Analysis of Market Demand for Biomass-Derived Solvents
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvents Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents represent a significant advancement in the field of green chemistry, emerging as sustainable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents. The evolution of these bio-solvents can be traced back to the early 2000s when increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures began driving research into renewable chemical sources. Over the past two decades, technological advancements in biomass processing, particularly in fractionation and conversion technologies, have accelerated the development of commercially viable bio-solvents.
The trajectory of biomass solvent development has followed several distinct phases: initial exploration of natural extracts, development of first-generation bio-solvents derived primarily from food crops, and the current focus on second-generation solutions utilizing agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops. This progression reflects broader sustainability trends and the growing emphasis on circular economy principles within the chemical industry.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward more sophisticated conversion processes, including advanced catalytic methods, enzymatic conversions, and integrated biorefinery concepts that maximize resource efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in process optimization represents an emerging frontier that promises to enhance both economic viability and environmental performance of biomass-derived solvents.
The primary technical objectives for biomass solvent development center around achieving performance parity with conventional solvents while maintaining economic competitiveness. Specific goals include developing solvents with enhanced selectivity, reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and broader application ranges across industries. Additionally, there is a focused effort to design processes that minimize energy consumption and waste generation throughout the production lifecycle.
From a sustainability perspective, key objectives include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50% compared to petroleum-based alternatives, achieving carbon neutrality in production processes, and establishing closed-loop systems where solvent waste can be effectively recycled or biodegraded without environmental harm. These objectives align with global sustainability frameworks, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and various national green chemistry initiatives.
The technical roadmap for biomass-derived solvents aims to address current limitations in scalability, consistency of performance, and production costs. Long-term goals include developing versatile bio-solvent platforms that can be tailored to specific industrial applications through molecular design and formulation strategies, ultimately creating a comprehensive portfolio of sustainable solutions that can effectively replace the entire spectrum of conventional solvents currently in use.
The trajectory of biomass solvent development has followed several distinct phases: initial exploration of natural extracts, development of first-generation bio-solvents derived primarily from food crops, and the current focus on second-generation solutions utilizing agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops. This progression reflects broader sustainability trends and the growing emphasis on circular economy principles within the chemical industry.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward more sophisticated conversion processes, including advanced catalytic methods, enzymatic conversions, and integrated biorefinery concepts that maximize resource efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in process optimization represents an emerging frontier that promises to enhance both economic viability and environmental performance of biomass-derived solvents.
The primary technical objectives for biomass solvent development center around achieving performance parity with conventional solvents while maintaining economic competitiveness. Specific goals include developing solvents with enhanced selectivity, reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and broader application ranges across industries. Additionally, there is a focused effort to design processes that minimize energy consumption and waste generation throughout the production lifecycle.
From a sustainability perspective, key objectives include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50% compared to petroleum-based alternatives, achieving carbon neutrality in production processes, and establishing closed-loop systems where solvent waste can be effectively recycled or biodegraded without environmental harm. These objectives align with global sustainability frameworks, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and various national green chemistry initiatives.
The technical roadmap for biomass-derived solvents aims to address current limitations in scalability, consistency of performance, and production costs. Long-term goals include developing versatile bio-solvent platforms that can be tailored to specific industrial applications through molecular design and formulation strategies, ultimately creating a comprehensive portfolio of sustainable solutions that can effectively replace the entire spectrum of conventional solvents currently in use.
Market Demand Analysis for Bio-based Solvents
The global market for bio-based solvents has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures to reduce dependence on petroleum-derived chemicals. Current market analysis indicates that the bio-based solvents market was valued at approximately 6.8 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 11.2 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% during the forecast period.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly products has become a major market driver, with end-users increasingly willing to pay premium prices for sustainable alternatives. This shift in consumer preference has prompted manufacturers across various industries to incorporate bio-based solvents into their production processes and final products. The packaging industry, in particular, has shown strong interest in bio-based solvents for inks and adhesives to meet growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly favoring bio-based alternatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar policies in North America and Asia-Pacific regions have imposed stricter controls on conventional petroleum-based solvents, creating market opportunities for biomass-derived alternatives. Tax incentives and subsidies for green chemistry initiatives in several countries have further stimulated market growth.
Industry segmentation reveals that bio-based alcohols currently dominate the market, accounting for approximately 42% of the total bio-based solvents market share. Glycols and diols derived from biomass sources follow at 28%, while esters and ketones collectively represent about 20% of the market. The remaining 10% consists of emerging bio-based solvent categories.
Application-wise, paints and coatings represent the largest end-use segment at 35% of market consumption, followed by pharmaceuticals (22%), cosmetics and personal care products (18%), cleaning products (15%), and other applications (10%). The pharmaceutical sector is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to increasing emphasis on green manufacturing practices in drug production.
Regional analysis shows that Europe leads the global market with a 38% share, followed by North America (32%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (6%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by rapid industrialization, growing environmental awareness, and supportive government policies in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Market challenges include higher production costs compared to conventional solvents, limited availability of raw materials, and technical performance gaps in certain applications. Despite these challenges, the long-term market outlook remains positive as technological advancements continue to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly products has become a major market driver, with end-users increasingly willing to pay premium prices for sustainable alternatives. This shift in consumer preference has prompted manufacturers across various industries to incorporate bio-based solvents into their production processes and final products. The packaging industry, in particular, has shown strong interest in bio-based solvents for inks and adhesives to meet growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly favoring bio-based alternatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar policies in North America and Asia-Pacific regions have imposed stricter controls on conventional petroleum-based solvents, creating market opportunities for biomass-derived alternatives. Tax incentives and subsidies for green chemistry initiatives in several countries have further stimulated market growth.
Industry segmentation reveals that bio-based alcohols currently dominate the market, accounting for approximately 42% of the total bio-based solvents market share. Glycols and diols derived from biomass sources follow at 28%, while esters and ketones collectively represent about 20% of the market. The remaining 10% consists of emerging bio-based solvent categories.
Application-wise, paints and coatings represent the largest end-use segment at 35% of market consumption, followed by pharmaceuticals (22%), cosmetics and personal care products (18%), cleaning products (15%), and other applications (10%). The pharmaceutical sector is expected to witness the fastest growth rate due to increasing emphasis on green manufacturing practices in drug production.
Regional analysis shows that Europe leads the global market with a 38% share, followed by North America (32%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (6%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by rapid industrialization, growing environmental awareness, and supportive government policies in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Market challenges include higher production costs compared to conventional solvents, limited availability of raw materials, and technical performance gaps in certain applications. Despite these challenges, the long-term market outlook remains positive as technological advancements continue to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Current Status and Technical Challenges
The global landscape for biomass-derived solvents shows significant regional variations in development status. North America and Europe currently lead in research and commercialization efforts, with established regulatory frameworks promoting bio-based chemicals. The European Union's Renewable Energy Directive and Circular Economy Action Plan have particularly accelerated adoption in European markets. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific regions are experiencing rapid growth in this sector, driven by increasing industrial activities and growing environmental awareness, especially in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Despite promising advancements, biomass-derived solvents face several critical technical challenges. Feedstock variability remains a primary concern, as seasonal fluctuations and geographical differences in biomass composition affect production consistency and solvent properties. This variability necessitates robust preprocessing technologies and flexible manufacturing processes that can accommodate diverse input materials while maintaining product quality.
Production scalability presents another significant hurdle. Current production methods often struggle with efficiency when scaled beyond laboratory or pilot plant levels. The conversion of complex biomass structures into uniform solvent molecules requires sophisticated catalytic processes that are difficult to maintain at industrial scales. Energy intensity of these processes further complicates commercial viability, with many conversion pathways requiring substantial thermal or chemical inputs that diminish the overall sustainability benefits.
Cost competitiveness remains perhaps the most pressing challenge. Conventional petroleum-derived solvents benefit from decades of process optimization and economies of scale, resulting in significantly lower production costs. Biomass-derived alternatives typically command a 20-50% price premium, limiting market penetration to specialty applications or environmentally conscious market segments willing to absorb higher costs.
Performance consistency issues also persist across different biomass-derived solvent types. While some bio-solvents like ethyl lactate and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran demonstrate comparable or superior performance to conventional alternatives in specific applications, others exhibit limitations in parameters such as solvency power, evaporation rate, or stability. These performance gaps restrict their adoption in precision industries like electronics manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate market development. The novel nature of many biomass-derived solvents means they lack comprehensive toxicological profiles and standardized testing protocols. This regulatory uncertainty creates barriers to market entry, particularly in highly regulated sectors like food processing, cosmetics, and healthcare applications where safety standards are stringent.
Despite promising advancements, biomass-derived solvents face several critical technical challenges. Feedstock variability remains a primary concern, as seasonal fluctuations and geographical differences in biomass composition affect production consistency and solvent properties. This variability necessitates robust preprocessing technologies and flexible manufacturing processes that can accommodate diverse input materials while maintaining product quality.
Production scalability presents another significant hurdle. Current production methods often struggle with efficiency when scaled beyond laboratory or pilot plant levels. The conversion of complex biomass structures into uniform solvent molecules requires sophisticated catalytic processes that are difficult to maintain at industrial scales. Energy intensity of these processes further complicates commercial viability, with many conversion pathways requiring substantial thermal or chemical inputs that diminish the overall sustainability benefits.
Cost competitiveness remains perhaps the most pressing challenge. Conventional petroleum-derived solvents benefit from decades of process optimization and economies of scale, resulting in significantly lower production costs. Biomass-derived alternatives typically command a 20-50% price premium, limiting market penetration to specialty applications or environmentally conscious market segments willing to absorb higher costs.
Performance consistency issues also persist across different biomass-derived solvent types. While some bio-solvents like ethyl lactate and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran demonstrate comparable or superior performance to conventional alternatives in specific applications, others exhibit limitations in parameters such as solvency power, evaporation rate, or stability. These performance gaps restrict their adoption in precision industries like electronics manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate market development. The novel nature of many biomass-derived solvents means they lack comprehensive toxicological profiles and standardized testing protocols. This regulatory uncertainty creates barriers to market entry, particularly in highly regulated sectors like food processing, cosmetics, and healthcare applications where safety standards are stringent.
Current Biomass Solvent Production Technologies
01 Production methods for biomass-derived solvents
Various methods are employed to produce solvents from biomass feedstocks, including fermentation, catalytic conversion, and thermochemical processes. These methods transform renewable biomass resources such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops into environmentally friendly solvents. The production techniques focus on optimizing yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness to make these solvents commercially viable alternatives to petroleum-based products.- Production methods for biomass-derived solvents: Various methods are employed to produce solvents from biomass feedstocks, including fermentation, catalytic conversion, and thermochemical processes. These methods transform renewable biomass resources such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops into sustainable solvents. The processes often involve breaking down complex biomass structures into simpler molecules that can function as effective solvents for industrial applications, offering alternatives to petroleum-based products.
- Applications in fuel and energy sectors: Biomass-derived solvents are increasingly being utilized in fuel formulations and energy applications. These bio-based solvents can be incorporated into biofuels to improve performance characteristics or used directly as fuel additives. They offer advantages such as reduced emissions, improved combustion properties, and compatibility with existing fuel infrastructure. The growing demand for cleaner energy solutions is driving market expansion for these renewable solvent alternatives in the transportation and energy sectors.
- Industrial and chemical applications: Biomass-derived solvents are finding widespread adoption in various industrial and chemical processes. These green solvents serve as substitutes for conventional petroleum-based solvents in applications such as coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, and chemical synthesis. Their favorable environmental profile, including biodegradability and lower toxicity, makes them attractive for industries seeking to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining performance requirements in manufacturing processes.
- Market growth drivers and sustainability benefits: The market for biomass-derived solvents is experiencing growth driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer preference for sustainable products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. These solvents offer significant environmental benefits including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower carbon footprint, and decreased dependence on fossil resources. The circular economy aspect of utilizing waste biomass streams for solvent production further enhances their sustainability profile, creating market demand across multiple industries seeking greener alternatives.
- Novel biomass-derived solvent formulations: Innovative formulations of biomass-derived solvents are being developed to enhance performance characteristics and expand application possibilities. These include solvent blends, functionalized bio-based solvents, and custom formulations designed for specific industrial needs. Research focuses on improving properties such as solvency power, volatility, stability, and compatibility with various substrates. These novel formulations aim to overcome performance limitations of first-generation bio-solvents and enable broader market adoption across diverse industrial sectors.
02 Applications in industrial processes and products
Biomass-derived solvents find applications across various industrial sectors including coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, pharmaceuticals, and personal care items. These renewable solvents serve as effective replacements for conventional petroleum-based solvents in manufacturing processes, offering comparable performance characteristics while reducing environmental impact. Their biodegradability and lower toxicity make them particularly valuable in consumer products where health and environmental concerns are paramount.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental benefits and sustainability aspects
Biomass-derived solvents offer significant environmental advantages over traditional petroleum-based alternatives, including reduced carbon footprint, lower toxicity, and enhanced biodegradability. These solvents contribute to circular economy principles by utilizing renewable resources and often generating fewer harmful emissions during production and use. Their sustainability profile is driving increased market demand, particularly in regions with strict environmental regulations and among companies with strong sustainability commitments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Market growth drivers and regional demand patterns
The market for biomass-derived solvents is experiencing growth driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer preference for sustainable products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. Regional demand patterns vary based on regulatory frameworks, industrial base, and availability of biomass feedstocks. North America and Europe lead in adoption due to stringent environmental policies, while Asia-Pacific shows rapid growth potential due to expanding manufacturing sectors and increasing environmental awareness. Price competitiveness relative to conventional solvents remains a key factor influencing market penetration rates.Expand Specific Solutions05 Technological innovations and future market trends
Ongoing research and development is focused on improving production efficiency, expanding the range of biomass feedstocks, and enhancing the performance characteristics of bio-based solvents. Emerging technologies include novel catalytic processes, integrated biorefinery concepts, and genetic engineering of biomass crops. Future market trends point toward increased integration with bioeconomy initiatives, development of specialized high-value applications, and growing partnerships between solvent producers and end-users to create tailored sustainable solutions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The biomass-derived solvents market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives. The global market is projected to expand significantly, with an estimated value of $9-12 billion by 2027. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include BASF Corp. and Archer-Daniels-Midland Co., who have established commercial-scale production capabilities, while companies like Virent, Inc. and Furanix Technologies BV are advancing innovative conversion technologies. Academic institutions such as University of Wisconsin (via Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation) and University of Delaware are contributing fundamental research. The competitive landscape is diversifying with petrochemical giants like Sinopec and UOP LLC entering the space, indicating growing mainstream interest in bio-based alternatives to conventional petroleum-derived solvents.
Virent, Inc.
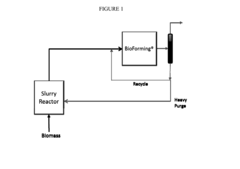
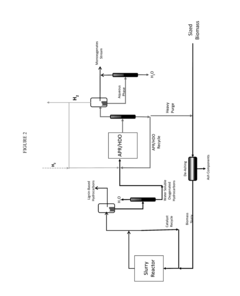
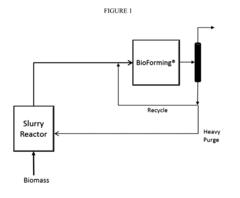
Technical Solution: Virent has developed BioForming® technology that converts plant-based sugars into a range of hydrocarbon products identical to those made from petroleum, including bio-based solvents. Their patented catalytic process transforms biomass-derived oxygenates to produce drop-in renewable solvents with properties matching or exceeding petroleum-based alternatives. The company's technology creates solvents through aqueous phase reforming (APR) followed by catalytic conversion steps that can be tailored to produce specific solvent molecules. Virent's bio-solvents demonstrate excellent performance in coatings, adhesives, and cleaning applications while offering reduced toxicity and VOC emissions compared to conventional alternatives. Their integrated biorefinery approach allows for efficient production of multiple high-value products from a single biomass feedstock, maximizing economic value and sustainability benefits.
Strengths: Produces drop-in replacements chemically identical to petroleum-based solvents, enabling direct substitution without reformulation. Flexible technology platform can create multiple solvent types from various biomass feedstocks. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents may limit market penetration without premium pricing or regulatory support. Scale-up challenges remain for full commercial deployment.
Furanix Technologies BV
Technical Solution: Furanix Technologies has developed groundbreaking technology for producing furan-based solvents from biomass feedstocks. Their core innovation centers on the efficient conversion of lignocellulosic materials into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and its derivatives, which serve as versatile bio-based solvents. The company's proprietary catalytic process enables selective dehydration of C6 sugars to produce furan compounds under mild conditions with high yields. Furanix has commercialized the production of methyl levulinate and ethyl levulinate, which function as effective solvents in applications ranging from paints and coatings to agricultural formulations. Their technology platform also produces 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA)-derived solvents that offer superior performance in specialized applications while providing significant carbon footprint reductions. Furanix has established partnerships with major chemical companies to scale up production and expand market applications for their furan-based solvent portfolio, positioning themselves as leaders in this emerging segment of the bio-based chemicals market.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in furan chemistry provides unique product offerings not widely available from competitors. Furan-based solvents offer distinctive performance properties that create differentiation in the marketplace. Weaknesses: Limited production scale compared to major chemical companies restricts market penetration. Relatively higher production costs for some specialty furan derivatives may limit adoption in price-sensitive applications.
Key Patents and Technical Literature Review
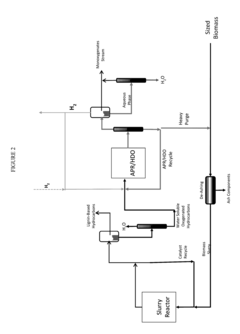
Solvolysis of biomass using solvent from a bioreforming process
PatentActiveUS20170058370A1
Innovation
- A method involving catalytically reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon with hydrogen in the presence of a deoxygenation catalyst to produce a biomass processing solvent, which is then used to deconstruct biomass at specific temperatures and pressures to produce a biomass hydrolysate containing soluble derivatives and carbohydrates.
Solvolysis of biomass to produce aqueous and organic products
PatentActiveUS20170137719A1
Innovation
- A method involving catalytic reactions with a biomass processing solvent produced by reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon with hydrogen in the presence of a deoxygenation catalyst, followed by condensation with a condensation catalyst to create a solvent that deconstructs biomass into water-soluble derivatives, carbohydrates, and polyols, facilitating their use in bioreforming processes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
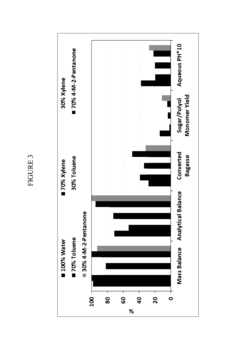
The environmental impact assessment of biomass-derived solvents reveals significant advantages over conventional petroleum-based alternatives. Life cycle analyses consistently demonstrate reduced greenhouse gas emissions, with studies indicating 40-70% lower carbon footprints depending on feedstock selection and processing methods. Biomass solvents derived from agricultural residues show particularly promising results, as they avoid the environmental burdens associated with dedicated crop cultivation.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture. While some biomass solvent production pathways require substantial water inputs, particularly for feedstock cultivation, advanced processing technologies have reduced process water requirements by approximately 30% over the past decade. Closed-loop water recycling systems implemented in newer production facilities have further minimized freshwater withdrawal impacts.
Land use considerations remain a critical sustainability factor. Second-generation biomass solvents utilizing agricultural waste streams, forestry residues, and non-food biomass sources effectively address land competition concerns with food production. This approach aligns with circular economy principles by transforming waste materials into valuable chemical products, thereby reducing overall environmental footprint.
Toxicity profiles of biomass-derived solvents demonstrate marked improvements in human and ecological safety parameters. Biodegradability testing indicates that most biomass solvents degrade 2-5 times faster than their petroleum counterparts in natural environments. Reduced bioaccumulation potential and lower aquatic toxicity levels further enhance their environmental credentials, making them increasingly attractive for applications in consumer products, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Energy efficiency assessments reveal that current biomass solvent production pathways typically require 15-25% more energy input than conventional petrochemical routes. However, this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements in catalysis, separation processes, and process intensification. Integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities has emerged as a promising strategy to further reduce the carbon intensity of manufacturing operations.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize the sustainability benefits of biomass-derived solvents. The implementation of green chemistry metrics in environmental impact assessments has provided standardized methodologies for comparing solvent options. These frameworks consider factors such as atom economy, process mass intensity, and reaction mass efficiency, offering comprehensive sustainability evaluations beyond simple carbon accounting.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture. While some biomass solvent production pathways require substantial water inputs, particularly for feedstock cultivation, advanced processing technologies have reduced process water requirements by approximately 30% over the past decade. Closed-loop water recycling systems implemented in newer production facilities have further minimized freshwater withdrawal impacts.
Land use considerations remain a critical sustainability factor. Second-generation biomass solvents utilizing agricultural waste streams, forestry residues, and non-food biomass sources effectively address land competition concerns with food production. This approach aligns with circular economy principles by transforming waste materials into valuable chemical products, thereby reducing overall environmental footprint.
Toxicity profiles of biomass-derived solvents demonstrate marked improvements in human and ecological safety parameters. Biodegradability testing indicates that most biomass solvents degrade 2-5 times faster than their petroleum counterparts in natural environments. Reduced bioaccumulation potential and lower aquatic toxicity levels further enhance their environmental credentials, making them increasingly attractive for applications in consumer products, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Energy efficiency assessments reveal that current biomass solvent production pathways typically require 15-25% more energy input than conventional petrochemical routes. However, this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements in catalysis, separation processes, and process intensification. Integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities has emerged as a promising strategy to further reduce the carbon intensity of manufacturing operations.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize the sustainability benefits of biomass-derived solvents. The implementation of green chemistry metrics in environmental impact assessments has provided standardized methodologies for comparing solvent options. These frameworks consider factors such as atom economy, process mass intensity, and reaction mass efficiency, offering comprehensive sustainability evaluations beyond simple carbon accounting.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Incentives
The regulatory landscape for biomass-derived solvents is rapidly evolving globally, with increasing policy support aimed at accelerating the transition from petroleum-based to bio-based chemicals. The European Union leads with its comprehensive regulatory framework, particularly through the Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II), which mandates that 32% of energy consumption must come from renewable sources by 2030. This directive specifically incentivizes the production and utilization of bio-based products, including solvents derived from biomass feedstocks.
In the United States, the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program and the USDA BioPreferred Program provide significant market advantages for biomass-derived products. The BioPreferred Program, in particular, requires federal agencies to give purchasing preference to bio-based products, creating a guaranteed market for manufacturers of biomass-derived solvents. Additionally, tax incentives such as the Biofuel Producer Tax Credit offer financial benefits to companies investing in bio-based solvent production facilities.
Asian markets, especially China and Japan, have implemented their own regulatory frameworks promoting bio-based chemicals. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly supports the development of bio-based materials, while Japan's Biomass Industrialization Strategy provides subsidies for research and commercialization of biomass-derived products, including solvents.
Environmental regulations are increasingly stringent regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants, many of which are conventional petroleum-based solvents. The EU's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in other regions have restricted or banned certain traditional solvents, creating market opportunities for safer biomass-derived alternatives. These regulatory pressures serve as indirect policy incentives driving market growth for bio-based solvents.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes in various jurisdictions further enhance the competitive position of biomass-derived solvents by internalizing the environmental costs associated with fossil-based alternatives. The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and similar programs in Canada, China, and elsewhere effectively increase the cost of petroleum-derived products, improving the relative economics of bio-based alternatives.
International agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals provide additional policy momentum for the transition to bio-based chemicals. Many countries have incorporated bio-economy strategies into their nationally determined contributions (NDCs), which often include specific targets for bio-based chemical production and utilization.
In the United States, the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program and the USDA BioPreferred Program provide significant market advantages for biomass-derived products. The BioPreferred Program, in particular, requires federal agencies to give purchasing preference to bio-based products, creating a guaranteed market for manufacturers of biomass-derived solvents. Additionally, tax incentives such as the Biofuel Producer Tax Credit offer financial benefits to companies investing in bio-based solvent production facilities.
Asian markets, especially China and Japan, have implemented their own regulatory frameworks promoting bio-based chemicals. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly supports the development of bio-based materials, while Japan's Biomass Industrialization Strategy provides subsidies for research and commercialization of biomass-derived products, including solvents.
Environmental regulations are increasingly stringent regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants, many of which are conventional petroleum-based solvents. The EU's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in other regions have restricted or banned certain traditional solvents, creating market opportunities for safer biomass-derived alternatives. These regulatory pressures serve as indirect policy incentives driving market growth for bio-based solvents.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes in various jurisdictions further enhance the competitive position of biomass-derived solvents by internalizing the environmental costs associated with fossil-based alternatives. The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and similar programs in Canada, China, and elsewhere effectively increase the cost of petroleum-derived products, improving the relative economics of bio-based alternatives.
International agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals provide additional policy momentum for the transition to bio-based chemicals. Many countries have incorporated bio-economy strategies into their nationally determined contributions (NDCs), which often include specific targets for bio-based chemical production and utilization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!