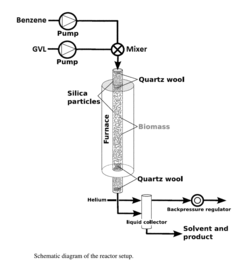
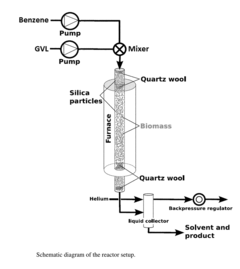
How Do Regulations Affect Biomass-Derived Solvent Production
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvent Regulatory Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents, gaining significant attention over the past two decades. The evolution of this technology has been shaped by increasing environmental concerns, depletion of fossil resources, and growing awareness of the principles of green chemistry. Initially focused on simple alcohols like bioethanol, the field has expanded to include more complex molecules such as esters, ethers, and terpenes derived from various biomass feedstocks.
The regulatory landscape governing biomass-derived solvents has evolved considerably, beginning with early environmental protection acts in the 1970s to more recent comprehensive frameworks specifically addressing bio-based products. Key milestones include the implementation of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) in Europe, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the United States, and similar regulatory frameworks in Asia-Pacific regions.
Current technological objectives in this field aim to address several critical challenges. Primary among these is achieving cost-competitive production processes that can rival conventional petroleum-based solvents while maintaining environmental benefits. Additionally, researchers are working to develop biomass-derived solvents with performance characteristics that match or exceed those of traditional solvents, particularly in terms of solvation power, volatility, and stability.
Another significant objective is the standardization of life cycle assessment methodologies for these bio-based products. This standardization is crucial for providing reliable comparisons between different biomass-derived solvents and their conventional counterparts, thereby informing both regulatory decisions and market adoption strategies.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly incorporating sustainability criteria, creating both challenges and opportunities for biomass-derived solvent production. The European Union's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and the Circular Economy Action Plan represent progressive regulatory approaches that actively promote bio-based alternatives. Similarly, the United States Department of Agriculture's BioPreferred program has established procurement preferences for bio-based products, including solvents.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory is expected to focus on developing next-generation biomass-derived solvents with enhanced functionality, reduced toxicity, and improved biodegradability. This will likely involve exploring novel biomass feedstocks, advancing conversion technologies, and optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
The intersection of technological innovation and regulatory evolution will be critical in determining the future market penetration of biomass-derived solvents across various industrial applications, from pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to paints, coatings, and industrial cleaning products.
The regulatory landscape governing biomass-derived solvents has evolved considerably, beginning with early environmental protection acts in the 1970s to more recent comprehensive frameworks specifically addressing bio-based products. Key milestones include the implementation of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) in Europe, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the United States, and similar regulatory frameworks in Asia-Pacific regions.
Current technological objectives in this field aim to address several critical challenges. Primary among these is achieving cost-competitive production processes that can rival conventional petroleum-based solvents while maintaining environmental benefits. Additionally, researchers are working to develop biomass-derived solvents with performance characteristics that match or exceed those of traditional solvents, particularly in terms of solvation power, volatility, and stability.
Another significant objective is the standardization of life cycle assessment methodologies for these bio-based products. This standardization is crucial for providing reliable comparisons between different biomass-derived solvents and their conventional counterparts, thereby informing both regulatory decisions and market adoption strategies.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly incorporating sustainability criteria, creating both challenges and opportunities for biomass-derived solvent production. The European Union's Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and the Circular Economy Action Plan represent progressive regulatory approaches that actively promote bio-based alternatives. Similarly, the United States Department of Agriculture's BioPreferred program has established procurement preferences for bio-based products, including solvents.
Looking forward, the technological trajectory is expected to focus on developing next-generation biomass-derived solvents with enhanced functionality, reduced toxicity, and improved biodegradability. This will likely involve exploring novel biomass feedstocks, advancing conversion technologies, and optimizing production processes to reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
The intersection of technological innovation and regulatory evolution will be critical in determining the future market penetration of biomass-derived solvents across various industrial applications, from pharmaceuticals and cosmetics to paints, coatings, and industrial cleaning products.
Market Demand Analysis for Sustainable Solvents
The global market for sustainable solvents has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Biomass-derived solvents represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with an estimated market value exceeding $7 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8%.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly products has become a major market driver, with surveys indicating that over 60% of consumers across North America and Europe are willing to pay premium prices for products manufactured using sustainable processes and materials. This trend is particularly evident in personal care, cosmetics, and household cleaning products, where "green" labeling has become a significant competitive advantage.
Industrial sectors are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional petroleum-based solvents due to both regulatory compliance requirements and corporate sustainability initiatives. The pharmaceutical industry has emerged as a leading adopter, with approximately 35% of pharmaceutical companies actively incorporating green solvents into their manufacturing processes. This adoption is partly driven by the FDA's and EMA's encouragement of green chemistry principles in drug development and production.
The paint and coatings industry represents another significant market, with water-based and bio-based formulations gaining substantial market share. Market research indicates that bio-based coatings are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional solvent-based systems in developed markets. Construction and automotive sectors are primary consumers of these sustainable coating solutions.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with Europe leading in market penetration due to stringent VOC regulations and well-established sustainability frameworks. North America follows closely, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, where industrial modernization is increasingly aligned with environmental considerations.
Price sensitivity remains a challenge, as biomass-derived solvents typically command a 15-30% premium over conventional alternatives. However, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and technologies mature. Market forecasts suggest price parity for several key bio-solvents may be achieved within the next 5-7 years, which would significantly accelerate adoption rates.
Supply chain resilience has emerged as an additional market driver following global disruptions in petrochemical supply chains. Manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the strategic advantage of locally sourced biomass feedstocks, which can reduce dependency on volatile petroleum markets and enhance production stability.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly products has become a major market driver, with surveys indicating that over 60% of consumers across North America and Europe are willing to pay premium prices for products manufactured using sustainable processes and materials. This trend is particularly evident in personal care, cosmetics, and household cleaning products, where "green" labeling has become a significant competitive advantage.
Industrial sectors are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional petroleum-based solvents due to both regulatory compliance requirements and corporate sustainability initiatives. The pharmaceutical industry has emerged as a leading adopter, with approximately 35% of pharmaceutical companies actively incorporating green solvents into their manufacturing processes. This adoption is partly driven by the FDA's and EMA's encouragement of green chemistry principles in drug development and production.
The paint and coatings industry represents another significant market, with water-based and bio-based formulations gaining substantial market share. Market research indicates that bio-based coatings are growing at nearly twice the rate of conventional solvent-based systems in developed markets. Construction and automotive sectors are primary consumers of these sustainable coating solutions.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with Europe leading in market penetration due to stringent VOC regulations and well-established sustainability frameworks. North America follows closely, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, where industrial modernization is increasingly aligned with environmental considerations.
Price sensitivity remains a challenge, as biomass-derived solvents typically command a 15-30% premium over conventional alternatives. However, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and technologies mature. Market forecasts suggest price parity for several key bio-solvents may be achieved within the next 5-7 years, which would significantly accelerate adoption rates.
Supply chain resilience has emerged as an additional market driver following global disruptions in petrochemical supply chains. Manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the strategic advantage of locally sourced biomass feedstocks, which can reduce dependency on volatile petroleum markets and enhance production stability.
Regulatory Challenges in Biomass Solvent Development
The regulatory landscape surrounding biomass-derived solvent production presents significant challenges for industry stakeholders. These regulations span multiple domains including environmental protection, chemical safety, agricultural policy, and industrial standards. At the international level, frameworks such as the Paris Agreement and various UN Sustainable Development Goals indirectly influence biomass solvent development by setting carbon reduction targets that favor bio-based alternatives to petrochemical solvents.
National and regional regulations exhibit considerable variation, creating a complex compliance environment for global operators. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes stringent requirements for chemical registration, with specific provisions for bio-based substances that can extend development timelines by 12-24 months compared to conventional products. Similarly, the U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires extensive safety data for new chemical substances, including biomass-derived solvents.
Regulatory inconsistencies between jurisdictions create significant market barriers. For instance, a biomass solvent approved in the EU may require completely different testing protocols for U.S. or Asian markets, increasing compliance costs by an estimated 30-45% per market entry. These inconsistencies particularly impact small and medium enterprises that lack resources for multiple parallel regulatory submissions.
Certification and labeling requirements add another layer of complexity. Various eco-labeling schemes such as the EU Ecolabel, USDA BioPreferred program, and private certification systems have different criteria for what constitutes a "bio-based" or "sustainable" solvent. The lack of harmonization creates market confusion and increases compliance burdens for manufacturers.
Regulatory approval timelines represent a critical challenge for innovation. The average approval process for a novel biomass-derived solvent ranges from 18-36 months in major markets, significantly longer than the 6-12 months typically required for conventional petrochemical alternatives. This regulatory lag creates competitive disadvantages for bio-based solutions despite their potential environmental benefits.
Tax policies and incentive structures also significantly impact market development. While some jurisdictions offer tax credits or subsidies for bio-based chemical production, these incentives are often inconsistent, temporary, or subject to political cycles. The resulting uncertainty complicates long-term investment decisions in production capacity and technology development.
Evolving regulations around feedstock sustainability add further complexity. Concerns about land use change, competition with food production, and biodiversity impacts have led to increasingly stringent sustainability criteria for biomass feedstocks. These requirements, while environmentally important, can restrict feedstock options and increase production costs by 15-25% compared to less regulated alternatives.
National and regional regulations exhibit considerable variation, creating a complex compliance environment for global operators. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes stringent requirements for chemical registration, with specific provisions for bio-based substances that can extend development timelines by 12-24 months compared to conventional products. Similarly, the U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requires extensive safety data for new chemical substances, including biomass-derived solvents.
Regulatory inconsistencies between jurisdictions create significant market barriers. For instance, a biomass solvent approved in the EU may require completely different testing protocols for U.S. or Asian markets, increasing compliance costs by an estimated 30-45% per market entry. These inconsistencies particularly impact small and medium enterprises that lack resources for multiple parallel regulatory submissions.
Certification and labeling requirements add another layer of complexity. Various eco-labeling schemes such as the EU Ecolabel, USDA BioPreferred program, and private certification systems have different criteria for what constitutes a "bio-based" or "sustainable" solvent. The lack of harmonization creates market confusion and increases compliance burdens for manufacturers.
Regulatory approval timelines represent a critical challenge for innovation. The average approval process for a novel biomass-derived solvent ranges from 18-36 months in major markets, significantly longer than the 6-12 months typically required for conventional petrochemical alternatives. This regulatory lag creates competitive disadvantages for bio-based solutions despite their potential environmental benefits.
Tax policies and incentive structures also significantly impact market development. While some jurisdictions offer tax credits or subsidies for bio-based chemical production, these incentives are often inconsistent, temporary, or subject to political cycles. The resulting uncertainty complicates long-term investment decisions in production capacity and technology development.
Evolving regulations around feedstock sustainability add further complexity. Concerns about land use change, competition with food production, and biodiversity impacts have led to increasingly stringent sustainability criteria for biomass feedstocks. These requirements, while environmentally important, can restrict feedstock options and increase production costs by 15-25% compared to less regulated alternatives.
Current Compliance Solutions for Biomass Solvent Production
01 Production of bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass
Lignocellulosic biomass can be processed to produce environmentally friendly solvents through various conversion methods. These processes typically involve the breakdown of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin components into smaller molecules that can function as effective solvents. The resulting bio-based solvents offer renewable alternatives to petroleum-derived products with comparable performance characteristics while reducing environmental impact and carbon footprint.- Production of bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass: Methods for producing bio-based solvents from lignocellulosic biomass through various conversion processes such as fermentation, hydrolysis, and chemical transformation. These processes convert biomass components like cellulose and hemicellulose into renewable solvents that can replace petroleum-derived alternatives. The resulting solvents offer environmental benefits while maintaining comparable performance characteristics to conventional solvents.
- Biomass-derived solvent applications in polymer processing: Biomass-derived solvents used in polymer processing applications, including as processing aids, plasticizers, and in polymer dissolution and precipitation. These green solvents can improve the sustainability profile of polymer manufacturing while maintaining or enhancing performance properties. Applications include bioplastic production, polymer recycling processes, and sustainable composite materials manufacturing.
- Biomass-derived solvents for extraction processes: Utilization of biomass-derived solvents in various extraction processes, including the isolation of valuable compounds from natural materials. These green solvents can effectively extract bioactive compounds, oils, and other valuable substances while reducing environmental impact compared to traditional petroleum-based solvents. The extraction efficiency is comparable to conventional methods while offering improved safety profiles and reduced toxicity.
- Microbial production of biomass-derived solvents: Methods for producing biomass-derived solvents through microbial fermentation processes. Engineered microorganisms convert biomass feedstocks into valuable solvents through metabolic pathways. These biological production routes offer advantages in terms of selectivity and can operate under mild conditions, reducing energy requirements compared to chemical synthesis methods. The processes can utilize various biomass sources including agricultural residues and dedicated energy crops.
- Biomass-derived solvents for sustainable chemical manufacturing: Integration of biomass-derived solvents into chemical manufacturing processes to enhance sustainability. These bio-based solvents can replace conventional petroleum-derived solvents in reaction media, separation processes, and cleaning applications. The implementation of these green solvents reduces environmental impact while maintaining process efficiency. Applications include pharmaceutical manufacturing, specialty chemicals production, and industrial cleaning operations.
02 Fermentation processes for biomass-derived solvent production
Microbial fermentation represents a key pathway for converting biomass into valuable solvents. These bioprocesses utilize specialized microorganisms to transform biomass sugars into solvents such as ethanol, butanol, and acetone. Advanced fermentation techniques have been developed to improve yields, selectivity, and efficiency of the conversion process, making it more economically viable for industrial applications while maintaining sustainability benefits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Green solvents derived from agricultural waste and residues
Agricultural waste streams and residues provide abundant feedstock for solvent production. These materials, which would otherwise be discarded, can be transformed into valuable solvents through various chemical and biological processes. The approach not only addresses waste management challenges but also creates economic value from agricultural byproducts. The resulting solvents can be used in various applications including cleaning products, coatings, and industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of biomass-derived solvents in industrial processes
Biomass-derived solvents find applications across numerous industrial sectors as replacements for conventional petroleum-based solvents. These bio-solvents are particularly valuable in manufacturing processes, cleaning applications, coatings, adhesives, and extraction procedures. Their adoption is driven by their comparable or superior performance characteristics, reduced toxicity, biodegradability, and contribution to sustainability goals. Industries are increasingly incorporating these solvents to meet environmental regulations and consumer demands for greener products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Chemical modification of biomass components for enhanced solvent properties
Chemical modification techniques can transform biomass components into solvents with tailored properties. These processes involve reactions such as esterification, etherification, and oxidation to modify the molecular structure of biomass derivatives. The modifications enhance solvent characteristics such as polarity, volatility, and solvation power, making them suitable for specific applications. This approach enables the creation of specialized bio-solvents that can directly compete with or outperform conventional petroleum-based alternatives.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Regulatory Stakeholders
The biomass-derived solvent production sector is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by sustainability regulations and environmental concerns. The regulatory landscape significantly impacts production processes, costs, and market access. Key players demonstrate varying levels of technological maturity: established energy corporations like ExxonMobil and BP Corporation North America leverage their infrastructure for scale, while specialized firms such as Renmatix, Cellufuel, and Capra Biosciences focus on innovative conversion technologies. Academic institutions (University of California, Wuhan University) and research organizations (INRA, Japan Science & Technology Agency) contribute fundamental research advancing the field. The industry is characterized by a mix of traditional petrochemical companies transitioning toward bio-based alternatives and emerging startups developing novel enzymatic and fermentation approaches to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
Renmatix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Renmatix has developed the Plantrose® Process, a proprietary technology platform that uses supercritical water to convert biomass into cellulosic sugars and lignin, which can be further processed into bio-based solvents. Their approach addresses regulatory challenges by utilizing a water-based process that eliminates the need for acids, enzymes, or other chemicals typically required in biomass conversion. This aligns with EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) requirements and European REACH regulations. Renmatix's technology has been recognized for meeting sustainability criteria under the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program, allowing their products to qualify for RIN credits. The company has also worked with regulatory bodies to establish their bio-derived solvents as drop-in replacements for petroleum-based alternatives, facilitating market adoption without extensive regulatory hurdles.
Strengths: Water-based process reduces regulatory compliance costs related to hazardous chemicals; products qualify for renewable incentives under multiple regulatory frameworks. Weaknesses: Supercritical water processes require significant energy input, potentially affecting carbon footprint calculations required by some regulatory schemes.
Cellufuel, Inc.
Technical Solution: Cellufuel has pioneered a regulatory-compliant approach to converting woody biomass into renewable diesel and bio-solvents through their proprietary thermochemical process. Their technology addresses key regulatory concerns by producing drop-in replacements that meet ASTM International standards, allowing their products to navigate existing fuel and chemical regulations without requiring new frameworks. The company has developed a modular production system that can be scaled according to local regulatory requirements and feedstock availability. Cellufuel's process has been designed to comply with emissions standards set by the EPA and Environment Canada, with their demonstration facility in Nova Scotia serving as a model for regulatory compliance. Their approach to biomass sourcing also aligns with sustainable forestry regulations, utilizing residual materials that meet criteria for renewable biomass under various national definitions.
Strengths: Modular approach allows adaptation to varying regional regulations; products meet existing industry standards, reducing regulatory barriers to market entry. Weaknesses: Reliance on forestry residues may face increasing regulatory scrutiny as competition for these resources grows under expanding renewable energy mandates.
Critical Regulatory Frameworks Impacting Biomass Solvents
Method to produce biomass-derived compounds using a co-solvent system containing gamma-valerolactone
PatentActiveUS9688845B2
Innovation
- A method involving a solvent system comprising polar aprotic solvents like beta-, gamma-, and delta-lactones, an organic co-solvent, and water, in the presence of an acid, to convert water-insoluble biomass polymers into water-soluble sugar oligomers and monomers, with a significant fraction of lignin precipitating out, simplifying post-reaction processing.
Method to convert monosaccharides to 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural (HMF) using biomass-derived solvents
PatentWO2014058859A3
Innovation
- Using biomass-derived solvents (beta-, gamma-, delta-lactones, THF, MTHF) as co-solvents in the conversion of monosaccharides to HMF, creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly process.
- Implementation of a monophasic or biphasic reaction system with water and biomass-derived co-solvents for efficient conversion of C5/C6 sugars to HMF.
- Utilization of dual catalyst system (acid catalyst and dehydration catalyst) in biomass-derived solvent medium for selective HMF production.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Sustainability Metrics
The environmental impact assessment of biomass-derived solvent production requires comprehensive analysis across multiple dimensions. Life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies have become the standard approach for evaluating these impacts, measuring everything from greenhouse gas emissions to water consumption throughout the entire production chain. Studies indicate that biomass-derived solvents typically demonstrate 30-70% lower carbon footprints compared to their petroleum-based counterparts, though results vary significantly based on feedstock selection and processing technologies.
Water usage metrics reveal complex trade-offs, as biomass cultivation may require substantial irrigation in certain regions, potentially offsetting other environmental benefits. Recent research indicates that advanced water recycling systems can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 40% in biorefinery operations, making regulatory incentives for such technologies particularly impactful.
Land use change impacts present another critical consideration, especially when agricultural land is repurposed for biomass cultivation. Regulations that encourage the use of marginal lands, agricultural residues, or waste streams rather than purpose-grown crops can significantly improve sustainability profiles. The indirect land use change (ILUC) factor has become increasingly important in regulatory frameworks, particularly in the EU's Renewable Energy Directive II.
Biodiversity impact metrics are gaining prominence in sustainability assessments, with regulations increasingly requiring documentation of habitat preservation measures. Companies demonstrating positive biodiversity outcomes through responsible sourcing practices may gain competitive advantages in markets with stringent environmental regulations.
Energy efficiency ratios throughout the production process serve as key performance indicators, with regulations in several jurisdictions now mandating minimum efficiency standards. The energy return on investment (EROI) for biomass-derived solvents typically ranges from 2:1 to 5:1, compared to 8:1 to 12:1 for conventional petroleum-based alternatives, though technological improvements continue to narrow this gap.
Waste generation and management metrics complete the sustainability assessment framework. Circular economy principles are increasingly embedded in regulations, with requirements for waste minimization, by-product valorization, and end-of-life considerations. Companies demonstrating closed-loop production systems often receive regulatory advantages, including expedited permitting processes and reduced compliance reporting requirements.
Water usage metrics reveal complex trade-offs, as biomass cultivation may require substantial irrigation in certain regions, potentially offsetting other environmental benefits. Recent research indicates that advanced water recycling systems can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 40% in biorefinery operations, making regulatory incentives for such technologies particularly impactful.
Land use change impacts present another critical consideration, especially when agricultural land is repurposed for biomass cultivation. Regulations that encourage the use of marginal lands, agricultural residues, or waste streams rather than purpose-grown crops can significantly improve sustainability profiles. The indirect land use change (ILUC) factor has become increasingly important in regulatory frameworks, particularly in the EU's Renewable Energy Directive II.
Biodiversity impact metrics are gaining prominence in sustainability assessments, with regulations increasingly requiring documentation of habitat preservation measures. Companies demonstrating positive biodiversity outcomes through responsible sourcing practices may gain competitive advantages in markets with stringent environmental regulations.
Energy efficiency ratios throughout the production process serve as key performance indicators, with regulations in several jurisdictions now mandating minimum efficiency standards. The energy return on investment (EROI) for biomass-derived solvents typically ranges from 2:1 to 5:1, compared to 8:1 to 12:1 for conventional petroleum-based alternatives, though technological improvements continue to narrow this gap.
Waste generation and management metrics complete the sustainability assessment framework. Circular economy principles are increasingly embedded in regulations, with requirements for waste minimization, by-product valorization, and end-of-life considerations. Companies demonstrating closed-loop production systems often receive regulatory advantages, including expedited permitting processes and reduced compliance reporting requirements.
Cross-Border Regulatory Harmonization Strategies
The harmonization of regulations across international borders represents a critical challenge and opportunity for the biomass-derived solvent industry. Currently, manufacturers face a complex patchwork of national and regional regulations that significantly impact production costs, market access, and innovation potential. Regulatory divergence between major markets such as the EU, North America, and Asia creates substantial compliance burdens that disproportionately affect small and medium enterprises attempting to scale their bio-solvent technologies.
Successful harmonization strategies must address several key dimensions simultaneously. Technical standardization of testing methodologies, safety protocols, and product specifications forms the foundation of any effective cross-border approach. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has begun developing unified standards for bio-based solvents, though implementation remains inconsistent across jurisdictions.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between regulatory authorities offer a pragmatic pathway toward reducing redundant compliance requirements. The EU-US MRA for chemical assessment methodologies provides a template that could be expanded specifically for biomass-derived solvents, potentially reducing certification costs by 15-30% according to industry estimates.
Regional regulatory clusters represent another promising approach, wherein neighboring countries with significant trade relationships develop aligned regulatory frameworks. The ASEAN Chemicals Regulatory Scheme demonstrates how regional harmonization can facilitate market access while maintaining appropriate safety standards. Similar initiatives could be developed for bio-solvents in regions with strong biomass production capabilities.
Industry consortia and public-private partnerships have emerged as effective vehicles for advancing regulatory harmonization. The Bio-based Industries Consortium in Europe has successfully advocated for consistent end-of-life regulations for bio-solvents across member states, creating more predictable market conditions for producers.
Digital solutions for regulatory compliance management are increasingly important for navigating cross-border requirements. Blockchain-based tracking systems and digital product passports can streamline verification of regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions, reducing administrative burdens while enhancing transparency.
Looking forward, international trade agreements present opportunities to embed harmonized approaches to bio-solvent regulation. Recent agreements have increasingly incorporated sustainability chapters that could serve as vehicles for aligning biomass-derived solvent standards, particularly regarding sustainability criteria, carbon accounting methodologies, and recognition of certification schemes.
Successful harmonization strategies must address several key dimensions simultaneously. Technical standardization of testing methodologies, safety protocols, and product specifications forms the foundation of any effective cross-border approach. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has begun developing unified standards for bio-based solvents, though implementation remains inconsistent across jurisdictions.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between regulatory authorities offer a pragmatic pathway toward reducing redundant compliance requirements. The EU-US MRA for chemical assessment methodologies provides a template that could be expanded specifically for biomass-derived solvents, potentially reducing certification costs by 15-30% according to industry estimates.
Regional regulatory clusters represent another promising approach, wherein neighboring countries with significant trade relationships develop aligned regulatory frameworks. The ASEAN Chemicals Regulatory Scheme demonstrates how regional harmonization can facilitate market access while maintaining appropriate safety standards. Similar initiatives could be developed for bio-solvents in regions with strong biomass production capabilities.
Industry consortia and public-private partnerships have emerged as effective vehicles for advancing regulatory harmonization. The Bio-based Industries Consortium in Europe has successfully advocated for consistent end-of-life regulations for bio-solvents across member states, creating more predictable market conditions for producers.
Digital solutions for regulatory compliance management are increasingly important for navigating cross-border requirements. Blockchain-based tracking systems and digital product passports can streamline verification of regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions, reducing administrative burdens while enhancing transparency.
Looking forward, international trade agreements present opportunities to embed harmonized approaches to bio-solvent regulation. Recent agreements have increasingly incorporated sustainability chapters that could serve as vehicles for aligning biomass-derived solvent standards, particularly regarding sustainability criteria, carbon accounting methodologies, and recognition of certification schemes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!