Data package requirements for cross-border transfer of CGT products: import/export regulatory considerations
SEP 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
CGT Products Regulatory Background and Objectives
Cell and gene therapy (CGT) products represent a revolutionary advancement in modern medicine, offering potential treatments for previously incurable diseases through genetic modification of cells or direct genetic interventions. The regulatory landscape governing these innovative therapies has evolved significantly over the past two decades, reflecting both scientific progress and growing safety concerns.
The development of CGT regulations began in earnest during the early 2000s when pioneering gene therapy clinical trials revealed unexpected safety issues, including oncogenesis in some patients. These events prompted regulatory authorities worldwide to establish specialized frameworks for CGT products, distinct from conventional pharmaceuticals and biologics.
By 2010, major regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA had established dedicated pathways for CGT products, though significant international divergence in requirements persisted. The 2015-2020 period marked a watershed moment with the first wave of CGT product approvals, necessitating more refined cross-border transfer regulations as these therapies entered global markets.
Currently, CGT products face unique regulatory challenges due to their complex nature, including short shelf-life, chain-of-identity requirements, and patient-specific manufacturing processes. These characteristics make traditional import/export frameworks inadequate for ensuring product quality and patient safety across international boundaries.
The technological evolution of CGT products continues to outpace regulatory harmonization efforts. While platforms like CAR-T cell therapies have established precedents, emerging modalities such as in vivo gene editing and next-generation viral vectors introduce novel regulatory considerations that remain inconsistently addressed across jurisdictions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively map the current data package requirements for cross-border transfer of CGT products, identifying regulatory convergence points and critical divergences that impact global development strategies. This analysis aims to establish a framework for anticipating documentation needs across major markets.
Secondary objectives include identifying emerging trends in regulatory approaches to CGT products, particularly regarding chain of custody documentation, raw material traceability, and patient-specific manufacturing data requirements. Additionally, this research seeks to forecast how regulatory requirements may evolve as next-generation CGT technologies enter clinical development and commercialization phases.
Understanding these regulatory dynamics is essential for CGT developers seeking to implement global development strategies, as regulatory divergence can significantly impact product development timelines, manufacturing strategies, and ultimately patient access to these transformative therapies.
The development of CGT regulations began in earnest during the early 2000s when pioneering gene therapy clinical trials revealed unexpected safety issues, including oncogenesis in some patients. These events prompted regulatory authorities worldwide to establish specialized frameworks for CGT products, distinct from conventional pharmaceuticals and biologics.
By 2010, major regulatory bodies including the FDA, EMA, and PMDA had established dedicated pathways for CGT products, though significant international divergence in requirements persisted. The 2015-2020 period marked a watershed moment with the first wave of CGT product approvals, necessitating more refined cross-border transfer regulations as these therapies entered global markets.
Currently, CGT products face unique regulatory challenges due to their complex nature, including short shelf-life, chain-of-identity requirements, and patient-specific manufacturing processes. These characteristics make traditional import/export frameworks inadequate for ensuring product quality and patient safety across international boundaries.
The technological evolution of CGT products continues to outpace regulatory harmonization efforts. While platforms like CAR-T cell therapies have established precedents, emerging modalities such as in vivo gene editing and next-generation viral vectors introduce novel regulatory considerations that remain inconsistently addressed across jurisdictions.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively map the current data package requirements for cross-border transfer of CGT products, identifying regulatory convergence points and critical divergences that impact global development strategies. This analysis aims to establish a framework for anticipating documentation needs across major markets.
Secondary objectives include identifying emerging trends in regulatory approaches to CGT products, particularly regarding chain of custody documentation, raw material traceability, and patient-specific manufacturing data requirements. Additionally, this research seeks to forecast how regulatory requirements may evolve as next-generation CGT technologies enter clinical development and commercialization phases.
Understanding these regulatory dynamics is essential for CGT developers seeking to implement global development strategies, as regulatory divergence can significantly impact product development timelines, manufacturing strategies, and ultimately patient access to these transformative therapies.
Market Analysis for Cross-Border CGT Transfer
The global Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) market has experienced exponential growth, with a market value reaching $25 billion in 2022 and projected to exceed $93 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of approximately 18%. This remarkable expansion is driven by increasing approvals of CGT products, growing investment in research and development, and rising prevalence of chronic diseases and genetic disorders that can be addressed through these innovative therapies.
North America currently dominates the cross-border CGT transfer market, accounting for approximately 45% of global market share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The United States, in particular, leads in both development and consumption of CGT products, with significant cross-border activities involving both import and export of these specialized therapies.
Key market segments within the cross-border CGT transfer include autologous therapies, allogeneic therapies, and viral vector manufacturing. Autologous therapies, which involve patient-specific treatments, present unique logistical challenges for cross-border transfer due to their time-sensitive nature and personalized characteristics. Allogeneic therapies, while offering "off-the-shelf" solutions, face different regulatory hurdles related to donor screening and cell banking across different jurisdictions.
The demand for cross-border CGT transfer is primarily driven by several factors: uneven global distribution of manufacturing capabilities, clinical trial activities spanning multiple countries, and the need to provide access to patients in regions where local manufacturing is not available. Additionally, specialized manufacturing expertise concentrated in certain regions necessitates international movement of these products.
Market barriers include complex and non-harmonized regulatory frameworks, logistical challenges related to temperature-controlled supply chains, customs delays affecting product viability, and high costs associated with regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions. These barriers have created a specialized service sector focused on CGT logistics and regulatory compliance.
Emerging markets in Asia, particularly China, South Korea, and Singapore, are rapidly developing their CGT capabilities and regulatory frameworks, potentially shifting the global landscape for cross-border transfers. These regions are expected to see the highest growth rates in the coming years, with China's CGT market growing at over 25% annually.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted cross-border CGT transfers, highlighting vulnerabilities in global supply chains but also accelerating regulatory innovations such as remote inspections and digital documentation systems that may permanently transform the regulatory landscape for international CGT product movement.
North America currently dominates the cross-border CGT transfer market, accounting for approximately 45% of global market share, followed by Europe at 30% and Asia-Pacific at 20%. The United States, in particular, leads in both development and consumption of CGT products, with significant cross-border activities involving both import and export of these specialized therapies.
Key market segments within the cross-border CGT transfer include autologous therapies, allogeneic therapies, and viral vector manufacturing. Autologous therapies, which involve patient-specific treatments, present unique logistical challenges for cross-border transfer due to their time-sensitive nature and personalized characteristics. Allogeneic therapies, while offering "off-the-shelf" solutions, face different regulatory hurdles related to donor screening and cell banking across different jurisdictions.
The demand for cross-border CGT transfer is primarily driven by several factors: uneven global distribution of manufacturing capabilities, clinical trial activities spanning multiple countries, and the need to provide access to patients in regions where local manufacturing is not available. Additionally, specialized manufacturing expertise concentrated in certain regions necessitates international movement of these products.
Market barriers include complex and non-harmonized regulatory frameworks, logistical challenges related to temperature-controlled supply chains, customs delays affecting product viability, and high costs associated with regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions. These barriers have created a specialized service sector focused on CGT logistics and regulatory compliance.
Emerging markets in Asia, particularly China, South Korea, and Singapore, are rapidly developing their CGT capabilities and regulatory frameworks, potentially shifting the global landscape for cross-border transfers. These regions are expected to see the highest growth rates in the coming years, with China's CGT market growing at over 25% annually.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted cross-border CGT transfers, highlighting vulnerabilities in global supply chains but also accelerating regulatory innovations such as remote inspections and digital documentation systems that may permanently transform the regulatory landscape for international CGT product movement.
Global Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
The global regulatory landscape for Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) products presents a complex mosaic of requirements that vary significantly across jurisdictions. Major regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States, the EMA in Europe, and the PMDA in Japan have established distinct frameworks for CGT products, creating challenges for cross-border transfers. These differences extend beyond mere documentation requirements to fundamental approaches in product classification, testing standards, and risk assessment methodologies.
Regulatory divergence is particularly pronounced in areas such as donor eligibility criteria, testing requirements for adventitious agents, and expectations for product characterization. For instance, while the FDA requires extensive testing for mycoplasma and endotoxins with specific methodological approaches, other jurisdictions may accept alternative testing methods or have different threshold requirements. This lack of harmonization necessitates product-specific strategies for international distribution.
A significant challenge in the global CGT landscape is the management of raw material documentation across borders. Materials that are considered acceptable in one region may face additional scrutiny or even rejection in another due to differences in quality standards or documentation expectations. This is particularly problematic for CGT products that often utilize specialized, limited-source materials with complex supply chains.
The evolving nature of CGT regulations compounds these challenges. Many jurisdictions are actively updating their regulatory frameworks to accommodate these innovative therapies, resulting in a constantly shifting compliance landscape. Companies must maintain vigilant regulatory intelligence functions to track these changes and adapt their documentation strategies accordingly.
Data integrity and electronic documentation present another layer of complexity. Different regions have varying requirements for electronic signatures, data verification, and chain of custody documentation. These differences can significantly impact the structure and content of data packages required for cross-border transfers.
Expedited approval pathways, while beneficial for accelerating patient access, introduce additional variability in documentation requirements. Programs such as the FDA's Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation or the EMA's PRIME scheme may modify standard documentation expectations, creating another dimension of regulatory complexity for international transfers.
The handling of patient-specific information in autologous therapies presents unique challenges for cross-border transfers. Privacy regulations such as GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the US create additional documentation requirements to ensure compliant transfer of necessary patient information while protecting privacy rights.
Regulatory divergence is particularly pronounced in areas such as donor eligibility criteria, testing requirements for adventitious agents, and expectations for product characterization. For instance, while the FDA requires extensive testing for mycoplasma and endotoxins with specific methodological approaches, other jurisdictions may accept alternative testing methods or have different threshold requirements. This lack of harmonization necessitates product-specific strategies for international distribution.
A significant challenge in the global CGT landscape is the management of raw material documentation across borders. Materials that are considered acceptable in one region may face additional scrutiny or even rejection in another due to differences in quality standards or documentation expectations. This is particularly problematic for CGT products that often utilize specialized, limited-source materials with complex supply chains.
The evolving nature of CGT regulations compounds these challenges. Many jurisdictions are actively updating their regulatory frameworks to accommodate these innovative therapies, resulting in a constantly shifting compliance landscape. Companies must maintain vigilant regulatory intelligence functions to track these changes and adapt their documentation strategies accordingly.
Data integrity and electronic documentation present another layer of complexity. Different regions have varying requirements for electronic signatures, data verification, and chain of custody documentation. These differences can significantly impact the structure and content of data packages required for cross-border transfers.
Expedited approval pathways, while beneficial for accelerating patient access, introduce additional variability in documentation requirements. Programs such as the FDA's Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation or the EMA's PRIME scheme may modify standard documentation expectations, creating another dimension of regulatory complexity for international transfers.
The handling of patient-specific information in autologous therapies presents unique challenges for cross-border transfers. Privacy regulations such as GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the US create additional documentation requirements to ensure compliant transfer of necessary patient information while protecting privacy rights.
Current Data Package Solutions
01 Quality control and characterization requirements for CGT products
Cell and gene therapy products require comprehensive quality control testing to ensure safety and efficacy. This includes characterization of identity, purity, potency, and stability of the therapeutic product. Advanced analytical methods are needed to assess critical quality attributes, genetic stability, and product consistency. Regulatory agencies require detailed characterization data to demonstrate product understanding and manufacturing control.- Regulatory data requirements for CGT product approval: Cell and Gene Therapy products require comprehensive regulatory data packages for approval. These packages must include detailed information on product characterization, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and stability data. Regulatory authorities such as FDA and EMA have established specific guidelines for CGT products that outline the necessary data requirements for market authorization, including demonstration of product consistency and comparability across manufacturing batches.
- Clinical trial data requirements for CGT products: Clinical trial data for Cell and Gene Therapy products must demonstrate safety, efficacy, and durability of therapeutic effect. This includes data from appropriate patient populations, with sufficient follow-up periods to assess long-term outcomes and delayed adverse events. Clinical data packages should include detailed information on patient demographics, dosing regimens, clinical endpoints, and biomarkers that correlate with therapeutic response. Post-marketing surveillance plans are also required to monitor long-term safety and efficacy.
- Manufacturing and quality control data for CGT products: Manufacturing and quality control data for Cell and Gene Therapy products must include detailed information on raw materials, production processes, and analytical methods. This encompasses donor screening procedures, cell isolation and expansion protocols, vector production methods, and final product formulation. Quality control data should demonstrate product purity, potency, identity, and sterility through validated assays. Process validation data must show consistency and reproducibility across manufacturing batches to ensure product quality and safety.
- Preclinical safety and efficacy data requirements: Preclinical data packages for Cell and Gene Therapy products must include comprehensive safety and efficacy studies in relevant animal models. This includes biodistribution studies to track the fate of administered cells or vectors, tumorigenicity assessments to evaluate oncogenic potential, and immunogenicity studies to assess potential immune responses. Efficacy studies should demonstrate proof-of-concept in disease-relevant models and provide insights into mechanism of action. Toxicology studies must evaluate both acute and long-term safety profiles to support clinical development.
- Product characterization and stability data: Cell and Gene Therapy products require extensive characterization data to define critical quality attributes and establish release specifications. This includes genetic, phenotypic, and functional analyses of cellular components, as well as molecular characterization of viral vectors. Stability data must demonstrate product integrity throughout the proposed shelf life under specified storage conditions. Accelerated and real-time stability studies are needed to establish expiration dating and storage requirements. For cryopreserved products, freeze-thaw stability data is essential to ensure product quality after storage.
02 Manufacturing process validation and documentation
The data package for CGT products must include comprehensive documentation of the manufacturing process, including validation of critical process parameters and in-process controls. This includes detailed information on cell isolation, genetic modification techniques, expansion processes, purification methods, and final formulation. Process validation data should demonstrate consistency, reproducibility, and control of the manufacturing process to ensure product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Preclinical safety and efficacy data requirements
Comprehensive preclinical data is essential for CGT products, including in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrating safety and efficacy. This includes biodistribution studies, tumorigenicity assessments, immunogenicity evaluations, and proof-of-concept efficacy models. The data package should address specific concerns related to the therapy type, such as off-target effects for gene editing products or cell persistence for cellular therapies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Clinical trial design and patient monitoring requirements
The data package for CGT products must include detailed clinical trial protocols with appropriate endpoints and long-term follow-up plans. This includes strategies for patient selection, dosing rationale, safety monitoring, and efficacy assessment. Due to the novel and potentially irreversible nature of these therapies, regulatory agencies require robust plans for long-term patient monitoring to detect delayed adverse events and evaluate durability of response.Expand Specific Solutions05 Vector and delivery system characterization
For gene therapy products, comprehensive characterization of the vector system is required, including genetic stability, purity, and safety profile. The data package must include information on vector design, production process, and quality control testing. For viral vectors, this includes assessments of replication competence, vector shedding, and potential for recombination. The delivery system must be characterized for its ability to effectively deliver the therapeutic payload to target tissues.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Industry Players
The cross-border transfer of Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) products is currently in an emerging growth phase, with the global market expanding rapidly due to increasing therapeutic applications. The regulatory landscape remains complex and evolving, with significant variations between jurisdictions. From a technical maturity perspective, companies like Janssen Pharmaceutica, Ricoh, and Red Hat are developing specialized digital solutions for regulatory compliance, while logistics providers such as NTT Communications and Westrock MWV are creating specialized packaging and tracking systems. Financial institutions including ICBC and Thomson Reuters are establishing cross-border payment frameworks specific to CGT products. The market faces challenges in harmonizing import/export requirements across different regulatory frameworks, with companies like 3M and Philips working on standardized documentation systems to facilitate smoother transfers.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has developed an integrated digital solution for managing CGT product data packages during cross-border transfers, leveraging their healthcare technology expertise. Their system employs a cloud-based platform that maintains regulatory dossiers with version control and market-specific variations, ensuring that the correct documentation is always available for each jurisdiction. The platform incorporates automated compliance checking against a continuously updated database of international regulations specific to biological products. Philips' solution features secure digital sharing capabilities that allow controlled access to regulatory authorities while maintaining data integrity and confidentiality. Their approach includes integration with hospital information systems to facilitate seamless data transfer between clinical sites and regulatory submissions, and implements standardized electronic forms that align with International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines while accommodating country-specific variations.
Strengths: Strong integration capabilities with existing healthcare IT infrastructure; extensive experience with medical device regulations that can be leveraged for CGT products. Weaknesses: May have less specialized experience with biological product regulations compared to pure pharmaceutical companies; potential challenges in addressing the unique cold chain documentation requirements of CGT products.
Thomson Reuters Enterprise Centre GmbH
Technical Solution: Thomson Reuters has developed a comprehensive regulatory intelligence platform specifically tailored for cross-border transfer of CGT products. Their solution leverages their extensive legal and regulatory databases to provide real-time updates on changing import/export requirements across global markets. The system employs advanced natural language processing to analyze regulatory publications and identify relevant changes that may impact CGT product transfers. Thomson Reuters' platform includes jurisdiction-specific document templates that automatically incorporate the latest regulatory requirements, reducing compliance risks during submissions. Their approach features comparative analysis tools that highlight differences in documentation requirements between origin and destination countries, allowing for efficient gap analysis. The system also incorporates regulatory forecasting capabilities that predict upcoming changes based on draft guidance documents and industry consultation papers, enabling proactive adaptation of data packages.
Strengths: Unparalleled access to global regulatory information and legal expertise; sophisticated data analytics capabilities for regulatory intelligence. Weaknesses: May require integration with other systems for complete supply chain management; potential focus on regulatory documentation rather than practical logistics aspects of CGT transfers.
Critical Documentation Requirements
An apparatus
PatentWO2021123762A1
Innovation
- An apparatus with resealable ports and a cover mechanism that allows for the introduction and removal of materials from a container without the need for pumps, enabling automated and multi-step processes within a single device with a smaller footprint, reducing manual intervention and maintaining an aseptic environment.
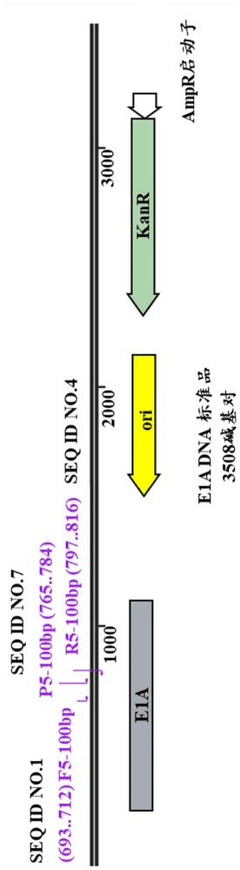
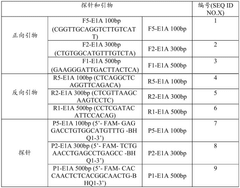
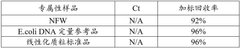
QPCR kit for detecting E1A residual DNA
PatentActiveCN118726618A
Innovation
- Provides a specific primer and probe combination and its qPCR kit for detecting E1A residual DNA, combining dNTP mixture, endonuclease RNase H, hot-start PCR enzyme and Mg2+ solution to achieve high sensitivity to E1A DNA and quantitative analysis.
Supply Chain Security Considerations
Supply chain security represents a critical dimension in the cross-border transfer of Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) products. The inherent sensitivity of these biological materials necessitates robust security protocols throughout the entire logistics network. Temperature excursions, tampering, or delays can compromise product integrity, potentially rendering these high-value therapies ineffective or even harmful to patients. Consequently, implementing end-to-end visibility systems with real-time monitoring capabilities has become essential for maintaining chain of custody and ensuring product quality.
Regulatory bodies worldwide increasingly mandate comprehensive security measures for CGT products. The FDA's Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the US and the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) in Europe establish frameworks requiring serialization, track-and-trace capabilities, and verification at multiple points in the supply chain. These regulations aim to prevent counterfeit products from entering legitimate distribution channels and ensure authenticity verification at the point of dispensing.
Cybersecurity considerations have emerged as a significant concern in CGT supply chains. Digital systems managing critical logistics data face threats from malicious actors seeking to compromise sensitive patient information or disrupt supply operations. Organizations must implement robust data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect against these vulnerabilities. The integration of blockchain technology offers promising solutions for creating immutable records of product handling throughout the supply chain.
Physical security measures remain equally important, particularly at border crossings where CGT products may face increased handling and inspection. Specialized packaging with tamper-evident seals, GPS-enabled containers, and dedicated security personnel may be necessary for high-value shipments. Customs clearance procedures should be expedited through pre-approval programs like the Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) in the US or Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) status in the EU.
Supplier qualification and ongoing monitoring constitute another critical security layer. Organizations must conduct thorough due diligence on all supply chain partners, including logistics providers, customs brokers, and storage facilities. Regular audits and performance reviews help ensure continued compliance with security protocols. Contingency planning for security breaches should include detailed response procedures, alternative routing options, and communication protocols to minimize potential damage to product integrity.
Human factors in security cannot be overlooked. Staff handling CGT products require specialized training on security protocols, recognition of tampering attempts, and proper documentation procedures. Creating a security-conscious culture throughout the organization and partner network significantly reduces vulnerability to both internal and external threats.
Regulatory bodies worldwide increasingly mandate comprehensive security measures for CGT products. The FDA's Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the US and the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) in Europe establish frameworks requiring serialization, track-and-trace capabilities, and verification at multiple points in the supply chain. These regulations aim to prevent counterfeit products from entering legitimate distribution channels and ensure authenticity verification at the point of dispensing.
Cybersecurity considerations have emerged as a significant concern in CGT supply chains. Digital systems managing critical logistics data face threats from malicious actors seeking to compromise sensitive patient information or disrupt supply operations. Organizations must implement robust data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect against these vulnerabilities. The integration of blockchain technology offers promising solutions for creating immutable records of product handling throughout the supply chain.
Physical security measures remain equally important, particularly at border crossings where CGT products may face increased handling and inspection. Specialized packaging with tamper-evident seals, GPS-enabled containers, and dedicated security personnel may be necessary for high-value shipments. Customs clearance procedures should be expedited through pre-approval programs like the Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) in the US or Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) status in the EU.
Supplier qualification and ongoing monitoring constitute another critical security layer. Organizations must conduct thorough due diligence on all supply chain partners, including logistics providers, customs brokers, and storage facilities. Regular audits and performance reviews help ensure continued compliance with security protocols. Contingency planning for security breaches should include detailed response procedures, alternative routing options, and communication protocols to minimize potential damage to product integrity.
Human factors in security cannot be overlooked. Staff handling CGT products require specialized training on security protocols, recognition of tampering attempts, and proper documentation procedures. Creating a security-conscious culture throughout the organization and partner network significantly reduces vulnerability to both internal and external threats.
Ethical and Patient Safety Implications
The ethical considerations surrounding cross-border transfer of Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) products extend beyond regulatory compliance to fundamental questions of patient safety and global equity. When CGT products cross international boundaries, maintaining chain of identity and chain of custody becomes critically important, as these therapies often represent personalized treatments where patient cells are collected, modified, and returned. Any breach in this process could result in patients receiving incorrect or compromised treatments with potentially fatal consequences.
Patient consent frameworks vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating ethical challenges when products move between regions with different standards. Some countries require explicit informed consent for international transfer of biological materials, while others operate under presumed consent models. This discrepancy necessitates careful navigation to ensure that patient autonomy is respected throughout the cross-border transfer process.
Data privacy concerns intersect with safety considerations, as CGT products inherently contain sensitive genetic information. The transfer of associated data packages must comply with regulations like GDPR in Europe or HIPAA in the United States, while simultaneously ensuring that sufficient information accompanies the product to guarantee safe administration. This balancing act between privacy protection and clinical necessity requires sophisticated data management protocols.
The potential for exploitation in global CGT supply chains raises additional ethical concerns. Disparities in regulatory oversight between developed and developing nations could create scenarios where vulnerable populations become sources of biological materials without adequate protections or benefits. Implementing fair compensation models and ensuring equitable access to resulting therapies represents an ongoing ethical challenge.
Risk mitigation strategies must account for cultural differences in risk perception and acceptance. What constitutes acceptable risk varies across cultures and healthcare systems, necessitating transparent communication about potential adverse events and long-term monitoring requirements when CGT products cross borders. This transparency extends to clear documentation of product origin, manufacturing conditions, and any modifications made during transit.
Ultimately, harmonized ethical frameworks that transcend national boundaries while respecting cultural differences are essential for responsible cross-border CGT transfer. These frameworks should prioritize patient welfare, ensure informed consent, maintain data integrity, and promote equitable access to innovative therapies regardless of geographic location.
Patient consent frameworks vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating ethical challenges when products move between regions with different standards. Some countries require explicit informed consent for international transfer of biological materials, while others operate under presumed consent models. This discrepancy necessitates careful navigation to ensure that patient autonomy is respected throughout the cross-border transfer process.
Data privacy concerns intersect with safety considerations, as CGT products inherently contain sensitive genetic information. The transfer of associated data packages must comply with regulations like GDPR in Europe or HIPAA in the United States, while simultaneously ensuring that sufficient information accompanies the product to guarantee safe administration. This balancing act between privacy protection and clinical necessity requires sophisticated data management protocols.
The potential for exploitation in global CGT supply chains raises additional ethical concerns. Disparities in regulatory oversight between developed and developing nations could create scenarios where vulnerable populations become sources of biological materials without adequate protections or benefits. Implementing fair compensation models and ensuring equitable access to resulting therapies represents an ongoing ethical challenge.
Risk mitigation strategies must account for cultural differences in risk perception and acceptance. What constitutes acceptable risk varies across cultures and healthcare systems, necessitating transparent communication about potential adverse events and long-term monitoring requirements when CGT products cross borders. This transparency extends to clear documentation of product origin, manufacturing conditions, and any modifications made during transit.
Ultimately, harmonized ethical frameworks that transcend national boundaries while respecting cultural differences are essential for responsible cross-border CGT transfer. These frameworks should prioritize patient welfare, ensure informed consent, maintain data integrity, and promote equitable access to innovative therapies regardless of geographic location.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!