How Biomass-Derived Solvent Technologies Influence Patent Filings
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvent Evolution and Research Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a significant area of research and development over the past three decades, evolving from conceptual environmental alternatives to commercially viable products. The trajectory of this technology began in the early 1990s with initial explorations into plant-based alternatives to petrochemical solvents, primarily driven by growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures on volatile organic compounds (VOCs). By the early 2000s, research had expanded significantly, focusing on extraction methodologies from various biomass sources including agricultural waste, forestry residues, and dedicated energy crops.
The technological evolution accelerated markedly after 2010, coinciding with broader sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles gaining traction globally. This period witnessed the transition from laboratory-scale demonstrations to pilot plant operations, with several biomass-derived solvents achieving commercial production status. Key technological milestones include the development of efficient conversion processes for lignocellulosic materials, innovations in separation technologies, and breakthroughs in catalytic systems that enable selective transformation of biomass components into targeted solvent molecules.
Patent activity in this domain reflects this evolutionary path, with filing patterns showing distinct phases: initial concept protection (1990-2005), process optimization patents (2005-2015), and more recently, application-specific innovations (2015-present). The geographical distribution of patent filings has shifted from predominantly North American and European origins to include significant contributions from Asian research institutions and companies, particularly from China, Japan, and South Korea.
Current research objectives in biomass-derived solvent technologies center around several critical areas. First, enhancing conversion efficiency to improve economic viability compared to conventional petrochemical alternatives. Second, expanding the range of biomass feedstocks that can be effectively utilized, with particular emphasis on non-food competing sources. Third, developing solvents with tailored properties for specific high-value applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and advanced materials manufacturing.
The patent landscape increasingly reflects these objectives, with a notable trend toward protecting intellectual property related to solvent systems designed for precision applications rather than general-purpose use. This shift indicates a maturation of the technology field, moving from broad conceptual patents to highly specialized implementations that deliver specific performance advantages in targeted industries.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of biomass-derived solvents with increasing focus on performance metrics beyond environmental attributes, including enhanced selectivity, stability, and functionality. This evolution is expected to generate new waves of patent filings as researchers and companies position themselves in this growing market segment that bridges renewable resources with advanced chemical applications.
The technological evolution accelerated markedly after 2010, coinciding with broader sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles gaining traction globally. This period witnessed the transition from laboratory-scale demonstrations to pilot plant operations, with several biomass-derived solvents achieving commercial production status. Key technological milestones include the development of efficient conversion processes for lignocellulosic materials, innovations in separation technologies, and breakthroughs in catalytic systems that enable selective transformation of biomass components into targeted solvent molecules.
Patent activity in this domain reflects this evolutionary path, with filing patterns showing distinct phases: initial concept protection (1990-2005), process optimization patents (2005-2015), and more recently, application-specific innovations (2015-present). The geographical distribution of patent filings has shifted from predominantly North American and European origins to include significant contributions from Asian research institutions and companies, particularly from China, Japan, and South Korea.
Current research objectives in biomass-derived solvent technologies center around several critical areas. First, enhancing conversion efficiency to improve economic viability compared to conventional petrochemical alternatives. Second, expanding the range of biomass feedstocks that can be effectively utilized, with particular emphasis on non-food competing sources. Third, developing solvents with tailored properties for specific high-value applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics, and advanced materials manufacturing.
The patent landscape increasingly reflects these objectives, with a notable trend toward protecting intellectual property related to solvent systems designed for precision applications rather than general-purpose use. This shift indicates a maturation of the technology field, moving from broad conceptual patents to highly specialized implementations that deliver specific performance advantages in targeted industries.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of biomass-derived solvents with increasing focus on performance metrics beyond environmental attributes, including enhanced selectivity, stability, and functionality. This evolution is expected to generate new waves of patent filings as researchers and companies position themselves in this growing market segment that bridges renewable resources with advanced chemical applications.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Solvent Solutions
The sustainable solvents market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The global green solvents market was valued at approximately $4.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $6.6 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.9%. Biomass-derived solvents represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with particularly strong growth in bio-alcohols, terpenes, and glycerol derivatives.
Regional analysis reveals that Europe currently leads the sustainable solvents market, accounting for roughly 35% of global demand, followed by North America at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. The European dominance stems from stringent environmental regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal, which actively promote the transition away from petroleum-based chemicals.
Key industry verticals driving demand include paints and coatings (32% market share), pharmaceuticals (21%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (8%). The paints and coatings sector represents the largest application area due to increasing VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) regulations and consumer preference for low-toxicity products.
Patent filing trends indicate accelerating innovation in biomass-derived solvents, with annual patent applications increasing by 12.7% over the past five years. This surge in intellectual property development correlates directly with expanding market opportunities and technological advancements in biomass processing techniques.
Price comparison analysis shows that while biomass-derived solvents typically command a 15-30% premium over conventional petroleum-based alternatives, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and processing technologies improve. The total cost of ownership calculations increasingly favor bio-based options when factoring in regulatory compliance costs, waste disposal, and workplace safety considerations.
Consumer willingness-to-pay studies demonstrate that 68% of industrial purchasers are prepared to accept a 10-15% price premium for sustainable solvents if performance characteristics match conventional options. This price tolerance increases to 25% in consumer-facing applications where marketing benefits can be realized.
Market forecasts suggest biomass-derived solvents will capture 18% of the total solvents market by 2030, up from 7% today, representing a substantial growth opportunity. This expansion is expected to accelerate as biorefineries achieve greater economies of scale and as carbon pricing mechanisms become more widespread globally.
Regional analysis reveals that Europe currently leads the sustainable solvents market, accounting for roughly 35% of global demand, followed by North America at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 25%. The European dominance stems from stringent environmental regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal, which actively promote the transition away from petroleum-based chemicals.
Key industry verticals driving demand include paints and coatings (32% market share), pharmaceuticals (21%), cosmetics and personal care (18%), cleaning products (15%), and adhesives (8%). The paints and coatings sector represents the largest application area due to increasing VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) regulations and consumer preference for low-toxicity products.
Patent filing trends indicate accelerating innovation in biomass-derived solvents, with annual patent applications increasing by 12.7% over the past five years. This surge in intellectual property development correlates directly with expanding market opportunities and technological advancements in biomass processing techniques.
Price comparison analysis shows that while biomass-derived solvents typically command a 15-30% premium over conventional petroleum-based alternatives, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and processing technologies improve. The total cost of ownership calculations increasingly favor bio-based options when factoring in regulatory compliance costs, waste disposal, and workplace safety considerations.
Consumer willingness-to-pay studies demonstrate that 68% of industrial purchasers are prepared to accept a 10-15% price premium for sustainable solvents if performance characteristics match conventional options. This price tolerance increases to 25% in consumer-facing applications where marketing benefits can be realized.
Market forecasts suggest biomass-derived solvents will capture 18% of the total solvents market by 2030, up from 7% today, representing a substantial growth opportunity. This expansion is expected to accelerate as biorefineries achieve greater economies of scale and as carbon pricing mechanisms become more widespread globally.
Global Landscape of Biomass-Derived Solvent Technologies
The biomass-derived solvent technology landscape has evolved significantly over the past decade, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures to reduce dependence on petroleum-based chemicals. Currently, the global distribution of research and development in this field shows distinct regional patterns, with North America, Europe, and East Asia emerging as the primary innovation hubs.
North America, particularly the United States, leads in patent filings related to lignocellulosic biomass conversion technologies, with significant contributions from both academic institutions and industrial players. The U.S. Department of Energy's Bioenergy Technologies Office has been instrumental in fostering innovation through substantial funding initiatives, resulting in a robust patent portfolio focused on cellulosic ethanol and bio-derived esters.
The European landscape is characterized by a strong emphasis on green chemistry principles, with countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands demonstrating particular strength in patents related to supercritical CO2 extraction methods and ionic liquid applications for biomass processing. The European Union's Horizon programs have strategically directed research funding toward sustainable solvent technologies, creating clusters of innovation around major research universities.
In Asia, China has rapidly emerged as a dominant force, with patent filings in biomass-derived solvents increasing at an annual rate of approximately 15% over the past five years. Japanese and South Korean companies maintain significant patent portfolios focused on high-value applications in electronics manufacturing and pharmaceutical processing, where bio-based solvents offer critical performance advantages.
Developing economies, particularly Brazil and India, are establishing specialized niches in the global landscape. Brazil's patents predominantly focus on sugarcane-based solvent technologies, leveraging their agricultural strengths, while India shows growing innovation in cost-effective production methods suitable for distributed manufacturing models.
Cross-border collaborations are increasingly evident in patent filings, with multinational corporations partnering with regional research institutions to develop technologies adapted to local biomass feedstocks. This trend is particularly pronounced in technologies targeting agricultural waste valorization, where regional biomass composition significantly influences solvent selection and process design.
The patent landscape reveals a gradual shift from first-generation biomass solvents (primarily ethanol) toward more sophisticated second and third-generation technologies incorporating designer solvents with enhanced selectivity and reduced environmental impact. Deep eutectic solvents and bio-derived supercritical fluids represent the fastest-growing patent categories, indicating the direction of future market development.
North America, particularly the United States, leads in patent filings related to lignocellulosic biomass conversion technologies, with significant contributions from both academic institutions and industrial players. The U.S. Department of Energy's Bioenergy Technologies Office has been instrumental in fostering innovation through substantial funding initiatives, resulting in a robust patent portfolio focused on cellulosic ethanol and bio-derived esters.
The European landscape is characterized by a strong emphasis on green chemistry principles, with countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands demonstrating particular strength in patents related to supercritical CO2 extraction methods and ionic liquid applications for biomass processing. The European Union's Horizon programs have strategically directed research funding toward sustainable solvent technologies, creating clusters of innovation around major research universities.
In Asia, China has rapidly emerged as a dominant force, with patent filings in biomass-derived solvents increasing at an annual rate of approximately 15% over the past five years. Japanese and South Korean companies maintain significant patent portfolios focused on high-value applications in electronics manufacturing and pharmaceutical processing, where bio-based solvents offer critical performance advantages.
Developing economies, particularly Brazil and India, are establishing specialized niches in the global landscape. Brazil's patents predominantly focus on sugarcane-based solvent technologies, leveraging their agricultural strengths, while India shows growing innovation in cost-effective production methods suitable for distributed manufacturing models.
Cross-border collaborations are increasingly evident in patent filings, with multinational corporations partnering with regional research institutions to develop technologies adapted to local biomass feedstocks. This trend is particularly pronounced in technologies targeting agricultural waste valorization, where regional biomass composition significantly influences solvent selection and process design.
The patent landscape reveals a gradual shift from first-generation biomass solvents (primarily ethanol) toward more sophisticated second and third-generation technologies incorporating designer solvents with enhanced selectivity and reduced environmental impact. Deep eutectic solvents and bio-derived supercritical fluids represent the fastest-growing patent categories, indicating the direction of future market development.
Current Technical Approaches to Biomass Solvent Development
01 Production methods for biomass-derived solvents
Various methods have been developed for producing solvents from biomass feedstocks. These processes typically involve conversion of biomass components such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin through biochemical or thermochemical pathways. The methods include fermentation, catalytic conversion, and chemical synthesis to transform biomass into useful solvents that can replace petroleum-based alternatives. These production technologies focus on improving yield, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing the purity of the final solvent products.- Bio-based solvents derived from lignocellulosic biomass: Technologies for converting lignocellulosic biomass into environmentally friendly solvents. These processes typically involve the breakdown of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin components through various chemical and biological pathways to produce solvents that can replace petroleum-based alternatives. The resulting bio-solvents offer reduced toxicity, improved biodegradability, and a smaller carbon footprint compared to conventional solvents.
- Green solvent production from agricultural waste: Methods for converting agricultural waste and residues into valuable solvents. These technologies focus on utilizing abundant and renewable feedstocks such as crop residues, food processing byproducts, and other agricultural waste streams to produce environmentally friendly solvents. The processes often involve fermentation, catalytic conversion, or other transformation methods to create solvents with properties suitable for industrial applications while reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Catalytic processes for biomass-to-solvent conversion: Advanced catalytic technologies that enable efficient conversion of biomass into solvents. These innovations focus on catalyst development, reaction optimization, and process engineering to improve yields and selectivity in biomass conversion reactions. The catalytic processes can operate under milder conditions, reduce energy requirements, and enhance the economic viability of bio-based solvent production while maintaining high product quality and performance characteristics.
- Biomass-derived solvent formulations for specific applications: Specialized formulations of biomass-derived solvents tailored for specific industrial applications. These technologies focus on developing solvent systems with properties optimized for particular uses such as coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, pharmaceutical processing, or extraction processes. The formulations may involve blending multiple bio-based solvents or combining them with additives to achieve desired performance characteristics while maintaining environmental benefits.
- Process integration and commercialization of bio-solvent technologies: Innovations focused on scaling up and commercializing biomass-derived solvent technologies. These developments address challenges in process integration, manufacturing scale-up, quality control, and market adoption of bio-based solvents. The technologies include improved production methods, supply chain optimization, and business models that enhance the economic viability and market competitiveness of biomass-derived solvents against conventional petroleum-based alternatives.
02 Novel biomass-derived solvent compositions
Innovative solvent compositions derived from biomass resources have been developed as alternatives to conventional petroleum-based solvents. These compositions include solvents derived from plant oils, cellulosic materials, and other renewable resources. The formulations often combine multiple biomass-derived components to achieve desired solvent properties such as polarity, volatility, and solvation power. These novel compositions aim to provide environmentally friendly alternatives while maintaining or improving performance compared to traditional solvents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of biomass-derived solvents in industrial processes
Biomass-derived solvents have found applications across various industrial processes as sustainable alternatives to conventional solvents. These applications include use in coatings, adhesives, cleaning products, pharmaceutical processing, and extraction processes. The implementation of these bio-based solvents helps reduce environmental impact while maintaining process efficiency. Research has focused on optimizing solvent properties for specific industrial applications and demonstrating their effectiveness in real-world industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biomass-derived solvent purification and quality control
Technologies for purifying biomass-derived solvents and ensuring their quality have been developed to meet industrial standards. These include distillation techniques, membrane separation, adsorption processes, and chromatographic methods tailored for bio-based solvents. Quality control measures involve analytical techniques to assess purity, stability, and performance characteristics. These purification technologies are essential for producing biomass-derived solvents that can effectively compete with conventional petroleum-based alternatives in terms of consistency and reliability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and economic assessment of biomass-derived solvents
Methods for evaluating the environmental impact and economic viability of biomass-derived solvents have been developed to support their commercialization. These assessment frameworks include life cycle analysis, carbon footprint calculation, and techno-economic modeling specific to bio-based solvent production and use. The evaluations consider factors such as feedstock sustainability, energy requirements, greenhouse gas emissions, production costs, and market competitiveness. These assessment tools help identify the most promising biomass-derived solvent technologies and guide further development efforts.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Bio-Solvents
Biomass-derived solvent technologies are currently in a growth phase, with increasing market interest driven by sustainability demands. The market is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant scale as industries seek eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with key players at different development stages. Shell and ExxonMobil leverage their petrochemical expertise to transition toward bio-based solutions, while specialized companies like Renmatix and Borregaard focus on innovative conversion technologies. Academic institutions such as Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation and Central China Normal University contribute fundamental research. Companies like Versalis, PTT Global Chemical, and Eni are developing commercial applications, indicating the technology's progression toward industrial implementation, though challenges in scalability and cost-effectiveness remain.
Shell Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Shell Oil has developed the IH² (Integrated Hydropyrolysis and Hydroconversion) technology that incorporates biomass-derived solvents in its biofuel production process. Their patented approach uses bio-derived solvents in a catalytic hydropyrolysis system that converts various biomass feedstocks directly into transportation fuels. The technology employs specially formulated bio-solvents for biomass pretreatment to enhance feedstock processability and increase overall conversion efficiency. Shell's patents cover specific solvent formulations derived from biomass processing itself, creating a partially self-sustaining system. The process integrates hydrogen generation from process byproducts, reducing external hydrogen requirements. Shell has demonstrated this technology at pilot scale, processing up to 5 tons/day of biomass, and their patent filings show continuous improvements in catalyst formulations and process integration to enhance economic viability for commercial deployment.
Strengths: Produces drop-in transportation fuels compatible with existing infrastructure; integrated process design improves energy efficiency; flexible feedstock capability including agricultural residues and woody biomass. Weaknesses: Complex process integration requirements; catalyst deactivation issues in presence of certain biomass contaminants; economic viability still dependent on policy support for biofuels.
Renmatix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Renmatix has developed the Plantrose® Process, a revolutionary technology that uses supercritical water as a solvent to convert biomass into valuable biochemicals. Their patented process employs water-based fractionation at high temperatures and pressures to break down plant material into cellulosic sugars and lignin, avoiding the need for enzymes or acids. The technology creates a cost-effective pathway for producing bio-based chemicals and materials from renewable feedstocks. Renmatix's approach focuses on using water as a green solvent in a continuous-flow process that can process various biomass inputs including agricultural residues, woody biomass, and energy crops. Their patent portfolio covers multiple aspects of this supercritical hydrolysis process, reaction conditions optimization, and equipment design for industrial-scale implementation.
Strengths: Uses water as an environmentally friendly solvent, eliminating toxic chemicals; operates at industrial scale with lower production costs than conventional methods; versatile feedstock processing capability. Weaknesses: High energy requirements for maintaining supercritical conditions; complex process control requirements; potential challenges with equipment durability under extreme operating conditions.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs in Bio-Solvents
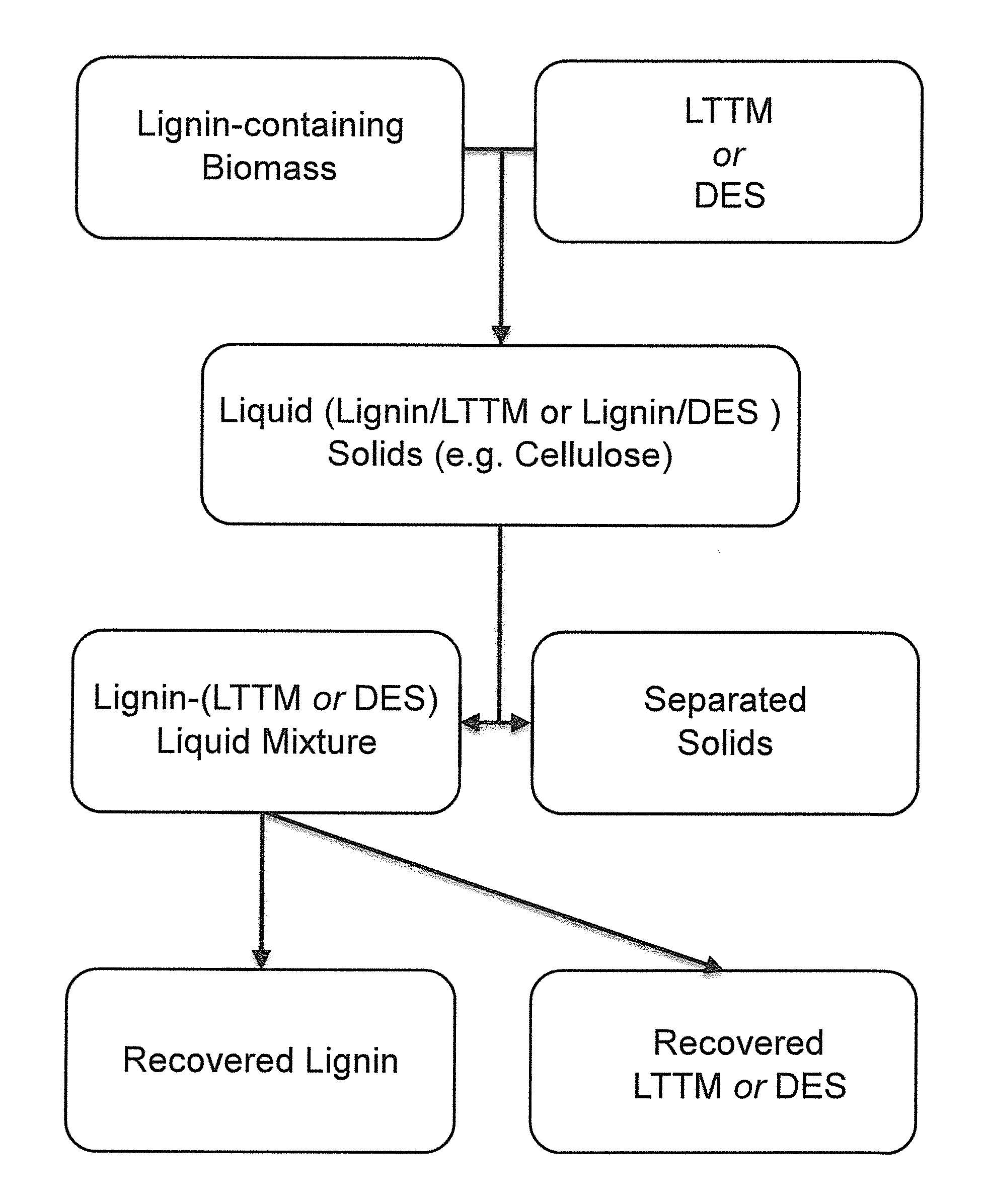
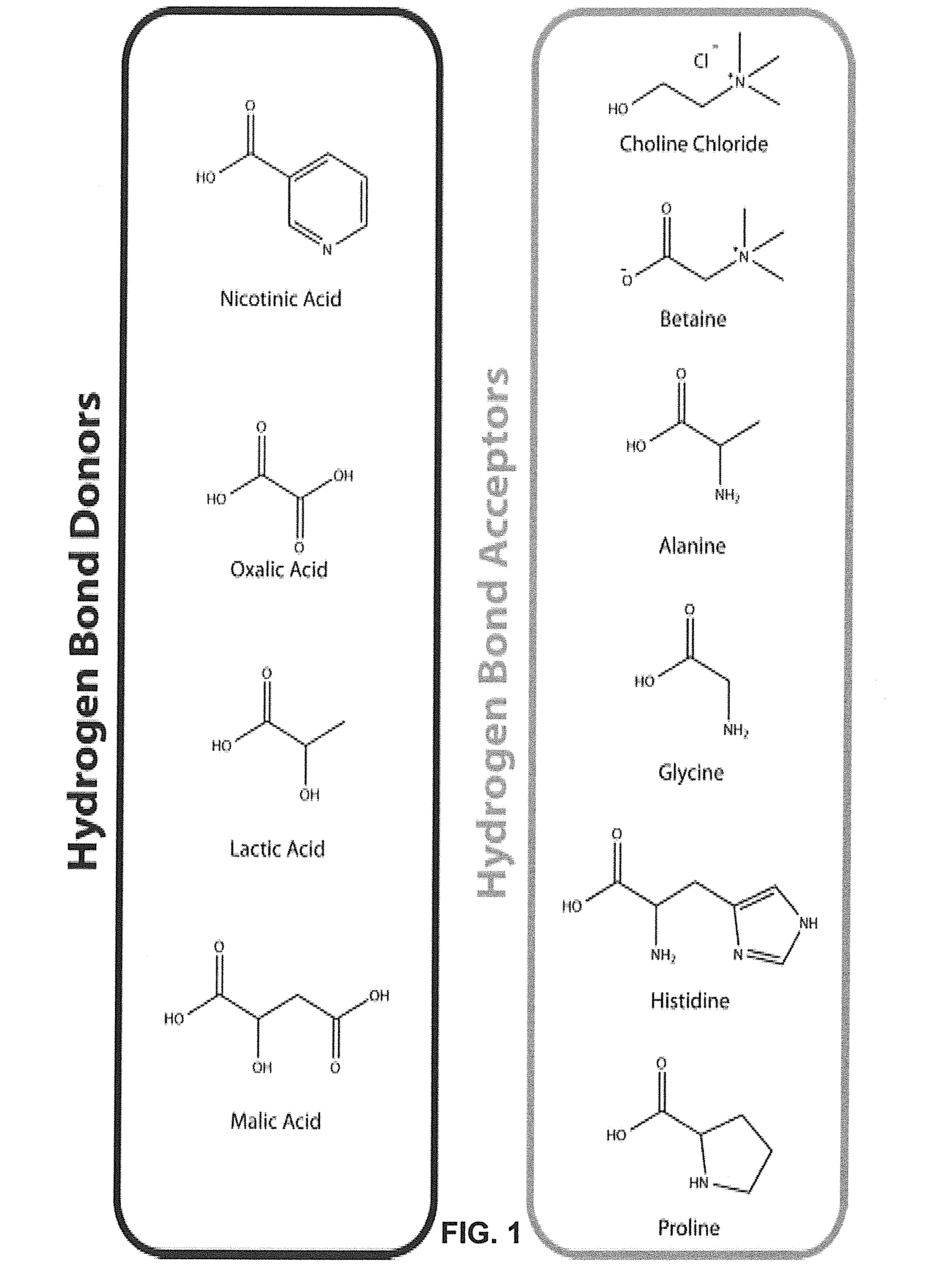
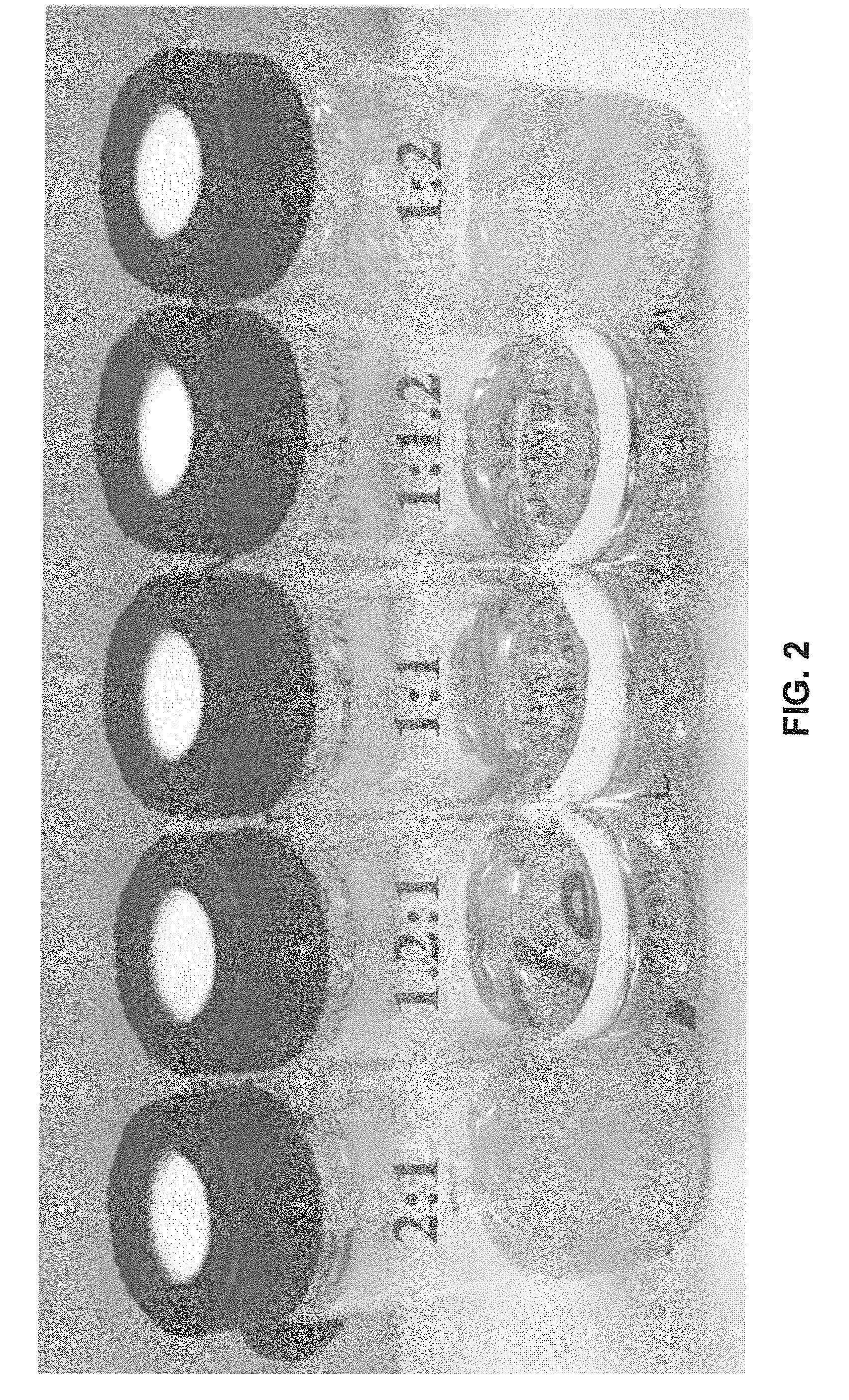
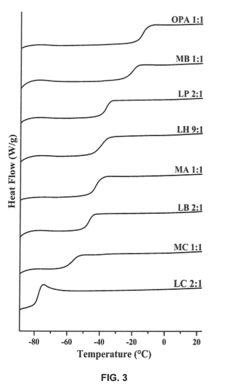
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
PatentInactiveUS20150094459A1
Innovation
- Development of low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) composed of renewable components, which selectively dissolve lignin from lignin-containing biomass at mild conditions, allowing for energy-efficient separation of lignin from cellulose without degradation, and enable recovery of high-quality lignin and cellulose.
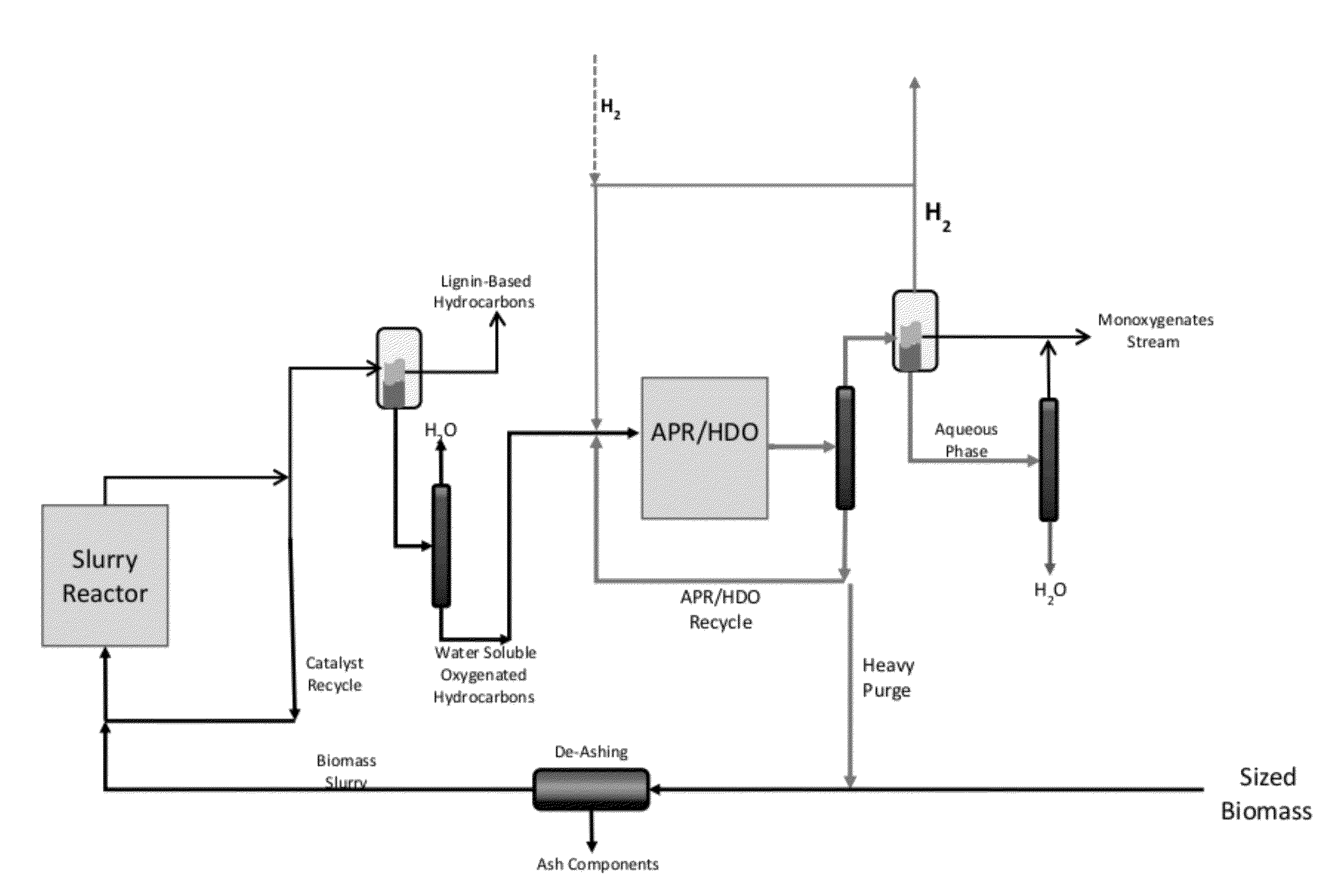
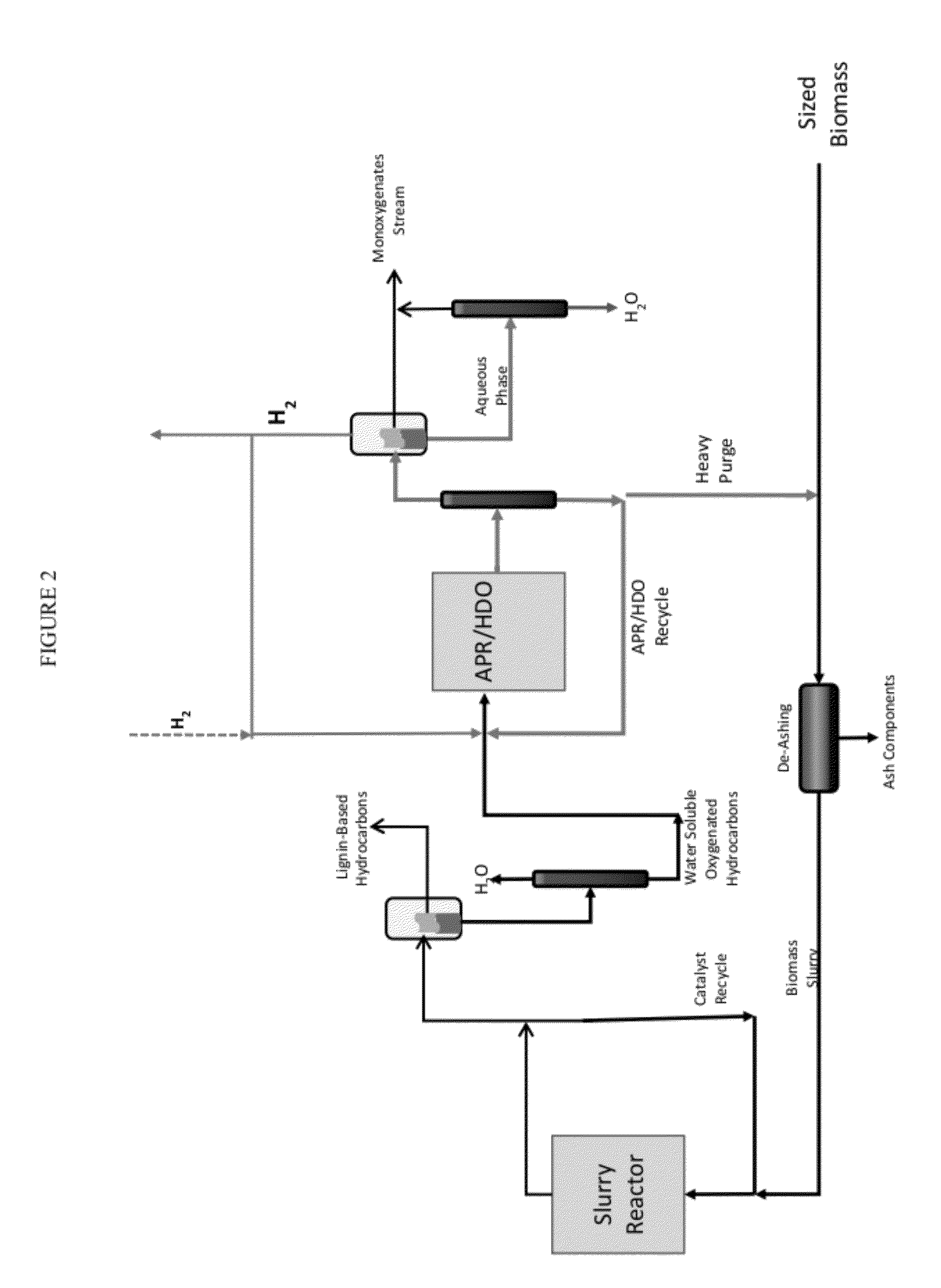
Solvolysis of biomass using solvent from a bioreforming process
PatentActiveUS20120167875A1
Innovation
- A method involving the catalytic reaction of water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon with hydrogen in the presence of a deoxygenation catalyst to produce a biomass processing solvent, which is then used to deconstruct biomass into a hydrolysate containing soluble derivatives and carbohydrates, facilitating further processing in bioreforming.
Patent Filing Trends and Strategic IP Considerations
The patent landscape for biomass-derived solvents has shown significant growth over the past decade, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 12.3% since 2015. This acceleration reflects the increasing industrial interest in sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. Analysis of global patent databases reveals that filings are concentrated primarily in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with China emerging as the fastest-growing jurisdiction for biomass solvent patents.
Key patent filing trends indicate a shift from broad composition claims toward more specific application-oriented patents. Early patents (2010-2015) typically covered fundamental solvent compositions, while recent filings (2018-present) increasingly focus on specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and advanced materials processing. This evolution suggests the technology is maturing from basic research toward commercial implementation.
Corporate patent strategies in this sector demonstrate interesting patterns. Established chemical companies tend to build defensive patent portfolios with broad claims, while startups and research institutions focus on narrower, application-specific innovations. Cross-licensing agreements between biomass technology developers and traditional solvent manufacturers have increased by 35% since 2019, indicating collaborative approaches to market entry.
Strategic IP considerations for organizations entering this space should include geographic filing strategies that prioritize regions with strong bioeconomy initiatives. The European Union, with its Green Deal framework, and Japan, with its biomass innovation policies, represent particularly valuable patent jurisdictions beyond the traditional US-China-EU triad.
Freedom-to-operate analyses reveal several patent thickets forming around specific biomass feedstocks, particularly lignin-derived solvents and cellulosic ethanol derivatives. Companies should conduct thorough landscape analyses before R&D investment to navigate these increasingly complex IP territories. The emergence of patent pools for fundamental biomass processing technologies offers potential pathways for reducing IP friction in the industry.
Litigation trends remain relatively limited compared to other green technologies, with only seven major cases recorded since 2018. However, as commercial adoption increases, enforcement activity is expected to accelerate, particularly around process patents for efficient biomass conversion methods.
Key patent filing trends indicate a shift from broad composition claims toward more specific application-oriented patents. Early patents (2010-2015) typically covered fundamental solvent compositions, while recent filings (2018-present) increasingly focus on specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and advanced materials processing. This evolution suggests the technology is maturing from basic research toward commercial implementation.
Corporate patent strategies in this sector demonstrate interesting patterns. Established chemical companies tend to build defensive patent portfolios with broad claims, while startups and research institutions focus on narrower, application-specific innovations. Cross-licensing agreements between biomass technology developers and traditional solvent manufacturers have increased by 35% since 2019, indicating collaborative approaches to market entry.
Strategic IP considerations for organizations entering this space should include geographic filing strategies that prioritize regions with strong bioeconomy initiatives. The European Union, with its Green Deal framework, and Japan, with its biomass innovation policies, represent particularly valuable patent jurisdictions beyond the traditional US-China-EU triad.
Freedom-to-operate analyses reveal several patent thickets forming around specific biomass feedstocks, particularly lignin-derived solvents and cellulosic ethanol derivatives. Companies should conduct thorough landscape analyses before R&D investment to navigate these increasingly complex IP territories. The emergence of patent pools for fundamental biomass processing technologies offers potential pathways for reducing IP friction in the industry.
Litigation trends remain relatively limited compared to other green technologies, with only seven major cases recorded since 2018. However, as commercial adoption increases, enforcement activity is expected to accelerate, particularly around process patents for efficient biomass conversion methods.
Regulatory Framework and Green Chemistry Standards
The regulatory landscape surrounding biomass-derived solvents has evolved significantly in response to growing environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives. Key international frameworks such as the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation have established stringent requirements for chemical substances, creating both challenges and opportunities for biomass-derived solvent technologies. These regulations increasingly favor bio-based alternatives over petroleum-derived solvents, directly influencing patent filing strategies across the chemical industry.
The Green Chemistry Principles, established by the EPA in the 1990s, have become fundamental standards guiding the development of biomass-derived solvents. These principles emphasize waste prevention, atom economy, safer chemical synthesis, and the use of renewable feedstocks—all areas where biomass-derived solvents excel. Patent filings increasingly reference compliance with these principles as a competitive advantage, demonstrating a clear correlation between regulatory frameworks and innovation direction.
Regional variations in regulatory approaches create complex patent landscapes. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and Circular Economy Action Plan have accelerated patent filings for biomass-derived solvents in European markets, while the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the United States has undergone reforms that increasingly favor green chemistry innovations. These regulatory differences have led to strategic patent filing behaviors, with companies often prioritizing regions with more favorable regulatory environments.
Industry-specific standards also play a crucial role in shaping patent activities. The pharmaceutical industry, governed by ICH (International Council for Harmonisation) guidelines, has seen a surge in patents for biomass-derived solvents that meet stringent purity and safety requirements. Similarly, the cosmetics industry's increasing adoption of ISO 16128 standards for natural and organic ingredients has catalyzed patent filings for bio-based extraction solvents.
Certification schemes like the USDA BioPreferred program and various ecolabels have created market incentives that directly influence patent strategies. Technologies that enable products to qualify for these certifications often receive priority in R&D pipelines and subsequent patent protection. This has resulted in patent clusters around specific biomass feedstocks and processing technologies that align with certification criteria.
Looking forward, emerging regulatory trends suggest continued tightening of restrictions on conventional solvents, particularly those with high VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) content or persistent environmental impacts. This regulatory pressure is likely to accelerate patent filings for novel biomass-derived alternatives, especially those addressing current performance limitations while maintaining environmental benefits.
The Green Chemistry Principles, established by the EPA in the 1990s, have become fundamental standards guiding the development of biomass-derived solvents. These principles emphasize waste prevention, atom economy, safer chemical synthesis, and the use of renewable feedstocks—all areas where biomass-derived solvents excel. Patent filings increasingly reference compliance with these principles as a competitive advantage, demonstrating a clear correlation between regulatory frameworks and innovation direction.
Regional variations in regulatory approaches create complex patent landscapes. The EU's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and Circular Economy Action Plan have accelerated patent filings for biomass-derived solvents in European markets, while the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the United States has undergone reforms that increasingly favor green chemistry innovations. These regulatory differences have led to strategic patent filing behaviors, with companies often prioritizing regions with more favorable regulatory environments.
Industry-specific standards also play a crucial role in shaping patent activities. The pharmaceutical industry, governed by ICH (International Council for Harmonisation) guidelines, has seen a surge in patents for biomass-derived solvents that meet stringent purity and safety requirements. Similarly, the cosmetics industry's increasing adoption of ISO 16128 standards for natural and organic ingredients has catalyzed patent filings for bio-based extraction solvents.
Certification schemes like the USDA BioPreferred program and various ecolabels have created market incentives that directly influence patent strategies. Technologies that enable products to qualify for these certifications often receive priority in R&D pipelines and subsequent patent protection. This has resulted in patent clusters around specific biomass feedstocks and processing technologies that align with certification criteria.
Looking forward, emerging regulatory trends suggest continued tightening of restrictions on conventional solvents, particularly those with high VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) content or persistent environmental impacts. This regulatory pressure is likely to accelerate patent filings for novel biomass-derived alternatives, especially those addressing current performance limitations while maintaining environmental benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!