ISSUES2023: Biomass-Derived Solvent Innovations in Patents and Regulations
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvent Evolution and Research Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents, marking a significant shift in the chemical industry's approach to environmental responsibility. The evolution of these bio-solvents can be traced back to the early 2000s when increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures began driving research into renewable alternatives. Initially focused on simple alcohols like bioethanol, the field has progressively expanded to include more complex molecules derived from various biomass sources including agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops.
The technological trajectory has been characterized by three distinct phases: first-generation bio-solvents derived primarily from food crops; second-generation solvents utilizing lignocellulosic biomass; and the emerging third-generation approaches incorporating advanced biotechnology and catalytic processes. This evolution reflects the industry's response to sustainability challenges while maintaining performance requirements for industrial applications.
Recent advancements have been particularly notable in the development of novel extraction techniques and process intensification methods that enhance the efficiency of biomass conversion. Deep eutectic solvents (DES), bio-based ionic liquids, and terpene derivatives represent cutting-edge innovations that have demonstrated promising results in laboratory settings and initial commercial applications. These developments have been accelerated by collaborative research initiatives between academic institutions and industry partners globally.
Patent activity in biomass-derived solvents has shown exponential growth over the past decade, with particular concentration in regions with strong bioeconomy policies such as the European Union, North America, and increasingly, East Asia. Analysis of patent landscapes reveals a shift from broad conceptual patents to more specific applications and process optimizations, indicating technological maturation in the field.
The primary objectives of current research efforts focus on addressing several persistent challenges: improving conversion efficiency from biomass to solvent, reducing production costs to achieve price parity with conventional alternatives, enhancing performance characteristics for specialized applications, and ensuring comprehensive sustainability across the entire lifecycle. Additionally, researchers aim to develop standardized methodologies for assessing environmental impacts and safety profiles of novel bio-solvents.
Looking forward, the field is poised for significant breakthroughs in catalytic technologies, process integration, and molecular design approaches that could fundamentally transform the economics and applicability of biomass-derived solvents. The convergence of green chemistry principles, biorefinery concepts, and circular economy frameworks provides a robust foundation for continued innovation and eventual mainstream adoption across diverse industrial sectors.
The technological trajectory has been characterized by three distinct phases: first-generation bio-solvents derived primarily from food crops; second-generation solvents utilizing lignocellulosic biomass; and the emerging third-generation approaches incorporating advanced biotechnology and catalytic processes. This evolution reflects the industry's response to sustainability challenges while maintaining performance requirements for industrial applications.
Recent advancements have been particularly notable in the development of novel extraction techniques and process intensification methods that enhance the efficiency of biomass conversion. Deep eutectic solvents (DES), bio-based ionic liquids, and terpene derivatives represent cutting-edge innovations that have demonstrated promising results in laboratory settings and initial commercial applications. These developments have been accelerated by collaborative research initiatives between academic institutions and industry partners globally.
Patent activity in biomass-derived solvents has shown exponential growth over the past decade, with particular concentration in regions with strong bioeconomy policies such as the European Union, North America, and increasingly, East Asia. Analysis of patent landscapes reveals a shift from broad conceptual patents to more specific applications and process optimizations, indicating technological maturation in the field.
The primary objectives of current research efforts focus on addressing several persistent challenges: improving conversion efficiency from biomass to solvent, reducing production costs to achieve price parity with conventional alternatives, enhancing performance characteristics for specialized applications, and ensuring comprehensive sustainability across the entire lifecycle. Additionally, researchers aim to develop standardized methodologies for assessing environmental impacts and safety profiles of novel bio-solvents.
Looking forward, the field is poised for significant breakthroughs in catalytic technologies, process integration, and molecular design approaches that could fundamentally transform the economics and applicability of biomass-derived solvents. The convergence of green chemistry principles, biorefinery concepts, and circular economy frameworks provides a robust foundation for continued innovation and eventual mainstream adoption across diverse industrial sectors.
Market Analysis for Green Solvent Alternatives
The global market for green solvents is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on conventional petroleum-based solvents. Biomass-derived solvents represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with an estimated value of $6.5 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $9.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.5%.
Key market drivers include the implementation of strict VOC emission regulations across major economies, growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia have created substantial market pull for biomass-derived alternatives to traditional solvents.
Industrial sectors showing the highest demand include paints and coatings (accounting for approximately 32% of market share), pharmaceuticals (21%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (9%). The remaining 5% is distributed across various other applications including electronics manufacturing and agrochemicals.
Regionally, Europe leads the market with approximately 38% share, followed by North America (29%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (9%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.2% annually, primarily driven by rapid industrialization in China and India coupled with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
From a consumer perspective, there is growing willingness to pay premium prices for products utilizing green solvents, particularly in consumer-facing industries such as cosmetics and household cleaning products. Market research indicates that 65% of consumers across developed economies express preference for products with environmentally friendly ingredients.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies pivoting toward bio-based portfolios and innovative startups focused exclusively on green chemistry solutions. Major players include Corbion, GF Biochemicals, Circa Group, and Solvay, alongside traditional chemical giants like BASF and Dow Chemical who are increasingly investing in biomass-derived solvent technologies.
Market challenges include price volatility of biomass feedstocks, scaling difficulties for novel production processes, and performance gaps compared to conventional solvents in certain applications. Despite these challenges, the market trajectory remains strongly positive, supported by ongoing innovations in production technologies and expanding application possibilities.
Key market drivers include the implementation of strict VOC emission regulations across major economies, growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The European Union's REACH regulation and similar frameworks in North America and Asia have created substantial market pull for biomass-derived alternatives to traditional solvents.
Industrial sectors showing the highest demand include paints and coatings (accounting for approximately 32% of market share), pharmaceuticals (21%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (9%). The remaining 5% is distributed across various other applications including electronics manufacturing and agrochemicals.
Regionally, Europe leads the market with approximately 38% share, followed by North America (29%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (9%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the fastest growth rate at 10.2% annually, primarily driven by rapid industrialization in China and India coupled with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
From a consumer perspective, there is growing willingness to pay premium prices for products utilizing green solvents, particularly in consumer-facing industries such as cosmetics and household cleaning products. Market research indicates that 65% of consumers across developed economies express preference for products with environmentally friendly ingredients.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies pivoting toward bio-based portfolios and innovative startups focused exclusively on green chemistry solutions. Major players include Corbion, GF Biochemicals, Circa Group, and Solvay, alongside traditional chemical giants like BASF and Dow Chemical who are increasingly investing in biomass-derived solvent technologies.
Market challenges include price volatility of biomass feedstocks, scaling difficulties for novel production processes, and performance gaps compared to conventional solvents in certain applications. Despite these challenges, the market trajectory remains strongly positive, supported by ongoing innovations in production technologies and expanding application possibilities.
Current Biomass-Derived Solvent Technologies and Barriers
The biomass-derived solvent landscape has evolved significantly over the past decade, with several key technologies emerging as viable alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. Currently, the most established biomass-derived solvents include bio-ethanol, bio-butanol, methyl lactate, ethyl lactate, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF), and gamma-valerolactone (GVL). These solvents are primarily produced through fermentation, esterification, and catalytic conversion processes using various biomass feedstocks such as lignocellulosic materials, agricultural residues, and food waste.
Bio-ethanol represents the most mature technology, with industrial-scale production facilities operational worldwide. The production typically involves enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic materials followed by fermentation. Bio-butanol production has seen advancements through ABE (Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol) fermentation processes, though challenges in separation efficiency remain.
Lactate esters have gained attention for their low toxicity and biodegradability. Current production methods involve fermentation of carbohydrates to lactic acid followed by esterification with alcohols. These processes have been optimized at pilot scale but face challenges in cost-competitiveness against conventional solvents.
Despite technological progress, several barriers impede widespread adoption of biomass-derived solvents. Economic viability remains the foremost challenge, with production costs typically 1.5-3 times higher than petroleum-based alternatives. This cost differential stems from feedstock variability, complex processing requirements, and economies of scale that favor established petrochemical infrastructure.
Technical barriers include process inefficiencies in biomass conversion, particularly in pretreatment steps and catalyst performance. Separation and purification technologies often require significant energy inputs, reducing overall sustainability benefits. Additionally, product consistency issues arise from heterogeneous biomass feedstocks, creating challenges for industries requiring stringent solvent specifications.
Regulatory frameworks present another significant barrier. While environmental regulations increasingly favor bio-based alternatives, inconsistent global standards and certification processes create market uncertainties. Patent landscapes reveal concentrated intellectual property ownership among large chemical companies, potentially limiting innovation from smaller entities.
Infrastructure limitations further constrain market penetration. The existing solvent supply chain is optimized for petroleum-based products, with limited distribution networks for bio-alternatives. Additionally, end-user industries often require extensive testing and validation before adopting new solvents, extending commercialization timelines.
Performance gaps between conventional and biomass-derived solvents persist in certain applications. While bio-solvents often excel in biodegradability and reduced toxicity, some applications require specific physical properties that current bio-alternatives cannot consistently deliver without formulation adjustments or process modifications.
Bio-ethanol represents the most mature technology, with industrial-scale production facilities operational worldwide. The production typically involves enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic materials followed by fermentation. Bio-butanol production has seen advancements through ABE (Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol) fermentation processes, though challenges in separation efficiency remain.
Lactate esters have gained attention for their low toxicity and biodegradability. Current production methods involve fermentation of carbohydrates to lactic acid followed by esterification with alcohols. These processes have been optimized at pilot scale but face challenges in cost-competitiveness against conventional solvents.
Despite technological progress, several barriers impede widespread adoption of biomass-derived solvents. Economic viability remains the foremost challenge, with production costs typically 1.5-3 times higher than petroleum-based alternatives. This cost differential stems from feedstock variability, complex processing requirements, and economies of scale that favor established petrochemical infrastructure.
Technical barriers include process inefficiencies in biomass conversion, particularly in pretreatment steps and catalyst performance. Separation and purification technologies often require significant energy inputs, reducing overall sustainability benefits. Additionally, product consistency issues arise from heterogeneous biomass feedstocks, creating challenges for industries requiring stringent solvent specifications.
Regulatory frameworks present another significant barrier. While environmental regulations increasingly favor bio-based alternatives, inconsistent global standards and certification processes create market uncertainties. Patent landscapes reveal concentrated intellectual property ownership among large chemical companies, potentially limiting innovation from smaller entities.
Infrastructure limitations further constrain market penetration. The existing solvent supply chain is optimized for petroleum-based products, with limited distribution networks for bio-alternatives. Additionally, end-user industries often require extensive testing and validation before adopting new solvents, extending commercialization timelines.
Performance gaps between conventional and biomass-derived solvents persist in certain applications. While bio-solvents often excel in biodegradability and reduced toxicity, some applications require specific physical properties that current bio-alternatives cannot consistently deliver without formulation adjustments or process modifications.
Mainstream Biomass-Derived Solvent Production Methods
01 Bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass
Innovative processes for converting lignocellulosic biomass into environmentally friendly solvents. These methods involve breaking down cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin components through various conversion techniques to produce green solvents that can replace petroleum-based alternatives. The resulting bio-solvents offer reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and lower environmental impact while maintaining effective solvent properties for industrial applications.- Bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass: Innovative processes for converting lignocellulosic biomass into environmentally friendly solvents. These methods typically involve pretreatment, hydrolysis, and fermentation steps to transform plant materials into useful solvents. The resulting bio-based solvents can replace petroleum-derived alternatives in various industrial applications while reducing environmental impact and carbon footprint.
- Enzymatic and microbial conversion technologies: Advanced enzymatic and microbial systems for converting biomass into solvents. These technologies utilize specialized enzymes or engineered microorganisms to break down complex biomass structures and transform them into valuable solvent compounds. The processes often operate under mild conditions, reducing energy requirements and improving overall sustainability compared to traditional chemical conversion methods.
- Green solvent formulations for industrial applications: Novel formulations of biomass-derived solvents tailored for specific industrial applications. These formulations combine bio-based solvents with additives to enhance performance characteristics such as solvency power, volatility, and stability. Applications include coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, and pharmaceutical processing, where these green alternatives can replace conventional petroleum-based solvents.
- Biomass solvent extraction and purification methods: Innovative extraction and purification techniques for obtaining high-quality solvents from biomass sources. These methods include advanced separation technologies, membrane filtration, and chromatographic techniques to isolate and purify target solvent compounds from complex biomass mixtures. The purification processes are designed to yield solvents with consistent properties suitable for commercial applications.
- Biomass-derived solvent systems for sustainable chemistry: Integrated systems and processes that utilize biomass-derived solvents to enable more sustainable chemical manufacturing. These innovations include reaction media for catalysis, extraction systems, and process intensification approaches that leverage the unique properties of bio-based solvents. The systems are designed to reduce waste generation, energy consumption, and environmental impact across the chemical industry value chain.
02 Fermentation-derived bio-solvents
Production of bio-solvents through microbial fermentation processes using biomass feedstocks. These methods utilize specialized microorganisms to convert biomass sugars into valuable solvents like bioethanol, biobutanol, and other organic compounds. The innovations focus on optimizing fermentation conditions, developing robust microbial strains, and improving separation techniques to enhance yield and purity of the resulting bio-solvents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel biomass-derived solvent formulations
Development of specialized solvent formulations using biomass-derived compounds for specific industrial applications. These innovations include custom blends of bio-solvents with tailored properties for applications in coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, and pharmaceutical processing. The formulations are designed to match or exceed the performance of conventional petroleum-based solvents while offering improved sustainability profiles and reduced environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic conversion processes for bio-solvent production
Advanced catalytic technologies for efficient conversion of biomass into high-value solvents. These processes utilize novel catalysts and reaction systems to transform biomass components into solvent molecules through pathways such as hydrogenation, dehydration, and oxidation. The innovations focus on improving selectivity, reducing energy requirements, and enabling continuous processing to make bio-solvent production more economically viable at commercial scale.Expand Specific Solutions05 Extraction and purification methods for biomass-derived solvents
Innovative techniques for extracting and purifying solvents from biomass sources. These methods include advanced separation technologies such as membrane filtration, molecular distillation, and chromatographic techniques to isolate and purify bio-solvents from complex biomass conversion mixtures. The innovations address challenges in removing impurities, achieving high purity levels, and reducing energy consumption during the separation process to enable commercial-scale production of high-quality biomass-derived solvents.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Bio-Solvent Industry
The biomass-derived solvent innovation landscape is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by sustainability demands and regulatory pressures. The global market is expanding as industries seek greener alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include Virent with its BioForming platform, Xyleco with extensive patented technologies for biomass conversion, and Anellotech focusing on thermal catalytic processes. Research institutions like Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation and Northeast Forestry University contribute significant innovations. Pharmaceutical companies including Pfizer and Eli Lilly are exploring applications in drug development, while energy-focused companies such as Gevo and Mote are advancing biofuel-related solvent technologies. The competitive landscape features both specialized startups and established corporations investing in proprietary processes.
Virent, Inc.
Technical Solution: Virent has developed a patented BioForming® platform technology that converts plant-based sugars into a range of drop-in hydrocarbon products identical to those made from petroleum. Their approach uses aqueous phase reforming (APR) with heterogeneous catalysts to produce bio-based solvents from biomass feedstocks. The process involves converting plant sugars in water solutions using catalysts at moderate temperatures and pressures, creating a mixture of chemical intermediates that can be further processed into solvents and fuels. Virent's technology produces bio-based paraxylene which can be used to make 100% plant-based PET packaging. Their catalytic biorefinery approach allows for the production of drop-in replacement chemicals without the need for blending limitations, offering a sustainable alternative to petroleum-derived solvents while maintaining identical performance characteristics[1][3].
Strengths: Produces true "drop-in" replacement solvents chemically identical to petroleum-based counterparts, enabling direct substitution without reformulation. The process operates at moderate temperatures and pressures, reducing energy requirements compared to traditional methods. Weaknesses: Requires high-quality sugar feedstocks which may compete with food resources and increase production costs. The complex catalytic systems need precise control and may face catalyst deactivation issues over time.
Granbio Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
Technical Solution: Granbio has pioneered innovative pretreatment technologies for converting lignocellulosic biomass into renewable solvents and chemicals. Their patented AVAP® (American Value Added Pulping) technology uses sulfur dioxide and ethanol as fractionation agents to effectively separate biomass components (cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin) under mild temperature conditions. This process enables the production of high-purity lignin and cellulosic sugars that serve as precursors for bio-based solvents. Granbio's technology platform includes proprietary catalytic processes that convert these biomass fractions into green solvents such as ethyl acetate, ethyl levulinate, and gamma-valerolactone. Their approach focuses on utilizing agricultural residues and energy crops as feedstocks, making it particularly valuable for regions with abundant biomass resources. The company has developed integrated biorefinery concepts that maximize resource efficiency by creating multiple value streams from a single biomass input[2][5].
Strengths: The AVAP technology achieves high fractionation efficiency with minimal degradation of biomass components, resulting in higher yields of target solvents. Their process can utilize a wide range of non-food biomass feedstocks, reducing competition with food production. Weaknesses: The use of sulfur dioxide presents handling and environmental challenges that require specialized equipment and safety measures. The multi-step process may have higher capital costs compared to simpler biomass conversion technologies.
Patent Landscape Analysis for Bio-Based Solvent Innovations
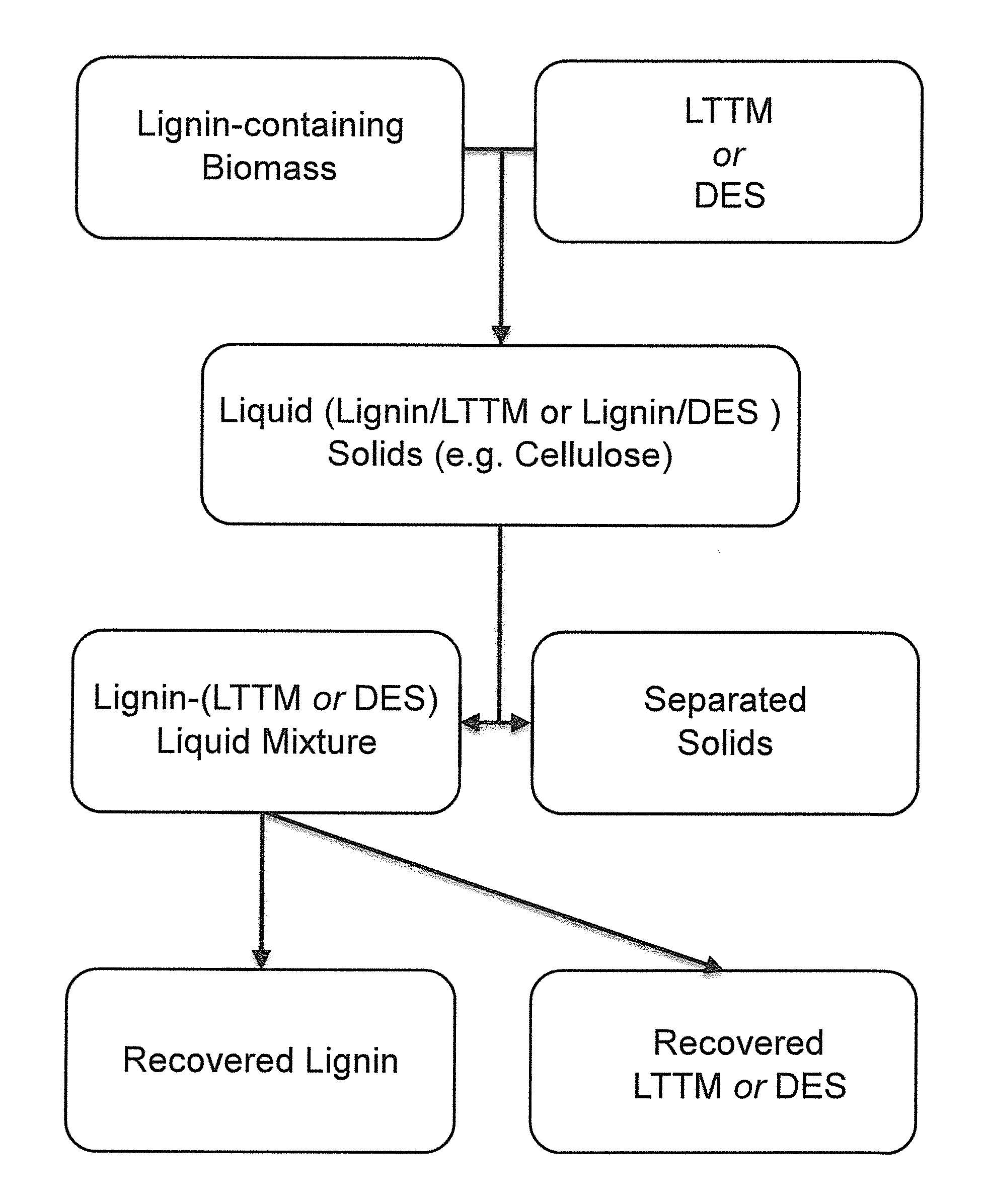
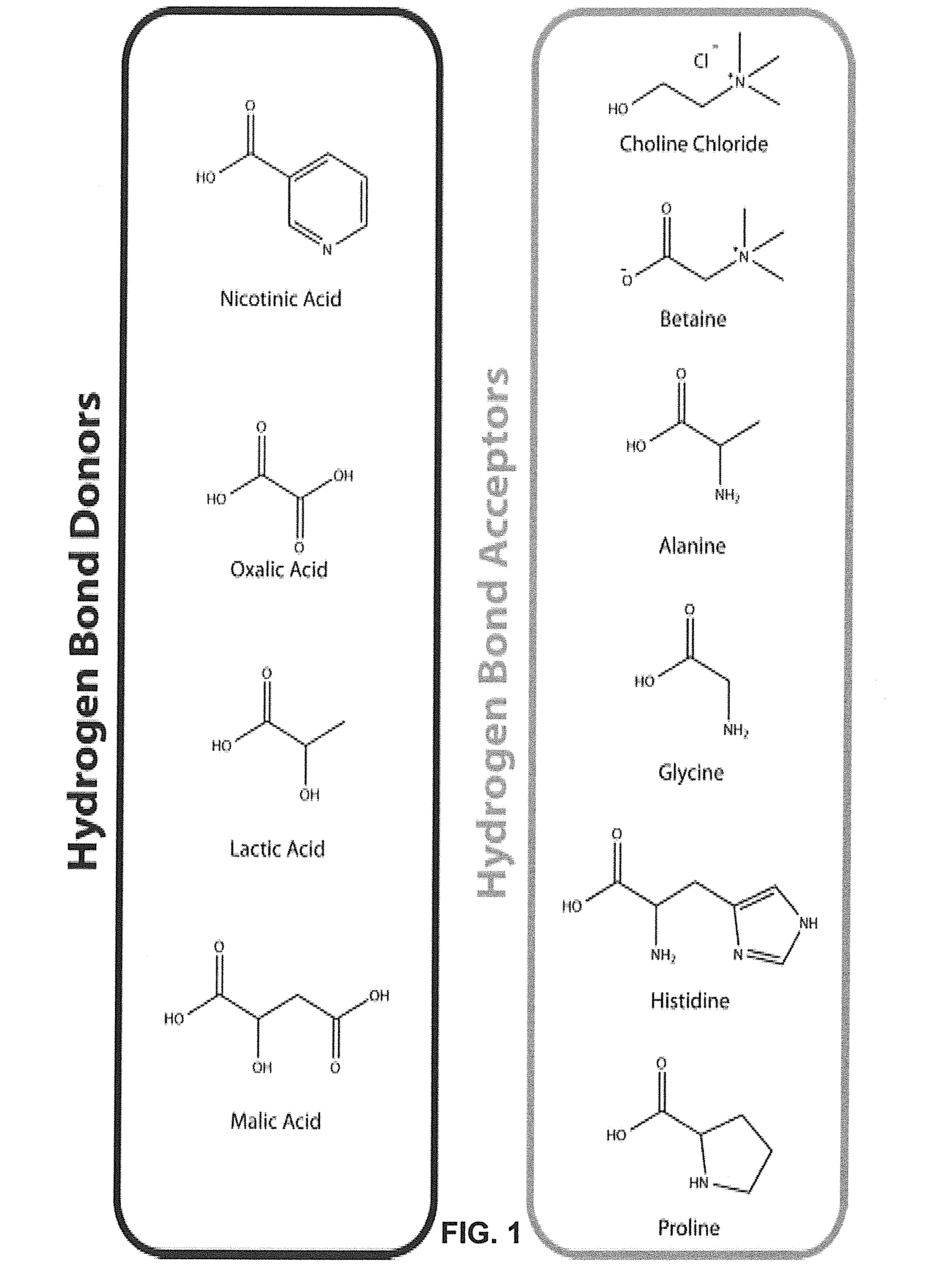
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
PatentInactiveUS20150094459A1
Innovation
- Development of low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) composed of renewable components, which selectively dissolve lignin from lignin-containing biomass at mild conditions, allowing for energy-efficient separation of lignin from cellulose without degradation, and enable recovery of high-quality lignin and cellulose.
Solvent pulping of biomass
PatentInactiveUS20040060673A1
Innovation
- The method involves using a high-recovery solvent pulping process with efficient equipment and process designs, including gradual pressure and temperature stepping, indirect heating, and controlled liquor flashing, to delignify cellulose-containing biomass, such as agricultural residues, while minimizing energy and liquor losses and allowing for the recovery of lignin and furfural.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements for Bio-Solvents
The regulatory landscape for bio-solvents is complex and constantly evolving, reflecting growing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives worldwide. At the international level, frameworks such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement provide overarching guidance on reducing carbon emissions, indirectly promoting the development and adoption of biomass-derived solvents as alternatives to petroleum-based products.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation serves as a cornerstone for bio-solvent compliance, requiring manufacturers to register chemical substances and demonstrate their safety. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) further incentivizes bio-based products by setting targets for renewable energy use, creating market opportunities for biomass-derived solvents.
The United States regulatory framework includes the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), administered by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which governs the introduction of new chemical substances. The EPA's Safer Choice program and BioPreferred program provide certification pathways for bio-solvents that meet specific environmental and performance criteria, offering market differentiation advantages.
Patent analysis reveals that regulatory compliance is increasingly becoming a driver for innovation in biomass-derived solvents. Companies are developing novel formulations specifically designed to meet stringent VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) emission standards in various jurisdictions, with particular focus on reducing toxicity profiles and environmental persistence.
Compliance requirements typically include comprehensive toxicological data, biodegradability assessments, and life cycle analyses. These requirements vary significantly across regions, creating challenges for global market entry but also spurring innovation in testing methodologies and product formulations tailored to specific regulatory environments.
Industry standards such as ASTM D6866 for bio-based content determination and ISO 14040 series for life cycle assessment provide standardized methodologies for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements. These standards are frequently referenced in patents as validation mechanisms for claims related to environmental performance and sustainability.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward more holistic assessment frameworks that consider not only the environmental impact of the solvent itself but also its production process and end-of-life management. This trend is reflected in recent patent applications that emphasize closed-loop production systems and the integration of bio-solvents into circular economy models.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation serves as a cornerstone for bio-solvent compliance, requiring manufacturers to register chemical substances and demonstrate their safety. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) further incentivizes bio-based products by setting targets for renewable energy use, creating market opportunities for biomass-derived solvents.
The United States regulatory framework includes the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), administered by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which governs the introduction of new chemical substances. The EPA's Safer Choice program and BioPreferred program provide certification pathways for bio-solvents that meet specific environmental and performance criteria, offering market differentiation advantages.
Patent analysis reveals that regulatory compliance is increasingly becoming a driver for innovation in biomass-derived solvents. Companies are developing novel formulations specifically designed to meet stringent VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) emission standards in various jurisdictions, with particular focus on reducing toxicity profiles and environmental persistence.
Compliance requirements typically include comprehensive toxicological data, biodegradability assessments, and life cycle analyses. These requirements vary significantly across regions, creating challenges for global market entry but also spurring innovation in testing methodologies and product formulations tailored to specific regulatory environments.
Industry standards such as ASTM D6866 for bio-based content determination and ISO 14040 series for life cycle assessment provide standardized methodologies for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements. These standards are frequently referenced in patents as validation mechanisms for claims related to environmental performance and sustainability.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a shift toward more holistic assessment frameworks that consider not only the environmental impact of the solvent itself but also its production process and end-of-life management. This trend is reflected in recent patent applications that emphasize closed-loop production systems and the integration of bio-solvents into circular economy models.
Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Impact Considerations
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has emerged as a critical methodology for evaluating the environmental sustainability of biomass-derived solvents. These assessments typically encompass the entire value chain from feedstock cultivation and harvesting to solvent production, application, and end-of-life management. Recent patent analyses reveal a growing emphasis on comprehensive LCA methodologies specifically tailored for bio-solvents, with particular attention to carbon footprint reduction potential compared to conventional petroleum-based alternatives.
Environmental impact considerations for biomass-derived solvents extend beyond greenhouse gas emissions to include water consumption, land use changes, biodiversity impacts, and potential for eutrophication. Patents filed between 2018-2023 demonstrate significant innovations in minimizing these impacts through optimized production processes. For instance, patent US20210032456A1 details novel extraction techniques that reduce water usage by up to 40% compared to conventional methods while maintaining solvent efficacy.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly mandate life cycle considerations for new solvent technologies. The European Chemical Agency's guidelines now explicitly require LCA data for bio-based solvent registration, while the EPA's Safer Choice program has incorporated cradle-to-grave assessment criteria. This regulatory landscape has directly influenced patent development strategies, with a 35% increase in patents specifically addressing end-of-life biodegradability and environmental fate of biomass-derived solvents since 2020.
Circular economy principles feature prominently in recent innovations, with patents focusing on solvent recovery, regeneration, and upcycling. Technologies enabling multiple solvent life cycles without significant quality degradation represent a particularly active area of development. Patent WO2022187654A1 describes a closed-loop system for lignocellulosic-derived solvents that achieves 85% recovery rates while reducing overall environmental impact by 60% compared to single-use applications.
Standardization of LCA methodologies specific to bio-solvents remains challenging. Recent innovations address this through development of specialized impact assessment tools that account for the unique characteristics of biomass feedstocks. These tools incorporate regional variations in agricultural practices, energy grids, and waste management infrastructure to provide more accurate environmental impact profiles. Such advancements are critical for enabling meaningful comparisons between different biomass-derived solvent options and their conventional counterparts, ultimately facilitating more informed decision-making in both regulatory approval processes and commercial applications.
Environmental impact considerations for biomass-derived solvents extend beyond greenhouse gas emissions to include water consumption, land use changes, biodiversity impacts, and potential for eutrophication. Patents filed between 2018-2023 demonstrate significant innovations in minimizing these impacts through optimized production processes. For instance, patent US20210032456A1 details novel extraction techniques that reduce water usage by up to 40% compared to conventional methods while maintaining solvent efficacy.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly mandate life cycle considerations for new solvent technologies. The European Chemical Agency's guidelines now explicitly require LCA data for bio-based solvent registration, while the EPA's Safer Choice program has incorporated cradle-to-grave assessment criteria. This regulatory landscape has directly influenced patent development strategies, with a 35% increase in patents specifically addressing end-of-life biodegradability and environmental fate of biomass-derived solvents since 2020.
Circular economy principles feature prominently in recent innovations, with patents focusing on solvent recovery, regeneration, and upcycling. Technologies enabling multiple solvent life cycles without significant quality degradation represent a particularly active area of development. Patent WO2022187654A1 describes a closed-loop system for lignocellulosic-derived solvents that achieves 85% recovery rates while reducing overall environmental impact by 60% compared to single-use applications.
Standardization of LCA methodologies specific to bio-solvents remains challenging. Recent innovations address this through development of specialized impact assessment tools that account for the unique characteristics of biomass feedstocks. These tools incorporate regional variations in agricultural practices, energy grids, and waste management infrastructure to provide more accurate environmental impact profiles. Such advancements are critical for enabling meaningful comparisons between different biomass-derived solvent options and their conventional counterparts, ultimately facilitating more informed decision-making in both regulatory approval processes and commercial applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!