Biomass-Derived Solvents in Next-Gen Manufacturing Technologies
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass-Derived Solvents Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a promising alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents, marking a significant shift in manufacturing technologies over the past two decades. These eco-friendly solvents, derived from renewable resources such as agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and dedicated energy crops, represent a sustainable approach to chemical processing that aligns with global sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
The evolution of biomass-derived solvents can be traced back to early research in green chemistry during the 1990s, which gained momentum in the early 2000s as environmental regulations tightened and petroleum prices fluctuated. Initial focus was primarily on simple bio-alcohols like ethanol and methanol, but research has progressively expanded to include more complex molecules such as gamma-valerolactone, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and cyrene, offering improved performance characteristics.
Recent technological advancements in biomass conversion processes, including fermentation, catalytic conversion, and thermochemical methods, have significantly enhanced the economic viability and scalability of these green solvents. The integration of biorefinery concepts has further optimized resource utilization, enabling cascading use of biomass components and minimizing waste generation.
The primary objective of current research in biomass-derived solvents is to develop cost-effective, high-performance alternatives that can directly replace conventional solvents without requiring modifications to existing manufacturing processes. This includes improving extraction efficiency, enhancing solvent stability, and reducing energy requirements during production and application phases.
Another critical goal is to establish comprehensive life cycle assessments that accurately quantify the environmental benefits of these bio-based alternatives, addressing potential concerns about land use, biodiversity impacts, and competition with food production. Research aims to ensure that the entire production chain delivers genuine sustainability advantages over petroleum-based counterparts.
Technical objectives also include developing standardized quality parameters and specifications for biomass-derived solvents to facilitate their integration into industrial applications. This standardization is essential for building market confidence and ensuring consistent performance across various manufacturing contexts.
Looking forward, the field is trending toward developing multi-functional biomass-derived solvents that can serve multiple purposes in manufacturing processes, thereby increasing their value proposition. Additionally, research is increasingly focused on designing solvents with inherent safety features, such as reduced flammability and toxicity, addressing both environmental and occupational health concerns in next-generation manufacturing environments.
The evolution of biomass-derived solvents can be traced back to early research in green chemistry during the 1990s, which gained momentum in the early 2000s as environmental regulations tightened and petroleum prices fluctuated. Initial focus was primarily on simple bio-alcohols like ethanol and methanol, but research has progressively expanded to include more complex molecules such as gamma-valerolactone, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and cyrene, offering improved performance characteristics.
Recent technological advancements in biomass conversion processes, including fermentation, catalytic conversion, and thermochemical methods, have significantly enhanced the economic viability and scalability of these green solvents. The integration of biorefinery concepts has further optimized resource utilization, enabling cascading use of biomass components and minimizing waste generation.
The primary objective of current research in biomass-derived solvents is to develop cost-effective, high-performance alternatives that can directly replace conventional solvents without requiring modifications to existing manufacturing processes. This includes improving extraction efficiency, enhancing solvent stability, and reducing energy requirements during production and application phases.
Another critical goal is to establish comprehensive life cycle assessments that accurately quantify the environmental benefits of these bio-based alternatives, addressing potential concerns about land use, biodiversity impacts, and competition with food production. Research aims to ensure that the entire production chain delivers genuine sustainability advantages over petroleum-based counterparts.
Technical objectives also include developing standardized quality parameters and specifications for biomass-derived solvents to facilitate their integration into industrial applications. This standardization is essential for building market confidence and ensuring consistent performance across various manufacturing contexts.
Looking forward, the field is trending toward developing multi-functional biomass-derived solvents that can serve multiple purposes in manufacturing processes, thereby increasing their value proposition. Additionally, research is increasingly focused on designing solvents with inherent safety features, such as reduced flammability and toxicity, addressing both environmental and occupational health concerns in next-generation manufacturing environments.
Market Demand Analysis for Green Solvents in Manufacturing
The global market for green solvents, particularly biomass-derived alternatives, has experienced significant growth in recent years driven by increasing environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives across manufacturing sectors. Current market analysis indicates that the global green solvent market reached approximately $4.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.5% through 2030, potentially reaching $7.8 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Manufacturing industries, particularly electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, represent the largest demand segments for biomass-derived solvents. This demand is primarily fueled by stringent volatile organic compound (VOC) emission regulations in North America, Europe, and increasingly in Asia-Pacific regions. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar frameworks worldwide have accelerated the transition from petroleum-based to bio-based solvents.
Consumer preferences have shifted dramatically toward environmentally responsible products, creating market pull for manufacturers to adopt green chemistry principles throughout their production processes. A 2023 industry survey revealed that 68% of global manufacturing companies have sustainability targets that specifically include transitioning to greener solvent alternatives within their operations.
Cost considerations remain a significant factor influencing market adoption. While traditional petroleum-based solvents maintain a price advantage, the gap has narrowed considerably as biomass-derived alternatives achieve economies of scale. The price premium for bio-based solvents has decreased from 30-40% five years ago to 15-20% currently, making them increasingly competitive, especially when considering total lifecycle costs including disposal and regulatory compliance.
Technical performance requirements vary significantly across manufacturing applications. Sectors requiring high-purity processing, such as semiconductor manufacturing and pharmaceutical production, demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for biomass-derived solvents that deliver equivalent or superior performance to conventional options. The electronics industry, in particular, has shown 22% year-over-year growth in green solvent adoption since 2020.
Regional market dynamics show notable differences, with Europe leading adoption rates at approximately 35% market penetration of bio-based solvents in manufacturing, followed by North America at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 17%. However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging economies, particularly India and China, where manufacturing expansion coincides with strengthening environmental regulations.
Supply chain considerations are increasingly influencing market development. Manufacturers express growing concern about solvent availability, consistency, and long-term supply security. This has prompted strategic partnerships between solvent producers and biomass feedstock suppliers to ensure stable production capabilities and consistent quality standards.
Manufacturing industries, particularly electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, represent the largest demand segments for biomass-derived solvents. This demand is primarily fueled by stringent volatile organic compound (VOC) emission regulations in North America, Europe, and increasingly in Asia-Pacific regions. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar frameworks worldwide have accelerated the transition from petroleum-based to bio-based solvents.
Consumer preferences have shifted dramatically toward environmentally responsible products, creating market pull for manufacturers to adopt green chemistry principles throughout their production processes. A 2023 industry survey revealed that 68% of global manufacturing companies have sustainability targets that specifically include transitioning to greener solvent alternatives within their operations.
Cost considerations remain a significant factor influencing market adoption. While traditional petroleum-based solvents maintain a price advantage, the gap has narrowed considerably as biomass-derived alternatives achieve economies of scale. The price premium for bio-based solvents has decreased from 30-40% five years ago to 15-20% currently, making them increasingly competitive, especially when considering total lifecycle costs including disposal and regulatory compliance.
Technical performance requirements vary significantly across manufacturing applications. Sectors requiring high-purity processing, such as semiconductor manufacturing and pharmaceutical production, demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for biomass-derived solvents that deliver equivalent or superior performance to conventional options. The electronics industry, in particular, has shown 22% year-over-year growth in green solvent adoption since 2020.
Regional market dynamics show notable differences, with Europe leading adoption rates at approximately 35% market penetration of bio-based solvents in manufacturing, followed by North America at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 17%. However, the fastest growth is occurring in emerging economies, particularly India and China, where manufacturing expansion coincides with strengthening environmental regulations.
Supply chain considerations are increasingly influencing market development. Manufacturers express growing concern about solvent availability, consistency, and long-term supply security. This has prompted strategic partnerships between solvent producers and biomass feedstock suppliers to ensure stable production capabilities and consistent quality standards.
Current Status and Technical Challenges of Bio-Solvents
The global landscape of bio-solvents has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, with current market valuation estimated at approximately $9.5 billion and projected to reach $13.7 billion by 2025. This growth trajectory is primarily driven by increasing environmental regulations against volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heightened consumer awareness regarding sustainable products. Currently, bio-solvents represent about 13% of the global solvent market, with Europe leading adoption at 41% market share, followed by North America at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 22%.
From a technical standpoint, bio-solvents derived from various biomass feedstocks have achieved commercial viability across several categories. Lactate esters, particularly ethyl lactate derived from corn fermentation, have established presence in coating applications. Glycerol derivatives, a byproduct of biodiesel production, have found applications in cleaning formulations. D-limonene extracted from citrus peels serves as an effective degreasing agent, while 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) produced from agricultural residues offers promising performance in pharmaceutical processing.
Despite these advancements, bio-solvents face significant technical challenges that impede wider industrial adoption. Production scalability remains problematic, with current biorefinery processes struggling to achieve economies of scale comparable to petrochemical routes. Most bio-solvent production facilities operate at capacities below 50,000 tons annually, whereas conventional solvent plants typically exceed 200,000 tons per year. This scale disparity contributes to bio-solvents' 1.5-3x cost premium over petroleum-based alternatives.
Performance consistency presents another major hurdle. Batch-to-batch variations in biomass feedstock composition lead to fluctuations in final solvent properties, creating challenges for manufacturing processes that require precise solvent specifications. Additionally, many bio-solvents exhibit limited chemical stability under certain processing conditions, particularly at elevated temperatures or in the presence of catalysts commonly used in manufacturing.
Purification technologies represent a critical bottleneck in bio-solvent development. Current separation methods, including distillation and extraction, are energy-intensive and often struggle to achieve the 99.5%+ purity levels required for high-precision manufacturing applications. This challenge is particularly pronounced for bio-solvents containing multiple functional groups or those derived from complex biomass streams.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide remain fragmented regarding bio-solvent classification and approval processes. While the EU has established the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) program with provisions for bio-based chemicals, many regions lack standardized protocols for evaluating bio-solvent safety and environmental impact, creating market entry barriers for innovative products.
From a technical standpoint, bio-solvents derived from various biomass feedstocks have achieved commercial viability across several categories. Lactate esters, particularly ethyl lactate derived from corn fermentation, have established presence in coating applications. Glycerol derivatives, a byproduct of biodiesel production, have found applications in cleaning formulations. D-limonene extracted from citrus peels serves as an effective degreasing agent, while 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) produced from agricultural residues offers promising performance in pharmaceutical processing.
Despite these advancements, bio-solvents face significant technical challenges that impede wider industrial adoption. Production scalability remains problematic, with current biorefinery processes struggling to achieve economies of scale comparable to petrochemical routes. Most bio-solvent production facilities operate at capacities below 50,000 tons annually, whereas conventional solvent plants typically exceed 200,000 tons per year. This scale disparity contributes to bio-solvents' 1.5-3x cost premium over petroleum-based alternatives.
Performance consistency presents another major hurdle. Batch-to-batch variations in biomass feedstock composition lead to fluctuations in final solvent properties, creating challenges for manufacturing processes that require precise solvent specifications. Additionally, many bio-solvents exhibit limited chemical stability under certain processing conditions, particularly at elevated temperatures or in the presence of catalysts commonly used in manufacturing.
Purification technologies represent a critical bottleneck in bio-solvent development. Current separation methods, including distillation and extraction, are energy-intensive and often struggle to achieve the 99.5%+ purity levels required for high-precision manufacturing applications. This challenge is particularly pronounced for bio-solvents containing multiple functional groups or those derived from complex biomass streams.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide remain fragmented regarding bio-solvent classification and approval processes. While the EU has established the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) program with provisions for bio-based chemicals, many regions lack standardized protocols for evaluating bio-solvent safety and environmental impact, creating market entry barriers for innovative products.
Current Technical Solutions for Biomass-Derived Solvents
01 Production of bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass
Lignocellulosic biomass can be processed to produce environmentally friendly solvents through various conversion methods. These processes typically involve the breakdown of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin components to create sustainable solvent alternatives. The resulting bio-based solvents offer reduced environmental impact compared to petroleum-derived counterparts while maintaining similar performance characteristics for industrial applications.- Production of biomass-derived solvents from lignocellulosic materials: Processes for converting lignocellulosic biomass into renewable solvents through various conversion pathways including fermentation, hydrolysis, and catalytic reactions. These methods typically involve breaking down cellulose and hemicellulose components into sugars, which are then further processed to produce solvents such as alcohols, esters, and ketones. The resulting bio-based solvents offer environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-derived products with comparable performance characteristics.
- Biomass-derived solvents for polymer applications: Utilization of biomass-derived solvents in polymer processing, formulation, and production. These bio-based solvents can be used in the synthesis of polymers, as processing aids during manufacturing, and as components in polymer formulations. They provide sustainable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents while maintaining or enhancing polymer properties. Applications include adhesives, coatings, and composite materials where the renewable nature of the solvent contributes to improved environmental profiles of the final products.
- Biomass-derived solvents for pulp and paper processing: Application of biomass-derived solvents in the pulp and paper industry for processes such as pulping, bleaching, and chemical recovery. These bio-based solvents can effectively dissolve lignin and other wood components, facilitating fiber separation and processing. The use of these renewable solvents reduces environmental impact compared to traditional chemical pulping methods while potentially improving process efficiency and product quality.
- Biomass-derived solvents for extraction processes: Utilization of biomass-derived solvents for various extraction applications, including the isolation of valuable compounds from natural materials. These green solvents can be used for extracting oils, flavors, fragrances, pharmaceuticals, and other high-value compounds from plant and animal sources. Their renewable origin and often lower toxicity make them attractive alternatives to petroleum-based solvents in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries, where solvent residues are a significant concern.
- Production of furan-based solvents from biomass: Methods for producing furan-based solvents such as furfural, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), and their derivatives from biomass feedstocks. These processes typically involve the dehydration of sugars derived from cellulosic and hemicellulosic materials. Furan-based solvents offer unique properties including high solvency power and biodegradability, making them suitable replacements for conventional solvents in applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to biofuels production.
02 Biomass-derived solvents for pulp and paper processing
Solvents derived from biomass sources can be effectively utilized in pulp and paper manufacturing processes. These green solvents facilitate the dissolution of lignin and other wood components, enabling more environmentally friendly pulping operations. The application of these bio-based solvents can reduce the environmental footprint of paper production while potentially improving process efficiency and product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fermentation-based production of biomass solvents
Microbial fermentation processes can convert biomass feedstocks into valuable solvents. These bioprocesses utilize specialized microorganisms to transform sugars and other biomass components into solvents such as alcohols, esters, and organic acids. The fermentation approach offers advantages including operation under mild conditions, high selectivity, and the ability to utilize diverse biomass sources as raw materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biomass-derived solvents for polymer applications
Bio-based solvents produced from renewable biomass can be utilized in various polymer applications including synthesis, processing, and formulation. These green solvents provide alternatives to traditional petroleum-based solvents in polymer manufacturing, offering benefits such as reduced toxicity, lower environmental impact, and potential improvements in polymer properties. The integration of biomass-derived solvents supports the development of more sustainable polymer production systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Catalytic conversion processes for biomass-to-solvent transformation
Advanced catalytic technologies enable the efficient conversion of biomass into high-quality solvents. These processes employ specialized catalysts to facilitate selective chemical transformations of biomass components under controlled conditions. Catalytic approaches can improve yield, selectivity, and energy efficiency in biomass-to-solvent conversion pathways, making the production of bio-based solvents more economically viable and environmentally sustainable.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Bio-Solvent Development
The biomass-derived solvents market in next-generation manufacturing is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption driven by sustainability demands. The market is expanding at approximately 7-8% CAGR, expected to reach $9-10 billion by 2027. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include Shell Oil and ExxonMobil, who are leveraging their extensive infrastructure to scale production; UOP LLC and Johnson Matthey, who are developing catalytic conversion technologies; and research-focused organizations like Renmatix and Virent pioneering novel extraction methods. Academic institutions such as Tsinghua University and University of Delaware are advancing fundamental research, while specialized companies like Borregaard and OriginClear are creating niche applications for specific industries, indicating a diversifying competitive landscape with both established players and innovative entrants.
Renmatix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Renmatix has developed the Plantrose® Process, a revolutionary technology that uses supercritical water as a biomass-derived solvent to convert plant materials into industrial sugars and lignin. This process operates at high temperatures and pressures where water becomes supercritical, enabling it to act as both a solvent and catalyst for biomass deconstruction. The technology breaks down cellulosic biomass through hydrolysis in minutes rather than days, using only water as the solvent without requiring acids, enzymes, or other chemicals. Their approach represents a significant advancement in biorefinery operations, allowing for the production of cost-competitive cellulosic sugars that can serve as building blocks for biofuels, biochemicals, and biomaterials. The process is particularly notable for its ability to handle diverse feedstocks including agricultural residues, woody biomass, and energy crops, making it highly adaptable to various manufacturing contexts.
Strengths: Environmentally friendly process using only water as solvent; rapid processing time (minutes vs days); versatility in handling multiple feedstock types; production of high-purity cellulosic sugars. Weaknesses: High energy requirements for maintaining supercritical water conditions; significant capital investment for specialized high-pressure equipment; challenges in scaling to industrial production volumes.
Virent, Inc.
Technical Solution: Virent has pioneered the BioForming® technology platform, which utilizes aqueous phase reforming (APR) to convert plant-based sugars into a range of hydrocarbon molecules. Their approach employs water as the primary reaction medium, complemented by proprietary catalysts that enable the transformation of biomass-derived oxygenates into valuable chemicals and fuels. The process begins with the dissolution of biomass-derived sugars in water, followed by catalytic reactions that reduce oxygen content and form C-C bonds, ultimately yielding drop-in replacements for petroleum-based products. A key innovation in Virent's technology is their Catalytic Biomass Liquefaction (CBL) process, which uses specific solvents to solubilize cellulosic biomass components, making them accessible for further conversion. This integrated biorefinery approach allows for the production of bio-based paraxylene, benzene, and gasoline-range molecules that are chemically identical to their fossil-derived counterparts, enabling seamless integration into existing manufacturing infrastructure.
Strengths: Production of true "drop-in" hydrocarbons chemically identical to petroleum-based counterparts; integration capability with existing manufacturing infrastructure; diverse product portfolio including fuels and chemicals; lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum processes. Weaknesses: Dependence on high-quality sugar feedstocks which can increase costs; complex multi-step process requiring precise control; catalyst sensitivity to impurities in biomass-derived streams.
Core Patents and Research in Bio-Solvent Technologies
Process of producing basic biosolvents using heterogeneous catalysts and obtained basic biosolvents by this process
PatentActiveUS20190241837A1
Innovation
- A process using a heterogeneous catalyst, KEYCAT-01, for producing basic biosolvents through inter-esterification and esterification reactions at sub-critical conditions, allowing for continuous operation and eliminating the need for separating residual reactants, with a one-pot reaction system that utilizes inedible vegetable oil or animal fat and waste fatty acids, achieving high yields and efficiency.
A process for the polymerization of vinyl monomers, a process for preparing an adhesive composition, an adhesive composition and a pressure-sensitive adhesive sheet
PatentWO2018033634A1
Innovation
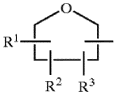
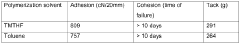
- The use of at least 99.95 wt% pure 2,2,5,5-tetramethyltetrahydrofuran (TMTHF) as a solvent for polymerizing vinyl monomers, which is biomass-based and has a low olefinic content, allowing for radical polymerization to achieve the desired molecular weight and forming a suitable adhesive composition.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Sustainability Metrics
The environmental impact assessment of biomass-derived solvents reveals significant advantages over conventional petroleum-based alternatives. Life cycle analyses demonstrate that these bio-solvents typically produce 30-70% lower greenhouse gas emissions, depending on feedstock source and processing methods. When derived from agricultural waste streams or sustainably harvested biomass, these solvents contribute to circular economy principles by valorizing materials that would otherwise be discarded.
Water consumption metrics show varied results across different biomass-derived solvent types. While some production processes require substantial water inputs, advanced manufacturing techniques have reduced water requirements by up to 40% in recent years. Particularly promising are processes utilizing lignocellulosic biomass, which demonstrate lower water footprints compared to first-generation biofuel-derived solvents.
Land use considerations remain a critical sustainability metric. Solvents derived from dedicated energy crops may compete with food production, potentially leading to indirect land use changes. However, second and third-generation biomass feedstocks that utilize agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, or algal sources significantly mitigate these concerns. Recent studies indicate that integrated biorefinery approaches can optimize land use efficiency by 25-35% compared to single-product systems.
Toxicity profiles of biomass-derived solvents generally show reduced human and ecological hazards. Compounds like ethyl lactate, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and cyrene demonstrate lower aquatic toxicity and improved biodegradability compared to traditional solvents such as acetone or dichloromethane. Standardized ecotoxicity testing protocols reveal that many bio-solvents degrade 60-90% within 28 days under aerobic conditions, compared to persistent conventional alternatives.
Energy intensity metrics indicate that current production methods for biomass-derived solvents often require more energy than petroleum-based counterparts. However, this gap is narrowing with technological advancements. Integrated biorefinery concepts that utilize process heat recovery and biomass-powered operations have demonstrated energy efficiency improvements of 15-25% in the past five years.
Standardized sustainability assessment frameworks, including the Green Chemistry Metrics Toolkit and Sustainable Process Index, provide quantitative measures for comparing solvent options. These frameworks incorporate multiple parameters including atom economy, process mass intensity, and renewable carbon index. When evaluated through these comprehensive metrics, biomass-derived solvents typically achieve sustainability scores 30-50% higher than their petroleum-based counterparts, despite remaining challenges in production scale and economic viability.
Water consumption metrics show varied results across different biomass-derived solvent types. While some production processes require substantial water inputs, advanced manufacturing techniques have reduced water requirements by up to 40% in recent years. Particularly promising are processes utilizing lignocellulosic biomass, which demonstrate lower water footprints compared to first-generation biofuel-derived solvents.
Land use considerations remain a critical sustainability metric. Solvents derived from dedicated energy crops may compete with food production, potentially leading to indirect land use changes. However, second and third-generation biomass feedstocks that utilize agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, or algal sources significantly mitigate these concerns. Recent studies indicate that integrated biorefinery approaches can optimize land use efficiency by 25-35% compared to single-product systems.
Toxicity profiles of biomass-derived solvents generally show reduced human and ecological hazards. Compounds like ethyl lactate, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, and cyrene demonstrate lower aquatic toxicity and improved biodegradability compared to traditional solvents such as acetone or dichloromethane. Standardized ecotoxicity testing protocols reveal that many bio-solvents degrade 60-90% within 28 days under aerobic conditions, compared to persistent conventional alternatives.
Energy intensity metrics indicate that current production methods for biomass-derived solvents often require more energy than petroleum-based counterparts. However, this gap is narrowing with technological advancements. Integrated biorefinery concepts that utilize process heat recovery and biomass-powered operations have demonstrated energy efficiency improvements of 15-25% in the past five years.
Standardized sustainability assessment frameworks, including the Green Chemistry Metrics Toolkit and Sustainable Process Index, provide quantitative measures for comparing solvent options. These frameworks incorporate multiple parameters including atom economy, process mass intensity, and renewable carbon index. When evaluated through these comprehensive metrics, biomass-derived solvents typically achieve sustainability scores 30-50% higher than their petroleum-based counterparts, despite remaining challenges in production scale and economic viability.
Regulatory Framework and Policy Incentives for Bio-Solvents
The regulatory landscape for biomass-derived solvents is rapidly evolving as governments worldwide recognize their potential to reduce environmental impact in manufacturing processes. In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has established stringent frameworks that favor bio-based alternatives over traditional petroleum-derived solvents. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) further supports this transition by setting targets for renewable content in industrial processes, creating a favorable environment for bio-solvent adoption.
In North America, the EPA's Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program has been instrumental in promoting environmentally preferable chemicals, including bio-solvents. The USDA's BioPreferred program offers certification and federal procurement preferences for bio-based products, providing market advantages for manufacturers utilizing biomass-derived solvents in their production processes.
Financial incentives play a crucial role in accelerating industry adoption. Tax credits for research and development in green chemistry, particularly in the United States and Canada, have stimulated innovation in bio-solvent technologies. The EU's Horizon Europe program allocates substantial funding for sustainable chemistry initiatives, with specific calls for projects focused on developing and scaling up bio-solvent applications in manufacturing.
Carbon pricing mechanisms in various regions have indirectly benefited bio-solvent adoption by increasing the cost of carbon-intensive traditional solvents. This economic pressure has prompted manufacturers to seek alternatives with lower carbon footprints, creating market pull for biomass-derived options.
Regional differences in regulatory approaches present both challenges and opportunities. Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have implemented green manufacturing initiatives that include preferential treatment for bio-based materials. However, the lack of harmonized global standards for bio-solvent certification creates market fragmentation and compliance challenges for international manufacturers.
Industry-specific regulations also influence adoption patterns. The pharmaceutical sector faces stringent solvent residue limitations in final products, making the generally lower toxicity profile of many bio-solvents particularly attractive. Similarly, the electronics manufacturing industry is increasingly subject to regulations restricting volatile organic compounds (VOCs), creating opportunities for bio-solvents with lower volatility and emissions profiles.
Future regulatory trends indicate increasing stringency regarding environmental impact assessments for chemical processes, likely accelerating the transition toward bio-based alternatives. Emerging policy frameworks around circular economy principles are expected to further incentivize the use of renewable feedstocks in solvent production, potentially creating new market opportunities for biomass valorization technologies.
In North America, the EPA's Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program has been instrumental in promoting environmentally preferable chemicals, including bio-solvents. The USDA's BioPreferred program offers certification and federal procurement preferences for bio-based products, providing market advantages for manufacturers utilizing biomass-derived solvents in their production processes.
Financial incentives play a crucial role in accelerating industry adoption. Tax credits for research and development in green chemistry, particularly in the United States and Canada, have stimulated innovation in bio-solvent technologies. The EU's Horizon Europe program allocates substantial funding for sustainable chemistry initiatives, with specific calls for projects focused on developing and scaling up bio-solvent applications in manufacturing.
Carbon pricing mechanisms in various regions have indirectly benefited bio-solvent adoption by increasing the cost of carbon-intensive traditional solvents. This economic pressure has prompted manufacturers to seek alternatives with lower carbon footprints, creating market pull for biomass-derived options.
Regional differences in regulatory approaches present both challenges and opportunities. Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have implemented green manufacturing initiatives that include preferential treatment for bio-based materials. However, the lack of harmonized global standards for bio-solvent certification creates market fragmentation and compliance challenges for international manufacturers.
Industry-specific regulations also influence adoption patterns. The pharmaceutical sector faces stringent solvent residue limitations in final products, making the generally lower toxicity profile of many bio-solvents particularly attractive. Similarly, the electronics manufacturing industry is increasingly subject to regulations restricting volatile organic compounds (VOCs), creating opportunities for bio-solvents with lower volatility and emissions profiles.
Future regulatory trends indicate increasing stringency regarding environmental impact assessments for chemical processes, likely accelerating the transition toward bio-based alternatives. Emerging policy frameworks around circular economy principles are expected to further incentivize the use of renewable feedstocks in solvent production, potentially creating new market opportunities for biomass valorization technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!