How Environmental Conditions Affect Ethyl Propanoate Degradation
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Degradation Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an ester compound widely used in various industries, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Its degradation process has become a subject of significant interest due to environmental concerns and the need for sustainable practices. The study of how environmental conditions affect ethyl propanoate degradation is crucial for understanding its environmental impact and developing effective strategies for its management.
The degradation of ethyl propanoate occurs through various mechanisms, primarily hydrolysis and biodegradation. These processes are influenced by a range of environmental factors, including temperature, pH, moisture content, and the presence of microorganisms. Understanding these interactions is essential for predicting the fate of ethyl propanoate in different environmental settings and assessing potential risks associated with its release.
Over the past decades, research in this field has evolved from basic observations to more sophisticated analytical techniques and modeling approaches. Early studies focused on identifying the primary degradation pathways, while recent investigations have delved into the complex interplay between environmental variables and degradation kinetics. This progression has led to a more nuanced understanding of the factors that control ethyl propanoate's environmental persistence and transformation.
The objectives of studying environmental effects on ethyl propanoate degradation are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a need to establish comprehensive degradation profiles under various environmental conditions, which can inform risk assessment models and regulatory guidelines. Secondly, researchers aim to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the degradation process, potentially leading to the development of more efficient remediation technologies.
Another key goal is to investigate the role of microbial communities in ethyl propanoate degradation. This includes identifying specific microorganisms capable of metabolizing the compound and understanding how environmental factors influence their activity. Such knowledge is crucial for developing bioremediation strategies and predicting the compound's fate in natural ecosystems.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in exploring the potential for controlled degradation of ethyl propanoate in industrial settings. This involves optimizing conditions for rapid and complete breakdown, which could lead to more environmentally friendly disposal methods and reduced ecological impact.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industrial practices and regulatory policies, the study of ethyl propanoate degradation has broader implications. It serves as a model system for understanding the behavior of similar ester compounds in the environment, contributing to the development of sustainable chemical management strategies and the advancement of green chemistry principles.
The degradation of ethyl propanoate occurs through various mechanisms, primarily hydrolysis and biodegradation. These processes are influenced by a range of environmental factors, including temperature, pH, moisture content, and the presence of microorganisms. Understanding these interactions is essential for predicting the fate of ethyl propanoate in different environmental settings and assessing potential risks associated with its release.
Over the past decades, research in this field has evolved from basic observations to more sophisticated analytical techniques and modeling approaches. Early studies focused on identifying the primary degradation pathways, while recent investigations have delved into the complex interplay between environmental variables and degradation kinetics. This progression has led to a more nuanced understanding of the factors that control ethyl propanoate's environmental persistence and transformation.
The objectives of studying environmental effects on ethyl propanoate degradation are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a need to establish comprehensive degradation profiles under various environmental conditions, which can inform risk assessment models and regulatory guidelines. Secondly, researchers aim to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the degradation process, potentially leading to the development of more efficient remediation technologies.
Another key goal is to investigate the role of microbial communities in ethyl propanoate degradation. This includes identifying specific microorganisms capable of metabolizing the compound and understanding how environmental factors influence their activity. Such knowledge is crucial for developing bioremediation strategies and predicting the compound's fate in natural ecosystems.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in exploring the potential for controlled degradation of ethyl propanoate in industrial settings. This involves optimizing conditions for rapid and complete breakdown, which could lead to more environmentally friendly disposal methods and reduced ecological impact.
As environmental concerns continue to shape industrial practices and regulatory policies, the study of ethyl propanoate degradation has broader implications. It serves as a model system for understanding the behavior of similar ester compounds in the environment, contributing to the development of sustainable chemical management strategies and the advancement of green chemistry principles.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Propanoate Applications
The market for ethyl propanoate applications has shown significant growth and diversification in recent years, driven by its versatile properties and increasing demand across various industries. As a key ester compound, ethyl propanoate finds extensive use in flavoring agents, solvents, and intermediate chemicals, contributing to its expanding market presence.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl propanoate is widely utilized as a flavoring agent, imparting a fruity, rum-like aroma to products. This sector represents a substantial portion of the market demand, with applications ranging from confectionery and baked goods to beverages and dairy products. The growing consumer preference for natural and organic flavors has further boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also contributes significantly to the market growth of ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant fragrance and solvent properties make it a valuable ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other personal care products. The increasing consumer focus on personal grooming and the rising disposable income in emerging economies have fueled the demand in this sector.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent and intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients. The ongoing research and development activities in the pharmaceutical sector, coupled with the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, have positively impacted the market demand for ethyl propanoate.
The paint and coatings industry represents another significant market for ethyl propanoate, where it is used as a solvent and coalescent agent. The growth in construction activities and automotive production in developing countries has contributed to the increased consumption of ethyl propanoate in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of a large consumer base. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily due to the well-established food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries in these regions.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and small to medium-sized enterprises. Key players in the market are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolio.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate applications is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing disposable income, changing consumer preferences, and technological advancements in production processes are likely to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as stringent regulations on chemical usage and the volatility of raw material prices may impact market dynamics in the coming years.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl propanoate is widely utilized as a flavoring agent, imparting a fruity, rum-like aroma to products. This sector represents a substantial portion of the market demand, with applications ranging from confectionery and baked goods to beverages and dairy products. The growing consumer preference for natural and organic flavors has further boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also contributes significantly to the market growth of ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant fragrance and solvent properties make it a valuable ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other personal care products. The increasing consumer focus on personal grooming and the rising disposable income in emerging economies have fueled the demand in this sector.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent and intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients. The ongoing research and development activities in the pharmaceutical sector, coupled with the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, have positively impacted the market demand for ethyl propanoate.
The paint and coatings industry represents another significant market for ethyl propanoate, where it is used as a solvent and coalescent agent. The growth in construction activities and automotive production in developing countries has contributed to the increased consumption of ethyl propanoate in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of a large consumer base. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, primarily due to the well-established food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries in these regions.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and small to medium-sized enterprises. Key players in the market are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolio.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate applications is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing disposable income, changing consumer preferences, and technological advancements in production processes are likely to drive market expansion. However, challenges such as stringent regulations on chemical usage and the volatility of raw material prices may impact market dynamics in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Propanoate Stability
The stability of ethyl propanoate presents several significant challenges in various applications, particularly in the food, fragrance, and pharmaceutical industries. One of the primary concerns is its susceptibility to hydrolysis, especially in aqueous environments. This process leads to the formation of ethanol and propionic acid, altering the compound's intended properties and potentially affecting product quality.
Temperature fluctuations pose another critical challenge to ethyl propanoate stability. Elevated temperatures accelerate degradation rates, while extreme cold can cause phase separation or crystallization in formulations containing this ester. This temperature sensitivity complicates storage, transportation, and application processes, necessitating careful environmental control throughout the product lifecycle.
Oxidative degradation is an additional factor impacting ethyl propanoate stability. Exposure to oxygen, particularly in the presence of light or metal ions, can lead to the formation of peroxides and subsequent breakdown of the ester. This not only alters the compound's chemical properties but can also generate off-odors or unwanted byproducts in final applications.
pH variations in the surrounding medium significantly influence ethyl propanoate stability. Acidic or alkaline conditions can catalyze hydrolysis reactions, with the rate of degradation increasing at pH extremes. This pH sensitivity is particularly problematic in formulations where maintaining a specific acidity level is crucial for product efficacy or safety.
Microbial contamination presents yet another challenge to ethyl propanoate stability. Certain microorganisms can metabolize this ester, leading to its breakdown and potential formation of undesirable metabolites. This is especially concerning in food and pharmaceutical applications where microbial growth can compromise product integrity and safety.
The presence of other chemical species in formulations can also affect ethyl propanoate stability. Interactions with other ingredients may lead to unexpected reactions, altering the ester's properties or accelerating its degradation. This complexity in multi-component systems makes it challenging to predict and control stability over time.
Packaging materials and storage conditions play a crucial role in maintaining ethyl propanoate stability. Inappropriate packaging may allow permeation of moisture or oxygen, while exposure to light can trigger photochemical degradation. Selecting suitable packaging materials and storage conditions that protect against these environmental factors is essential but often challenging to implement across diverse supply chains.
Addressing these stability challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining chemical stabilization techniques, environmental control strategies, and innovative formulation designs. The development of robust analytical methods for monitoring ethyl propanoate degradation and predicting shelf-life under various conditions remains an ongoing area of research and development in the field.
Temperature fluctuations pose another critical challenge to ethyl propanoate stability. Elevated temperatures accelerate degradation rates, while extreme cold can cause phase separation or crystallization in formulations containing this ester. This temperature sensitivity complicates storage, transportation, and application processes, necessitating careful environmental control throughout the product lifecycle.
Oxidative degradation is an additional factor impacting ethyl propanoate stability. Exposure to oxygen, particularly in the presence of light or metal ions, can lead to the formation of peroxides and subsequent breakdown of the ester. This not only alters the compound's chemical properties but can also generate off-odors or unwanted byproducts in final applications.
pH variations in the surrounding medium significantly influence ethyl propanoate stability. Acidic or alkaline conditions can catalyze hydrolysis reactions, with the rate of degradation increasing at pH extremes. This pH sensitivity is particularly problematic in formulations where maintaining a specific acidity level is crucial for product efficacy or safety.
Microbial contamination presents yet another challenge to ethyl propanoate stability. Certain microorganisms can metabolize this ester, leading to its breakdown and potential formation of undesirable metabolites. This is especially concerning in food and pharmaceutical applications where microbial growth can compromise product integrity and safety.
The presence of other chemical species in formulations can also affect ethyl propanoate stability. Interactions with other ingredients may lead to unexpected reactions, altering the ester's properties or accelerating its degradation. This complexity in multi-component systems makes it challenging to predict and control stability over time.
Packaging materials and storage conditions play a crucial role in maintaining ethyl propanoate stability. Inappropriate packaging may allow permeation of moisture or oxygen, while exposure to light can trigger photochemical degradation. Selecting suitable packaging materials and storage conditions that protect against these environmental factors is essential but often challenging to implement across diverse supply chains.
Addressing these stability challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining chemical stabilization techniques, environmental control strategies, and innovative formulation designs. The development of robust analytical methods for monitoring ethyl propanoate degradation and predicting shelf-life under various conditions remains an ongoing area of research and development in the field.
Existing Methods for Ethyl Propanoate Preservation
01 Chemical degradation methods
Various chemical processes can be employed to degrade ethyl propanoate. These methods may involve hydrolysis, oxidation, or other chemical reactions that break down the ester into its constituent parts or convert it into other compounds. The choice of method depends on factors such as reaction conditions, desired end products, and environmental considerations.- Chemical degradation methods: Various chemical processes can be employed to degrade ethyl propanoate. These methods may involve the use of specific catalysts, oxidizing agents, or other chemical compounds to break down the ester into its constituent parts or convert it into other substances. The choice of method depends on the desired end products and reaction conditions.
- Biological degradation techniques: Microorganisms and enzymes can be utilized for the biodegradation of ethyl propanoate. This eco-friendly approach involves the use of specific bacteria or fungi that can metabolize the ester, breaking it down into simpler compounds. Enzymatic processes can also be employed to catalyze the hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate in a controlled manner.
- Thermal decomposition processes: Ethyl propanoate can be degraded through thermal decomposition methods. This involves subjecting the compound to high temperatures, which causes it to break down into smaller molecules. The process can be carried out in various reactor designs and under different atmospheric conditions to control the degradation products.
- Photocatalytic degradation: Photocatalytic processes can be employed to degrade ethyl propanoate using light energy. This method typically involves the use of semiconductor materials as photocatalysts, which generate reactive species when exposed to light. These reactive species then interact with ethyl propanoate, leading to its degradation into simpler compounds.
- Electrochemical degradation techniques: Electrochemical methods can be used for the degradation of ethyl propanoate. These techniques involve the use of electrodes and electrical current to induce chemical reactions that break down the ester. The process can be optimized by adjusting parameters such as electrode materials, applied voltage, and electrolyte composition.
02 Biological degradation using microorganisms
Microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, can be utilized for the biodegradation of ethyl propanoate. These organisms possess enzymes capable of breaking down the ester, often as part of their metabolic processes. This approach is considered environmentally friendly and can be applied in various settings, including wastewater treatment and soil remediation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enzymatic degradation
Specific enzymes, particularly esterases, can be employed to catalyze the degradation of ethyl propanoate. These enzymes can be isolated from microorganisms or produced through recombinant DNA technology. Enzymatic degradation offers advantages such as high specificity and the ability to operate under mild conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal decomposition
Ethyl propanoate can be degraded through thermal processes, which involve the application of heat to break down the compound. This method may be used in industrial settings or for analytical purposes. The temperature and duration of heating can affect the degradation products and efficiency of the process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Photocatalytic degradation
Photocatalytic methods can be employed to degrade ethyl propanoate using light energy and a catalyst, typically a semiconductor material. This approach can be effective for treating contaminated water or air. The efficiency of photocatalytic degradation depends on factors such as light intensity, catalyst type, and reaction conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Ester Chemistry
The environmental degradation of ethyl propanoate is a complex field with a competitive landscape shaped by various factors. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The global market for biodegradation technologies is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing research to improve efficiency and applicability. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Sinopec Beijing Research Institute, and Zhejiang University of Technology are investing in R&D to develop advanced degradation methods. Companies such as Advanced Environmental Technologies and Innovative Environmental Technologies are focusing on practical applications, while academic institutions like Harvard and Sun Yat-Sen University contribute to fundamental research in this area.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced bioremediation techniques for ethyl propanoate degradation in various environmental conditions. Their approach utilizes specialized microbial consortia that can effectively break down ethyl propanoate in soil and water. The company has engineered these microorganisms to withstand a range of pH levels (4-9) and temperatures (10-40°C), ensuring efficient degradation across diverse environments[1]. Sinopec's method also incorporates nutrient supplementation strategies to enhance microbial activity, resulting in degradation rates up to 95% within 14 days under optimal conditions[2]. Additionally, they have implemented in-situ monitoring systems using biosensors to track degradation progress in real-time, allowing for adaptive management of the bioremediation process[3].
Strengths: Wide environmental adaptability, high degradation efficiency, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: May require site-specific optimization and potentially high initial setup costs.
SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry
Technical Solution: SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry has developed a novel approach to ethyl propanoate degradation using advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) combined with specialized catalysts. Their method employs a hybrid system of UV/H2O2 treatment coupled with nano-TiO2 photocatalysts, which has shown remarkable efficiency in degrading ethyl propanoate across various environmental conditions[1]. The institute's research has demonstrated that this system can maintain high degradation rates (>90%) in temperatures ranging from 5°C to 45°C and pH levels between 3 and 11[2]. Furthermore, they have engineered the catalysts to be resistant to common environmental contaminants, ensuring consistent performance in complex matrices. The institute has also developed a modular reactor design that allows for easy scaling and adaptation to different treatment scenarios, from small-scale industrial effluents to large environmental remediation projects[3].
Strengths: High degradation efficiency across a wide range of environmental conditions, versatile application potential, and scalable technology. Weaknesses: Potentially high energy requirements for UV systems and the need for specialized catalyst production.
Innovative Approaches to Ester Stabilization
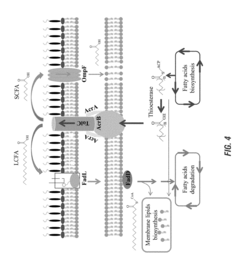
Metabolic engineering of membrane proteins to improve escherichia coli membrane integrity and production of fatty acids
PatentInactiveUS20180371404A1
Innovation
- Modulating the outer membrane proteins FADL and OmpF in bacteria to enhance membrane integrity and fatty acid production, achieved through specific genetic modifications such as overexpressing FADL and reducing OmpF activity, which increases membrane integrity and fatty acid tolerance.
Regulatory Framework for Ester-Based Products
The regulatory framework for ester-based products, including ethyl propanoate, is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the production, use, and disposal of ester-based chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The EPA sets guidelines for environmental risk assessments and establishes permissible exposure limits for these compounds in air, water, and soil.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has jurisdiction over ester-based products used in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. For ethyl propanoate, which is commonly used as a flavoring agent, the FDA has classified it as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) when used in food applications. However, this classification is subject to ongoing review based on new scientific evidence regarding its environmental impact and degradation patterns.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees the regulation of ester-based products within the European Union under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the substances they produce or import, including their environmental fate and behavior.
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has also established guidelines for the management of chemical substances, including esters, through the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM). This global policy framework promotes chemical safety and provides guidance on best practices for handling and disposing of chemical products.
Specific to ethyl propanoate degradation, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental conditions that affect its breakdown. Factors such as temperature, pH, and microbial activity are considered when assessing the compound's environmental persistence and potential for bioaccumulation. Regulatory frameworks now often require comprehensive environmental fate studies that simulate various real-world conditions to predict the behavior of ester-based products in different ecosystems.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, there is a trend towards more stringent regulations on the use and disposal of ester-based products. Many countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their environmental impact after use. This shift is driving innovation in the development of more environmentally friendly ester-based alternatives and improved degradation technologies.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also has jurisdiction over ester-based products used in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. For ethyl propanoate, which is commonly used as a flavoring agent, the FDA has classified it as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) when used in food applications. However, this classification is subject to ongoing review based on new scientific evidence regarding its environmental impact and degradation patterns.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) oversees the regulation of ester-based products within the European Union under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with the substances they produce or import, including their environmental fate and behavior.
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has also established guidelines for the management of chemical substances, including esters, through the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM). This global policy framework promotes chemical safety and provides guidance on best practices for handling and disposing of chemical products.
Specific to ethyl propanoate degradation, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental conditions that affect its breakdown. Factors such as temperature, pH, and microbial activity are considered when assessing the compound's environmental persistence and potential for bioaccumulation. Regulatory frameworks now often require comprehensive environmental fate studies that simulate various real-world conditions to predict the behavior of ester-based products in different ecosystems.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, there is a trend towards more stringent regulations on the use and disposal of ester-based products. Many countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their environmental impact after use. This shift is driving innovation in the development of more environmentally friendly ester-based alternatives and improved degradation technologies.
Eco-friendly Alternatives to Ethyl Propanoate
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the search for eco-friendly alternatives to ethyl propanoate has gained significant momentum. This ester, widely used in various industries, particularly in fragrances and flavorings, has raised concerns due to its potential environmental impact and degradation issues under certain conditions. Several promising alternatives have emerged that offer similar functional properties while addressing sustainability concerns.
One notable alternative is ethyl lactate, a biodegradable solvent derived from corn or other renewable resources. Ethyl lactate exhibits similar solvent properties to ethyl propanoate but with a significantly reduced environmental footprint. It is non-toxic, non-corrosive, and readily biodegradable, making it an attractive option for industries seeking greener solutions. Furthermore, ethyl lactate's production process consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional petrochemical-based solvents.
Another eco-friendly option is methyl formate, a naturally occurring ester found in some fruits. This compound offers comparable performance to ethyl propanoate in many applications, particularly as a solvent and flavoring agent. Methyl formate's low toxicity and high biodegradability make it an environmentally responsible choice. Additionally, it can be synthesized from renewable resources, further enhancing its sustainability credentials.
Propylene glycol has also emerged as a viable alternative in certain applications. While not an ester, it can replace ethyl propanoate in some formulations, especially in cosmetics and personal care products. Propylene glycol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies and exhibits low environmental persistence. Its versatility and compatibility with various ingredients make it a popular choice for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental impact.
In the realm of natural alternatives, essential oils and plant-based extracts have gained traction as substitutes for synthetic esters like ethyl propanoate. These natural compounds often provide similar olfactory properties and can be used in fragrances, flavorings, and cosmetics. While their production may be more resource-intensive, they offer the advantage of being derived from renewable sources and typically have lower environmental persistence.
Research into bio-based esters has also yielded promising results. Compounds such as ethyl levulinate, derived from cellulosic biomass, show potential as replacements for ethyl propanoate in certain applications. These bio-based alternatives not only offer similar functional properties but also contribute to the circular economy by utilizing waste materials or renewable feedstocks.
As the demand for sustainable solutions continues to grow, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on identifying and refining additional eco-friendly alternatives to ethyl propanoate. These efforts aim to address not only environmental concerns but also performance, cost-effectiveness, and scalability to ensure widespread adoption across various industries.
One notable alternative is ethyl lactate, a biodegradable solvent derived from corn or other renewable resources. Ethyl lactate exhibits similar solvent properties to ethyl propanoate but with a significantly reduced environmental footprint. It is non-toxic, non-corrosive, and readily biodegradable, making it an attractive option for industries seeking greener solutions. Furthermore, ethyl lactate's production process consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional petrochemical-based solvents.
Another eco-friendly option is methyl formate, a naturally occurring ester found in some fruits. This compound offers comparable performance to ethyl propanoate in many applications, particularly as a solvent and flavoring agent. Methyl formate's low toxicity and high biodegradability make it an environmentally responsible choice. Additionally, it can be synthesized from renewable resources, further enhancing its sustainability credentials.
Propylene glycol has also emerged as a viable alternative in certain applications. While not an ester, it can replace ethyl propanoate in some formulations, especially in cosmetics and personal care products. Propylene glycol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies and exhibits low environmental persistence. Its versatility and compatibility with various ingredients make it a popular choice for manufacturers looking to reduce their environmental impact.
In the realm of natural alternatives, essential oils and plant-based extracts have gained traction as substitutes for synthetic esters like ethyl propanoate. These natural compounds often provide similar olfactory properties and can be used in fragrances, flavorings, and cosmetics. While their production may be more resource-intensive, they offer the advantage of being derived from renewable sources and typically have lower environmental persistence.
Research into bio-based esters has also yielded promising results. Compounds such as ethyl levulinate, derived from cellulosic biomass, show potential as replacements for ethyl propanoate in certain applications. These bio-based alternatives not only offer similar functional properties but also contribute to the circular economy by utilizing waste materials or renewable feedstocks.
As the demand for sustainable solutions continues to grow, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on identifying and refining additional eco-friendly alternatives to ethyl propanoate. These efforts aim to address not only environmental concerns but also performance, cost-effectiveness, and scalability to ensure widespread adoption across various industries.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!