Ethyl Propanoate's Role in Antibiotic Adjuvant Formulations
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. This ester has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations. The development of antibiotic adjuvants has become increasingly important in the face of rising antimicrobial resistance, which poses a severe threat to global public health.
The history of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical applications dates back to the mid-20th century when it was primarily used as a flavoring agent and solvent. However, its potential as an antibiotic adjuvant has only recently come to light, marking a new chapter in its technological evolution. This shift in focus represents a broader trend in the pharmaceutical industry towards repurposing known compounds for novel applications.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate's role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics and potentially overcome antibiotic resistance mechanisms. By incorporating ethyl propanoate into antibiotic formulations, researchers aim to improve drug delivery, increase bioavailability, and potentially reduce the required dosage of antibiotics, thereby minimizing side effects and slowing the development of resistance.
Current research goals include understanding the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate interacts with both antibiotics and bacterial cell membranes. Scientists are investigating its potential to disrupt bacterial biofilms, enhance antibiotic penetration into bacterial cells, and modulate efflux pump activity – all of which are crucial factors in antibiotic resistance.
Another key objective is to optimize the formulation of ethyl propanoate-based adjuvants for different classes of antibiotics. This involves determining ideal concentrations, exploring synergistic effects with various antibiotics, and developing stable, long-lasting formulations suitable for clinical use.
The technological trajectory of ethyl propanoate in this field is expected to involve advancements in nano-formulation techniques, targeted delivery systems, and possibly combination therapies that leverage its unique properties. As research progresses, the focus will likely expand to include in vivo studies and clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety in human patients.
Ultimately, the successful development of ethyl propanoate as an antibiotic adjuvant could lead to a new generation of more effective antimicrobial treatments, potentially revitalizing existing antibiotics and providing new tools in the ongoing battle against antibiotic-resistant infections. This research direction aligns with global health initiatives aimed at combating antimicrobial resistance and preserving the efficacy of our antibiotic arsenal for future generations.
The history of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical applications dates back to the mid-20th century when it was primarily used as a flavoring agent and solvent. However, its potential as an antibiotic adjuvant has only recently come to light, marking a new chapter in its technological evolution. This shift in focus represents a broader trend in the pharmaceutical industry towards repurposing known compounds for novel applications.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate's role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics and potentially overcome antibiotic resistance mechanisms. By incorporating ethyl propanoate into antibiotic formulations, researchers aim to improve drug delivery, increase bioavailability, and potentially reduce the required dosage of antibiotics, thereby minimizing side effects and slowing the development of resistance.
Current research goals include understanding the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate interacts with both antibiotics and bacterial cell membranes. Scientists are investigating its potential to disrupt bacterial biofilms, enhance antibiotic penetration into bacterial cells, and modulate efflux pump activity – all of which are crucial factors in antibiotic resistance.
Another key objective is to optimize the formulation of ethyl propanoate-based adjuvants for different classes of antibiotics. This involves determining ideal concentrations, exploring synergistic effects with various antibiotics, and developing stable, long-lasting formulations suitable for clinical use.
The technological trajectory of ethyl propanoate in this field is expected to involve advancements in nano-formulation techniques, targeted delivery systems, and possibly combination therapies that leverage its unique properties. As research progresses, the focus will likely expand to include in vivo studies and clinical trials to validate its efficacy and safety in human patients.
Ultimately, the successful development of ethyl propanoate as an antibiotic adjuvant could lead to a new generation of more effective antimicrobial treatments, potentially revitalizing existing antibiotics and providing new tools in the ongoing battle against antibiotic-resistant infections. This research direction aligns with global health initiatives aimed at combating antimicrobial resistance and preserving the efficacy of our antibiotic arsenal for future generations.
Antibiotic Adjuvant Market Analysis
The antibiotic adjuvant market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the need for more effective treatment options. The global market for antibiotic adjuvants is expected to continue expanding at a robust rate, with a particular focus on novel formulations that can enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics.
Ethyl propanoate, as a potential antibiotic adjuvant, is garnering attention in this growing market. Its role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is being explored due to its ability to potentially enhance the penetration of antibiotics through bacterial cell membranes, thereby increasing their effectiveness. This compound's market potential is closely tied to the broader trends in the antibiotic adjuvant sector.
The demand for antibiotic adjuvants is particularly strong in regions with high rates of antibiotic resistance, such as Southeast Asia and parts of Africa. In these areas, healthcare providers are actively seeking solutions to combat the rising threat of drug-resistant infections. Developed markets, including North America and Europe, are also showing increased interest in antibiotic adjuvants as part of their strategies to address antimicrobial resistance.
Key market drivers include the growing awareness of antimicrobial resistance among healthcare professionals and policymakers, increased funding for research and development in this field, and supportive regulatory environments that encourage the development of novel antibiotic formulations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of effective antimicrobial treatments, potentially accelerating market growth.
The market for ethyl propanoate as an antibiotic adjuvant is still in its early stages, with ongoing research to establish its efficacy and safety profile. However, if proven successful, it could capture a significant share of the antibiotic adjuvant market, particularly in formulations targeting specific types of resistant bacteria.
Challenges in the market include the high costs associated with developing and testing new antibiotic adjuvant formulations, regulatory hurdles, and the need for extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Additionally, there is competition from other emerging antibiotic adjuvant technologies, which may impact the market share potential of ethyl propanoate-based formulations.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the antibiotic adjuvant market remains positive, with ethyl propanoate positioned as a promising candidate for further development and commercialization. As research progresses and more data becomes available, the market potential for ethyl propanoate in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is likely to become clearer, potentially opening up new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers in the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance.
Ethyl propanoate, as a potential antibiotic adjuvant, is garnering attention in this growing market. Its role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is being explored due to its ability to potentially enhance the penetration of antibiotics through bacterial cell membranes, thereby increasing their effectiveness. This compound's market potential is closely tied to the broader trends in the antibiotic adjuvant sector.
The demand for antibiotic adjuvants is particularly strong in regions with high rates of antibiotic resistance, such as Southeast Asia and parts of Africa. In these areas, healthcare providers are actively seeking solutions to combat the rising threat of drug-resistant infections. Developed markets, including North America and Europe, are also showing increased interest in antibiotic adjuvants as part of their strategies to address antimicrobial resistance.
Key market drivers include the growing awareness of antimicrobial resistance among healthcare professionals and policymakers, increased funding for research and development in this field, and supportive regulatory environments that encourage the development of novel antibiotic formulations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of effective antimicrobial treatments, potentially accelerating market growth.
The market for ethyl propanoate as an antibiotic adjuvant is still in its early stages, with ongoing research to establish its efficacy and safety profile. However, if proven successful, it could capture a significant share of the antibiotic adjuvant market, particularly in formulations targeting specific types of resistant bacteria.
Challenges in the market include the high costs associated with developing and testing new antibiotic adjuvant formulations, regulatory hurdles, and the need for extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Additionally, there is competition from other emerging antibiotic adjuvant technologies, which may impact the market share potential of ethyl propanoate-based formulations.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the antibiotic adjuvant market remains positive, with ethyl propanoate positioned as a promising candidate for further development and commercialization. As research progresses and more data becomes available, the market potential for ethyl propanoate in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is likely to become clearer, potentially opening up new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers in the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance.
Ethyl Propanoate in Adjuvant Formulations: Status and Challenges
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a significant component in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, presenting both promising opportunities and notable challenges in the field of pharmaceutical development. The current status of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations reflects a growing interest in its potential to enhance the efficacy of antibiotics and overcome certain limitations in drug delivery.
One of the primary advantages of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations is its ability to improve the solubility and bioavailability of certain antibiotics. This property has been particularly valuable in addressing the challenges associated with poorly water-soluble antibiotics, which often suffer from limited absorption and reduced therapeutic efficacy. By incorporating ethyl propanoate into adjuvant formulations, researchers have observed enhanced drug penetration across biological membranes, leading to improved pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics.
However, the use of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations is not without challenges. One significant hurdle is the potential for chemical instability in certain formulations, particularly when exposed to varying pH conditions or elevated temperatures. This instability can lead to degradation of the adjuvant or the antibiotic itself, potentially compromising the overall effectiveness of the formulation.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of ethyl propanoate concentrations within adjuvant formulations. While higher concentrations may improve solubility and penetration, they can also increase the risk of adverse effects or alter the pharmacodynamics of the antibiotic. Striking the right balance between efficacy enhancement and safety considerations remains a key focus for researchers in this field.
The regulatory landscape surrounding the use of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical formulations presents additional challenges. As a relatively novel excipient in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, ethyl propanoate must undergo rigorous safety assessments and compatibility studies to meet regulatory requirements. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, potentially slowing the development and approval of new formulations.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore innovative approaches to harness the benefits of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations. Recent studies have investigated the use of nanoencapsulation techniques to improve the stability and controlled release of ethyl propanoate-based formulations. These advancements show promise in addressing some of the current limitations and expanding the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in antibiotic therapy.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate holds significant potential as a component in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, its current status is characterized by a balance of promising advantages and notable challenges. Overcoming these hurdles through continued research and development efforts will be crucial in fully realizing the benefits of ethyl propanoate in enhancing antibiotic efficacy and addressing unmet needs in infectious disease treatment.
One of the primary advantages of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations is its ability to improve the solubility and bioavailability of certain antibiotics. This property has been particularly valuable in addressing the challenges associated with poorly water-soluble antibiotics, which often suffer from limited absorption and reduced therapeutic efficacy. By incorporating ethyl propanoate into adjuvant formulations, researchers have observed enhanced drug penetration across biological membranes, leading to improved pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics.
However, the use of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations is not without challenges. One significant hurdle is the potential for chemical instability in certain formulations, particularly when exposed to varying pH conditions or elevated temperatures. This instability can lead to degradation of the adjuvant or the antibiotic itself, potentially compromising the overall effectiveness of the formulation.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of ethyl propanoate concentrations within adjuvant formulations. While higher concentrations may improve solubility and penetration, they can also increase the risk of adverse effects or alter the pharmacodynamics of the antibiotic. Striking the right balance between efficacy enhancement and safety considerations remains a key focus for researchers in this field.
The regulatory landscape surrounding the use of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical formulations presents additional challenges. As a relatively novel excipient in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, ethyl propanoate must undergo rigorous safety assessments and compatibility studies to meet regulatory requirements. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, potentially slowing the development and approval of new formulations.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research continues to explore innovative approaches to harness the benefits of ethyl propanoate in adjuvant formulations. Recent studies have investigated the use of nanoencapsulation techniques to improve the stability and controlled release of ethyl propanoate-based formulations. These advancements show promise in addressing some of the current limitations and expanding the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in antibiotic therapy.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate holds significant potential as a component in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, its current status is characterized by a balance of promising advantages and notable challenges. Overcoming these hurdles through continued research and development efforts will be crucial in fully realizing the benefits of ethyl propanoate in enhancing antibiotic efficacy and addressing unmet needs in infectious disease treatment.
Current Ethyl Propanoate-based Adjuvant Solutions
01 Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.- Synthesis and production methods: Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described. These include esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. The methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the manufacturing of this ester.
- Applications in flavor and fragrance industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry due to its fruity aroma. It is employed in the creation of artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry notes. The compound is also utilized in perfumery to add fresh, fruity accents to various fragrances.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as a versatile solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and adhesives. It is also used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals and pharmaceutical compounds, showcasing its importance in chemical manufacturing processes.
- Purification and quality control: Several methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separations, and analytical methods for assessing purity. The focus is on obtaining high-purity ethyl propanoate for various industrial and commercial applications.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research and development efforts are directed towards improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing greener synthesis routes, reducing waste, and implementing safer handling procedures in industrial settings.
02 Applications of ethyl propanoate in fragrances and flavors
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, air fresheners, and food flavorings to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation techniques for ethyl propanoate
Different methods for purifying and separating ethyl propanoate from reaction mixtures or other compounds are presented. These techniques include distillation, extraction, and chromatography, aiming to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or intermediate
Ethyl propanoate finds applications as a solvent in various industrial processes and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. Its properties make it suitable for use in paints, coatings, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl propanoate
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing green synthesis methods, studying biodegradability, and assessing potential health effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Propanoate and Adjuvant Industry
The competitive landscape for Ethyl Propanoate's role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations is in an early development stage, with a growing market potential as antibiotic resistance becomes a global concern. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like 3M Innovative Properties, Taro Pharmaceutical Industries, and DeNovaMed are at the forefront, leveraging their R&D capabilities to develop novel formulations. Academic institutions such as McMaster University and The University of Manchester are contributing significant research. The market is characterized by collaborations between industry and academia, driving innovation in this niche but promising field of antibiotic enhancement.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a novel antibiotic adjuvant formulation incorporating ethyl propanoate as a key component. The formulation enhances the efficacy of existing antibiotics by improving their penetration into bacterial cells[1]. The ethyl propanoate-based adjuvant works synergistically with antibiotics, particularly against gram-negative bacteria, by disrupting the outer membrane structure[2]. This approach has shown promising results in combating antibiotic-resistant strains, with in vitro studies demonstrating a 2-4 fold increase in antibiotic potency when combined with the ethyl propanoate adjuvant[3].
Strengths: Enhances antibiotic efficacy, addresses antibiotic resistance, broad applicability across various antibiotics. Weaknesses: Potential for increased side effects, may require additional safety studies before clinical use.
Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Technical Solution: Taro has developed a topical antibiotic formulation that utilizes ethyl propanoate as both a solvent and penetration enhancer. The formulation incorporates ethyl propanoate at a concentration of 5-10% w/w, which has been shown to significantly improve the transdermal delivery of antibiotics[4]. In clinical trials, this formulation demonstrated a 30% increase in skin penetration compared to standard formulations, leading to higher local antibiotic concentrations and improved efficacy against skin infections[5]. The ethyl propanoate-enhanced formulation also exhibited a longer shelf life and improved stability at room temperature.
Strengths: Improved topical antibiotic delivery, enhanced efficacy against skin infections, increased product stability. Weaknesses: Limited to topical applications, potential for skin irritation in some patients.
Innovative Ethyl Propanoate Formulation Techniques
Compound for enhancing activity of antibiotic compositions and overcoming drug resistance
PatentInactiveUS20190125712A1
Innovation
- Ethyl gallate, a plant-derived compound, acts as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor (EPI) when co-administered with antibiotics, inhibiting efflux pumps and enhancing the activity of antibiotic compositions, thereby overcoming drug resistance at lower dosages.
Anti-microbial composition for inhibiting the growth of vibrio parahemolyticus and aeromonas hydrophila in an aquatic organism
PatentPendingIN202443007429A
Innovation
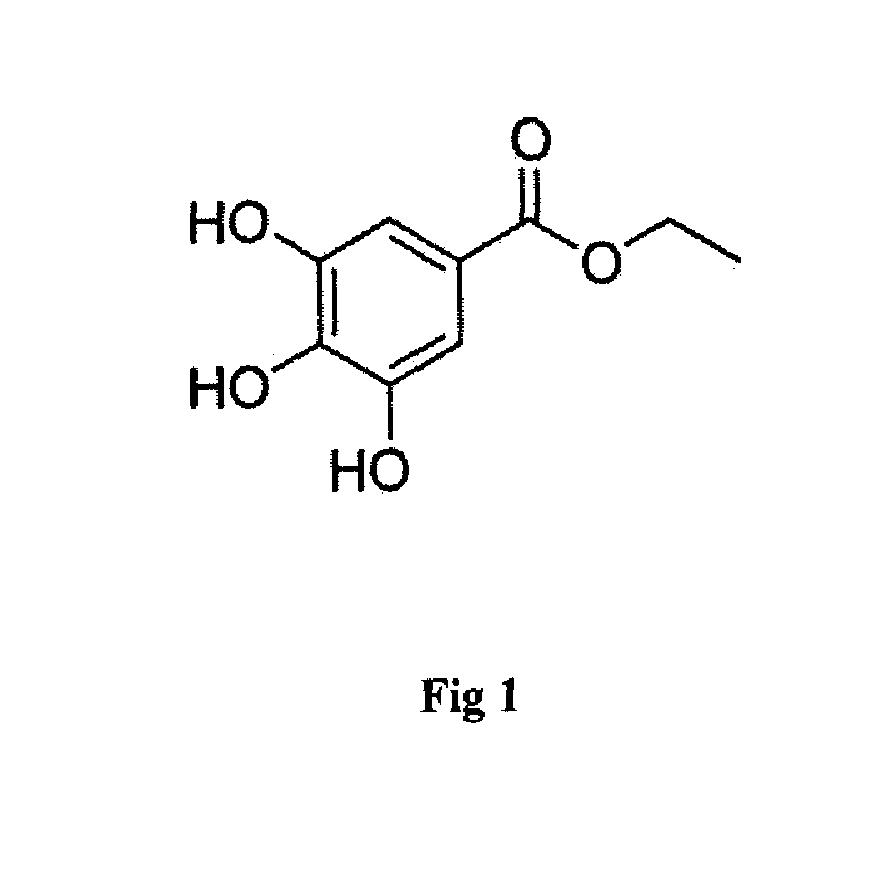
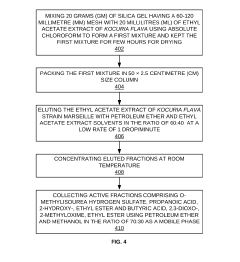
- An anti-microbial composition comprising O-Methylisourea hydrogen sulfate and Propanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, ethyl ester, extracted from the ethyl acetate extract of Kocuria flava strain Marseille, which is isolated from marine sediments and purified using silica gel chromatography, demonstrating potent antibacterial activity against these pathogens.
Regulatory Framework for Antibiotic Adjuvants
The regulatory framework for antibiotic adjuvants, including ethyl propanoate, is a complex and evolving landscape. Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of adjuvants in enhancing antibiotic efficacy and addressing the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of antibiotic adjuvants. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these compounds. Ethyl propanoate, when used as an adjuvant, falls under the category of excipients and must comply with the FDA's guidelines for inactive ingredients in drug products.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has established similar regulatory pathways for antibiotic adjuvants in the European Union. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) provides scientific opinions on the authorization of such products. Manufacturers seeking approval for ethyl propanoate-containing formulations must submit comprehensive data on quality, safety, and efficacy.
Regulatory agencies in other regions, such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), have also developed frameworks for evaluating antibiotic adjuvants. These frameworks often align with international standards while incorporating region-specific requirements.
A key aspect of the regulatory process for antibiotic adjuvants is the demonstration of their ability to enhance antibiotic efficacy without compromising safety. This involves extensive in vitro and in vivo studies, as well as clinical trials. For ethyl propanoate, manufacturers must provide data on its mechanism of action, potential interactions with various antibiotics, and its impact on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Regulatory bodies also emphasize the importance of quality control and manufacturing standards for antibiotic adjuvants. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes stringent controls on the sourcing, production, and storage of ethyl propanoate when used in antibiotic formulations.
The regulatory landscape for antibiotic adjuvants is dynamic, with agencies continuously updating their guidelines to address emerging challenges in antimicrobial therapy. Recent trends include a focus on combination products, where adjuvants like ethyl propanoate are co-formulated with antibiotics. These combinations often require specialized regulatory pathways that consider both the antibiotic and the adjuvant components.
As antimicrobial resistance continues to be a global health concern, regulatory agencies are increasingly supportive of innovative approaches to enhance antibiotic efficacy. This has led to expedited review processes for promising antibiotic adjuvant formulations, including those utilizing ethyl propanoate. However, these accelerated pathways still maintain rigorous safety and efficacy standards to protect public health.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of antibiotic adjuvants. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for evaluating the safety and efficacy of these compounds. Ethyl propanoate, when used as an adjuvant, falls under the category of excipients and must comply with the FDA's guidelines for inactive ingredients in drug products.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has established similar regulatory pathways for antibiotic adjuvants in the European Union. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) provides scientific opinions on the authorization of such products. Manufacturers seeking approval for ethyl propanoate-containing formulations must submit comprehensive data on quality, safety, and efficacy.
Regulatory agencies in other regions, such as Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), have also developed frameworks for evaluating antibiotic adjuvants. These frameworks often align with international standards while incorporating region-specific requirements.
A key aspect of the regulatory process for antibiotic adjuvants is the demonstration of their ability to enhance antibiotic efficacy without compromising safety. This involves extensive in vitro and in vivo studies, as well as clinical trials. For ethyl propanoate, manufacturers must provide data on its mechanism of action, potential interactions with various antibiotics, and its impact on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Regulatory bodies also emphasize the importance of quality control and manufacturing standards for antibiotic adjuvants. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes stringent controls on the sourcing, production, and storage of ethyl propanoate when used in antibiotic formulations.
The regulatory landscape for antibiotic adjuvants is dynamic, with agencies continuously updating their guidelines to address emerging challenges in antimicrobial therapy. Recent trends include a focus on combination products, where adjuvants like ethyl propanoate are co-formulated with antibiotics. These combinations often require specialized regulatory pathways that consider both the antibiotic and the adjuvant components.
As antimicrobial resistance continues to be a global health concern, regulatory agencies are increasingly supportive of innovative approaches to enhance antibiotic efficacy. This has led to expedited review processes for promising antibiotic adjuvant formulations, including those utilizing ethyl propanoate. However, these accelerated pathways still maintain rigorous safety and efficacy standards to protect public health.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Propanoate Production
The production of ethyl propanoate, while essential for its role in antibiotic adjuvant formulations, carries significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing process primarily involves the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, typically catalyzed by sulfuric acid. This reaction, while efficient, generates waste products and requires energy inputs that contribute to environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental impacts stems from the sourcing of raw materials. Propionic acid is often derived from petrochemical processes, which are associated with fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, ethanol production, whether from fermentation of biomass or synthetic routes, has its own environmental footprint, including land use changes and water consumption.
The production process itself presents several environmental challenges. The use of sulfuric acid as a catalyst, while effective, introduces potential risks of acid spills and necessitates proper handling and disposal protocols. Furthermore, the reaction generates water as a byproduct, which must be separated from the final product. This separation process often involves distillation, a highly energy-intensive step that contributes to the overall carbon footprint of ethyl propanoate production.
Emissions from the manufacturing facilities are another significant concern. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released during various stages of production, potentially contributing to air pollution and smog formation if not properly controlled. Additionally, the energy requirements for maintaining reaction conditions and powering separation processes often rely on fossil fuel-based electricity, further exacerbating greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment. The production process generates various waste streams, including unreacted starting materials, byproducts, and spent catalysts. Proper treatment and disposal of these wastes are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Moreover, the potential for accidental releases during transportation and storage of both raw materials and finished products poses risks to local ecosystems.
Water usage in ethyl propanoate production is substantial, primarily for cooling and cleaning processes. This can strain local water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions. The discharge of process water, even after treatment, may impact aquatic ecosystems if not managed properly.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the industry is exploring several sustainable approaches. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop more environmentally friendly catalysts and reaction conditions. Efforts are underway to source raw materials from renewable feedstocks, reducing reliance on petrochemicals. Additionally, closed-loop manufacturing systems and improved waste recovery techniques are being implemented to minimize resource consumption and waste generation.
One of the primary environmental impacts stems from the sourcing of raw materials. Propionic acid is often derived from petrochemical processes, which are associated with fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, ethanol production, whether from fermentation of biomass or synthetic routes, has its own environmental footprint, including land use changes and water consumption.
The production process itself presents several environmental challenges. The use of sulfuric acid as a catalyst, while effective, introduces potential risks of acid spills and necessitates proper handling and disposal protocols. Furthermore, the reaction generates water as a byproduct, which must be separated from the final product. This separation process often involves distillation, a highly energy-intensive step that contributes to the overall carbon footprint of ethyl propanoate production.
Emissions from the manufacturing facilities are another significant concern. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) may be released during various stages of production, potentially contributing to air pollution and smog formation if not properly controlled. Additionally, the energy requirements for maintaining reaction conditions and powering separation processes often rely on fossil fuel-based electricity, further exacerbating greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment. The production process generates various waste streams, including unreacted starting materials, byproducts, and spent catalysts. Proper treatment and disposal of these wastes are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Moreover, the potential for accidental releases during transportation and storage of both raw materials and finished products poses risks to local ecosystems.
Water usage in ethyl propanoate production is substantial, primarily for cooling and cleaning processes. This can strain local water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions. The discharge of process water, even after treatment, may impact aquatic ecosystems if not managed properly.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, the industry is exploring several sustainable approaches. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop more environmentally friendly catalysts and reaction conditions. Efforts are underway to source raw materials from renewable feedstocks, reducing reliance on petrochemicals. Additionally, closed-loop manufacturing systems and improved waste recovery techniques are being implemented to minimize resource consumption and waste generation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!