Regulatory Insights into Biomass-Derived Solvents for Industrial Standards
OCT 23, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass-Derived Solvents Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents represent a significant advancement in the pursuit of sustainable industrial practices, emerging as viable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents. The evolution of these bio-solvents traces back to early 21st century research initiatives, accelerating notably in the past decade due to increasing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability commitments. This technological domain has witnessed exponential growth, with annual research publications increasing by approximately 300% between 2010 and 2023.
The fundamental principle behind biomass-derived solvents involves the extraction and processing of natural compounds from agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops. These renewable feedstocks undergo various conversion processes—including fermentation, thermochemical treatment, and catalytic transformation—to yield solvents with properties comparable to their fossil-based counterparts. Key biomass sources include lignocellulosic materials, vegetable oils, and carbohydrate-rich substrates.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward more efficient extraction methodologies and advanced catalytic systems that enhance yield while reducing energy requirements. The integration of biorefinery concepts has further streamlined production processes, creating synergistic opportunities for co-product development alongside solvent production. Recent breakthroughs in enzyme engineering and heterogeneous catalysis have significantly improved conversion efficiencies, addressing previous economic barriers.
The primary objective of biomass-derived solvent development centers on establishing regulatory frameworks that facilitate industrial adoption while ensuring environmental and safety standards. This includes developing comprehensive toxicological profiles, standardizing performance metrics, and creating lifecycle assessment protocols specific to bio-solvents. Additionally, the technology aims to achieve cost parity with conventional solvents—a critical threshold for widespread market penetration.
Future technological goals include enhancing solvent functionality through molecular design, improving production scalability, and developing closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation. Particular emphasis is placed on creating drop-in replacements that require minimal modifications to existing industrial infrastructure, thereby lowering adoption barriers. The ultimate technological vision encompasses the development of bio-solvent platforms with tunable properties that can be customized for specific industrial applications.
The regulatory landscape surrounding biomass-derived solvents remains fragmented globally, with varying standards across jurisdictions creating market uncertainties. A key technological objective involves harmonizing these regulatory approaches through evidence-based safety assessments and performance validation methodologies. This standardization effort represents a crucial step toward establishing biomass-derived solvents as mainstream industrial chemicals rather than niche alternatives.
The fundamental principle behind biomass-derived solvents involves the extraction and processing of natural compounds from agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops. These renewable feedstocks undergo various conversion processes—including fermentation, thermochemical treatment, and catalytic transformation—to yield solvents with properties comparable to their fossil-based counterparts. Key biomass sources include lignocellulosic materials, vegetable oils, and carbohydrate-rich substrates.
Current technological trajectories indicate a shift toward more efficient extraction methodologies and advanced catalytic systems that enhance yield while reducing energy requirements. The integration of biorefinery concepts has further streamlined production processes, creating synergistic opportunities for co-product development alongside solvent production. Recent breakthroughs in enzyme engineering and heterogeneous catalysis have significantly improved conversion efficiencies, addressing previous economic barriers.
The primary objective of biomass-derived solvent development centers on establishing regulatory frameworks that facilitate industrial adoption while ensuring environmental and safety standards. This includes developing comprehensive toxicological profiles, standardizing performance metrics, and creating lifecycle assessment protocols specific to bio-solvents. Additionally, the technology aims to achieve cost parity with conventional solvents—a critical threshold for widespread market penetration.
Future technological goals include enhancing solvent functionality through molecular design, improving production scalability, and developing closed-loop systems that minimize waste generation. Particular emphasis is placed on creating drop-in replacements that require minimal modifications to existing industrial infrastructure, thereby lowering adoption barriers. The ultimate technological vision encompasses the development of bio-solvent platforms with tunable properties that can be customized for specific industrial applications.
The regulatory landscape surrounding biomass-derived solvents remains fragmented globally, with varying standards across jurisdictions creating market uncertainties. A key technological objective involves harmonizing these regulatory approaches through evidence-based safety assessments and performance validation methodologies. This standardization effort represents a crucial step toward establishing biomass-derived solvents as mainstream industrial chemicals rather than niche alternatives.
Market Demand Analysis for Sustainable Industrial Solvents
The global market for sustainable industrial solvents has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on conventional petroleum-based solvents. Biomass-derived solvents represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with an estimated market value exceeding $7 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8%.
Industrial sectors including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, paints and coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products are demonstrating heightened demand for bio-based solvents. This shift is primarily motivated by corporate sustainability commitments, consumer preferences for environmentally friendly products, and regulatory pressures to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and carbon footprints.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has emerged as a significant consumer of biomass-derived solvents, accounting for nearly 24% of the total market share. This trend is attributed to the industry's focus on green chemistry principles and the need for safer solvent alternatives in drug manufacturing processes. Similarly, the paints and coatings sector represents approximately 22% of the market, driven by the transition toward water-based and bio-based formulations.
Regional analysis reveals Europe as the leading market for sustainable industrial solvents, holding approximately 35% of the global market share. This dominance stems from the region's advanced regulatory framework, including REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal initiatives. North America follows with a 28% market share, while the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 10.2% annually, primarily fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
Consumer preferences are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 67% of global consumers expressing willingness to pay premium prices for products manufactured using sustainable processes and materials. This consumer-driven demand has prompted major chemical manufacturers to expand their bio-based solvent portfolios and invest in research and development of novel biomass-derived alternatives.
Supply chain considerations are becoming increasingly critical, with manufacturers seeking reliable sources of biomass feedstocks. Agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops serve as primary raw materials, creating new value chains and economic opportunities in rural areas. However, challenges related to feedstock availability, price volatility, and competition with food production remain significant concerns for market stakeholders.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted market growth in 2020 but subsequently accelerated demand for bio-based solvents in cleaning and disinfection applications, creating new market opportunities and reinforcing the importance of sustainable chemical solutions in public health contexts.
Industrial sectors including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, paints and coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products are demonstrating heightened demand for bio-based solvents. This shift is primarily motivated by corporate sustainability commitments, consumer preferences for environmentally friendly products, and regulatory pressures to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and carbon footprints.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has emerged as a significant consumer of biomass-derived solvents, accounting for nearly 24% of the total market share. This trend is attributed to the industry's focus on green chemistry principles and the need for safer solvent alternatives in drug manufacturing processes. Similarly, the paints and coatings sector represents approximately 22% of the market, driven by the transition toward water-based and bio-based formulations.
Regional analysis reveals Europe as the leading market for sustainable industrial solvents, holding approximately 35% of the global market share. This dominance stems from the region's advanced regulatory framework, including REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal initiatives. North America follows with a 28% market share, while the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 10.2% annually, primarily fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
Consumer preferences are increasingly influencing market dynamics, with 67% of global consumers expressing willingness to pay premium prices for products manufactured using sustainable processes and materials. This consumer-driven demand has prompted major chemical manufacturers to expand their bio-based solvent portfolios and invest in research and development of novel biomass-derived alternatives.
Supply chain considerations are becoming increasingly critical, with manufacturers seeking reliable sources of biomass feedstocks. Agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops serve as primary raw materials, creating new value chains and economic opportunities in rural areas. However, challenges related to feedstock availability, price volatility, and competition with food production remain significant concerns for market stakeholders.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted market growth in 2020 but subsequently accelerated demand for bio-based solvents in cleaning and disinfection applications, creating new market opportunities and reinforcing the importance of sustainable chemical solutions in public health contexts.
Current Regulatory Landscape and Technical Challenges
The regulatory landscape for biomass-derived solvents is currently characterized by a complex patchwork of standards across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates these solvents primarily through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program. The EU has implemented more stringent frameworks through REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation and the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II), which specifically addresses sustainability criteria for bio-based products.
Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks that emphasize green chemistry principles, while China's regulatory approach remains less developed but is rapidly evolving with increasing emphasis on environmental protection. This regulatory fragmentation creates significant compliance challenges for manufacturers operating in global markets.
Technical challenges in meeting these diverse regulatory requirements are multifaceted. First, analytical method standardization remains inconsistent across jurisdictions, making it difficult to demonstrate compliance with varying purity and quality specifications. Current analytical techniques often struggle to accurately characterize complex biomass-derived solvent compositions, particularly regarding trace impurities that may have toxicological significance.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies for biomass-derived solvents lack harmonization, creating uncertainty in sustainability claims and carbon footprint calculations. Different regulatory bodies employ varying LCA frameworks, resulting in inconsistent evaluations of environmental impact. This presents a major obstacle for companies seeking to validate green credentials across multiple markets.
Toxicological data gaps represent another significant challenge. Many biomass-derived solvents lack comprehensive toxicity profiles compared to their petroleum-based counterparts, which have decades of accumulated safety data. Regulatory bodies increasingly require extensive hazard assessments, but generating such data is time-consuming and costly, particularly for small and medium enterprises entering this space.
Feedstock sustainability certification presents additional complications. Regulations increasingly demand traceability throughout the supply chain to verify that biomass sources meet sustainability criteria. However, verification systems vary by region, and the infrastructure for tracking biomass from field to final product remains underdeveloped in many areas.
Technical specifications for performance equivalency also pose challenges. While regulations encourage substitution of conventional solvents with bio-based alternatives, they often require demonstration of technical equivalence. The inherent chemical differences between petroleum and biomass-derived solvents can make achieving identical performance parameters difficult, necessitating adaptation of existing industrial processes and standards.
Japan and South Korea have established their own regulatory frameworks that emphasize green chemistry principles, while China's regulatory approach remains less developed but is rapidly evolving with increasing emphasis on environmental protection. This regulatory fragmentation creates significant compliance challenges for manufacturers operating in global markets.
Technical challenges in meeting these diverse regulatory requirements are multifaceted. First, analytical method standardization remains inconsistent across jurisdictions, making it difficult to demonstrate compliance with varying purity and quality specifications. Current analytical techniques often struggle to accurately characterize complex biomass-derived solvent compositions, particularly regarding trace impurities that may have toxicological significance.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies for biomass-derived solvents lack harmonization, creating uncertainty in sustainability claims and carbon footprint calculations. Different regulatory bodies employ varying LCA frameworks, resulting in inconsistent evaluations of environmental impact. This presents a major obstacle for companies seeking to validate green credentials across multiple markets.
Toxicological data gaps represent another significant challenge. Many biomass-derived solvents lack comprehensive toxicity profiles compared to their petroleum-based counterparts, which have decades of accumulated safety data. Regulatory bodies increasingly require extensive hazard assessments, but generating such data is time-consuming and costly, particularly for small and medium enterprises entering this space.
Feedstock sustainability certification presents additional complications. Regulations increasingly demand traceability throughout the supply chain to verify that biomass sources meet sustainability criteria. However, verification systems vary by region, and the infrastructure for tracking biomass from field to final product remains underdeveloped in many areas.
Technical specifications for performance equivalency also pose challenges. While regulations encourage substitution of conventional solvents with bio-based alternatives, they often require demonstration of technical equivalence. The inherent chemical differences between petroleum and biomass-derived solvents can make achieving identical performance parameters difficult, necessitating adaptation of existing industrial processes and standards.
Current Compliance Frameworks for Bio-based Solvents
01 Regulatory compliance for biomass-derived solvents
Biomass-derived solvents must comply with various regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. These regulations often focus on environmental impact assessments, safety standards, and usage limitations. Manufacturers and users must navigate complex approval processes that may include toxicity testing, biodegradability assessments, and environmental persistence evaluations. Regulatory insights in this area help companies ensure their biomass-derived solvents meet all legal requirements before market introduction.- Regulatory compliance for biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents must comply with various regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. These regulations govern aspects such as production methods, safety standards, and environmental impact assessments. Manufacturers need to ensure their biomass-derived solvents meet these regulatory requirements before commercialization. This includes obtaining necessary certifications and conducting required testing to demonstrate compliance with applicable laws and standards.
- Environmental impact assessment of bio-based solvents: Environmental impact assessments are crucial for biomass-derived solvents to evaluate their sustainability credentials. These assessments typically include lifecycle analyses that measure carbon footprint, biodegradability, and potential ecological effects. Compared to petroleum-based alternatives, biomass-derived solvents often demonstrate reduced environmental impact, which can be a significant regulatory advantage in jurisdictions with strict environmental protection laws.
- Safety classification and toxicity regulations: Regulatory frameworks require thorough safety assessments for biomass-derived solvents, including toxicity testing, exposure limits, and handling guidelines. These solvents must be classified according to established hazard classification systems, with appropriate labeling and safety data sheets. Many biomass-derived solvents offer improved safety profiles compared to conventional solvents, potentially qualifying for preferred regulatory status in certain applications where human exposure is a concern.
- Production standards and quality control requirements: Regulatory bodies impose specific production standards and quality control requirements for biomass-derived solvents. These include specifications for purity levels, acceptable contaminant thresholds, and consistency in composition. Manufacturers must implement robust quality management systems to ensure compliance with these standards. Regular testing and documentation are typically required to maintain regulatory approval, with particular attention to batch-to-batch consistency and stability during storage and transportation.
- Market authorization and application-specific regulations: Different applications of biomass-derived solvents are subject to specific regulatory requirements. For example, solvents used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, or consumer products face more stringent regulations than those used in industrial applications. Market authorization processes vary by region and application, often requiring extensive documentation of the solvent's properties, production methods, and safety data. Some jurisdictions offer expedited approval pathways or incentives for bio-based alternatives that meet certain sustainability criteria.
02 Environmental classification of bio-based solvents
Bio-based solvents derived from biomass are classified according to their environmental impact profiles. These classifications consider factors such as carbon footprint, biodegradability, toxicity levels, and renewable content percentage. Environmental classification systems help industries select appropriate biomass-derived solvents that align with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. The classification frameworks vary by region but generally assess lifecycle environmental impacts from production through disposal.Expand Specific Solutions03 Production standards for biomass-derived solvents
Production standards for biomass-derived solvents establish quality benchmarks and manufacturing protocols. These standards specify acceptable feedstock sources, conversion processes, purity levels, and contaminant thresholds. Standardized production methods ensure consistency across batches and compliance with industry specifications. The standards also address sustainable sourcing practices, energy efficiency during manufacturing, and waste management considerations to minimize environmental impact throughout the production lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety requirements for biomass-derived solvent applications
Safety requirements for biomass-derived solvents cover handling procedures, storage conditions, exposure limits, and application-specific guidelines. These requirements address flammability risks, toxicity concerns, and potential health impacts on workers and end-users. Safety data sheets must document physical properties, hazard classifications, and emergency response protocols. Industries using these solvents must implement appropriate engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and training programs to ensure safe handling throughout the product lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market authorization pathways for novel bio-solvents
Market authorization pathways for novel biomass-derived solvents involve multi-stage approval processes across different regulatory bodies. These pathways typically include preliminary assessments, technical dossier submissions, risk evaluations, and final authorization decisions. Developers must demonstrate both technical performance and safety compliance through standardized testing protocols. The authorization process may include provisional approvals with monitoring requirements before granting full market access, particularly for innovative bio-solvents with limited usage history.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Stakeholders and Regulatory Bodies
The biomass-derived solvents market is in a growth phase, with increasing regulatory focus driving industrial adoption. The global market is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant scale as industries seek sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players like Virent, Inc. have pioneered BioForming platform technology for renewable fuels and chemicals, while established corporations such as UOP LLC, ExxonMobil, and BP Corporation North America bring significant R&D capabilities. Academic institutions including Washington State University and University of Copenhagen contribute fundamental research. Specialized innovators like Renmatix and OriginClear focus on specific biomass conversion technologies, while industrial giants including Asahi Kasei and UPM-Kymmene integrate these solutions into broader sustainability strategies, creating a competitive landscape balanced between specialized technology developers and diversified industrial players.
Virent, Inc.
Technical Solution: Virent has developed BioForming® technology, a catalytic process that converts plant-based sugars into hydrocarbon molecules identical to those produced from petroleum. Their patented approach uses aqueous phase reforming (APR) to produce bio-based solvents that meet or exceed industrial standards. The company's BioForm® solvents are derived from 100% renewable plant sugars and demonstrate performance characteristics comparable to petroleum-based alternatives while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by up to 60%. Virent has established partnerships with major corporations like Shell and Coca-Cola to scale their technology, focusing on regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions. Their biomass-derived solvents have received TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act) approval in the US and REACH registration in Europe, positioning them as industry leaders in sustainable solvent development.
Strengths: Produces drop-in replacements chemically identical to petroleum-based solvents, enabling seamless integration into existing industrial processes without equipment modifications. Comprehensive regulatory approvals across major markets. Weaknesses: Production costs remain higher than conventional petroleum-based solvents, potentially limiting widespread adoption in price-sensitive applications. Process requires high-quality sugar feedstocks, which may create sustainability concerns regarding land use.
Renmatix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Renmatix has pioneered the Plantrose® Process, a supercritical hydrolysis technology that uses water at high temperatures and pressures to break down biomass into valuable biochemicals and bio-derived solvents. This process operates without enzymes or acids, significantly reducing production costs and environmental impact. Their technology converts cellulosic biomass (agricultural residues, wood chips, etc.) into bio-derived solvents that meet industrial standards across multiple sectors. Renmatix has developed comprehensive regulatory documentation for their Plantro® line of bio-solvents, including safety data sheets that comply with GHS (Globally Harmonized System) requirements. The company has secured EPA approval under the Renewable Fuel Standard program and has worked with regulatory bodies to establish appropriate classification for their novel bio-based materials. Their water-based process has been recognized for its environmental benefits, earning green chemistry certifications that facilitate market acceptance in environmentally conscious industries.
Strengths: Uses supercritical water technology that eliminates the need for expensive enzymes or harsh chemicals, reducing production costs and environmental impact. Can process a wide variety of non-food biomass feedstocks, avoiding food vs. fuel concerns. Weaknesses: High energy requirements for the supercritical water process may offset some environmental benefits. Technology is relatively new to commercial scale, creating potential regulatory uncertainties in some markets.
Critical Patents and Technical Standards Analysis
Process of producing basic biosolvents using heterogeneous catalysts and obtained basic biosolvents by this process
PatentActiveUS20190241837A1
Innovation
- A process using a heterogeneous catalyst, KEYCAT-01, for producing basic biosolvents through inter-esterification and esterification reactions at sub-critical conditions, allowing for continuous operation and eliminating the need for separating residual reactants, with a one-pot reaction system that utilizes inedible vegetable oil or animal fat and waste fatty acids, achieving high yields and efficiency.
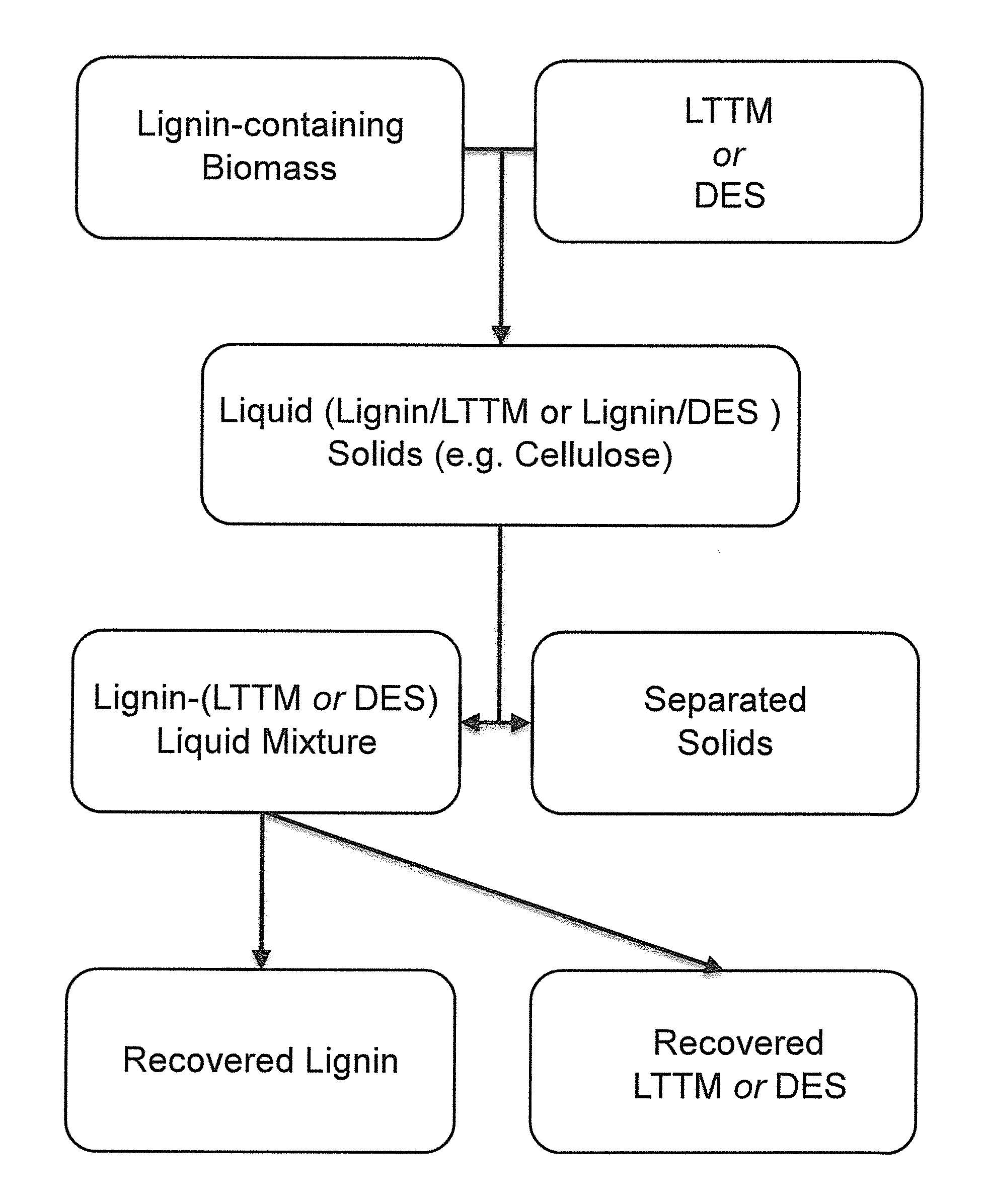
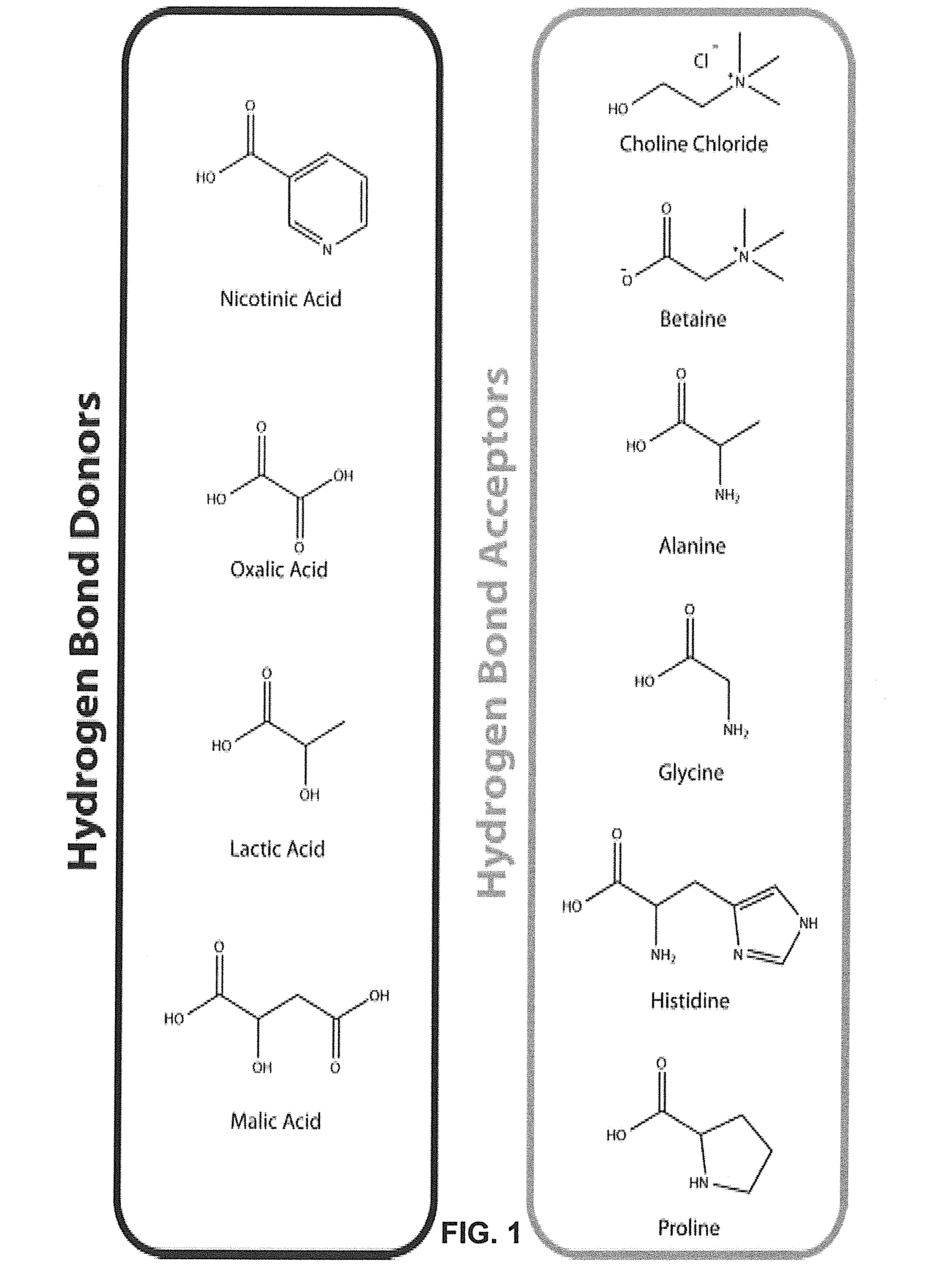
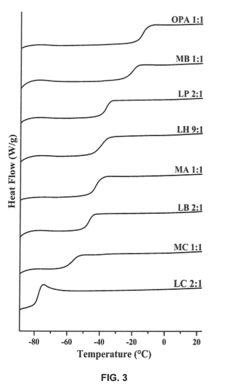
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
PatentInactiveUS20150094459A1
Innovation
- Development of low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) composed of renewable components, which selectively dissolve lignin from lignin-containing biomass at mild conditions, allowing for energy-efficient separation of lignin from cellulose without degradation, and enable recovery of high-quality lignin and cellulose.
Environmental Impact Assessment Methodologies
The assessment of environmental impacts from biomass-derived solvents requires robust methodologies that can accurately capture their full lifecycle effects. Traditional environmental impact assessment (EIA) frameworks often fall short when evaluating these novel bio-based alternatives, necessitating specialized approaches that account for their unique characteristics and production pathways.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) stands as the cornerstone methodology for evaluating biomass-derived solvents, offering a comprehensive cradle-to-grave analysis that encompasses raw material extraction, processing, manufacturing, distribution, use, and end-of-life management. When applying LCA to biomass-derived solvents, practitioners must carefully define system boundaries to include agricultural practices, land use changes, and biorefinery operations that conventional solvent assessments might overlook.
Carbon footprint analysis methodologies have evolved specifically for bio-based products, incorporating biogenic carbon accounting principles that distinguish between short-cycle carbon (from recently grown biomass) and fossil carbon emissions. These methodologies must address temporal considerations in carbon sequestration and release patterns unique to biomass feedstocks, which conventional carbon accounting frameworks may not adequately capture.
Water footprint assessment techniques for biomass-derived solvents require particular attention to agricultural water consumption, including green water (rainwater), blue water (surface and groundwater), and grey water (pollution) components. The regional variability of water stress makes geographically-specific water impact factors essential when comparing different biomass feedstock options.
Biodiversity impact assessment methodologies have recently advanced to better quantify the effects of biomass cultivation on ecosystem services and species diversity. These approaches typically employ land use characterization factors combined with species abundance metrics to estimate potential biodiversity losses or gains compared to reference scenarios.
Toxicity assessment frameworks for biomass-derived solvents must address both the reduced hazards they often present compared to petrochemical alternatives and any novel toxicity concerns from impurities or byproducts specific to bio-based production routes. USEtox and similar models have been adapted to incorporate bio-specific exposure pathways and effect factors.
Standardization efforts by organizations such as ISO, ASTM, and CEN have begun developing specific environmental assessment protocols for bio-based products, including solvents. These emerging standards aim to harmonize assessment methodologies across regions and provide consistent frameworks for regulatory compliance and market acceptance of biomass-derived alternatives.
Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) approaches increasingly complement traditional assessment methodologies by integrating environmental impacts with technical performance, economic viability, and social acceptance factors, offering a more holistic evaluation framework for biomass-derived solvents in industrial applications.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) stands as the cornerstone methodology for evaluating biomass-derived solvents, offering a comprehensive cradle-to-grave analysis that encompasses raw material extraction, processing, manufacturing, distribution, use, and end-of-life management. When applying LCA to biomass-derived solvents, practitioners must carefully define system boundaries to include agricultural practices, land use changes, and biorefinery operations that conventional solvent assessments might overlook.
Carbon footprint analysis methodologies have evolved specifically for bio-based products, incorporating biogenic carbon accounting principles that distinguish between short-cycle carbon (from recently grown biomass) and fossil carbon emissions. These methodologies must address temporal considerations in carbon sequestration and release patterns unique to biomass feedstocks, which conventional carbon accounting frameworks may not adequately capture.
Water footprint assessment techniques for biomass-derived solvents require particular attention to agricultural water consumption, including green water (rainwater), blue water (surface and groundwater), and grey water (pollution) components. The regional variability of water stress makes geographically-specific water impact factors essential when comparing different biomass feedstock options.
Biodiversity impact assessment methodologies have recently advanced to better quantify the effects of biomass cultivation on ecosystem services and species diversity. These approaches typically employ land use characterization factors combined with species abundance metrics to estimate potential biodiversity losses or gains compared to reference scenarios.
Toxicity assessment frameworks for biomass-derived solvents must address both the reduced hazards they often present compared to petrochemical alternatives and any novel toxicity concerns from impurities or byproducts specific to bio-based production routes. USEtox and similar models have been adapted to incorporate bio-specific exposure pathways and effect factors.
Standardization efforts by organizations such as ISO, ASTM, and CEN have begun developing specific environmental assessment protocols for bio-based products, including solvents. These emerging standards aim to harmonize assessment methodologies across regions and provide consistent frameworks for regulatory compliance and market acceptance of biomass-derived alternatives.
Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) approaches increasingly complement traditional assessment methodologies by integrating environmental impacts with technical performance, economic viability, and social acceptance factors, offering a more holistic evaluation framework for biomass-derived solvents in industrial applications.
Cross-Industry Adoption Barriers and Opportunities
The adoption of biomass-derived solvents across different industries faces significant barriers despite their environmental benefits. Regulatory frameworks vary substantially between sectors, creating compliance challenges for manufacturers attempting to introduce these sustainable alternatives. For instance, pharmaceutical companies must adhere to stringent Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines that require extensive validation of any new solvent, while food processing industries face different but equally rigorous safety standards from organizations like the FDA and EFSA.
Technical barriers present another major challenge, as many industrial processes have been optimized for conventional petroleum-based solvents. Retrofitting existing equipment or redesigning processes to accommodate the different chemical properties of biomass-derived solvents often requires substantial capital investment. This is particularly evident in precision manufacturing and electronics industries where performance specifications leave little room for variation in solvent properties.
Economic considerations further complicate adoption, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding price premiums of 15-30% over conventional alternatives. This cost differential creates competitive disadvantages in price-sensitive markets and industries with thin profit margins. Supply chain reliability also remains problematic, with production volumes of bio-solvents still relatively small and geographically concentrated, creating concerns about consistent availability.
Despite these challenges, significant opportunities exist across multiple sectors. The consumer goods industry has demonstrated willingness to absorb higher costs for sustainable ingredients, driven by growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers are willing to pay more for products with sustainable credentials, creating a premium market segment.
Regulatory incentives are emerging as powerful adoption drivers in certain regions. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan and similar initiatives in North America provide tax benefits and compliance advantages for companies transitioning to bio-based materials. These policy frameworks are creating favorable conditions particularly in construction, automotive, and consumer product sectors.
Cross-industry collaborations present another promising pathway, with consortia forming to share development costs and establish common standards for biomass-derived solvents. The Sustainable Chemistry Alliance, comprising companies from diverse sectors, has successfully developed shared testing protocols and performance benchmarks that reduce individual company validation costs by approximately 40%.
Technical barriers present another major challenge, as many industrial processes have been optimized for conventional petroleum-based solvents. Retrofitting existing equipment or redesigning processes to accommodate the different chemical properties of biomass-derived solvents often requires substantial capital investment. This is particularly evident in precision manufacturing and electronics industries where performance specifications leave little room for variation in solvent properties.
Economic considerations further complicate adoption, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding price premiums of 15-30% over conventional alternatives. This cost differential creates competitive disadvantages in price-sensitive markets and industries with thin profit margins. Supply chain reliability also remains problematic, with production volumes of bio-solvents still relatively small and geographically concentrated, creating concerns about consistent availability.
Despite these challenges, significant opportunities exist across multiple sectors. The consumer goods industry has demonstrated willingness to absorb higher costs for sustainable ingredients, driven by growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. Market research indicates that 64% of consumers are willing to pay more for products with sustainable credentials, creating a premium market segment.
Regulatory incentives are emerging as powerful adoption drivers in certain regions. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan and similar initiatives in North America provide tax benefits and compliance advantages for companies transitioning to bio-based materials. These policy frameworks are creating favorable conditions particularly in construction, automotive, and consumer product sectors.
Cross-industry collaborations present another promising pathway, with consortia forming to share development costs and establish common standards for biomass-derived solvents. The Sustainable Chemistry Alliance, comprising companies from diverse sectors, has successfully developed shared testing protocols and performance benchmarks that reduce individual company validation costs by approximately 40%.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!