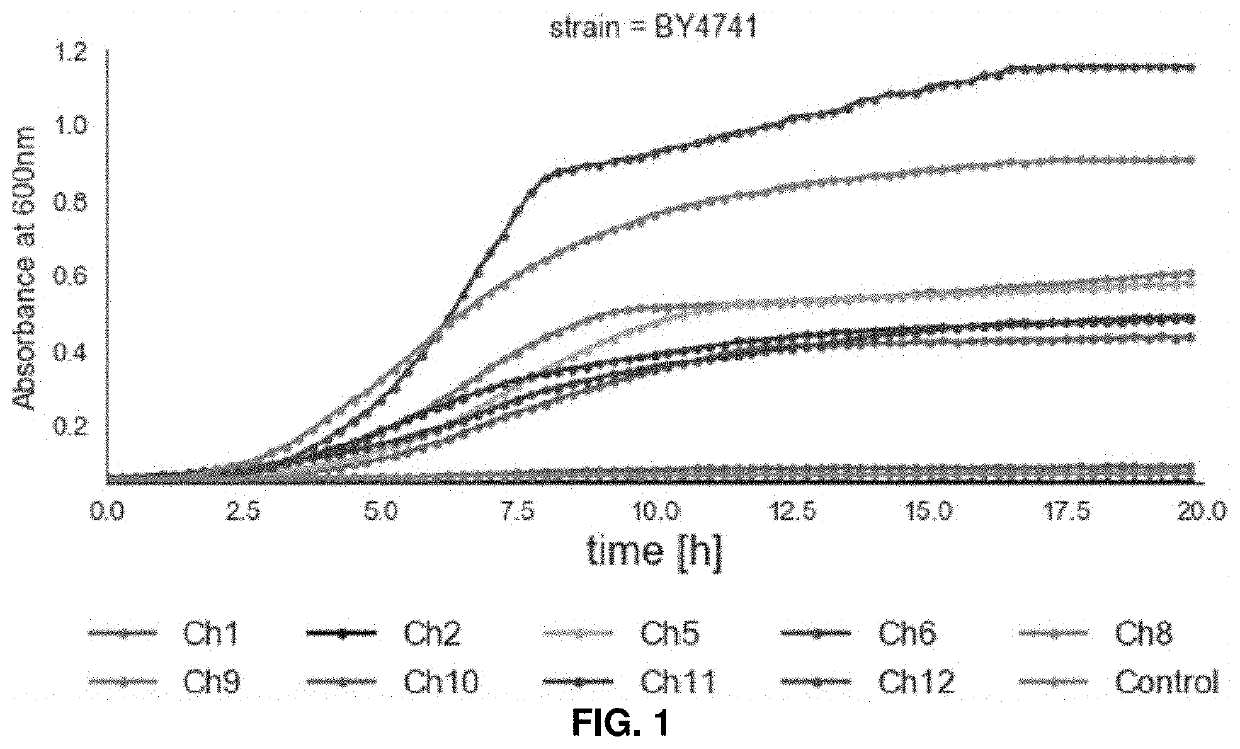
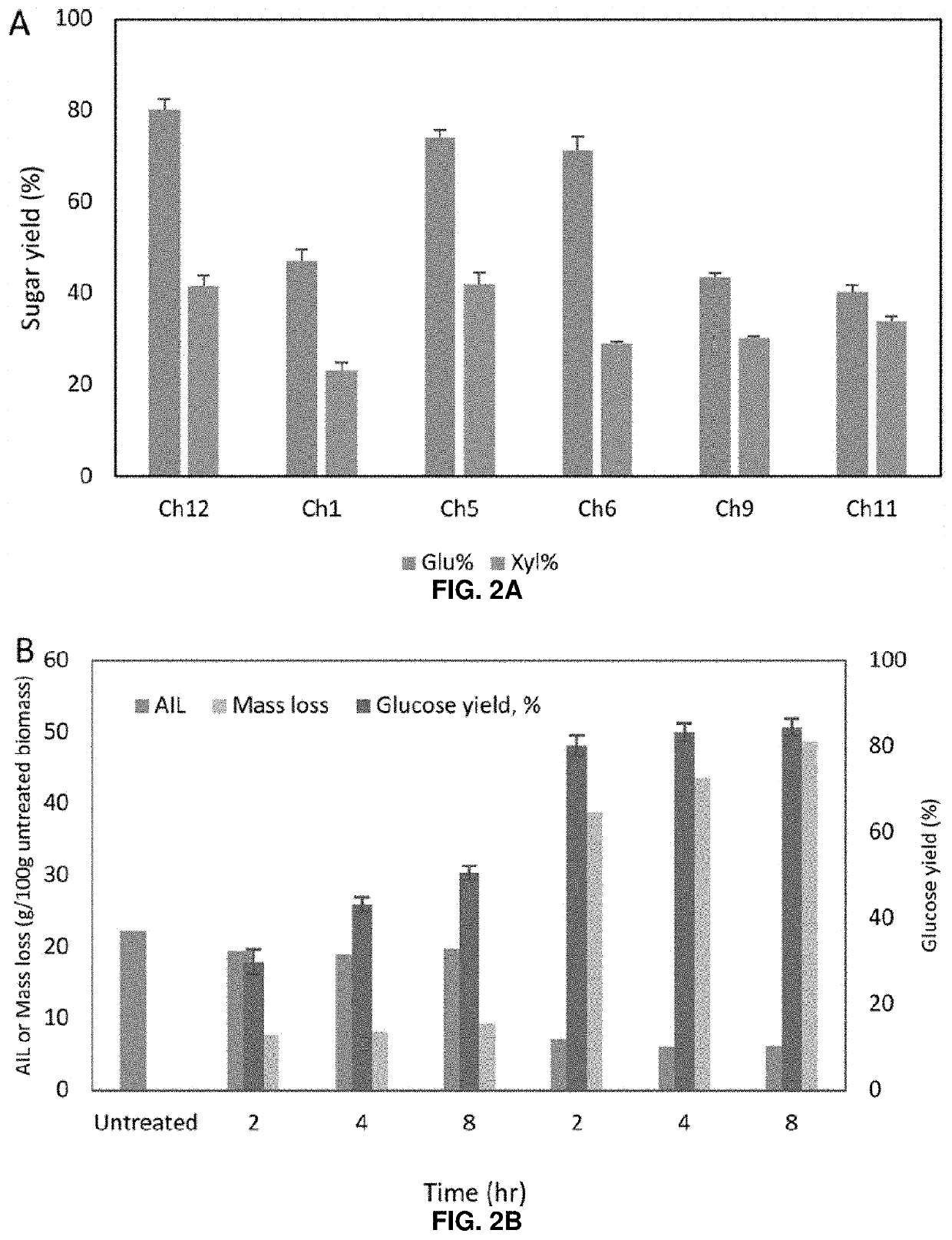
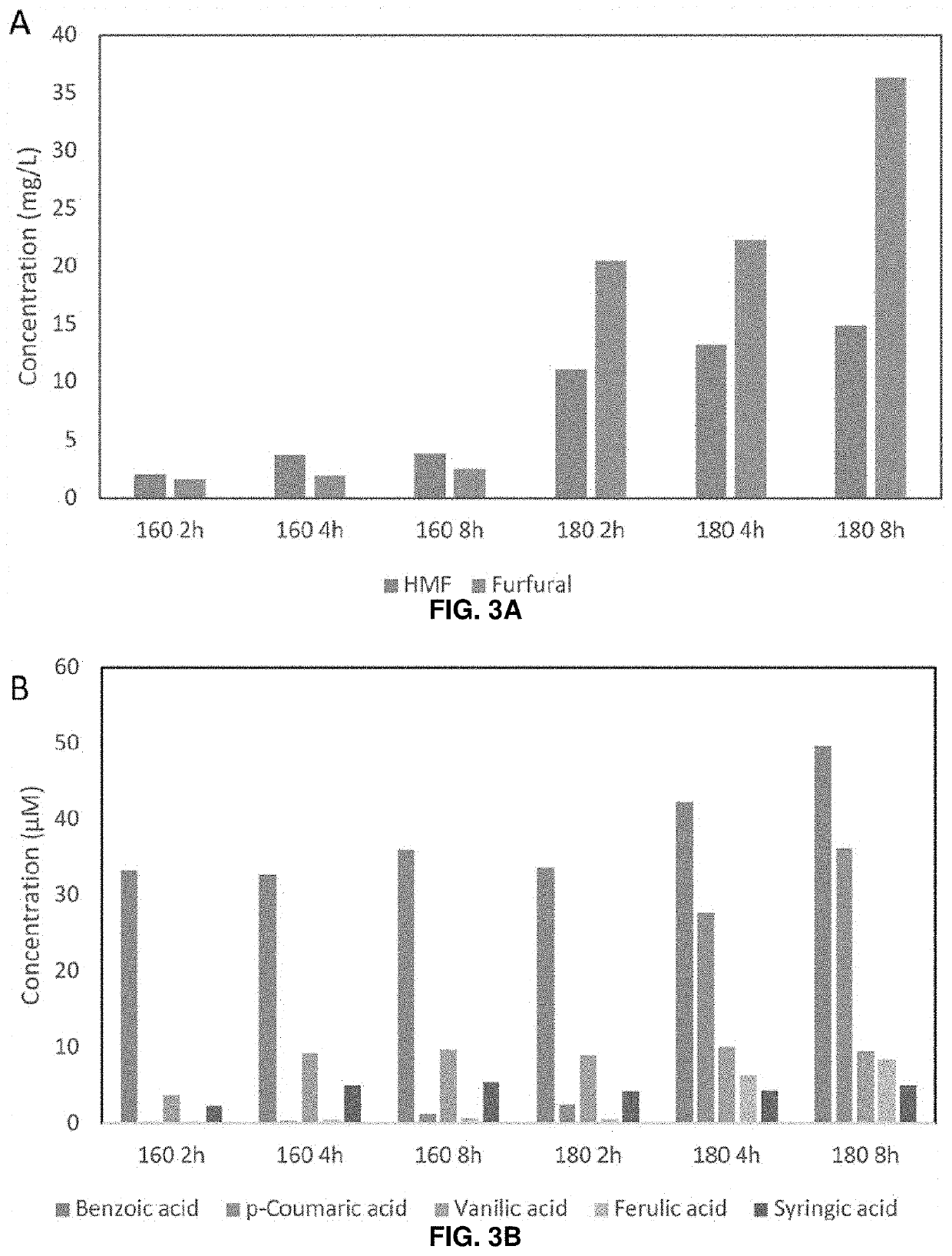
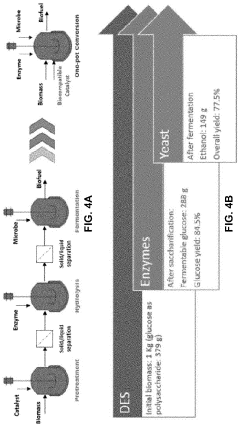
The Role of Biomass-Derived Solvents in Energy-Efficient Manufacturing
OCT 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biomass Solvents Evolution and Objectives
Biomass-derived solvents have emerged as a sustainable alternative to conventional petroleum-based solvents, marking a significant shift in manufacturing paradigms over the past few decades. The evolution of these bio-solvents began in the early 1990s with simple alcohols like bioethanol, gradually expanding to include more complex molecules such as esters, lactates, and terpenes derived from renewable feedstocks. This progression has been driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and the growing emphasis on circular economy principles.
The technological trajectory of biomass solvents has been characterized by three distinct phases. The first phase (1990-2005) focused primarily on direct substitution, where bio-derived alternatives simply replaced conventional solvents without significant process modifications. The second phase (2005-2015) witnessed the development of tailored bio-solvents with enhanced performance characteristics, specifically designed for particular industrial applications. The current third phase (2015-present) emphasizes integrated biorefinery approaches, where solvent production is incorporated into broader biomass valorization strategies.
Recent advancements in biotechnology and catalytic conversion have substantially expanded the range of available biomass-derived solvents. Particularly noteworthy is the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES) from biomass components, which offer tunable physicochemical properties while maintaining biodegradability. Similarly, lignin-derived aromatic solvents have shown promise in specialized applications where conventional bio-solvents fall short.
The primary objective of biomass solvent technology is to achieve a triple benefit: environmental sustainability through reduced carbon footprint, economic viability through competitive pricing and performance, and enhanced safety profiles compared to conventional alternatives. Specific technical goals include developing solvents with lower volatility to reduce emissions, improved selectivity for target applications, and enhanced energy efficiency in both production and application phases.
Looking forward, the field aims to overcome several persistent challenges. These include reducing the energy intensity of biomass solvent production, expanding the range of applications where bio-solvents can effectively replace petroleum-based alternatives, and addressing scalability issues that currently limit widespread industrial adoption. The ultimate technological objective is to develop next-generation biomass solvents that not only match but exceed the performance of conventional solvents while offering significant energy savings throughout the manufacturing value chain.
The technological trajectory of biomass solvents has been characterized by three distinct phases. The first phase (1990-2005) focused primarily on direct substitution, where bio-derived alternatives simply replaced conventional solvents without significant process modifications. The second phase (2005-2015) witnessed the development of tailored bio-solvents with enhanced performance characteristics, specifically designed for particular industrial applications. The current third phase (2015-present) emphasizes integrated biorefinery approaches, where solvent production is incorporated into broader biomass valorization strategies.
Recent advancements in biotechnology and catalytic conversion have substantially expanded the range of available biomass-derived solvents. Particularly noteworthy is the development of deep eutectic solvents (DES) from biomass components, which offer tunable physicochemical properties while maintaining biodegradability. Similarly, lignin-derived aromatic solvents have shown promise in specialized applications where conventional bio-solvents fall short.
The primary objective of biomass solvent technology is to achieve a triple benefit: environmental sustainability through reduced carbon footprint, economic viability through competitive pricing and performance, and enhanced safety profiles compared to conventional alternatives. Specific technical goals include developing solvents with lower volatility to reduce emissions, improved selectivity for target applications, and enhanced energy efficiency in both production and application phases.
Looking forward, the field aims to overcome several persistent challenges. These include reducing the energy intensity of biomass solvent production, expanding the range of applications where bio-solvents can effectively replace petroleum-based alternatives, and addressing scalability issues that currently limit widespread industrial adoption. The ultimate technological objective is to develop next-generation biomass solvents that not only match but exceed the performance of conventional solvents while offering significant energy savings throughout the manufacturing value chain.
Market Analysis for Green Manufacturing Solvents
The global market for green manufacturing solvents is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability initiatives. The biomass-derived solvents segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% through 2030, outpacing traditional petroleum-based solvents which are growing at only 3.5% annually. This accelerated growth reflects the shifting priorities in manufacturing industries toward more sustainable practices.
Key market drivers include stringent VOC emission regulations in Europe and North America, consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, and corporate commitments to carbon neutrality. The EU's Green Deal and similar policies in other regions are creating regulatory frameworks that favor bio-based alternatives, effectively reshaping market dynamics across multiple industries.
Manufacturing sectors showing the highest adoption rates for biomass-derived solvents include pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing, where product purity and safety considerations align with the benefits of bio-based solvents. The automotive and electronics industries are emerging as significant growth sectors, particularly for cleaning applications in precision manufacturing.
Regional analysis reveals Europe leading the market with approximately 38% share, followed by North America at 29% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the fastest growth rate due to rapid industrialization coupled with increasing environmental awareness and regulatory development in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Price sensitivity remains a significant market barrier, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding a 15-30% premium over conventional alternatives. However, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and process efficiencies improve. Market research indicates that manufacturers are increasingly willing to absorb higher costs when total lifecycle benefits, including waste reduction and worker safety improvements, are considered.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies pivoting toward bio-based portfolios and innovative startups focused exclusively on green chemistry solutions. Strategic partnerships between solvent manufacturers and biomass producers are becoming increasingly common, creating vertically integrated supply chains that enhance cost competitiveness and supply security.
Market forecasts suggest that biomass-derived solvents could capture up to 25% of the total industrial solvents market by 2035, representing a significant shift from the current 8% market share. This transition is expected to accelerate as technological improvements in biomass processing continue to enhance the performance characteristics and economic viability of these sustainable alternatives.
Key market drivers include stringent VOC emission regulations in Europe and North America, consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, and corporate commitments to carbon neutrality. The EU's Green Deal and similar policies in other regions are creating regulatory frameworks that favor bio-based alternatives, effectively reshaping market dynamics across multiple industries.
Manufacturing sectors showing the highest adoption rates for biomass-derived solvents include pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing, where product purity and safety considerations align with the benefits of bio-based solvents. The automotive and electronics industries are emerging as significant growth sectors, particularly for cleaning applications in precision manufacturing.
Regional analysis reveals Europe leading the market with approximately 38% share, followed by North America at 29% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to demonstrate the fastest growth rate due to rapid industrialization coupled with increasing environmental awareness and regulatory development in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Price sensitivity remains a significant market barrier, with biomass-derived solvents typically commanding a 15-30% premium over conventional alternatives. However, this gap is narrowing as production scales increase and process efficiencies improve. Market research indicates that manufacturers are increasingly willing to absorb higher costs when total lifecycle benefits, including waste reduction and worker safety improvements, are considered.
The competitive landscape features both established chemical companies pivoting toward bio-based portfolios and innovative startups focused exclusively on green chemistry solutions. Strategic partnerships between solvent manufacturers and biomass producers are becoming increasingly common, creating vertically integrated supply chains that enhance cost competitiveness and supply security.
Market forecasts suggest that biomass-derived solvents could capture up to 25% of the total industrial solvents market by 2035, representing a significant shift from the current 8% market share. This transition is expected to accelerate as technological improvements in biomass processing continue to enhance the performance characteristics and economic viability of these sustainable alternatives.
Global Status and Challenges in Biomass Solvent Development
The global landscape of biomass-derived solvents is characterized by significant regional disparities in research, development, and implementation. North America and Europe currently lead in advanced research and commercialization efforts, with established biorefinery infrastructures and supportive policy frameworks. The European Union, through initiatives like the Renewable Energy Directive II, has created a conducive environment for biomass solvent development, resulting in several commercial-scale facilities.
Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is rapidly expanding its biomass solvent capabilities, leveraging abundant agricultural residues and growing manufacturing sectors. These countries are increasingly investing in research facilities and pilot plants, though they still lag behind Western counterparts in terms of technological sophistication and scale.
Despite these advancements, the global biomass solvent industry faces significant challenges. Technical barriers remain prominent, including the need for more efficient conversion processes to transform biomass into high-quality solvents. Current extraction and purification methods often require substantial energy inputs, potentially undermining the sustainability benefits of bio-based alternatives.
Economic viability presents another major hurdle. Biomass-derived solvents typically cost 1.5-3 times more than their petroleum-based counterparts, making widespread industrial adoption difficult without policy incentives or premium market positioning. The fluctuating availability of feedstock and seasonal variations in biomass quality further complicate consistent production and pricing structures.
Infrastructure limitations also impede progress, with many regions lacking the necessary supply chains and processing facilities to support large-scale biomass solvent production. The transition from laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial manufacturing remains challenging, requiring significant capital investment and technical expertise.
Regulatory frameworks vary considerably across regions, creating an uneven playing field for developers and manufacturers. While some jurisdictions have implemented favorable policies for bio-based chemicals, others lack clear guidelines or incentives, hampering market development and international trade.
Standardization issues further complicate global adoption, with inconsistent quality parameters and performance metrics making it difficult for end-users to confidently switch from conventional solvents. The absence of universally accepted certification systems for sustainability claims also creates market confusion and skepticism.
Research gaps persist in understanding the full lifecycle impacts of biomass-derived solvents, particularly regarding land use changes, water consumption, and potential competition with food production. More comprehensive sustainability assessments are needed to ensure these alternatives deliver genuine environmental benefits across their entire value chain.
Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is rapidly expanding its biomass solvent capabilities, leveraging abundant agricultural residues and growing manufacturing sectors. These countries are increasingly investing in research facilities and pilot plants, though they still lag behind Western counterparts in terms of technological sophistication and scale.
Despite these advancements, the global biomass solvent industry faces significant challenges. Technical barriers remain prominent, including the need for more efficient conversion processes to transform biomass into high-quality solvents. Current extraction and purification methods often require substantial energy inputs, potentially undermining the sustainability benefits of bio-based alternatives.
Economic viability presents another major hurdle. Biomass-derived solvents typically cost 1.5-3 times more than their petroleum-based counterparts, making widespread industrial adoption difficult without policy incentives or premium market positioning. The fluctuating availability of feedstock and seasonal variations in biomass quality further complicate consistent production and pricing structures.
Infrastructure limitations also impede progress, with many regions lacking the necessary supply chains and processing facilities to support large-scale biomass solvent production. The transition from laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial manufacturing remains challenging, requiring significant capital investment and technical expertise.
Regulatory frameworks vary considerably across regions, creating an uneven playing field for developers and manufacturers. While some jurisdictions have implemented favorable policies for bio-based chemicals, others lack clear guidelines or incentives, hampering market development and international trade.
Standardization issues further complicate global adoption, with inconsistent quality parameters and performance metrics making it difficult for end-users to confidently switch from conventional solvents. The absence of universally accepted certification systems for sustainability claims also creates market confusion and skepticism.
Research gaps persist in understanding the full lifecycle impacts of biomass-derived solvents, particularly regarding land use changes, water consumption, and potential competition with food production. More comprehensive sustainability assessments are needed to ensure these alternatives deliver genuine environmental benefits across their entire value chain.
Current Biomass Solvent Implementation Strategies
01 Production of biomass-derived solvents from renewable feedstocks
Various processes have been developed to produce solvents from biomass feedstocks as alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. These processes involve the conversion of biomass materials such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops into valuable solvents through biochemical or thermochemical pathways. The resulting bio-based solvents offer improved energy efficiency in production compared to conventional petroleum-derived alternatives while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil resources.- Production of biomass-derived solvents from renewable feedstocks: Various processes have been developed to produce solvents from biomass feedstocks as alternatives to petroleum-based solvents. These processes involve converting biomass materials such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and dedicated energy crops into valuable solvents through biochemical or thermochemical pathways. The resulting bio-based solvents offer improved energy efficiency in production compared to conventional petroleum-derived alternatives, with reduced carbon footprints and environmental impacts.
- Energy-efficient extraction and separation processes using biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents can be utilized in extraction and separation processes with enhanced energy efficiency. These solvents often require lower temperatures for effective extraction compared to conventional solvents, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, some bio-based solvents demonstrate selective extraction capabilities, minimizing the need for multiple separation steps and further improving overall process efficiency. The reduced energy requirements for solvent recovery and recycling contribute to the sustainability of these processes.
- Biomass-derived solvents for biofuel production: Biomass-derived solvents play a crucial role in energy-efficient biofuel production processes. These solvents can facilitate the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, enhancing the accessibility of cellulose and hemicellulose for enzymatic hydrolysis. The use of bio-based solvents in biofuel production creates a closed-loop system where both the process solvents and the end products are derived from renewable resources, maximizing energy efficiency and sustainability throughout the production chain.
- Green chemistry applications of biomass-derived solvents: Biomass-derived solvents enable energy-efficient green chemistry applications across various industries. These solvents often feature lower toxicity, higher biodegradability, and reduced volatility compared to conventional solvents. Their application in chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and consumer products can significantly reduce energy consumption associated with waste treatment, emissions control, and environmental remediation. The improved safety profile of many bio-based solvents also reduces energy requirements for handling and storage.
- Energy recovery systems for biomass-derived solvent processes: Advanced energy recovery systems have been developed specifically for processes involving biomass-derived solvents. These systems capture and utilize waste heat from solvent production and application processes, improving overall energy efficiency. Integrated biorefinery approaches combine solvent production with energy generation, creating synergistic effects that maximize resource utilization. Some processes incorporate cogeneration systems that produce both bio-based solvents and energy, further enhancing the energy efficiency of the entire production system.
02 Energy-efficient extraction and separation processes using biomass-derived solvents
Biomass-derived solvents can be utilized in extraction and separation processes with enhanced energy efficiency. These bio-based solvents often require lower energy inputs for solvent recovery due to their favorable physical properties such as lower boiling points or the ability to form phase separations under mild conditions. Applications include the extraction of valuable compounds from natural materials, separation of reaction products, and purification processes in various industries, all while reducing the overall energy footprint compared to conventional solvent-based processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biomass-derived solvents for biofuel production and biorefineries
Biomass-derived solvents play a crucial role in improving the energy efficiency of biofuel production processes and biorefinery operations. These solvents facilitate the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass, enhance enzymatic hydrolysis, and improve the extraction and separation of biofuels and high-value co-products. The integration of biomass-derived solvents in biorefineries creates closed-loop systems where solvents are produced and utilized within the same facility, maximizing resource utilization and overall process energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy-efficient reaction media and catalytic systems
Biomass-derived solvents can serve as energy-efficient reaction media for various chemical transformations and catalytic processes. These bio-based solvents often enable reactions to proceed under milder conditions, reducing energy requirements while maintaining or improving reaction rates and selectivities. Some biomass-derived solvents also exhibit unique properties that enhance catalyst performance, stability, and recyclability, further contributing to the overall energy efficiency of chemical production processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Thermal applications and heat transfer systems using biomass-derived solvents
Biomass-derived solvents can be utilized in thermal applications and heat transfer systems to improve energy efficiency. These solvents often possess favorable thermophysical properties such as high heat capacity, thermal stability, and appropriate phase change characteristics. Applications include heat exchange fluids, thermal energy storage media, and working fluids in thermodynamic cycles. The renewable nature of these solvents, combined with their performance characteristics, contributes to more sustainable and energy-efficient thermal management systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders in Sustainable Solvent Production
The biomass-derived solvents market in energy-efficient manufacturing is in its growth phase, with increasing adoption driven by sustainability demands. The market is projected to expand significantly as industries transition from petroleum-based to bio-based chemicals. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across applications. Leading players include UOP LLC and Virent, Inc., who have established commercial-scale production capabilities, while research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and King Abdullah University of Science & Technology are advancing fundamental innovations. European companies such as Walter Tosto SpA and Johnson Matthey Plc are focusing on process optimization and catalysis improvements. The competitive landscape features collaboration between academic institutions and industrial partners, with Asian players like South China University of Technology increasingly contributing to technological advancements.
UOP LLC
Technical Solution: UOP LLC has developed innovative biomass-derived solvent technologies for energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Their BioForming® platform converts plant sugars into high-performance chemicals and fuels, including bio-derived solvents like 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (2-MeTHF) and gamma-valerolactone (GVL). These solvents are produced through catalytic conversion of biomass-derived feedstocks using proprietary catalysts and process technologies. UOP's integrated biorefinery approach enables the production of these green solvents alongside other valuable co-products, maximizing resource utilization and process efficiency. Their technology incorporates advanced separation techniques to achieve high-purity solvents suitable for industrial applications while minimizing energy consumption during manufacturing. The company has demonstrated significant reductions in carbon footprint compared to conventional petroleum-derived solvents, with lifecycle assessments showing up to 70% lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Strengths: Extensive experience in refining and petrochemical processes provides strong foundation for scaling biomass solvent production; proprietary catalyst technology enables efficient conversion of various biomass feedstocks. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents; technology still requires optimization for certain biomass feedstock types.
Furanix Technologies BV
Technical Solution: Furanix Technologies has pioneered the development of furan-based chemistry for biomass-derived solvents, particularly focusing on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and its derivatives. Their patented YXY® Technology platform converts plant-based carbohydrates into these valuable chemical building blocks. The process utilizes catalytic dehydration of C6 sugars (primarily fructose) in biphasic reactor systems with specialized catalysts to achieve high yields of furan derivatives. These furan-based compounds serve as excellent green solvents for various industrial applications, offering properties comparable or superior to traditional petroleum-derived alternatives. Furanix has optimized their manufacturing process to operate at moderate temperatures (80-180°C) and pressures, significantly reducing energy requirements compared to conventional solvent production. Their integrated biorefinery concept incorporates energy recovery systems and process intensification techniques to further enhance energy efficiency. The company has demonstrated commercial-scale production capabilities with solvent purity exceeding 99.5% while maintaining lower energy consumption than traditional solvent manufacturing routes.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in furan chemistry provides unique positioning in the biomass-derived solvents market; technology produces high-purity solvents with excellent performance characteristics. Weaknesses: Limited to carbohydrate-based feedstocks; process economics still challenged by feedstock costs and availability in some regions.
Key Innovations in Biomass Extraction Technologies
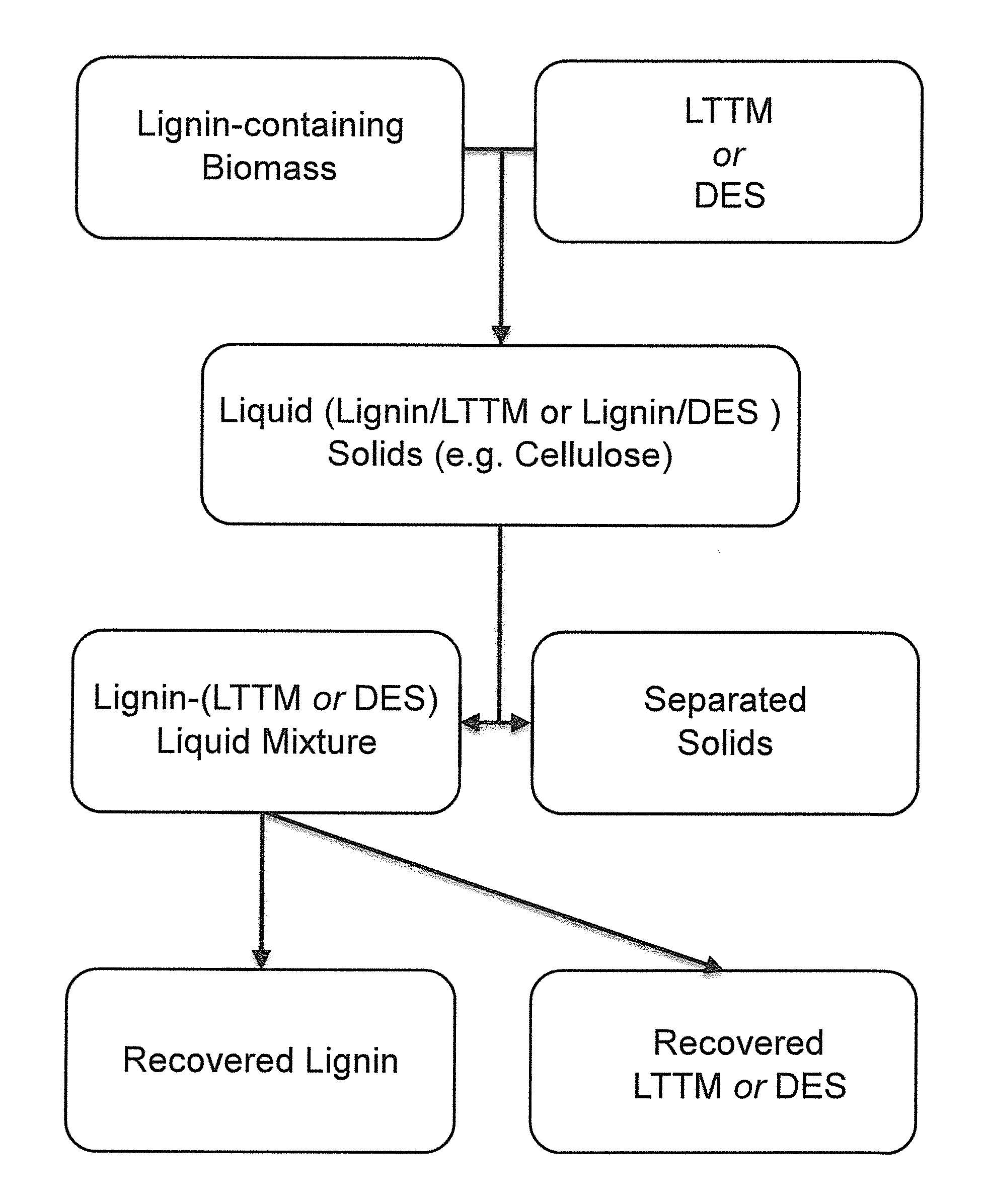
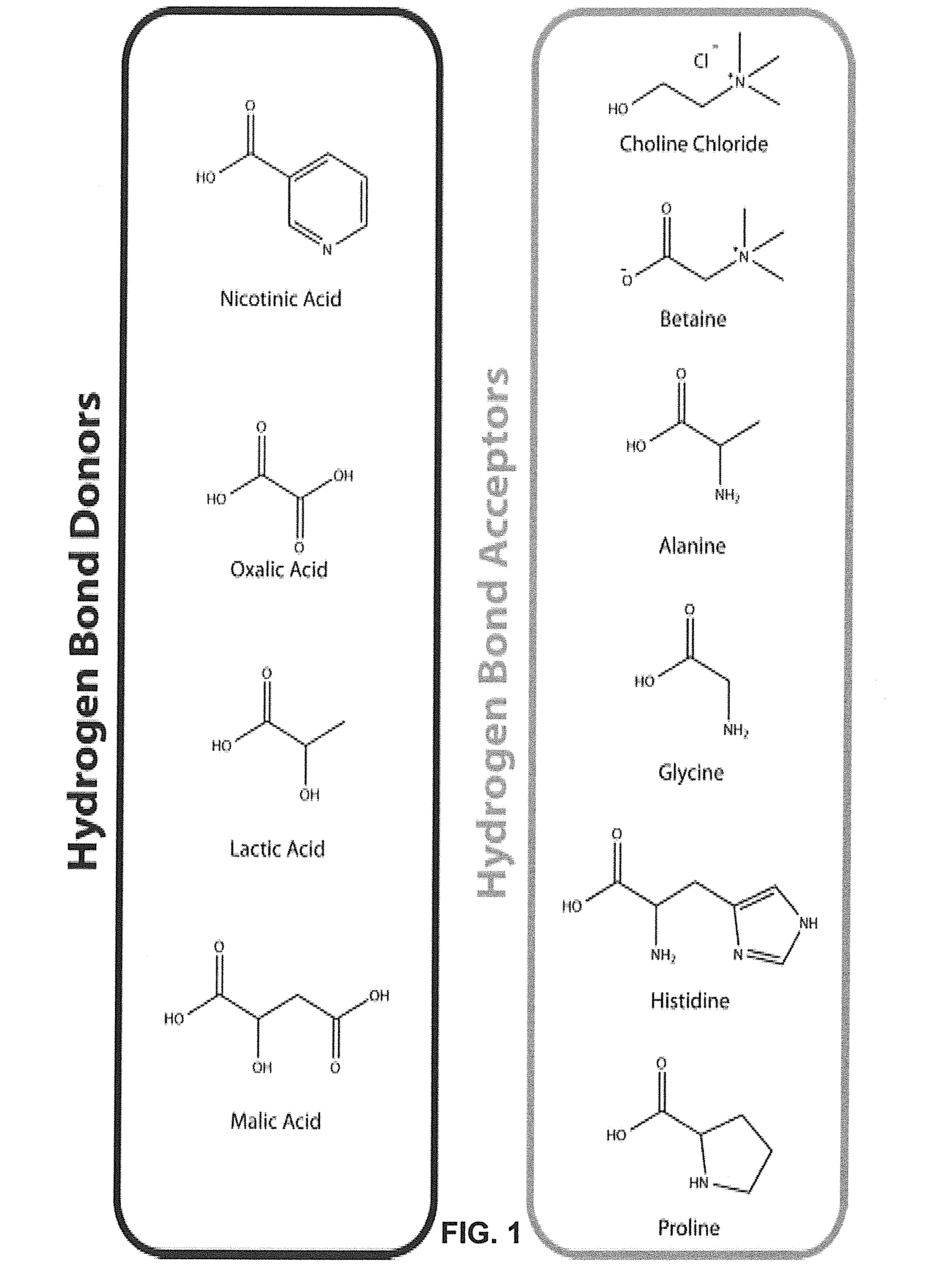
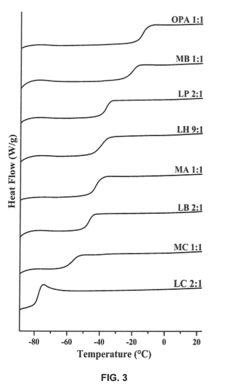
Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Recovery of Substituents using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents/Compound Mixtures with Low Transition Temperatures
PatentInactiveUS20150094459A1
Innovation
- Development of low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) composed of renewable components, which selectively dissolve lignin from lignin-containing biomass at mild conditions, allowing for energy-efficient separation of lignin from cellulose without degradation, and enable recovery of high-quality lignin and cellulose.
Use of renewable deep eutectic solvents in a one-pot process for a biomass
PatentInactiveUS20200216863A1
Innovation
- The use of biocompatible deep eutectic solvents (DESs), specifically choline chloride and glycerol mixtures, for a one-pot biomass pretreatment, saccharification, and fermentation process that eliminates the need for pH adjustments, water dilution, and solid-liquid separations, allowing for continuous operation and compatibility with enzymes and microbes.
Life Cycle Assessment of Biomass-Derived Solvents
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of biomass-derived solvents provides critical insights into their environmental impacts across the entire value chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. These assessments typically evaluate four key impact categories: global warming potential, energy consumption, resource depletion, and ecotoxicity. When compared to conventional petroleum-based solvents, biomass-derived alternatives generally demonstrate significant reductions in carbon footprint, with studies indicating 30-70% lower greenhouse gas emissions depending on feedstock selection and processing methods.
The feedstock source plays a crucial role in determining overall sustainability. Agricultural residues and waste streams typically offer superior environmental performance compared to purpose-grown crops, which may compete with food production and potentially cause indirect land use changes. For instance, solvents derived from corn stover or sugarcane bagasse show approximately 40% lower environmental impact than those from dedicated corn or sugarcane cultivation.
Manufacturing processes for biomass-derived solvents have evolved substantially, with recent technological innovations reducing energy requirements by up to 35% compared to earlier generation processes. Particularly noteworthy are advances in enzymatic conversion pathways and integrated biorefinery concepts that maximize resource efficiency. However, solvent purification remains energy-intensive, often accounting for 40-60% of the total process energy consumption.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional advantages of biomass-derived solvents. Their inherently higher biodegradability results in reduced persistence in the environment, with typical degradation rates 3-5 times faster than petroleum-based counterparts. This characteristic is particularly valuable in manufacturing applications where complete solvent recovery is challenging.
Regional variations in energy grid composition significantly influence LCA outcomes. Production facilities powered by renewable energy can achieve carbon footprint reductions of up to 85% compared to fossil fuel-powered operations. This highlights the importance of considering geographical factors when evaluating environmental performance.
Economic viability remains closely linked to environmental performance through resource efficiency. Recent techno-economic analyses indicate that biomass-derived solvents become cost-competitive with petroleum-based alternatives when crude oil prices exceed approximately $70-80 per barrel, with this threshold continuing to decrease as processing technologies mature and achieve greater economies of scale.
Future LCA research priorities include developing more comprehensive models that capture cascading environmental effects, standardizing methodologies to enable more accurate cross-study comparisons, and incorporating social sustainability metrics to provide a more holistic assessment of these promising alternatives for energy-efficient manufacturing applications.
The feedstock source plays a crucial role in determining overall sustainability. Agricultural residues and waste streams typically offer superior environmental performance compared to purpose-grown crops, which may compete with food production and potentially cause indirect land use changes. For instance, solvents derived from corn stover or sugarcane bagasse show approximately 40% lower environmental impact than those from dedicated corn or sugarcane cultivation.
Manufacturing processes for biomass-derived solvents have evolved substantially, with recent technological innovations reducing energy requirements by up to 35% compared to earlier generation processes. Particularly noteworthy are advances in enzymatic conversion pathways and integrated biorefinery concepts that maximize resource efficiency. However, solvent purification remains energy-intensive, often accounting for 40-60% of the total process energy consumption.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional advantages of biomass-derived solvents. Their inherently higher biodegradability results in reduced persistence in the environment, with typical degradation rates 3-5 times faster than petroleum-based counterparts. This characteristic is particularly valuable in manufacturing applications where complete solvent recovery is challenging.
Regional variations in energy grid composition significantly influence LCA outcomes. Production facilities powered by renewable energy can achieve carbon footprint reductions of up to 85% compared to fossil fuel-powered operations. This highlights the importance of considering geographical factors when evaluating environmental performance.
Economic viability remains closely linked to environmental performance through resource efficiency. Recent techno-economic analyses indicate that biomass-derived solvents become cost-competitive with petroleum-based alternatives when crude oil prices exceed approximately $70-80 per barrel, with this threshold continuing to decrease as processing technologies mature and achieve greater economies of scale.
Future LCA research priorities include developing more comprehensive models that capture cascading environmental effects, standardizing methodologies to enable more accurate cross-study comparisons, and incorporating social sustainability metrics to provide a more holistic assessment of these promising alternatives for energy-efficient manufacturing applications.
Regulatory Framework for Bio-Based Chemical Manufacturing
The regulatory landscape for bio-based chemical manufacturing, particularly concerning biomass-derived solvents, has evolved significantly in recent years as governments worldwide recognize the importance of sustainable industrial practices. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) which requires manufacturers to register new chemical substances, including bio-based solvents, before commercial production. Additionally, the EPA's Significant New Use Rules (SNURs) may apply to novel applications of biomass-derived solvents in manufacturing processes.
The European Union has implemented more stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework, which places greater responsibility on industry to manage risks from chemicals and provide safety information. The EU has also established specific incentives for bio-based products through its Bioeconomy Strategy and the Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II), which promotes the use of renewable resources in industrial applications.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have developed their own regulatory frameworks that increasingly favor bio-based chemicals. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's K-REACH both incorporate provisions that can expedite approval processes for environmentally beneficial substances, including biomass-derived solvents.
Certification systems play a crucial role in the regulatory ecosystem. Standards such as ASTM D6866 for measuring biobased content and ISO 14044 for life cycle assessment provide methodologies for verifying environmental claims. The USDA's BioPreferred program offers certification for bio-based products, creating market advantages through federal procurement preferences.
Tax incentives and subsidies represent another regulatory mechanism supporting the transition to bio-based manufacturing. Several countries offer tax credits for research and development in green chemistry, accelerated depreciation for equipment used in bio-based manufacturing, and direct subsidies for facilities producing renewable chemicals.
Challenges in the regulatory framework include the lack of harmonization across jurisdictions, creating compliance complexities for global manufacturers. Additionally, regulations often lag behind technological innovations in biomass-derived solvents, creating uncertainty for investors and developers. The classification of waste biomass feedstocks also presents regulatory challenges, as different jurisdictions may categorize the same material differently.
Future regulatory trends indicate movement toward more comprehensive life cycle approaches, where the environmental impact of biomass-derived solvents will be evaluated from feedstock cultivation through end-of-life disposal. Carbon pricing mechanisms are also expected to increasingly influence the competitiveness of bio-based manufacturing processes relative to conventional petroleum-based approaches.
The European Union has implemented more stringent regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework, which places greater responsibility on industry to manage risks from chemicals and provide safety information. The EU has also established specific incentives for bio-based products through its Bioeconomy Strategy and the Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II), which promotes the use of renewable resources in industrial applications.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have developed their own regulatory frameworks that increasingly favor bio-based chemicals. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's K-REACH both incorporate provisions that can expedite approval processes for environmentally beneficial substances, including biomass-derived solvents.
Certification systems play a crucial role in the regulatory ecosystem. Standards such as ASTM D6866 for measuring biobased content and ISO 14044 for life cycle assessment provide methodologies for verifying environmental claims. The USDA's BioPreferred program offers certification for bio-based products, creating market advantages through federal procurement preferences.
Tax incentives and subsidies represent another regulatory mechanism supporting the transition to bio-based manufacturing. Several countries offer tax credits for research and development in green chemistry, accelerated depreciation for equipment used in bio-based manufacturing, and direct subsidies for facilities producing renewable chemicals.
Challenges in the regulatory framework include the lack of harmonization across jurisdictions, creating compliance complexities for global manufacturers. Additionally, regulations often lag behind technological innovations in biomass-derived solvents, creating uncertainty for investors and developers. The classification of waste biomass feedstocks also presents regulatory challenges, as different jurisdictions may categorize the same material differently.
Future regulatory trends indicate movement toward more comprehensive life cycle approaches, where the environmental impact of biomass-derived solvents will be evaluated from feedstock cultivation through end-of-life disposal. Carbon pricing mechanisms are also expected to increasingly influence the competitiveness of bio-based manufacturing processes relative to conventional petroleum-based approaches.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!