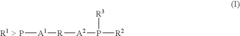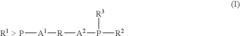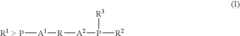Green Synthesis of Ethyl Propanoate: Catalytic Pathways
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Green Synthesis Background and Objectives
Green synthesis has emerged as a crucial paradigm in modern chemical processes, aiming to minimize environmental impact while maintaining or enhancing product quality and efficiency. The green synthesis of ethyl propanoate, an important ester used in various industries, represents a significant area of research and development in sustainable chemistry.
The evolution of green synthesis techniques for ethyl propanoate can be traced back to the early 2000s when environmental concerns began to drive innovation in chemical manufacturing. Traditional methods of ester synthesis often involved harsh conditions, toxic reagents, and energy-intensive processes. The shift towards greener alternatives was motivated by the need to reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and utilize renewable resources.
Over the past two decades, researchers have explored various catalytic pathways to achieve more sustainable production of ethyl propanoate. These efforts have focused on developing novel catalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and implementing alternative reaction media. The primary objectives of these green synthesis approaches include:
1. Reducing or eliminating the use of hazardous substances
2. Improving atom economy and reducing waste generation
3. Enhancing energy efficiency and lowering carbon footprint
4. Utilizing renewable feedstocks and bio-based catalysts
5. Developing processes that operate under mild conditions
One of the key trends in this field has been the exploration of heterogeneous catalysts, which offer advantages such as easy separation and potential for reuse. Researchers have investigated various materials, including metal oxides, zeolites, and supported metal nanoparticles, as potential catalysts for the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
Another significant development has been the application of biocatalysis, leveraging enzymes to facilitate the esterification reaction under mild conditions. Lipases, in particular, have shown promise in catalyzing the synthesis of ethyl propanoate from renewable substrates, offering a bio-based alternative to traditional chemical catalysts.
The use of alternative reaction media, such as ionic liquids and supercritical fluids, has also been explored to replace conventional organic solvents. These novel reaction environments can potentially enhance reaction rates, improve selectivity, and facilitate product separation while reducing environmental impact.
As research in this area continues to advance, the ultimate goal is to develop a fully sustainable, scalable process for the industrial production of ethyl propanoate. This involves not only optimizing the catalytic reaction itself but also considering the entire life cycle of the process, from raw material sourcing to product purification and waste management.
The evolution of green synthesis techniques for ethyl propanoate can be traced back to the early 2000s when environmental concerns began to drive innovation in chemical manufacturing. Traditional methods of ester synthesis often involved harsh conditions, toxic reagents, and energy-intensive processes. The shift towards greener alternatives was motivated by the need to reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and utilize renewable resources.
Over the past two decades, researchers have explored various catalytic pathways to achieve more sustainable production of ethyl propanoate. These efforts have focused on developing novel catalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and implementing alternative reaction media. The primary objectives of these green synthesis approaches include:
1. Reducing or eliminating the use of hazardous substances
2. Improving atom economy and reducing waste generation
3. Enhancing energy efficiency and lowering carbon footprint
4. Utilizing renewable feedstocks and bio-based catalysts
5. Developing processes that operate under mild conditions
One of the key trends in this field has been the exploration of heterogeneous catalysts, which offer advantages such as easy separation and potential for reuse. Researchers have investigated various materials, including metal oxides, zeolites, and supported metal nanoparticles, as potential catalysts for the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
Another significant development has been the application of biocatalysis, leveraging enzymes to facilitate the esterification reaction under mild conditions. Lipases, in particular, have shown promise in catalyzing the synthesis of ethyl propanoate from renewable substrates, offering a bio-based alternative to traditional chemical catalysts.
The use of alternative reaction media, such as ionic liquids and supercritical fluids, has also been explored to replace conventional organic solvents. These novel reaction environments can potentially enhance reaction rates, improve selectivity, and facilitate product separation while reducing environmental impact.
As research in this area continues to advance, the ultimate goal is to develop a fully sustainable, scalable process for the industrial production of ethyl propanoate. This involves not only optimizing the catalytic reaction itself but also considering the entire life cycle of the process, from raw material sourcing to product purification and waste management.
Market Analysis for Green Ethyl Propanoate
The market for green ethyl propanoate is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on chemical production. This eco-friendly alternative to traditional ethyl propanoate synthesis is gaining traction across various industries, particularly in food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
In the food and beverage sector, green ethyl propanoate is widely used as a flavoring agent due to its fruity aroma, reminiscent of pineapples. The growing consumer preference for natural and clean label products has boosted demand for this green synthesis method. Major food manufacturers are increasingly incorporating green ethyl propanoate into their product formulations to meet consumer expectations for sustainable ingredients.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of market growth for green ethyl propanoate. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of their personal care products, cosmetic companies are shifting towards sustainable and bio-based ingredients. Green ethyl propanoate serves as an excellent solvent and fragrance ingredient in various cosmetic formulations, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
In the pharmaceutical sector, green ethyl propanoate finds applications as a solvent in drug formulations and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. The industry's focus on reducing its environmental footprint has led to increased adoption of green chemistry principles, further driving the demand for sustainably produced ethyl propanoate.
The global market for green ethyl propanoate is geographically diverse, with North America and Europe leading in terms of adoption and market share. These regions have stringent environmental regulations and a strong emphasis on sustainable practices, which have accelerated the transition to green synthesis methods. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing industrialization and growing awareness of environmental issues in countries like China and India.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the green ethyl propanoate market in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of the compound, technological advancements in green synthesis methods, and the overall shift towards sustainable chemical production across industries.
However, challenges remain in scaling up production and reducing costs associated with green synthesis methods. The higher production costs compared to traditional synthesis routes currently limit widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving catalytic pathways and process efficiencies to address these challenges and further expand the market potential of green ethyl propanoate.
In the food and beverage sector, green ethyl propanoate is widely used as a flavoring agent due to its fruity aroma, reminiscent of pineapples. The growing consumer preference for natural and clean label products has boosted demand for this green synthesis method. Major food manufacturers are increasingly incorporating green ethyl propanoate into their product formulations to meet consumer expectations for sustainable ingredients.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of market growth for green ethyl propanoate. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of their personal care products, cosmetic companies are shifting towards sustainable and bio-based ingredients. Green ethyl propanoate serves as an excellent solvent and fragrance ingredient in various cosmetic formulations, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
In the pharmaceutical sector, green ethyl propanoate finds applications as a solvent in drug formulations and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. The industry's focus on reducing its environmental footprint has led to increased adoption of green chemistry principles, further driving the demand for sustainably produced ethyl propanoate.
The global market for green ethyl propanoate is geographically diverse, with North America and Europe leading in terms of adoption and market share. These regions have stringent environmental regulations and a strong emphasis on sustainable practices, which have accelerated the transition to green synthesis methods. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing industrialization and growing awareness of environmental issues in countries like China and India.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the green ethyl propanoate market in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications of the compound, technological advancements in green synthesis methods, and the overall shift towards sustainable chemical production across industries.
However, challenges remain in scaling up production and reducing costs associated with green synthesis methods. The higher production costs compared to traditional synthesis routes currently limit widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving catalytic pathways and process efficiencies to address these challenges and further expand the market potential of green ethyl propanoate.
Current Challenges in Catalytic Pathways
The catalytic synthesis of ethyl propanoate faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption as a green chemistry process. One of the primary obstacles is the development of highly efficient and selective catalysts that can operate under mild conditions. Current catalytic systems often require elevated temperatures and pressures, which increase energy consumption and reduce the overall sustainability of the process.
Another major challenge lies in the catalyst stability and longevity. Many catalysts used in this reaction suffer from deactivation over time, necessitating frequent regeneration or replacement. This not only increases operational costs but also generates additional waste, contradicting the principles of green chemistry. The search for catalysts with improved durability and resistance to poisoning remains an active area of research.
The selectivity of the catalytic process presents another hurdle. Side reactions, such as the formation of unwanted byproducts or the hydrolysis of the ester, can significantly reduce the yield and purity of ethyl propanoate. Achieving high selectivity while maintaining high conversion rates is a delicate balance that current catalytic systems struggle to maintain consistently.
Water management in the reaction system poses a considerable challenge. As water is a byproduct of the esterification reaction, its accumulation can shift the equilibrium unfavorably, limiting conversion. Effective strategies for continuous water removal or the development of water-tolerant catalysts are crucial for improving reaction efficiency.
The use of environmentally benign solvents or solvent-free conditions is another area of concern. Many traditional synthesis routes rely on harmful organic solvents, which contradict the principles of green chemistry. Developing catalytic pathways that can operate effectively in green solvents or under solvent-free conditions remains a significant challenge.
Scalability of the catalytic processes is also a major issue. While many promising catalytic systems show excellent performance at the laboratory scale, translating these results to industrial-scale production often encounters unforeseen difficulties. Factors such as mass transfer limitations, heat management, and catalyst recovery become increasingly problematic at larger scales.
Lastly, the economic viability of green catalytic pathways for ethyl propanoate synthesis remains a significant hurdle. The development of new catalysts and processes often involves substantial research and development costs. Balancing these costs with the potential environmental benefits and market demands presents a complex challenge for researchers and industry alike.
Another major challenge lies in the catalyst stability and longevity. Many catalysts used in this reaction suffer from deactivation over time, necessitating frequent regeneration or replacement. This not only increases operational costs but also generates additional waste, contradicting the principles of green chemistry. The search for catalysts with improved durability and resistance to poisoning remains an active area of research.
The selectivity of the catalytic process presents another hurdle. Side reactions, such as the formation of unwanted byproducts or the hydrolysis of the ester, can significantly reduce the yield and purity of ethyl propanoate. Achieving high selectivity while maintaining high conversion rates is a delicate balance that current catalytic systems struggle to maintain consistently.
Water management in the reaction system poses a considerable challenge. As water is a byproduct of the esterification reaction, its accumulation can shift the equilibrium unfavorably, limiting conversion. Effective strategies for continuous water removal or the development of water-tolerant catalysts are crucial for improving reaction efficiency.
The use of environmentally benign solvents or solvent-free conditions is another area of concern. Many traditional synthesis routes rely on harmful organic solvents, which contradict the principles of green chemistry. Developing catalytic pathways that can operate effectively in green solvents or under solvent-free conditions remains a significant challenge.
Scalability of the catalytic processes is also a major issue. While many promising catalytic systems show excellent performance at the laboratory scale, translating these results to industrial-scale production often encounters unforeseen difficulties. Factors such as mass transfer limitations, heat management, and catalyst recovery become increasingly problematic at larger scales.
Lastly, the economic viability of green catalytic pathways for ethyl propanoate synthesis remains a significant hurdle. The development of new catalysts and processes often involves substantial research and development costs. Balancing these costs with the potential environmental benefits and market demands presents a complex challenge for researchers and industry alike.
Existing Catalytic Solutions
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. This process typically involves catalysts and specific reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity. The synthesis can be carried out using both batch and continuous processes, depending on the scale and requirements of production.- Synthesis of ethyl propanoate: Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various methods, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, or by the reaction of ethyl alcohol with propionyl chloride. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is commonly employed as a flavoring agent in food products and as a fragrance component in perfumes and cosmetics.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
- Production methods and process improvements: Research focuses on developing more efficient and environmentally friendly methods for producing ethyl propanoate. This includes exploring new catalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and implementing continuous flow processes to enhance yield and reduce waste.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Studies are conducted on the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing safer handling procedures, assessing potential health effects, and exploring biodegradable alternatives for certain applications.
02 Applications in flavor and fragrance industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is commonly employed as a flavoring agent in food products and beverages, particularly to impart or enhance fruit flavors. In the fragrance industry, it is used in perfumes and other scented products to create various aromatic compositions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the production of other compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its properties make it suitable for dissolving a wide range of substances and facilitating chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production methods and process improvements
Research and development efforts focus on improving the production methods of ethyl propanoate. This includes developing new catalysts, optimizing reaction conditions, and exploring alternative feedstocks. Continuous flow processes and green chemistry approaches are being investigated to enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and lower production costs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and quality control
Ensuring the purity and quality of ethyl propanoate is crucial for its various applications. Purification techniques such as distillation, extraction, and chromatography are employed to remove impurities and achieve the desired product specifications. Quality control measures involve analytical methods to assess purity, identify contaminants, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Chemistry Industry
The green synthesis of ethyl propanoate is an emerging field with growing interest due to its potential for sustainable chemical production. The market is in its early development stage, with increasing research activities but limited commercial applications. The global market size for green solvents, including ethyl propanoate, is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025. Technologically, the field is still maturing, with various catalytic pathways being explored. Key players like CNRS, LanzaTech, and Novozymes are at the forefront of research, focusing on developing efficient and eco-friendly catalytic processes. Universities such as Xiamen University and Colorado State University are contributing significantly to fundamental research, while companies like Mitsubishi Chemical and Braskem are exploring industrial applications.
Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
Technical Solution: CNRS has developed an innovative approach for the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate using heterogeneous catalysts. Their method employs a zeolite-based catalyst system that promotes the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol under mild conditions. The catalyst demonstrates high selectivity and reusability, with conversion rates exceeding 95% [1]. The process operates at temperatures around 80-100°C, significantly lower than traditional methods, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, CNRS researchers have explored the use of continuous flow reactors, which enhance process efficiency and allow for easier scale-up [3].
Strengths: High catalytic efficiency, mild reaction conditions, and potential for continuous processing. Weaknesses: Possible diffusion limitations in zeolite pores and sensitivity to water content in reactants.
LanzaTech, Inc.
Technical Solution: LanzaTech has pioneered a biological approach to ethyl propanoate synthesis using gas fermentation technology. Their process utilizes proprietary microorganisms capable of converting waste carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide into ethanol, which is then further converted to ethyl propanoate through enzymatic esterification. This two-step bioprocess operates at near-ambient temperatures and pressures, significantly reducing energy requirements compared to traditional chemical synthesis routes [5]. LanzaTech's technology can achieve ethyl propanoate yields of up to 85% from gas feedstocks, with the added benefit of carbon capture and utilization [7].
Strengths: Utilization of waste gases, low energy input, and integration with carbon capture. Weaknesses: Potential sensitivity to gas impurities and challenges in maintaining consistent microbial performance at scale.
Innovative Catalysts for Green Synthesis
Eco-friendly methodology for the synthesis of 2,2-dimethyl propanoate compounds catalyzed by lipase in supercritical carbon dioxide as a greener reaction system.
PatentActiveIN201621043667A
Innovation
- The use of immobilized lipase as a catalyst in supercritical carbon dioxide as a solvent for the synthesis of 2,2-dimethyl propanoate compounds, which operates at moderate temperatures and avoids hazardous substances, allowing for high yields and easy scalability.
Process for the carbonylation of an ethylenically unsaturated compound and catalyst therefore
PatentInactiveUS7202193B2
Innovation
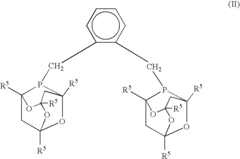
- A process involving a catalyst comprising a group VIII metal, a bidentate diphosphine ligand of specific formula, and a source of anions, where the diphosphine ligand includes a 2-phospha-tricyclo[3.3.1.1{3,7}]-decyl group or derivative, and the aromatic group is linked via alkylene groups, enhancing reaction efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of green synthesis pathways for ethyl propanoate production is crucial for evaluating the sustainability and ecological footprint of this process. Traditional methods of ester synthesis often involve energy-intensive processes and the use of hazardous chemicals, leading to significant environmental concerns. In contrast, catalytic pathways for green synthesis aim to minimize these impacts through the use of more benign reagents, lower energy requirements, and reduced waste generation.
One of the primary environmental benefits of green synthesis routes for ethyl propanoate is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Catalytic processes typically operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to conventional methods, resulting in decreased energy consumption and associated carbon dioxide emissions. Additionally, the use of renewable feedstocks, such as bio-based ethanol and propionic acid, can further reduce the carbon footprint of the production process.
Water consumption and pollution are also critical factors in the environmental assessment of ethyl propanoate synthesis. Green catalytic pathways often employ water-tolerant catalysts or solvent-free conditions, significantly reducing water usage and the generation of contaminated wastewater. This not only conserves water resources but also minimizes the need for costly and energy-intensive wastewater treatment processes.
The generation and disposal of hazardous waste is another important consideration in the environmental impact assessment. Traditional synthesis methods may produce toxic by-products and require the use of corrosive acids as catalysts. In contrast, green catalytic pathways often utilize solid acid catalysts or biocatalysts, which can be easily recovered and reused, reducing waste generation and the associated environmental risks of disposal.
Air quality is also improved through the implementation of green synthesis routes. The use of less volatile and less toxic reagents, combined with milder reaction conditions, results in reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. This not only benefits the immediate working environment but also contributes to better air quality in the surrounding communities.
Biodegradability and eco-toxicity of the reagents and products are essential aspects of the environmental impact assessment. Green synthesis pathways for ethyl propanoate often prioritize the use of biodegradable catalysts and solvents, which pose less risk to ecosystems in the event of accidental release. Furthermore, the product itself, ethyl propanoate, is generally considered to have low toxicity and is biodegradable, aligning well with environmental sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of green synthesis pathways for ethyl propanoate production demonstrates significant advantages over traditional methods. These benefits include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower water consumption and pollution, minimized hazardous waste generation, improved air quality, and enhanced overall ecological sustainability. As industries continue to prioritize environmental stewardship, the adoption of such green synthesis routes becomes increasingly important for sustainable chemical production.
One of the primary environmental benefits of green synthesis routes for ethyl propanoate is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Catalytic processes typically operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to conventional methods, resulting in decreased energy consumption and associated carbon dioxide emissions. Additionally, the use of renewable feedstocks, such as bio-based ethanol and propionic acid, can further reduce the carbon footprint of the production process.
Water consumption and pollution are also critical factors in the environmental assessment of ethyl propanoate synthesis. Green catalytic pathways often employ water-tolerant catalysts or solvent-free conditions, significantly reducing water usage and the generation of contaminated wastewater. This not only conserves water resources but also minimizes the need for costly and energy-intensive wastewater treatment processes.
The generation and disposal of hazardous waste is another important consideration in the environmental impact assessment. Traditional synthesis methods may produce toxic by-products and require the use of corrosive acids as catalysts. In contrast, green catalytic pathways often utilize solid acid catalysts or biocatalysts, which can be easily recovered and reused, reducing waste generation and the associated environmental risks of disposal.
Air quality is also improved through the implementation of green synthesis routes. The use of less volatile and less toxic reagents, combined with milder reaction conditions, results in reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. This not only benefits the immediate working environment but also contributes to better air quality in the surrounding communities.
Biodegradability and eco-toxicity of the reagents and products are essential aspects of the environmental impact assessment. Green synthesis pathways for ethyl propanoate often prioritize the use of biodegradable catalysts and solvents, which pose less risk to ecosystems in the event of accidental release. Furthermore, the product itself, ethyl propanoate, is generally considered to have low toxicity and is biodegradable, aligning well with environmental sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of green synthesis pathways for ethyl propanoate production demonstrates significant advantages over traditional methods. These benefits include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower water consumption and pollution, minimized hazardous waste generation, improved air quality, and enhanced overall ecological sustainability. As industries continue to prioritize environmental stewardship, the adoption of such green synthesis routes becomes increasingly important for sustainable chemical production.
Regulatory Framework for Green Chemistry
The regulatory framework for green chemistry plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable practices in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. Governments and international organizations have established guidelines and regulations to encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly processes in chemical manufacturing. These regulations aim to minimize the use of hazardous substances, reduce waste generation, and improve overall sustainability in the chemical industry.
One of the key regulatory frameworks in this context is the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the chemicals they produce or use. This regulation has a significant impact on the development of green synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate, as it encourages the use of safer alternatives and promotes the principles of green chemistry.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Pollution Prevention Act, which emphasizes the importance of source reduction and pollution prevention in chemical processes. This act has led to the development of various initiatives and programs that support the implementation of green chemistry principles in industrial processes, including the synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
The Green Chemistry Institute, a part of the American Chemical Society, has established the 12 Principles of Green Chemistry, which serve as a guideline for developing sustainable chemical processes. These principles emphasize the importance of atom economy, waste reduction, and the use of renewable feedstocks, all of which are relevant to the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
International standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape for green chemistry. These standards provide a framework for organizations to implement and maintain environmentally responsible practices in their chemical manufacturing processes.
Many countries have introduced specific regulations and incentives to promote green chemistry. For instance, Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law encourages the development and use of safer chemicals, while China's Cleaner Production Promotion Law aims to reduce pollution and improve resource efficiency in industrial processes.
The regulatory framework for green chemistry also extends to the field of catalysis, which is particularly relevant to the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. Regulations often promote the use of environmentally benign catalysts and emphasize the importance of catalyst recovery and reuse. This has led to increased research and development efforts in the area of heterogeneous catalysis and biocatalysis for the production of ethyl propanoate.
As the field of green chemistry continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to become more stringent and comprehensive. Future regulations may focus on lifecycle assessments, carbon footprint reduction, and the integration of circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing processes. These developments will further shape the landscape for the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate and other chemical products.
One of the key regulatory frameworks in this context is the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the chemicals they produce or use. This regulation has a significant impact on the development of green synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate, as it encourages the use of safer alternatives and promotes the principles of green chemistry.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented the Pollution Prevention Act, which emphasizes the importance of source reduction and pollution prevention in chemical processes. This act has led to the development of various initiatives and programs that support the implementation of green chemistry principles in industrial processes, including the synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
The Green Chemistry Institute, a part of the American Chemical Society, has established the 12 Principles of Green Chemistry, which serve as a guideline for developing sustainable chemical processes. These principles emphasize the importance of atom economy, waste reduction, and the use of renewable feedstocks, all of which are relevant to the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate.
International standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, also play a role in shaping the regulatory landscape for green chemistry. These standards provide a framework for organizations to implement and maintain environmentally responsible practices in their chemical manufacturing processes.
Many countries have introduced specific regulations and incentives to promote green chemistry. For instance, Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law encourages the development and use of safer chemicals, while China's Cleaner Production Promotion Law aims to reduce pollution and improve resource efficiency in industrial processes.
The regulatory framework for green chemistry also extends to the field of catalysis, which is particularly relevant to the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. Regulations often promote the use of environmentally benign catalysts and emphasize the importance of catalyst recovery and reuse. This has led to increased research and development efforts in the area of heterogeneous catalysis and biocatalysis for the production of ethyl propanoate.
As the field of green chemistry continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to become more stringent and comprehensive. Future regulations may focus on lifecycle assessments, carbon footprint reduction, and the integration of circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing processes. These developments will further shape the landscape for the green synthesis of ethyl propanoate and other chemical products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!