What are the Technical Barriers to Biomass-Derived Solvent Adoption
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass-Derived Solvents Background and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents represent a significant advancement in green chemistry, emerging from the growing need to replace petroleum-based solvents with sustainable alternatives. The evolution of these bio-solvents can be traced back to the early 2000s when increasing environmental concerns and stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) prompted researchers to explore renewable resources. Initially focused on simple alcohols like bioethanol, the field has progressively expanded to include more complex molecules derived from various biomass feedstocks.
The technological trajectory has been shaped by advancements in biorefinery processes, catalytic conversion methods, and separation technologies. Early developments concentrated on first-generation bio-solvents derived from edible biomass sources, while recent innovations have shifted toward second and third-generation feedstocks that do not compete with food production, such as lignocellulosic materials, agricultural residues, and algal biomass.
Current research is increasingly focused on developing bio-solvents with tailored properties for specific applications, moving beyond simple drop-in replacements to create solvents with enhanced performance characteristics. This includes the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES), bio-based ionic liquids, and terpene-derived solvents with specialized functionalities.
The primary objective of biomass-derived solvent research is to overcome several critical barriers to widespread adoption. These include addressing performance gaps compared to conventional solvents, reducing production costs, scaling up manufacturing processes, and ensuring consistent quality across production batches. Additionally, there is a need to develop comprehensive life cycle assessments to validate the environmental benefits of these bio-solvents.
Technical objectives specifically target improving extraction efficiency, enhancing solvent stability, reducing energy requirements for production, and developing more efficient recovery and recycling methods. Research aims to optimize catalytic pathways for converting biomass into high-value solvent molecules while minimizing waste generation and energy consumption.
The field is also evolving to meet emerging market demands for specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and advanced materials processing, where conventional solvents face increasing restrictions due to toxicity concerns. This requires developing bio-solvents with extremely high purity levels and precisely controlled properties.
Long-term goals include establishing integrated biorefinery concepts where biomass-derived solvents are produced as part of a broader portfolio of bio-based chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. The ultimate vision is to create a circular economy for solvents, where they are derived from renewable resources and can be either safely biodegraded or efficiently recycled after use.
The technological trajectory has been shaped by advancements in biorefinery processes, catalytic conversion methods, and separation technologies. Early developments concentrated on first-generation bio-solvents derived from edible biomass sources, while recent innovations have shifted toward second and third-generation feedstocks that do not compete with food production, such as lignocellulosic materials, agricultural residues, and algal biomass.
Current research is increasingly focused on developing bio-solvents with tailored properties for specific applications, moving beyond simple drop-in replacements to create solvents with enhanced performance characteristics. This includes the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES), bio-based ionic liquids, and terpene-derived solvents with specialized functionalities.
The primary objective of biomass-derived solvent research is to overcome several critical barriers to widespread adoption. These include addressing performance gaps compared to conventional solvents, reducing production costs, scaling up manufacturing processes, and ensuring consistent quality across production batches. Additionally, there is a need to develop comprehensive life cycle assessments to validate the environmental benefits of these bio-solvents.
Technical objectives specifically target improving extraction efficiency, enhancing solvent stability, reducing energy requirements for production, and developing more efficient recovery and recycling methods. Research aims to optimize catalytic pathways for converting biomass into high-value solvent molecules while minimizing waste generation and energy consumption.
The field is also evolving to meet emerging market demands for specialized applications in pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and advanced materials processing, where conventional solvents face increasing restrictions due to toxicity concerns. This requires developing bio-solvents with extremely high purity levels and precisely controlled properties.
Long-term goals include establishing integrated biorefinery concepts where biomass-derived solvents are produced as part of a broader portfolio of bio-based chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency and economic viability. The ultimate vision is to create a circular economy for solvents, where they are derived from renewable resources and can be either safely biodegraded or efficiently recycled after use.
Market Demand Analysis for Green Solvents
The global market for green solvents has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations, consumer awareness, and corporate sustainability initiatives. Biomass-derived solvents represent a crucial segment within this market, offering renewable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based products. Current market analysis indicates that the global green solvent market is valued at several billion dollars, with projections showing a compound annual growth rate exceeding 6% through 2030.
Industrial sectors including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, paints and coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products constitute the primary demand drivers for green solvents. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has demonstrated increasing adoption rates due to stringent regulatory requirements and the need for safer processing environments. Similarly, the personal care and cosmetics industry has embraced green solvents to meet consumer demand for sustainable and non-toxic products.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with Europe leading in market penetration due to advanced regulatory frameworks such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal. North America follows closely, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea where environmental policies are becoming increasingly stringent.
Market research indicates that price sensitivity remains a significant factor influencing adoption rates. Currently, biomass-derived solvents typically command a premium of 20-50% over conventional alternatives, creating a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive applications and emerging markets. However, this price gap is expected to narrow as production scales increase and processing technologies mature.
End-user surveys reveal that performance characteristics remain paramount in solvent selection decisions. Technical specifications including solvency power, evaporation rate, stability, and compatibility with existing processes often outweigh sustainability considerations in many industrial applications. This highlights the importance of developing biomass-derived solvents that match or exceed the performance of conventional alternatives.
Market segmentation analysis shows varying degrees of green solvent penetration across different applications. High-value, consumer-facing products have demonstrated greater willingness to absorb premium costs associated with sustainable ingredients, while industrial and bulk applications remain more resistant to adoption without clear cost parity or regulatory pressure.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by regulatory developments, technological advancements reducing production costs, and increasing corporate commitments to sustainability targets. The implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms in various regions is anticipated to further enhance the competitive position of biomass-derived solvents by internalizing environmental externalities associated with conventional solvent production and use.
Industrial sectors including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, paints and coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products constitute the primary demand drivers for green solvents. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has demonstrated increasing adoption rates due to stringent regulatory requirements and the need for safer processing environments. Similarly, the personal care and cosmetics industry has embraced green solvents to meet consumer demand for sustainable and non-toxic products.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with Europe leading in market penetration due to advanced regulatory frameworks such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) and the European Green Deal. North America follows closely, while Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea where environmental policies are becoming increasingly stringent.
Market research indicates that price sensitivity remains a significant factor influencing adoption rates. Currently, biomass-derived solvents typically command a premium of 20-50% over conventional alternatives, creating a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive applications and emerging markets. However, this price gap is expected to narrow as production scales increase and processing technologies mature.
End-user surveys reveal that performance characteristics remain paramount in solvent selection decisions. Technical specifications including solvency power, evaporation rate, stability, and compatibility with existing processes often outweigh sustainability considerations in many industrial applications. This highlights the importance of developing biomass-derived solvents that match or exceed the performance of conventional alternatives.
Market segmentation analysis shows varying degrees of green solvent penetration across different applications. High-value, consumer-facing products have demonstrated greater willingness to absorb premium costs associated with sustainable ingredients, while industrial and bulk applications remain more resistant to adoption without clear cost parity or regulatory pressure.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by regulatory developments, technological advancements reducing production costs, and increasing corporate commitments to sustainability targets. The implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms in various regions is anticipated to further enhance the competitive position of biomass-derived solvents by internalizing environmental externalities associated with conventional solvent production and use.
Technical Barriers and Global Development Status
Despite significant advancements in biomass-derived solvent technologies, several technical barriers continue to impede widespread industrial adoption. The primary challenge remains the economic viability of production processes, with biomass-derived solvents typically costing 2-5 times more than their petroleum-based counterparts. This cost differential stems from complex extraction and purification processes that require specialized equipment and significant energy inputs.
Conversion efficiency represents another substantial hurdle. Current biomass-to-solvent conversion rates average 30-40%, significantly lower than the 70-80% efficiency achieved in conventional petrochemical processes. This inefficiency increases resource consumption and further impacts economic feasibility.
Inconsistent product quality poses additional challenges for manufacturers. Biomass feedstocks exhibit natural variability in composition depending on growing conditions, harvest timing, and storage methods. This variability translates to fluctuations in solvent properties, creating difficulties for industries requiring precise specifications.
Globally, research efforts addressing these barriers show geographic concentration. North America leads with approximately 35% of research publications and patents, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and other regions (10%). The United States, Germany, China, and Japan have established themselves as innovation hubs, with significant government funding supporting research initiatives.
Technological development has progressed through distinct phases. The period from 2000-2010 focused primarily on proof-of-concept research, while 2010-2015 saw increased attention to process optimization. Since 2015, integration with existing industrial systems has become the predominant focus, with particular emphasis on scalability solutions.
Current technical solutions focus on three main approaches: enzymatic conversion processes, thermochemical pathways, and hybrid systems. Enzymatic approaches offer selectivity advantages but struggle with reaction rates, while thermochemical methods provide higher throughput but with reduced selectivity. Hybrid systems attempt to combine these advantages but introduce additional complexity.
Regulatory frameworks vary significantly by region, creating an uneven global development landscape. The European Union has implemented supportive policies through its Circular Economy Action Plan, while the United States focuses on market-driven adoption with targeted research funding. Asian markets, particularly China, are rapidly expanding research capacity but face implementation challenges in existing industrial infrastructure.
Conversion efficiency represents another substantial hurdle. Current biomass-to-solvent conversion rates average 30-40%, significantly lower than the 70-80% efficiency achieved in conventional petrochemical processes. This inefficiency increases resource consumption and further impacts economic feasibility.
Inconsistent product quality poses additional challenges for manufacturers. Biomass feedstocks exhibit natural variability in composition depending on growing conditions, harvest timing, and storage methods. This variability translates to fluctuations in solvent properties, creating difficulties for industries requiring precise specifications.
Globally, research efforts addressing these barriers show geographic concentration. North America leads with approximately 35% of research publications and patents, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and other regions (10%). The United States, Germany, China, and Japan have established themselves as innovation hubs, with significant government funding supporting research initiatives.
Technological development has progressed through distinct phases. The period from 2000-2010 focused primarily on proof-of-concept research, while 2010-2015 saw increased attention to process optimization. Since 2015, integration with existing industrial systems has become the predominant focus, with particular emphasis on scalability solutions.
Current technical solutions focus on three main approaches: enzymatic conversion processes, thermochemical pathways, and hybrid systems. Enzymatic approaches offer selectivity advantages but struggle with reaction rates, while thermochemical methods provide higher throughput but with reduced selectivity. Hybrid systems attempt to combine these advantages but introduce additional complexity.
Regulatory frameworks vary significantly by region, creating an uneven global development landscape. The European Union has implemented supportive policies through its Circular Economy Action Plan, while the United States focuses on market-driven adoption with targeted research funding. Asian markets, particularly China, are rapidly expanding research capacity but face implementation challenges in existing industrial infrastructure.
Current Technical Solutions for Biomass Solvents
01 Production of biomass-derived solvents from lignocellulosic materials
Lignocellulosic materials can be processed to produce various biomass-derived solvents through methods such as fermentation, hydrolysis, and chemical conversion. These processes typically involve breaking down cellulose and hemicellulose components into sugars, which are then further converted into solvents like ethanol, butanol, and acetone. These renewable solvents offer environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-based products while utilizing agricultural and forestry residues as feedstock.- Production of biomass-derived solvents from lignocellulosic materials: Lignocellulosic materials can be processed to produce various biomass-derived solvents through methods such as hydrolysis, fermentation, and chemical conversion. These processes typically involve breaking down cellulose and hemicellulose components into sugars, which are then further converted into solvents like ethanol, butanol, and acetone. These renewable solvents offer environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-based products while utilizing abundant agricultural and forestry residues.
- Biomass-derived solvents for polymer applications: Biomass-derived solvents have shown significant potential in polymer applications, including as processing aids, reaction media, and components in polymer formulations. These bio-based solvents can improve the sustainability profile of polymer production and processing while maintaining or enhancing performance characteristics. Applications include use in adhesives, coatings, and as replacements for traditional petroleum-derived solvents in polymer synthesis and modification processes.
- Green extraction processes using biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents offer sustainable alternatives for extraction processes in various industries. These solvents, including esters, alcohols, and terpenes derived from renewable resources, can be used for the extraction of valuable compounds from plant materials, pharmaceutical ingredients, and in food processing. The extraction processes using these solvents typically have lower environmental impacts compared to conventional methods while maintaining extraction efficiency and product quality.
- Novel biomass-derived solvent compositions: Innovative compositions of biomass-derived solvents have been developed to enhance performance characteristics for specific applications. These compositions may include mixtures of different bio-based solvents, additives to improve stability or functionality, or specially formulated blends designed to replace specific petroleum-derived solvents. The novel compositions aim to overcome limitations of individual bio-solvents while maximizing their environmental benefits and application-specific performance.
- Production methods for gamma-valerolactone and other cyclic biomass-derived solvents: Cyclic biomass-derived solvents, particularly gamma-valerolactone (GVL) and related compounds, can be produced through various catalytic conversion processes using biomass feedstocks. These production methods typically involve hydrogenation, dehydration, and cyclization reactions of platform chemicals derived from biomass. The resulting cyclic solvents offer advantageous properties including low volatility, high boiling points, and good dissolving capabilities for various substances, making them valuable green alternatives to traditional petroleum-based solvents.
02 Green solvents derived from biomass for industrial applications
Biomass-derived green solvents are being developed for various industrial applications including cleaning, degreasing, paint removal, and as reaction media for chemical processes. These solvents offer advantages such as low toxicity, biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents. Examples include esters, ethers, alcohols, and terpenes derived from plant materials, which can be tailored for specific industrial needs while meeting sustainability requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biomass-derived solvents for pulp and paper processing
Solvents derived from biomass are being utilized in pulp and paper processing as alternatives to traditional chemical treatments. These bio-based solvents can effectively dissolve lignin and separate cellulose fibers while reducing the environmental impact of paper manufacturing. The process often involves using organic acids, alcohols, or other compounds obtained from renewable resources to create more sustainable pulping and bleaching methods that consume less energy and produce fewer harmful byproducts.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biofuel production processes utilizing biomass-derived solvents
Biomass-derived solvents play a crucial role in biofuel production processes, serving as reaction media, extraction agents, or as components of the final fuel products. These solvents can enhance the efficiency of biomass conversion to biofuels by improving the dissolution of feedstocks, facilitating reactions, and aiding in product separation. The integration of bio-based solvents in biofuel production creates more sustainable and circular production systems where byproducts from one process become inputs for another.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel biomass-derived solvent formulations and synthesis methods
Research is advancing in the development of novel biomass-derived solvent formulations and improved synthesis methods. These innovations focus on creating solvents with enhanced properties such as higher selectivity, better stability, and improved performance for specific applications. New catalytic processes, enzymatic conversions, and thermochemical treatments are being explored to efficiently transform biomass components into valuable solvents. These methods aim to reduce energy requirements, minimize waste generation, and increase the economic viability of bio-based solvents.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The biomass-derived solvent market is in a transitional growth phase, with increasing adoption driven by sustainability demands despite technical barriers. The global market is expanding at approximately 7-8% CAGR, reaching $6-7 billion, though still representing a small fraction of the conventional solvent market. Technical maturity varies significantly across applications, with companies demonstrating different levels of innovation. Shell, DuPont, and Eni are leading with established commercial-scale operations, while Synata Bio and Graphyte are advancing novel fermentation and carbon storage technologies. Academic institutions like Sichuan University and Dartmouth College are contributing fundamental research to overcome technical challenges. The industry faces a critical inflection point where technical barriers around scalability, cost-effectiveness, and performance consistency must be addressed to achieve mainstream adoption.
Shell Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Shell has developed an advanced thermochemical platform for biomass-derived solvent production that addresses key technical barriers. Their approach utilizes a multi-stage gasification process operating at temperatures between 800-1000°C that converts various biomass feedstocks into synthesis gas (syngas) with hydrogen-to-carbon monoxide ratios optimized for downstream solvent synthesis. Shell's proprietary catalysts, based on modified Fischer-Tropsch technology, enable direct conversion of syngas to oxygenated solvents including alcohols and ketones with selectivity exceeding 85%. The company has implemented innovative heat integration systems that recover approximately 60% of process heat, significantly improving energy efficiency. Shell's IH² (Integrated Hydropyrolysis and Hydroconversion) technology combines fast pyrolysis with immediate hydrogenation, reducing oxygen content in bio-oils from typical 35-40% to below 1%, enabling direct use as solvents or solvent precursors. Their demonstration facility in Houston has validated continuous operation for over 5,000 hours, proving process stability and catalyst longevity, with solvent production costs approaching competitive levels with petroleum-derived alternatives when carbon pricing mechanisms are considered.
Strengths: Feedstock flexibility allowing use of diverse biomass sources; thermochemical approach avoiding biological limitations; integration with existing petroleum infrastructure; scalable technology with clear pathway to commercial implementation. Weaknesses: High energy requirements despite heat integration; significant capital costs; process complexity requiring specialized operation expertise; still partially dependent on external hydrogen sources for optimal performance.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed a comprehensive biorefinery platform addressing multiple barriers to biomass-derived solvent adoption. Their approach centers on a two-stage fractionation process that separates lignocellulosic biomass into cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin streams with over 90% purity. For solvent production, DuPont employs genetically engineered microorganisms capable of fermenting both C5 and C6 sugars, significantly improving yield by approximately 40% compared to conventional yeast fermentation. Their proprietary AFEX (Ammonia Fiber Expansion) pretreatment technology reduces recalcitrance while preserving valuable biomass components and minimizing inhibitor formation. DuPont has also pioneered catalytic conversion pathways for producing bio-based acetone, butanol, and ethanol (ABE) solvents with selectivity exceeding 95%. Their integrated biorefinery in Nevada, Iowa demonstrated commercial-scale production of bio-based solvents with carbon intensity 60-70% lower than petroleum-derived alternatives, while achieving cost parity through process intensification and valorization of all biomass fractions.
Strengths: Comprehensive technology portfolio spanning the entire value chain; proven commercial-scale implementation; advanced genetic engineering capabilities for microbial catalysts; integrated approach addressing multiple technical barriers simultaneously. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements; technology complexity requiring specialized expertise; some processes still dependent on specific feedstock characteristics limiting flexibility.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Bio-Solvent Technology
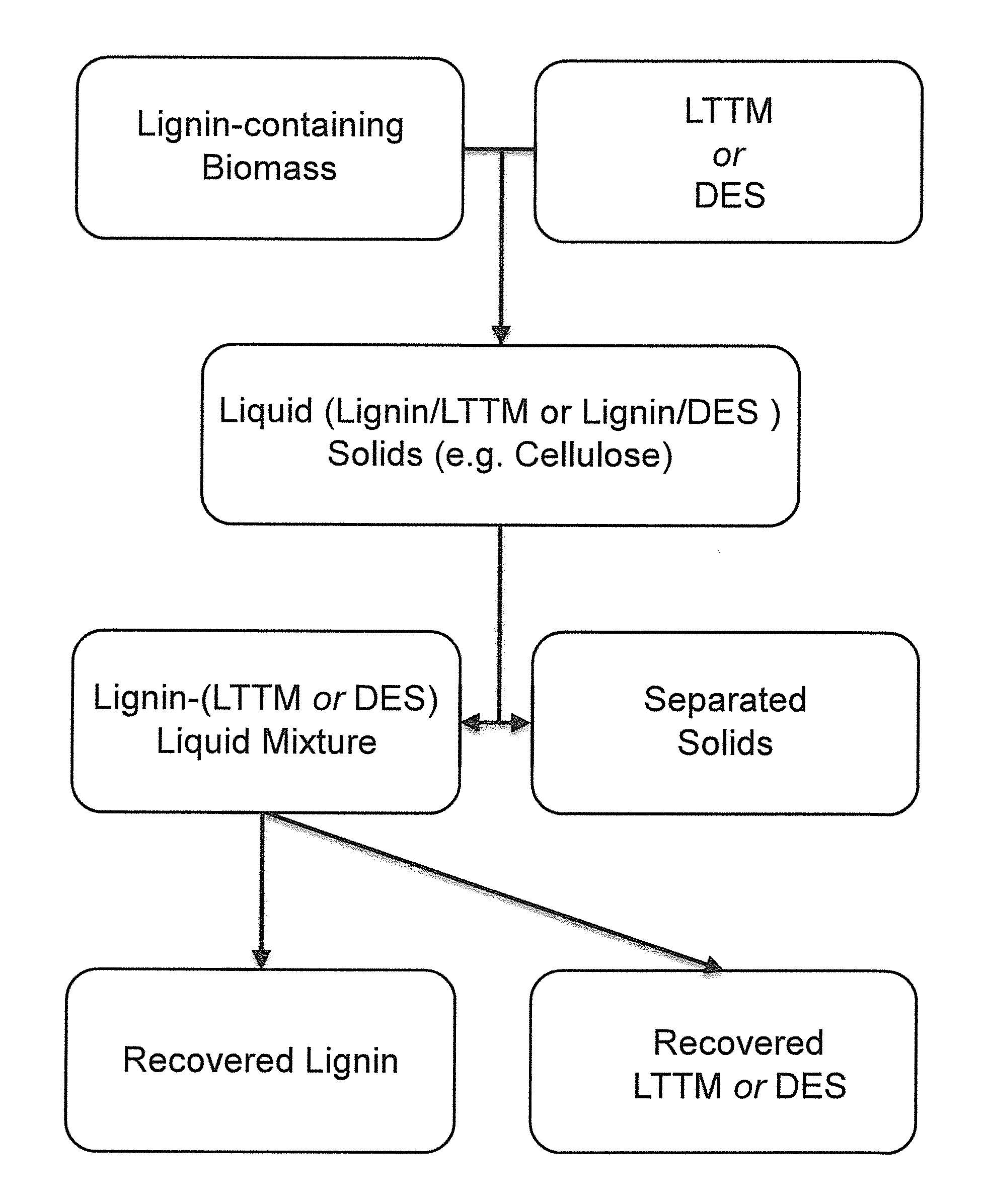
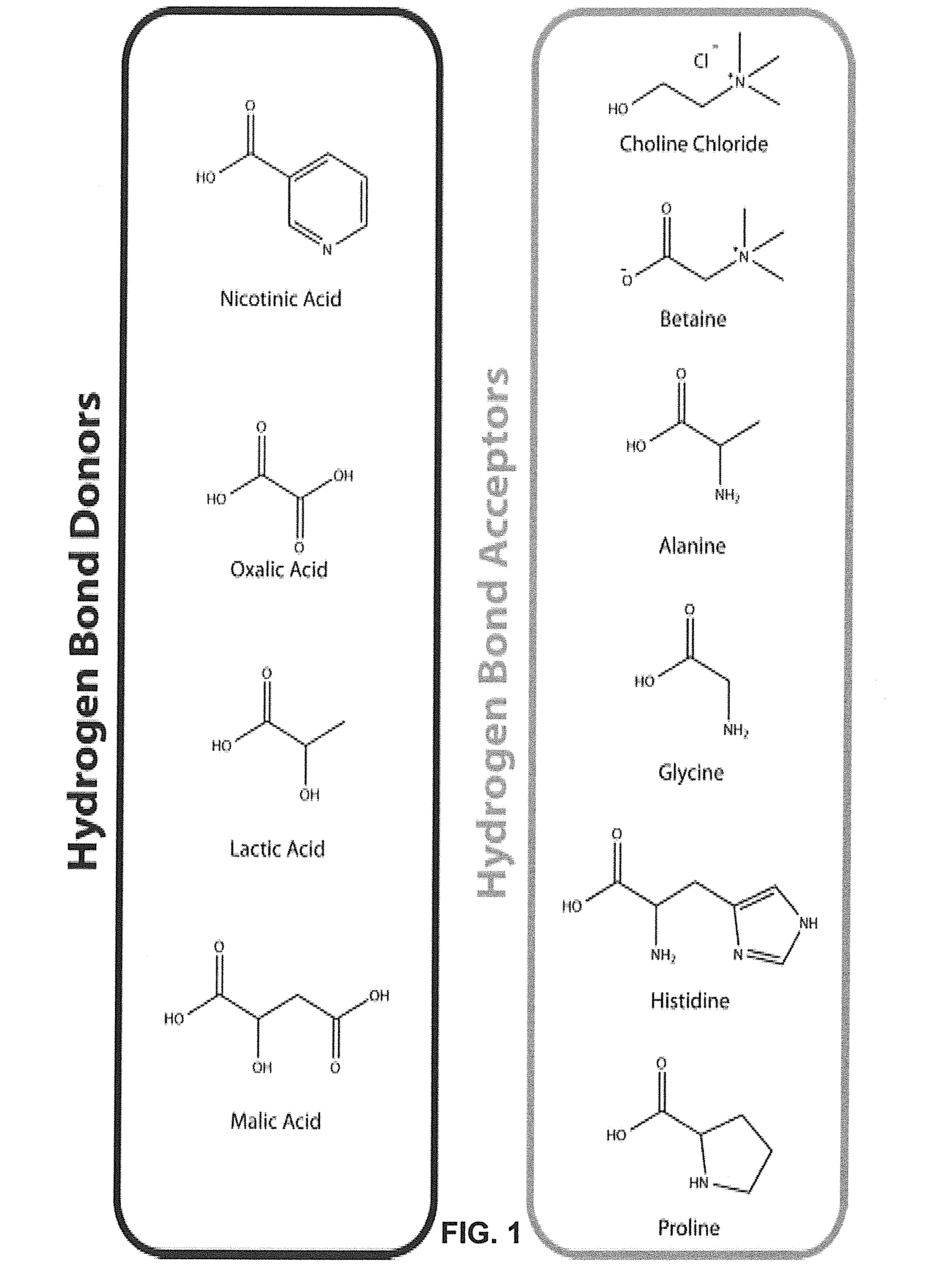
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
PatentInactiveUS20150094459A1
Innovation
- Development of low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) composed of renewable components, which selectively dissolve lignin from lignin-containing biomass at mild conditions, allowing for energy-efficient separation of lignin from cellulose without degradation, and enable recovery of high-quality lignin and cellulose.
Solvent pulping of biomass
PatentInactiveUS20040060673A1
Innovation
- The method involves using a high-recovery solvent pulping process with efficient equipment and process designs, including gradual pressure and temperature stepping, indirect heating, and controlled liquor flashing, to delignify cellulose-containing biomass, such as agricultural residues, while minimizing energy and liquor losses and allowing for the recovery of lignin and furfural.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape for biomass-derived solvents presents a complex framework that significantly impacts their market adoption. Current regulations across major markets exhibit considerable variation, with the European Union leading through its REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) program, which requires comprehensive safety assessments for new chemical substances, including bio-based solvents. This regulatory framework demands extensive toxicological data, environmental impact assessments, and lifecycle analyses that can cost manufacturers millions of dollars and several years to complete.
In the United States, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) governs chemical substances, with recent amendments emphasizing safer alternatives to conventional petrochemical products. The EPA's Safer Choice program offers potential pathways for biomass-derived solvents to gain recognition, though the certification process remains rigorous and time-consuming. Additionally, California's Proposition 65 and various state-level VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) regulations create a patchwork of compliance requirements that manufacturers must navigate.
Globally, the inconsistency in regulatory standards creates significant market entry barriers. Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have implemented their own chemical management systems that often require duplicate testing and documentation. This regulatory fragmentation increases compliance costs and extends time-to-market for innovative biomass-derived solvents, disadvantaging them against established petrochemical alternatives with grandfathered regulatory approvals.
Food-contact applications present particularly stringent requirements. The FDA in the US and EFSA in Europe maintain strict protocols for solvents that may come into contact with food products, requiring extensive migration studies and safety assessments. Many promising biomass-derived solvents lack these approvals, limiting their potential market applications despite favorable performance characteristics.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a gradual shift toward harmonization and simplified pathways for bio-based chemicals. The OECD's mutual acceptance of data initiative represents progress in reducing duplicate testing requirements. Additionally, several jurisdictions are developing specific frameworks for bio-based products that acknowledge their renewable origins and potential sustainability benefits, potentially streamlining approval processes.
Compliance costs remain a significant barrier, particularly for startups and smaller manufacturers. The investment required for comprehensive toxicological testing, environmental fate studies, and regulatory submissions can exceed $2-5 million per substance, creating an asymmetric advantage for established petrochemical companies with greater regulatory resources and experience. This financial burden often delays or prevents promising biomass-derived solvents from reaching commercial scale.
In the United States, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) governs chemical substances, with recent amendments emphasizing safer alternatives to conventional petrochemical products. The EPA's Safer Choice program offers potential pathways for biomass-derived solvents to gain recognition, though the certification process remains rigorous and time-consuming. Additionally, California's Proposition 65 and various state-level VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) regulations create a patchwork of compliance requirements that manufacturers must navigate.
Globally, the inconsistency in regulatory standards creates significant market entry barriers. Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have implemented their own chemical management systems that often require duplicate testing and documentation. This regulatory fragmentation increases compliance costs and extends time-to-market for innovative biomass-derived solvents, disadvantaging them against established petrochemical alternatives with grandfathered regulatory approvals.
Food-contact applications present particularly stringent requirements. The FDA in the US and EFSA in Europe maintain strict protocols for solvents that may come into contact with food products, requiring extensive migration studies and safety assessments. Many promising biomass-derived solvents lack these approvals, limiting their potential market applications despite favorable performance characteristics.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a gradual shift toward harmonization and simplified pathways for bio-based chemicals. The OECD's mutual acceptance of data initiative represents progress in reducing duplicate testing requirements. Additionally, several jurisdictions are developing specific frameworks for bio-based products that acknowledge their renewable origins and potential sustainability benefits, potentially streamlining approval processes.
Compliance costs remain a significant barrier, particularly for startups and smaller manufacturers. The investment required for comprehensive toxicological testing, environmental fate studies, and regulatory submissions can exceed $2-5 million per substance, creating an asymmetric advantage for established petrochemical companies with greater regulatory resources and experience. This financial burden often delays or prevents promising biomass-derived solvents from reaching commercial scale.
Life Cycle Assessment and Sustainability Metrics
Life cycle assessment (LCA) provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the environmental impacts of biomass-derived solvents across their entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. When comparing these bio-solvents with conventional petroleum-based alternatives, several key sustainability metrics emerge as critical evaluation points. Carbon footprint analysis typically reveals significant advantages for biomass-derived solvents, with potential greenhouse gas emission reductions of 30-80% depending on feedstock selection and processing methods.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture, as biomass cultivation may require substantial irrigation in certain regions, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits. Studies indicate that water footprints can vary by a factor of 5-10 across different biomass feedstocks, with agricultural residues generally performing better than dedicated energy crops in water-limited environments.
Land use change impacts constitute another crucial sustainability consideration. The conversion of natural ecosystems to biomass production can release significant carbon stores and reduce biodiversity. Sustainability certification schemes increasingly incorporate indirect land use change factors to provide more accurate environmental impact assessments.
Energy return on investment (EROI) calculations for biomass-derived solvents typically range from 2:1 to 5:1, compared to 8:1 to 12:1 for conventional petroleum-based solvents. This efficiency gap represents a significant technical barrier to widespread adoption, though it continues to narrow with processing improvements.
Toxicity profiles and biodegradability metrics generally favor biomass-derived solvents, with many demonstrating reduced aquatic toxicity and faster environmental degradation compared to petroleum-based counterparts. These advantages can translate into reduced environmental persistence and lower ecotoxicological impacts throughout the product lifecycle.
Economic sustainability metrics, while not strictly environmental, play a crucial role in adoption potential. Current production cost differentials between bio-based and conventional solvents range from 1.2-2.5 times higher for bio-alternatives, though this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements and economies of scale.
Standardization of sustainability metrics remains challenging, with various competing frameworks including the ASTM D6866 standard for bio-based content determination, ISO 14040/14044 for LCA methodology, and industry-specific certification schemes. This fragmentation creates barriers to consistent evaluation and market recognition of sustainability benefits.
Water consumption metrics present a more complex picture, as biomass cultivation may require substantial irrigation in certain regions, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits. Studies indicate that water footprints can vary by a factor of 5-10 across different biomass feedstocks, with agricultural residues generally performing better than dedicated energy crops in water-limited environments.
Land use change impacts constitute another crucial sustainability consideration. The conversion of natural ecosystems to biomass production can release significant carbon stores and reduce biodiversity. Sustainability certification schemes increasingly incorporate indirect land use change factors to provide more accurate environmental impact assessments.
Energy return on investment (EROI) calculations for biomass-derived solvents typically range from 2:1 to 5:1, compared to 8:1 to 12:1 for conventional petroleum-based solvents. This efficiency gap represents a significant technical barrier to widespread adoption, though it continues to narrow with processing improvements.
Toxicity profiles and biodegradability metrics generally favor biomass-derived solvents, with many demonstrating reduced aquatic toxicity and faster environmental degradation compared to petroleum-based counterparts. These advantages can translate into reduced environmental persistence and lower ecotoxicological impacts throughout the product lifecycle.
Economic sustainability metrics, while not strictly environmental, play a crucial role in adoption potential. Current production cost differentials between bio-based and conventional solvents range from 1.2-2.5 times higher for bio-alternatives, though this gap continues to narrow with technological advancements and economies of scale.
Standardization of sustainability metrics remains challenging, with various competing frameworks including the ASTM D6866 standard for bio-based content determination, ISO 14040/14044 for LCA methodology, and industry-specific certification schemes. This fragmentation creates barriers to consistent evaluation and market recognition of sustainability benefits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!