditions, reducing energy requirements and harmful byproducts compared to chemical methods. Various strains and enzyme systems have been developed to optimize yields and target specific solvent products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Green solvent applications in pulp and paper processing
Application of biomass-derived solvents in the pulp and paper industry as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional chemicals. These bio-solvents can be used for delignification, pulping, and bleaching processes, reducing the environmental impact of paper production. The solvents effectively dissolve lignin while preserving cellulose fibers, resulting in high-quality paper products with reduced chemical waste and emissions. Integration of these solvents into existing production systems offers both environmental and economic advantages.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biomass-derived solvents for polymer processing and composites
Use of biomass-derived solvents in polymer processing, composite manufacturing, and plastic recycling applications. These bio-solvents serve as effective media for dissolving, processing, and modifying polymers while reducing environmental impact. They can be incorporated into composite materials to improve properties or used as processing aids during manufacturing. The compatibility with various polymer systems makes them versatile alternatives to traditional petroleum-based solvents in multiple industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biomass-derived solvents for extraction and separation processes
Application of biomass-derived solvents in extraction and separation processes across various industries including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. These green solvents offer selective extraction capabilities for valuable compounds from natural materials while maintaining product purity. Their tunable properties allow for optimized separation processes with reduced environmental impact compared to conventional solvents. The biodegradability and low toxicity make them particularly suitable for applications where solvent residues are a concern.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Stakeholders
The biomass-derived solvents market is in its growth phase, with increasing regulatory challenges impeding widespread adoption despite growing market potential estimated at $9-12 billion by 2027. Technical maturity varies significantly across key players: established companies like DuPont, Shell, and Eni have advanced commercial-scale technologies, while innovative startups such as Virent, Gevo, and Origin Materials are developing novel conversion processes but face regulatory hurdles in scaling up. Academic institutions (MIT, Wuhan University) and research organizations (Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) are contributing fundamental research, but regulatory frameworks lag behind technological advancements, creating barriers for commercialization particularly regarding safety assessments, standardization, and cross-border compliance.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has implemented a comprehensive regulatory strategy for their portfolio of biomass-derived solvents, leveraging their extensive experience in chemical regulation compliance. Their approach centers on their Bio-PDO™ (bio-based 1,3-propanediol) platform and other bio-based offerings. DuPont has established dedicated regulatory teams that work across jurisdictions to ensure compliance with varying requirements, from TSCA in the US to REACH in Europe and similar frameworks in Asia. They've developed standardized testing protocols to verify the renewable content and environmental impact of their bio-based solvents, addressing key regulatory concerns around sustainability claims[4]. DuPont's strategy includes extensive toxicological and ecotoxicological testing programs that generate comprehensive data packages for regulatory submissions. They've also pioneered the use of read-across approaches where appropriate, leveraging existing data on chemically similar substances to streamline regulatory approvals for novel bio-based variants. Additionally, DuPont actively participates in industry associations and regulatory discussions, helping shape policies that recognize the unique aspects of biomass-derived chemicals while ensuring appropriate safety standards are maintained. Their approach includes close collaboration with customers to address application-specific regulatory requirements in diverse sectors from electronics to personal care.
Strengths: Extensive global regulatory expertise and established relationships with regulatory bodies; comprehensive toxicological data generation capabilities; experience in bringing novel bio-based chemicals to market across multiple jurisdictions. Weaknesses: As a large corporation, may face more regulatory scrutiny than smaller companies; diverse product portfolio means regulatory resources are spread across many initiatives rather than focused solely on biomass-derived solvents.
Origin Materials Operating, Inc.
Technical Solution: Origin Materials has pioneered a regulatory compliance strategy centered on their patented technology platform that converts lignocellulosic biomass into chemical building blocks, particularly focused on CMF (chloromethylfurfural) and HTC (hydrothermal carbon) technologies. Their approach to regulatory challenges involves developing a comprehensive chemical registration strategy that addresses the novel nature of their biomass-derived solvents. Origin has worked extensively with the EPA to register their products under TSCA, creating precedents for similar bio-based chemicals. They've implemented a systematic approach to characterization and toxicological assessment of their novel molecules, generating data packages that satisfy regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions[2]. Origin Materials has also developed partnerships with downstream users to conduct application-specific testing that addresses industry-specific regulatory hurdles. Their strategy includes obtaining third-party certifications for renewable carbon content and sustainability metrics, which helps address the evolving regulatory landscape that increasingly demands verification of environmental claims for bio-based products.
Strengths: Innovative technology platform that produces drop-in compatible chemicals with established regulatory pathways; strong partnerships with major brands that help navigate end-use regulatory requirements; comprehensive approach to sustainability metrics that satisfies emerging regulatory frameworks. Weaknesses: Some of their novel molecules require extensive toxicological testing, creating longer regulatory timelines; their technology platform is still scaling, which can create challenges in generating sufficient data for comprehensive regulatory submissions.
Critical Patents and Technical Literature
Use of renewable deep eutectic solvents in a one-pot process for a biomass
PatentInactiveUS20200216863A1
Innovation
- The use of biocompatible deep eutectic solvents (DESs), specifically choline chloride and glycerol mixtures, for a one-pot biomass pretreatment, saccharification, and fermentation process that eliminates the need for pH adjustments, water dilution, and solid-liquid separations, allowing for continuous operation and compatibility with enzymes and microbes.
Process of producing liquid fuels from coal using biomass-derived solvents
PatentActiveCA2998874C
Innovation
- A process using biomass-derived solvents as hydrogen-donor agents to facilitate coal liquefaction, which includes preparing biomass-derived coal solvents, dissolving coal in these solvents, and subjecting the resulting syncrude to hydrotreatment/hydrogenation to produce distillate fuels, thereby reducing capital and operating costs and greenhouse gas emissions without the need for carbon capture and storage.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of biomass-derived solvents reveals a complex interplay between their potential benefits and ecological considerations. These solvents, derived from renewable biological materials such as agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops, generally demonstrate lower carbon footprints compared to their petroleum-based counterparts when assessed through comprehensive life cycle analyses.
Biomass-derived solvents typically produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions during their production and use phases. Studies indicate potential reductions of 30-80% in carbon dioxide equivalent emissions depending on the specific solvent and biomass feedstock utilized. This significant variation underscores the importance of feedstock selection and processing methods in determining overall environmental performance.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental parameter. While some biomass-derived solvents require substantial water inputs during feedstock cultivation, others utilizing agricultural waste streams or forestry residues may present more favorable water usage profiles. The geographic context of production facilities significantly influences this metric, with water-stressed regions facing heightened scrutiny regarding solvent manufacturing operations.
Land use change implications must be carefully evaluated when considering biomass-derived solvents. Concerns about indirect land use change, particularly the conversion of natural habitats to cropland for solvent feedstock production, could potentially offset carbon benefits if not properly managed through sustainable sourcing practices and certification systems.
Biodegradability and aquatic toxicity profiles generally favor biomass-derived solvents over conventional alternatives. Many bio-based solvents demonstrate enhanced biodegradability in both aerobic and anaerobic environments, reducing persistence in natural systems. However, this advantage is not universal across all biomass-derived options, with some exhibiting toxicity profiles requiring careful waste management protocols.
Air quality impacts present a mixed picture. While biomass-derived solvents typically emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during use, certain production processes may generate particulate matter and other air pollutants, particularly if biomass feedstocks undergo thermal conversion. Advanced emission control technologies and process optimizations can mitigate these concerns but may increase production costs.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate these environmental impact considerations through mechanisms such as carbon accounting systems, water permitting requirements, and chemical registration processes. The heterogeneity of biomass-derived solvents necessitates case-by-case environmental assessment rather than blanket categorizations, creating challenges for streamlined regulatory approaches and market adoption.
Biomass-derived solvents typically produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions during their production and use phases. Studies indicate potential reductions of 30-80% in carbon dioxide equivalent emissions depending on the specific solvent and biomass feedstock utilized. This significant variation underscores the importance of feedstock selection and processing methods in determining overall environmental performance.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental parameter. While some biomass-derived solvents require substantial water inputs during feedstock cultivation, others utilizing agricultural waste streams or forestry residues may present more favorable water usage profiles. The geographic context of production facilities significantly influences this metric, with water-stressed regions facing heightened scrutiny regarding solvent manufacturing operations.
Land use change implications must be carefully evaluated when considering biomass-derived solvents. Concerns about indirect land use change, particularly the conversion of natural habitats to cropland for solvent feedstock production, could potentially offset carbon benefits if not properly managed through sustainable sourcing practices and certification systems.
Biodegradability and aquatic toxicity profiles generally favor biomass-derived solvents over conventional alternatives. Many bio-based solvents demonstrate enhanced biodegradability in both aerobic and anaerobic environments, reducing persistence in natural systems. However, this advantage is not universal across all biomass-derived options, with some exhibiting toxicity profiles requiring careful waste management protocols.
Air quality impacts present a mixed picture. While biomass-derived solvents typically emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during use, certain production processes may generate particulate matter and other air pollutants, particularly if biomass feedstocks undergo thermal conversion. Advanced emission control technologies and process optimizations can mitigate these concerns but may increase production costs.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate these environmental impact considerations through mechanisms such as carbon accounting systems, water permitting requirements, and chemical registration processes. The heterogeneity of biomass-derived solvents necessitates case-by-case environmental assessment rather than blanket categorizations, creating challenges for streamlined regulatory approaches and market adoption.
Policy Harmonization Strategies
Achieving global adoption of biomass-derived solvents requires coordinated regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Currently, the fragmented regulatory landscape presents significant barriers to market entry and scalability for these sustainable alternatives. Effective policy harmonization strategies must address these disparities while maintaining appropriate safety and environmental standards.
International standardization bodies such as ISO and ASTM can play a pivotal role in developing unified testing protocols and classification systems for biomass-derived solvents. These standards would enable consistent evaluation of safety profiles, environmental impacts, and performance characteristics across global markets. The establishment of mutual recognition agreements between major regulatory regions would further facilitate cross-border trade and reduce compliance costs for manufacturers.
Regional policy alignment initiatives, particularly between the EU, North America, and Asia-Pacific regions, represent a critical pathway toward harmonization. The EU's REACH regulation could serve as a potential model for comprehensive chemical management, though adaptations would be necessary to accommodate the unique characteristics of bio-based solvents. Creating specialized regulatory pathways for renewable chemicals that recognize their sustainability benefits while ensuring safety would streamline approval processes.
Collaborative governance mechanisms involving industry consortia, academic institutions, and regulatory authorities can accelerate harmonization efforts. These multi-stakeholder platforms enable knowledge sharing, joint research initiatives, and coordinated policy development. The International Bioeconomy Forum and similar organizations already provide frameworks for such collaboration that could be leveraged specifically for biomass-derived solvents.
Transitional regulatory frameworks offer a pragmatic approach to harmonization by establishing phase-in periods and temporary equivalence arrangements. These mechanisms allow manufacturers to adapt to evolving standards while maintaining market access. Implementing regulatory sandboxes for biomass-derived solvents would permit controlled market testing under modified regulatory requirements, generating valuable data to inform permanent regulatory frameworks.
Digital tools and shared databases for regulatory information can significantly reduce compliance complexity. Blockchain-based systems for tracking regulatory approvals and certifications across jurisdictions would enhance transparency and efficiency. Additionally, harmonized labeling and safety data sheet requirements would simplify communication throughout global supply chains and reduce barriers to international trade of biomass-derived solvents.
International standardization bodies such as ISO and ASTM can play a pivotal role in developing unified testing protocols and classification systems for biomass-derived solvents. These standards would enable consistent evaluation of safety profiles, environmental impacts, and performance characteristics across global markets. The establishment of mutual recognition agreements between major regulatory regions would further facilitate cross-border trade and reduce compliance costs for manufacturers.
Regional policy alignment initiatives, particularly between the EU, North America, and Asia-Pacific regions, represent a critical pathway toward harmonization. The EU's REACH regulation could serve as a potential model for comprehensive chemical management, though adaptations would be necessary to accommodate the unique characteristics of bio-based solvents. Creating specialized regulatory pathways for renewable chemicals that recognize their sustainability benefits while ensuring safety would streamline approval processes.
Collaborative governance mechanisms involving industry consortia, academic institutions, and regulatory authorities can accelerate harmonization efforts. These multi-stakeholder platforms enable knowledge sharing, joint research initiatives, and coordinated policy development. The International Bioeconomy Forum and similar organizations already provide frameworks for such collaboration that could be leveraged specifically for biomass-derived solvents.
Transitional regulatory frameworks offer a pragmatic approach to harmonization by establishing phase-in periods and temporary equivalence arrangements. These mechanisms allow manufacturers to adapt to evolving standards while maintaining market access. Implementing regulatory sandboxes for biomass-derived solvents would permit controlled market testing under modified regulatory requirements, generating valuable data to inform permanent regulatory frameworks.
Digital tools and shared databases for regulatory information can significantly reduce compliance complexity. Blockchain-based systems for tracking regulatory approvals and certifications across jurisdictions would enhance transparency and efficiency. Additionally, harmonized labeling and safety data sheet requirements would simplify communication throughout global supply chains and reduce barriers to international trade of biomass-derived solvents.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!