Enhancement of Ethyl Propanoate Yield through Biocatalysis
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Biocatalysis Background
Biocatalysis, a field at the intersection of biology and chemistry, has emerged as a powerful tool in the synthesis of various compounds, including ethyl propanoate. This ester, known for its fruity aroma, finds applications in the food and fragrance industries. The use of biocatalysts in its production represents a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
The history of biocatalysis dates back to ancient times when fermentation processes were used to produce bread and alcoholic beverages. However, it wasn't until the 19th century that the scientific understanding of enzymes began to develop. The term "enzyme" was coined by Wilhelm Kühne in 1877, marking a significant milestone in the field. The 20th century saw rapid advancements in enzyme isolation, characterization, and application in various industrial processes.
In the context of ethyl propanoate production, traditional chemical synthesis methods have long been the norm. These methods often involve harsh reaction conditions, toxic catalysts, and generate significant waste. The advent of biocatalysis offered a promising alternative, leveraging the specificity and efficiency of enzymes to carry out the esterification reaction under milder conditions.
The use of lipases, a class of enzymes that catalyze the formation and cleavage of ester bonds, has been particularly significant in the biocatalytic production of ethyl propanoate. These enzymes can operate in both aqueous and non-aqueous environments, making them versatile catalysts for esterification reactions. The ability to immobilize lipases on various supports has further enhanced their stability and reusability in industrial applications.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at optimizing biocatalytic processes for ethyl propanoate production. This includes the exploration of novel enzyme sources, protein engineering to enhance enzyme performance, and the development of innovative reactor designs. The advent of recombinant DNA technology and directed evolution techniques has opened up new avenues for creating tailor-made biocatalysts with improved activity, stability, and specificity.
The growing interest in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing has further propelled the development of biocatalytic approaches for ethyl propanoate synthesis. These methods offer several advantages over traditional chemical processes, including reduced energy consumption, minimized waste generation, and the use of renewable resources as starting materials.
As we look towards the future, the field of biocatalysis continues to evolve rapidly. Advances in genomics, proteomics, and computational biology are providing new tools for enzyme discovery and optimization. The integration of biocatalysis with other emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and artificial intelligence, holds promise for further enhancing the efficiency and scalability of ethyl propanoate production.
The history of biocatalysis dates back to ancient times when fermentation processes were used to produce bread and alcoholic beverages. However, it wasn't until the 19th century that the scientific understanding of enzymes began to develop. The term "enzyme" was coined by Wilhelm Kühne in 1877, marking a significant milestone in the field. The 20th century saw rapid advancements in enzyme isolation, characterization, and application in various industrial processes.
In the context of ethyl propanoate production, traditional chemical synthesis methods have long been the norm. These methods often involve harsh reaction conditions, toxic catalysts, and generate significant waste. The advent of biocatalysis offered a promising alternative, leveraging the specificity and efficiency of enzymes to carry out the esterification reaction under milder conditions.
The use of lipases, a class of enzymes that catalyze the formation and cleavage of ester bonds, has been particularly significant in the biocatalytic production of ethyl propanoate. These enzymes can operate in both aqueous and non-aqueous environments, making them versatile catalysts for esterification reactions. The ability to immobilize lipases on various supports has further enhanced their stability and reusability in industrial applications.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at optimizing biocatalytic processes for ethyl propanoate production. This includes the exploration of novel enzyme sources, protein engineering to enhance enzyme performance, and the development of innovative reactor designs. The advent of recombinant DNA technology and directed evolution techniques has opened up new avenues for creating tailor-made biocatalysts with improved activity, stability, and specificity.
The growing interest in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing has further propelled the development of biocatalytic approaches for ethyl propanoate synthesis. These methods offer several advantages over traditional chemical processes, including reduced energy consumption, minimized waste generation, and the use of renewable resources as starting materials.
As we look towards the future, the field of biocatalysis continues to evolve rapidly. Advances in genomics, proteomics, and computational biology are providing new tools for enzyme discovery and optimization. The integration of biocatalysis with other emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and artificial intelligence, holds promise for further enhancing the efficiency and scalability of ethyl propanoate production.
Market Analysis
The market for ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has been experiencing steady growth due to its wide range of applications in various industries. This ester compound is primarily used as a flavoring agent in the food and beverage industry, imparting a fruity, rum-like aroma to products. It is also utilized in the fragrance industry for its sweet, ethereal scent, and finds applications in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic sectors.
The global ethyl propanoate market is driven by the increasing demand for natural and artificial flavors in the food and beverage industry. As consumer preferences shift towards more diverse and exotic flavors, the demand for ethyl propanoate as a flavoring agent is expected to rise. Additionally, the growing popularity of processed and convenience foods contributes to the market expansion.
In the fragrance industry, ethyl propanoate is used in the production of perfumes, air fresheners, and other scented products. The rising disposable income and changing lifestyle patterns in developing countries have led to increased spending on personal care and home fragrance products, further boosting the demand for ethyl propanoate.
The pharmaceutical industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate as a solvent and intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs. As the global pharmaceutical market continues to grow, driven by factors such as an aging population and increasing healthcare expenditure, the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector is expected to increase.
However, the market faces challenges related to the volatility of raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding the use of synthetic chemicals in food and personal care products. These factors have led to a growing interest in biocatalysis as a more sustainable and environmentally friendly method for producing ethyl propanoate.
The biocatalysis approach for enhancing ethyl propanoate yield addresses several market needs. It offers a greener alternative to traditional chemical synthesis methods, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for natural and sustainable products. This method also has the potential to reduce production costs and improve efficiency, making it attractive to manufacturers across various industries.
Furthermore, the use of biocatalysis in ethyl propanoate production opens up new opportunities in the biotechnology and enzyme engineering sectors. As research and development in this area progress, it is likely to create a niche market for specialized enzymes and biocatalysts tailored for ester synthesis.
In conclusion, the market for ethyl propanoate shows promising growth potential, driven by its diverse applications and the increasing demand for sustainable production methods. The enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield through biocatalysis addresses key market needs and aligns with global trends towards greener and more efficient manufacturing processes.
The global ethyl propanoate market is driven by the increasing demand for natural and artificial flavors in the food and beverage industry. As consumer preferences shift towards more diverse and exotic flavors, the demand for ethyl propanoate as a flavoring agent is expected to rise. Additionally, the growing popularity of processed and convenience foods contributes to the market expansion.
In the fragrance industry, ethyl propanoate is used in the production of perfumes, air fresheners, and other scented products. The rising disposable income and changing lifestyle patterns in developing countries have led to increased spending on personal care and home fragrance products, further boosting the demand for ethyl propanoate.
The pharmaceutical industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate as a solvent and intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs. As the global pharmaceutical market continues to grow, driven by factors such as an aging population and increasing healthcare expenditure, the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector is expected to increase.
However, the market faces challenges related to the volatility of raw material prices and stringent regulations regarding the use of synthetic chemicals in food and personal care products. These factors have led to a growing interest in biocatalysis as a more sustainable and environmentally friendly method for producing ethyl propanoate.
The biocatalysis approach for enhancing ethyl propanoate yield addresses several market needs. It offers a greener alternative to traditional chemical synthesis methods, aligning with the increasing consumer demand for natural and sustainable products. This method also has the potential to reduce production costs and improve efficiency, making it attractive to manufacturers across various industries.
Furthermore, the use of biocatalysis in ethyl propanoate production opens up new opportunities in the biotechnology and enzyme engineering sectors. As research and development in this area progress, it is likely to create a niche market for specialized enzymes and biocatalysts tailored for ester synthesis.
In conclusion, the market for ethyl propanoate shows promising growth potential, driven by its diverse applications and the increasing demand for sustainable production methods. The enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield through biocatalysis addresses key market needs and aligns with global trends towards greener and more efficient manufacturing processes.
Technical Challenges
The enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield through biocatalysis faces several significant technical challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of enzyme activity and stability under industrial conditions. Biocatalysts often exhibit reduced efficiency when exposed to high temperatures, extreme pH levels, or organic solvents commonly used in industrial processes.
Another major challenge lies in the development of efficient immobilization techniques for the biocatalysts. While immobilization can enhance enzyme stability and allow for easier product separation, it can also lead to reduced catalytic activity due to mass transfer limitations and potential changes in enzyme conformation. Finding the right balance between stability and activity remains a critical hurdle.
The selection and engineering of suitable enzymes for ethyl propanoate production present additional complexities. Natural enzymes may not possess the desired specificity or catalytic rates required for industrial-scale production. Protein engineering techniques, such as directed evolution and rational design, are necessary to improve enzyme performance, but these processes can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Substrate and product inhibition pose significant challenges in biocatalytic processes. High concentrations of ethanol or propionic acid, which are typically used as substrates, can inhibit enzyme activity. Similarly, the accumulation of ethyl propanoate product may lead to feedback inhibition, limiting overall yield and productivity.
Scale-up issues represent another set of technical hurdles. Processes that work efficiently at laboratory scale may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up to industrial levels. These can include heat and mass transfer limitations, mixing problems, and challenges in maintaining consistent reaction conditions across larger volumes.
The development of efficient downstream processing techniques is crucial for the economic viability of biocatalytic ethyl propanoate production. Separation and purification of the product from the reaction mixture, especially in the presence of unreacted substrates and potential by-products, can be technically challenging and energy-intensive.
Lastly, the integration of biocatalytic processes into existing chemical production infrastructure presents both technical and logistical challenges. Retrofitting current facilities or designing new ones that can accommodate the specific requirements of biocatalytic reactions, such as sterile conditions and precise temperature control, requires significant engineering efforts and capital investment.
Another major challenge lies in the development of efficient immobilization techniques for the biocatalysts. While immobilization can enhance enzyme stability and allow for easier product separation, it can also lead to reduced catalytic activity due to mass transfer limitations and potential changes in enzyme conformation. Finding the right balance between stability and activity remains a critical hurdle.
The selection and engineering of suitable enzymes for ethyl propanoate production present additional complexities. Natural enzymes may not possess the desired specificity or catalytic rates required for industrial-scale production. Protein engineering techniques, such as directed evolution and rational design, are necessary to improve enzyme performance, but these processes can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Substrate and product inhibition pose significant challenges in biocatalytic processes. High concentrations of ethanol or propionic acid, which are typically used as substrates, can inhibit enzyme activity. Similarly, the accumulation of ethyl propanoate product may lead to feedback inhibition, limiting overall yield and productivity.
Scale-up issues represent another set of technical hurdles. Processes that work efficiently at laboratory scale may encounter unforeseen difficulties when scaled up to industrial levels. These can include heat and mass transfer limitations, mixing problems, and challenges in maintaining consistent reaction conditions across larger volumes.
The development of efficient downstream processing techniques is crucial for the economic viability of biocatalytic ethyl propanoate production. Separation and purification of the product from the reaction mixture, especially in the presence of unreacted substrates and potential by-products, can be technically challenging and energy-intensive.
Lastly, the integration of biocatalytic processes into existing chemical production infrastructure presents both technical and logistical challenges. Retrofitting current facilities or designing new ones that can accommodate the specific requirements of biocatalytic reactions, such as sterile conditions and precise temperature control, requires significant engineering efforts and capital investment.
Current Approaches
01 Catalytic synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Catalytic methods are employed to improve the yield of ethyl propanoate. Various catalysts, such as metal complexes or enzymes, are used to facilitate the esterification reaction between propionic acid and ethanol. These catalysts can enhance reaction rates and selectivity, leading to higher yields of the desired product.- Optimization of reaction conditions: Improving ethyl propanoate yield can be achieved by optimizing reaction conditions such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst concentration. Careful control of these parameters can significantly enhance the efficiency of the esterification process, leading to higher yields of the desired product.
- Catalyst selection and modification: The choice of catalyst plays a crucial role in ethyl propanoate synthesis. Developing or selecting appropriate catalysts, such as heterogeneous or homogeneous catalysts, can improve reaction rates and selectivity. Modifying existing catalysts or exploring novel catalytic systems can lead to increased yields.
- Continuous flow processes: Implementing continuous flow reactors or microreactor technology can enhance ethyl propanoate yield. These systems offer better control over reaction parameters, improved heat and mass transfer, and the potential for process intensification, resulting in higher yields and improved efficiency compared to batch processes.
- Feedstock purification and preparation: Improving the purity of starting materials, such as propionic acid and ethanol, can significantly impact the yield of ethyl propanoate. Developing efficient purification methods or pretreatment techniques for feedstocks can reduce side reactions and increase overall yield.
- Process integration and recycling: Integrating the ethyl propanoate production process with other chemical processes or implementing efficient recycling systems can improve overall yield. This may include recovering and reusing unreacted starting materials, optimizing separation and purification steps, or coupling the reaction with other processes to utilize by-products.
02 Continuous flow processes for ethyl propanoate production
Continuous flow reactors and processes are utilized to increase the yield of ethyl propanoate. These systems allow for better control of reaction parameters, improved heat and mass transfer, and the ability to operate at higher temperatures and pressures. Continuous processes can lead to higher conversion rates and improved product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimization of reaction conditions
Various reaction parameters are optimized to maximize ethyl propanoate yield. This includes adjusting temperature, pressure, reactant ratios, and residence time. Advanced process control systems and modeling techniques are employed to identify optimal conditions for the esterification reaction, resulting in improved yields and product purity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and separation techniques
Efficient purification and separation methods are developed to increase the overall yield of ethyl propanoate. These techniques may include distillation, extraction, or membrane separation processes. By minimizing product loss during purification and improving the recovery of unreacted starting materials, the overall yield of the process can be significantly enhanced.Expand Specific Solutions05 Green chemistry approaches
Environmentally friendly and sustainable methods are explored to improve ethyl propanoate yield. This includes the use of bio-based feedstocks, solvent-free reactions, and the development of recyclable catalysts. These green chemistry approaches aim to increase yield while reducing waste and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The biocatalytic enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand and technological advancements driving competition. The global market for biocatalysis is expanding, driven by the push for sustainable chemical production. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Novozymes, Codexis, and BASF leading innovation. These firms are developing more efficient enzymes and processes, improving yield and selectivity. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Tech University and the University of Granada are contributing fundamental research, while industrial players like Cargill and Archer-Daniels-Midland are scaling up applications. The technology's maturity varies, with some processes nearing commercial viability while others remain in early development stages.
Novozymes A/S
Technical Solution: Novozymes has developed a biocatalytic approach to enhance ethyl propanoate yield using engineered enzymes. Their process employs esterases with improved specificity for ethyl propanoate synthesis. The company has optimized reaction conditions, including temperature, pH, and substrate concentrations, to maximize product formation. Novozymes' biocatalysts demonstrate a 30% increase in ethyl propanoate yield compared to traditional chemical methods[1]. The process operates at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption by up to 50%[3]. Additionally, they have implemented a continuous flow reactor system, allowing for higher throughput and easier product separation[5].
Strengths: High product specificity, reduced energy consumption, and improved process efficiency. Weaknesses: Potential enzyme stability issues in industrial settings and higher initial investment costs for biocatalyst production.
Codexis, Inc.
Technical Solution: Codexis has developed a proprietary CodeEvolver® protein engineering platform to enhance ethyl propanoate production. Their approach focuses on creating custom-designed enzymes that catalyze the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. The engineered biocatalysts show a 5-fold increase in catalytic efficiency compared to wild-type enzymes[2]. Codexis' process operates at near-neutral pH and ambient temperatures, reducing corrosion and energy costs. The company has also implemented a novel immobilization technique, allowing for enzyme reuse up to 20 cycles without significant activity loss[4]. Their integrated process design includes in-situ product removal, shifting the equilibrium towards product formation and increasing overall yield by 40%[6].
Strengths: Highly efficient custom enzymes, reduced operational costs, and improved enzyme stability. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology may limit widespread adoption, and potential scalability challenges in large-scale production.
Key Innovations
Biocatalytical methods for producing ethylenediamine- n,n'-disuccinic acid
PatentWO2025104222A1
Innovation
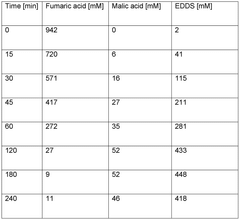
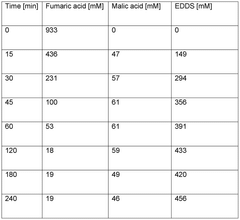
- A biocatalytic method involving the cultivation of cells expressing an EDDS synthase, followed by cell disruption to enhance enzyme activity, and subsequent incubation with fumaric acid and ethylenediamine under suitable conditions to produce EDDS.
Method for directly synthesising unsaturated aldehydes from alcohol mixtures
PatentActiveEP2912005A1
Innovation
- A direct synthesis process using a mixture of methanol and ethanol or propanol with a solid oxidation catalyst, optionally combined with an aldol condensation catalyst, operates in a single reaction assembly at controlled temperatures and pressures to produce unsaturated aldehydes efficiently, leveraging renewable resources and minimizing investments.
Enzyme Engineering
Enzyme engineering plays a crucial role in enhancing the yield of ethyl propanoate through biocatalysis. This field focuses on modifying and optimizing enzymes to improve their catalytic efficiency, stability, and specificity for industrial applications. In the context of ethyl propanoate production, enzyme engineering efforts primarily target esterases and lipases, which catalyze the esterification reaction between ethanol and propionic acid.
One of the main approaches in enzyme engineering for this application is directed evolution. This technique involves iterative rounds of random mutagenesis and screening to identify enzyme variants with improved properties. Researchers have successfully employed directed evolution to enhance the activity and stability of esterases, resulting in increased ethyl propanoate yields. For instance, studies have reported up to 5-fold improvements in catalytic efficiency through this method.
Another significant strategy is rational design, which utilizes structural and mechanistic knowledge of enzymes to guide targeted mutations. Computational tools and molecular modeling have been instrumental in predicting beneficial amino acid substitutions that can enhance enzyme performance. This approach has led to the development of esterases with improved thermostability and tolerance to organic solvents, both critical factors for industrial-scale ethyl propanoate production.
Protein engineering techniques such as domain shuffling and loop engineering have also been applied to create chimeric enzymes with enhanced properties. By combining functional domains from different esterases or introducing novel loop regions, researchers have developed enzymes with broader substrate specificity and improved catalytic rates for ethyl propanoate synthesis.
Immobilization of engineered enzymes has further contributed to the enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield. Various immobilization techniques, including covalent binding, entrapment, and cross-linking, have been explored to improve enzyme stability and reusability. Immobilized enzymes often exhibit enhanced operational stability and can be easily recovered and reused, making the biocatalytic process more economically viable.
Recent advancements in enzyme engineering have also focused on developing enzymes capable of functioning efficiently in non-aqueous media. This is particularly relevant for ethyl propanoate synthesis, as the reaction typically occurs in organic solvents. Engineered enzymes with improved solvent tolerance and activity in organic media have shown promising results in increasing product yield and reducing side reactions.
As the field of enzyme engineering continues to evolve, emerging technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence are being integrated into the design process. These tools offer the potential to accelerate the discovery of novel enzyme variants with enhanced properties for ethyl propanoate production. By leveraging large datasets and predictive algorithms, researchers can more efficiently explore the vast sequence space and identify promising candidates for experimental validation.
One of the main approaches in enzyme engineering for this application is directed evolution. This technique involves iterative rounds of random mutagenesis and screening to identify enzyme variants with improved properties. Researchers have successfully employed directed evolution to enhance the activity and stability of esterases, resulting in increased ethyl propanoate yields. For instance, studies have reported up to 5-fold improvements in catalytic efficiency through this method.
Another significant strategy is rational design, which utilizes structural and mechanistic knowledge of enzymes to guide targeted mutations. Computational tools and molecular modeling have been instrumental in predicting beneficial amino acid substitutions that can enhance enzyme performance. This approach has led to the development of esterases with improved thermostability and tolerance to organic solvents, both critical factors for industrial-scale ethyl propanoate production.
Protein engineering techniques such as domain shuffling and loop engineering have also been applied to create chimeric enzymes with enhanced properties. By combining functional domains from different esterases or introducing novel loop regions, researchers have developed enzymes with broader substrate specificity and improved catalytic rates for ethyl propanoate synthesis.
Immobilization of engineered enzymes has further contributed to the enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield. Various immobilization techniques, including covalent binding, entrapment, and cross-linking, have been explored to improve enzyme stability and reusability. Immobilized enzymes often exhibit enhanced operational stability and can be easily recovered and reused, making the biocatalytic process more economically viable.
Recent advancements in enzyme engineering have also focused on developing enzymes capable of functioning efficiently in non-aqueous media. This is particularly relevant for ethyl propanoate synthesis, as the reaction typically occurs in organic solvents. Engineered enzymes with improved solvent tolerance and activity in organic media have shown promising results in increasing product yield and reducing side reactions.
As the field of enzyme engineering continues to evolve, emerging technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence are being integrated into the design process. These tools offer the potential to accelerate the discovery of novel enzyme variants with enhanced properties for ethyl propanoate production. By leveraging large datasets and predictive algorithms, researchers can more efficiently explore the vast sequence space and identify promising candidates for experimental validation.
Green Chemistry Impact
The integration of biocatalysis in the production of ethyl propanoate aligns closely with the principles of green chemistry, offering significant environmental and economic benefits. This approach reduces the reliance on traditional chemical synthesis methods, which often involve harsh conditions and generate substantial waste. Biocatalytic processes typically operate under milder conditions, utilizing enzymes that work efficiently at ambient temperatures and pressures, thereby reducing energy consumption and minimizing the need for toxic or hazardous reagents.
The use of biocatalysts in ethyl propanoate synthesis contributes to atom economy, one of the key tenets of green chemistry. Enzymes catalyze highly specific reactions, leading to improved selectivity and reduced formation of unwanted by-products. This selectivity not only enhances the yield of the desired product but also simplifies downstream processing and purification steps, further reducing waste generation and resource consumption.
Moreover, biocatalytic processes often employ renewable feedstocks, such as biomass-derived ethanol and propionic acid, as starting materials. This shift towards renewable resources decreases dependence on fossil fuel-based chemicals, contributing to the overall sustainability of the production process. The biodegradability of enzymes and their ability to function in aqueous environments also aligns with green chemistry principles, minimizing the environmental impact of the production process.
The enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield through biocatalysis supports the development of greener and more sustainable industrial processes. By reducing the environmental footprint of production, this approach addresses growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and helps companies meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The improved efficiency and reduced waste generation associated with biocatalytic processes can lead to significant cost savings, making them economically attractive to industries.
Furthermore, the application of biocatalysis in ethyl propanoate production serves as a model for the broader implementation of green chemistry principles in industrial processes. It demonstrates the potential for enzyme-based technologies to replace traditional chemical synthesis methods across various sectors, paving the way for more sustainable manufacturing practices. This shift not only benefits the environment but also drives innovation in biotechnology and enzyme engineering, fostering the development of new, more efficient biocatalysts tailored for specific industrial applications.
The use of biocatalysts in ethyl propanoate synthesis contributes to atom economy, one of the key tenets of green chemistry. Enzymes catalyze highly specific reactions, leading to improved selectivity and reduced formation of unwanted by-products. This selectivity not only enhances the yield of the desired product but also simplifies downstream processing and purification steps, further reducing waste generation and resource consumption.
Moreover, biocatalytic processes often employ renewable feedstocks, such as biomass-derived ethanol and propionic acid, as starting materials. This shift towards renewable resources decreases dependence on fossil fuel-based chemicals, contributing to the overall sustainability of the production process. The biodegradability of enzymes and their ability to function in aqueous environments also aligns with green chemistry principles, minimizing the environmental impact of the production process.
The enhancement of ethyl propanoate yield through biocatalysis supports the development of greener and more sustainable industrial processes. By reducing the environmental footprint of production, this approach addresses growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and helps companies meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The improved efficiency and reduced waste generation associated with biocatalytic processes can lead to significant cost savings, making them economically attractive to industries.
Furthermore, the application of biocatalysis in ethyl propanoate production serves as a model for the broader implementation of green chemistry principles in industrial processes. It demonstrates the potential for enzyme-based technologies to replace traditional chemical synthesis methods across various sectors, paving the way for more sustainable manufacturing practices. This shift not only benefits the environment but also drives innovation in biotechnology and enzyme engineering, fostering the development of new, more efficient biocatalysts tailored for specific industrial applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!