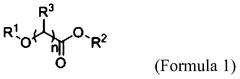How Ethyl Propanoate Assists in Pesticide Formulation
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate in Pesticides: Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a significant component in modern pesticide formulations. This ester compound, with its unique chemical properties, has been increasingly utilized in the agricultural sector to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of pest control solutions. The evolution of pesticide technology has seen a shift from traditional, often harmful chemicals to more sophisticated and environmentally conscious formulations.
The primary objective of incorporating ethyl propanoate into pesticide formulations is to improve the overall performance and safety profile of these products. This compound serves multiple functions, including acting as a solvent, emulsifier, and synergist in various pesticide preparations. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to develop more sustainable pest control solutions.
Historically, the use of ethyl propanoate in pesticides can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when researchers began exploring alternatives to conventional pesticide carriers and additives. The compound's ability to dissolve a wide range of active ingredients while maintaining stability in different environmental conditions made it a subject of interest for agrochemical scientists.
As environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have intensified over the years, the role of ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations has become increasingly prominent. Its low volatility and minimal impact on non-target organisms align well with the growing demand for eco-friendly agricultural practices. Furthermore, the compound's compatibility with various active ingredients has allowed for the development of more targeted and efficient pesticide formulations.
The technical goals associated with ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations include enhancing the solubility and dispersion of active ingredients, improving the penetration of pesticides through plant cuticles, and extending the shelf life of products. Additionally, researchers aim to optimize the synergistic effects of ethyl propanoate with other components to reduce the overall quantity of active ingredients required, thereby minimizing environmental impact while maintaining efficacy.
As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, the trajectory of ethyl propanoate in pesticide technology is expected to follow a path of increased sophistication and integration with other advanced technologies. This may include its incorporation into smart delivery systems, nanotechnology-based formulations, and precision agriculture applications. The ongoing research in this field is likely to uncover new potential uses and benefits of ethyl propanoate, further cementing its role in the future of sustainable pest management strategies.
The primary objective of incorporating ethyl propanoate into pesticide formulations is to improve the overall performance and safety profile of these products. This compound serves multiple functions, including acting as a solvent, emulsifier, and synergist in various pesticide preparations. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to develop more sustainable pest control solutions.
Historically, the use of ethyl propanoate in pesticides can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when researchers began exploring alternatives to conventional pesticide carriers and additives. The compound's ability to dissolve a wide range of active ingredients while maintaining stability in different environmental conditions made it a subject of interest for agrochemical scientists.
As environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have intensified over the years, the role of ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations has become increasingly prominent. Its low volatility and minimal impact on non-target organisms align well with the growing demand for eco-friendly agricultural practices. Furthermore, the compound's compatibility with various active ingredients has allowed for the development of more targeted and efficient pesticide formulations.
The technical goals associated with ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations include enhancing the solubility and dispersion of active ingredients, improving the penetration of pesticides through plant cuticles, and extending the shelf life of products. Additionally, researchers aim to optimize the synergistic effects of ethyl propanoate with other components to reduce the overall quantity of active ingredients required, thereby minimizing environmental impact while maintaining efficacy.
As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, the trajectory of ethyl propanoate in pesticide technology is expected to follow a path of increased sophistication and integration with other advanced technologies. This may include its incorporation into smart delivery systems, nanotechnology-based formulations, and precision agriculture applications. The ongoing research in this field is likely to uncover new potential uses and benefits of ethyl propanoate, further cementing its role in the future of sustainable pest management strategies.
Market Analysis of Ethyl Propanoate-based Pesticides
The market for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly crop protection solutions. As a key ingredient in pesticide formulations, ethyl propanoate offers unique properties that enhance the performance and efficacy of various agricultural chemicals.
The global market for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides is primarily segmented into herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. Among these, herbicides represent the largest market share, accounting for a substantial portion of the overall demand. This is largely due to the rising need for weed control in intensive farming practices and the growing adoption of conservation agriculture techniques.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides, owing to their advanced agricultural sectors and stringent regulations promoting sustainable farming practices. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid agricultural modernization in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by a growing preference for integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which has boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate-based formulations. These products are valued for their ability to improve the stability and shelf life of pesticides while enhancing their penetration and absorption capabilities.
Key market drivers include the increasing global population and subsequent food demand, shrinking arable land, and the need for higher crop yields. Additionally, the shift towards organic farming and sustainable agriculture practices has created new opportunities for ethyl propanoate-based biopesticides.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements, particularly in developed countries, and the growing resistance of pests to conventional pesticides. These factors are pushing manufacturers to invest in research and development to create more innovative and sustainable formulations.
The competitive landscape of the ethyl propanoate-based pesticide market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized agrochemical companies. Major players are focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing awareness about food safety, the adoption of precision agriculture techniques, and ongoing research into novel formulations are likely to drive market expansion in the coming years.
The global market for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides is primarily segmented into herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. Among these, herbicides represent the largest market share, accounting for a substantial portion of the overall demand. This is largely due to the rising need for weed control in intensive farming practices and the growing adoption of conservation agriculture techniques.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides, owing to their advanced agricultural sectors and stringent regulations promoting sustainable farming practices. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by rapid agricultural modernization in countries like China and India.
The market is characterized by a growing preference for integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which has boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate-based formulations. These products are valued for their ability to improve the stability and shelf life of pesticides while enhancing their penetration and absorption capabilities.
Key market drivers include the increasing global population and subsequent food demand, shrinking arable land, and the need for higher crop yields. Additionally, the shift towards organic farming and sustainable agriculture practices has created new opportunities for ethyl propanoate-based biopesticides.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements, particularly in developed countries, and the growing resistance of pests to conventional pesticides. These factors are pushing manufacturers to invest in research and development to create more innovative and sustainable formulations.
The competitive landscape of the ethyl propanoate-based pesticide market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized agrochemical companies. Major players are focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate-based pesticides is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as increasing awareness about food safety, the adoption of precision agriculture techniques, and ongoing research into novel formulations are likely to drive market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Pesticide Formulation
Pesticide formulation faces several significant challenges in the current landscape of agricultural and environmental sciences. One of the primary issues is the need for more effective and sustainable delivery systems. Traditional formulations often suffer from rapid degradation, leading to reduced efficacy and increased environmental contamination. This necessitates frequent reapplication, which is both costly and potentially harmful to ecosystems.
Another critical challenge is the development of resistance in target pests. As pests evolve to withstand existing formulations, there is a constant pressure to innovate and create new, more potent pesticide compositions. This arms race between pest resistance and pesticide development poses significant research and development challenges for the industry.
Environmental concerns also play a crucial role in shaping the challenges of pesticide formulation. There is an increasing demand for formulations that minimize off-target effects, reduce soil and water contamination, and have lower toxicity profiles for non-target organisms. This push for eco-friendly solutions requires a delicate balance between efficacy and environmental stewardship.
The regulatory landscape presents another hurdle for pesticide formulation. Stringent approval processes and evolving regulations across different regions necessitate the development of formulations that can meet diverse safety and efficacy standards. This often results in increased development costs and longer time-to-market for new products.
Formulation stability is an ongoing challenge, particularly in diverse environmental conditions. Pesticides must maintain their efficacy across a range of temperatures, humidity levels, and storage durations. Achieving this stability while also ensuring ease of application and mixing compatibility with other agrochemicals is a complex task.
The need for precision agriculture and targeted application methods is driving the demand for advanced formulation technologies. There is a growing emphasis on developing smart formulations that can be precisely delivered to target areas, reducing overall pesticide use while maximizing effectiveness. This requires innovative approaches to particle size control, adhesion properties, and controlled release mechanisms.
Lastly, the challenge of cost-effectiveness looms large in pesticide formulation. Developing formulations that are both highly effective and economically viable for large-scale agricultural use is a constant balancing act. This economic pressure often conflicts with the need for more sophisticated, environmentally friendly formulations, creating a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Another critical challenge is the development of resistance in target pests. As pests evolve to withstand existing formulations, there is a constant pressure to innovate and create new, more potent pesticide compositions. This arms race between pest resistance and pesticide development poses significant research and development challenges for the industry.
Environmental concerns also play a crucial role in shaping the challenges of pesticide formulation. There is an increasing demand for formulations that minimize off-target effects, reduce soil and water contamination, and have lower toxicity profiles for non-target organisms. This push for eco-friendly solutions requires a delicate balance between efficacy and environmental stewardship.
The regulatory landscape presents another hurdle for pesticide formulation. Stringent approval processes and evolving regulations across different regions necessitate the development of formulations that can meet diverse safety and efficacy standards. This often results in increased development costs and longer time-to-market for new products.
Formulation stability is an ongoing challenge, particularly in diverse environmental conditions. Pesticides must maintain their efficacy across a range of temperatures, humidity levels, and storage durations. Achieving this stability while also ensuring ease of application and mixing compatibility with other agrochemicals is a complex task.
The need for precision agriculture and targeted application methods is driving the demand for advanced formulation technologies. There is a growing emphasis on developing smart formulations that can be precisely delivered to target areas, reducing overall pesticide use while maximizing effectiveness. This requires innovative approaches to particle size control, adhesion properties, and controlled release mechanisms.
Lastly, the challenge of cost-effectiveness looms large in pesticide formulation. Developing formulations that are both highly effective and economically viable for large-scale agricultural use is a constant balancing act. This economic pressure often conflicts with the need for more sophisticated, environmentally friendly formulations, creating a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate Formulation Methods
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various methods, including the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. This process typically involves catalysts and specific reaction conditions to optimize yield and purity. The synthesis can be carried out using both batch and continuous processes, depending on the scale and requirements of production.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl alcohol with propionyl chloride, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry aromas. The compound is also used in perfumery to add sweet, ethereal notes to various fragrances.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds. Its low toxicity and high solvency make it a preferred choice in many processes.
- Purification and quality control: Various methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on biodegradability, ecotoxicity, and potential health effects. Efforts are being made to develop greener production methods and safer handling practices for this widely used compound.
02 Applications in fragrance and flavor industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is commonly employed as a flavoring agent in food products and as a fragrance component in perfumes and cosmetics. The compound's low toxicity and pleasant aroma make it a versatile ingredient in various consumer products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, particularly in the production of paints, inks, and coatings. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its low boiling point and good solvency properties make it suitable for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production methods and process optimization
Various methods have been developed to optimize the production of ethyl propanoate, including continuous flow reactors, microwave-assisted synthesis, and the use of novel catalysts. These approaches aim to improve yield, reduce reaction time, and minimize waste generation. Process optimization also focuses on enhancing the purity of the final product and reducing energy consumption during production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
As with many chemical compounds, the production and use of ethyl propanoate require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes developing green synthesis methods, implementing proper handling and storage procedures, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. Research in this area focuses on reducing the environmental impact of production processes and improving the overall safety profile of the compound.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pesticide and Chemical Industries
The pesticide formulation industry utilizing ethyl propanoate is in a mature stage, with a stable global market size estimated at several billion dollars. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of established agrochemical companies like BASF, Syngenta, and Bayer Bioscience. These industry leaders, along with specialized firms such as M.S. Technologies and Stine Seed Farm, are driving innovation in pesticide formulations. Academic institutions like Zhejiang University and Nanjing Agricultural University contribute to research and development efforts. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of multinational corporations and regional players, with ongoing focus on improving efficacy and environmental sustainability of pesticide formulations incorporating ethyl propanoate.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed an innovative approach to incorporating ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations. Their method involves using ethyl propanoate as a co-solvent and emulsifier in microemulsion concentrates (MEs) [1]. This technique enhances the solubility and stability of active ingredients, particularly for lipophilic pesticides. The company has also explored the use of ethyl propanoate in combination with other solvents to create synergistic effects, improving the overall efficacy of the pesticide formulation [3]. BASF's research has shown that ethyl propanoate can significantly reduce the crystallization of active ingredients during storage, thereby extending the shelf life of pesticide products [5].
Strengths: Improved solubility and stability of active ingredients, extended shelf life of products, and potential for synergistic effects with other solvents. Weaknesses: May require additional formulation adjustments for certain active ingredients and potential cost increase due to the use of multiple solvents.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Chemical has focused on leveraging ethyl propanoate's properties in developing controlled-release formulations for pesticides. Their approach involves using ethyl propanoate as a key component in polymer-based microencapsulation techniques [1]. This method allows for the slow release of active ingredients over time, potentially reducing the frequency of pesticide applications. The company has also explored the use of ethyl propanoate in creating nanoemulsions, which can improve the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble pesticides [3]. Sumitomo's research has demonstrated that ethyl propanoate-based formulations can enhance the photostability of certain light-sensitive pesticides, extending their effectiveness in field conditions [5].
Strengths: Controlled release of active ingredients, improved bioavailability of poorly water-soluble pesticides, enhanced photostability of light-sensitive compounds. Weaknesses: Potentially complex formulation process, may require specialized equipment for production.
Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate Pesticide Formulations
Solvents for agricultural applications and pesticide formulations
PatentWO2019084896A1
Innovation
- Novel solvent blend consisting of ethyl-3-ethoxy propionate and N,N-diethyl acetamide or N,N-dimethyl propanamide for pesticide formulations.
- Versatile solvent system compatible with a wide range of pesticides, including abamectin, tebuconazole, difenoconazole, and others.
- Incorporation of emulsifiers such as TERGITOL 15-S-9 and DOWFAX D-800 to enhance the formulation's stability and performance.
Solvents for agricultural applications and pesticide formulations
PatentWO2019084895A1
Innovation
- Use of high purity ethyl-3-ethoxy propionate (at least 95% by weight) as a solvent for pesticide formulations.
- Flexible composition range of 1-90% solvent and 10-99% pesticide in the formulation, allowing for customization based on specific pesticide properties.
- Compatibility with a wide range of pesticides, including insecticides, fungicides, and herbicides.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of ethyl propanoate in pesticide formulations necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment to ensure its safe and sustainable application. This assessment primarily focuses on the potential effects of ethyl propanoate on various environmental components, including soil, water, air, and biodiversity.
In soil environments, ethyl propanoate exhibits relatively low persistence due to its volatile nature and susceptibility to microbial degradation. Studies have shown that it typically dissipates within a few days to weeks, depending on soil conditions. However, repeated applications in agricultural settings may lead to temporary accumulation in topsoil layers, potentially affecting soil microbial communities and enzymatic activities.
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to pesticide contamination. Ethyl propanoate's water solubility and potential for runoff from treated areas pose risks to aquatic organisms. While its acute toxicity to fish and aquatic invertebrates is generally considered low to moderate, chronic exposure may lead to sublethal effects on growth, reproduction, and behavior of sensitive species. Monitoring programs in water bodies adjacent to treated areas are crucial for assessing long-term impacts.
Atmospheric dispersion of ethyl propanoate during application or through volatilization from treated surfaces contributes to air quality concerns. Although it is not classified as a persistent organic pollutant, its presence in the air can lead to the formation of secondary organic aerosols, potentially affecting local air quality and contributing to the overall atmospheric burden of volatile organic compounds.
Biodiversity impacts of ethyl propanoate-containing pesticides extend beyond target pest species. Non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and small mammals, may be exposed through various routes such as direct contact, ingestion of treated plant material, or consumption of contaminated prey. While ethyl propanoate itself has relatively low toxicity to most vertebrates, its use in combination with other active ingredients in pesticide formulations may amplify ecological risks.
Ecosystem-level effects of ethyl propanoate application require careful consideration. Alterations in pest-predator dynamics, pollination services, and soil nutrient cycling may occur as indirect consequences of its use. Long-term ecological studies are essential to fully understand these complex interactions and potential cascading effects through food webs.
Mitigation strategies to minimize environmental impacts include optimizing application methods, timing, and frequencies to reduce off-target exposure. Buffer zones around sensitive habitats, integrated pest management approaches, and the development of more targeted formulations can further mitigate risks. Additionally, ongoing research into alternative, environmentally friendly pesticide carriers and adjuvants may lead to reduced reliance on compounds like ethyl propanoate in future formulations.
In soil environments, ethyl propanoate exhibits relatively low persistence due to its volatile nature and susceptibility to microbial degradation. Studies have shown that it typically dissipates within a few days to weeks, depending on soil conditions. However, repeated applications in agricultural settings may lead to temporary accumulation in topsoil layers, potentially affecting soil microbial communities and enzymatic activities.
Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to pesticide contamination. Ethyl propanoate's water solubility and potential for runoff from treated areas pose risks to aquatic organisms. While its acute toxicity to fish and aquatic invertebrates is generally considered low to moderate, chronic exposure may lead to sublethal effects on growth, reproduction, and behavior of sensitive species. Monitoring programs in water bodies adjacent to treated areas are crucial for assessing long-term impacts.
Atmospheric dispersion of ethyl propanoate during application or through volatilization from treated surfaces contributes to air quality concerns. Although it is not classified as a persistent organic pollutant, its presence in the air can lead to the formation of secondary organic aerosols, potentially affecting local air quality and contributing to the overall atmospheric burden of volatile organic compounds.
Biodiversity impacts of ethyl propanoate-containing pesticides extend beyond target pest species. Non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and small mammals, may be exposed through various routes such as direct contact, ingestion of treated plant material, or consumption of contaminated prey. While ethyl propanoate itself has relatively low toxicity to most vertebrates, its use in combination with other active ingredients in pesticide formulations may amplify ecological risks.
Ecosystem-level effects of ethyl propanoate application require careful consideration. Alterations in pest-predator dynamics, pollination services, and soil nutrient cycling may occur as indirect consequences of its use. Long-term ecological studies are essential to fully understand these complex interactions and potential cascading effects through food webs.
Mitigation strategies to minimize environmental impacts include optimizing application methods, timing, and frequencies to reduce off-target exposure. Buffer zones around sensitive habitats, integrated pest management approaches, and the development of more targeted formulations can further mitigate risks. Additionally, ongoing research into alternative, environmentally friendly pesticide carriers and adjuvants may lead to reduced reliance on compounds like ethyl propanoate in future formulations.
Regulatory Framework for Pesticide Formulations
The regulatory framework for pesticide formulations involving ethyl propanoate is complex and multifaceted, encompassing various national and international guidelines. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating pesticide formulations under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This act requires all pesticides to be registered with the EPA before they can be sold or distributed.
For formulations containing ethyl propanoate, manufacturers must provide detailed information on the chemical composition, toxicological data, environmental impact, and efficacy studies. The EPA evaluates this information to ensure that the pesticide, when used according to label instructions, will not pose unreasonable risks to human health or the environment. Specific attention is given to the role of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or adjuvant in the formulation, assessing its potential effects on the pesticide's performance and safety profile.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market. This regulation sets stringent criteria for the approval of active substances and co-formulants, including solvents like ethyl propanoate. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the formulation meets safety standards for human health, animal welfare, and environmental protection.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) also plays a significant role in the international regulatory framework. It provides standardized criteria for classifying chemicals and communicating hazard information. Pesticide formulations containing ethyl propanoate must be labeled according to GHS guidelines, ensuring consistent hazard communication across different countries.
Regulatory bodies often require specific studies on the interaction between ethyl propanoate and the active ingredients in the pesticide formulation. These studies aim to assess the stability of the formulation, potential synergistic or antagonistic effects, and any changes in the toxicological profile of the active ingredients when combined with ethyl propanoate.
Additionally, many countries have established maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides in food products. While ethyl propanoate itself may not be subject to MRLs, its presence in pesticide formulations may influence the residue profile of the active ingredients. Regulatory authorities consider this factor when setting or revising MRLs for specific crop-pesticide combinations.
The regulatory framework also addresses the environmental fate of pesticide formulations. Manufacturers must provide data on the degradation, mobility, and potential bioaccumulation of all components, including ethyl propanoate. This information is crucial for assessing the long-term environmental impact of the formulation and determining appropriate use restrictions or mitigation measures.
For formulations containing ethyl propanoate, manufacturers must provide detailed information on the chemical composition, toxicological data, environmental impact, and efficacy studies. The EPA evaluates this information to ensure that the pesticide, when used according to label instructions, will not pose unreasonable risks to human health or the environment. Specific attention is given to the role of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or adjuvant in the formulation, assessing its potential effects on the pesticide's performance and safety profile.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market. This regulation sets stringent criteria for the approval of active substances and co-formulants, including solvents like ethyl propanoate. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the formulation meets safety standards for human health, animal welfare, and environmental protection.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) also plays a significant role in the international regulatory framework. It provides standardized criteria for classifying chemicals and communicating hazard information. Pesticide formulations containing ethyl propanoate must be labeled according to GHS guidelines, ensuring consistent hazard communication across different countries.
Regulatory bodies often require specific studies on the interaction between ethyl propanoate and the active ingredients in the pesticide formulation. These studies aim to assess the stability of the formulation, potential synergistic or antagonistic effects, and any changes in the toxicological profile of the active ingredients when combined with ethyl propanoate.
Additionally, many countries have established maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides in food products. While ethyl propanoate itself may not be subject to MRLs, its presence in pesticide formulations may influence the residue profile of the active ingredients. Regulatory authorities consider this factor when setting or revising MRLs for specific crop-pesticide combinations.
The regulatory framework also addresses the environmental fate of pesticide formulations. Manufacturers must provide data on the degradation, mobility, and potential bioaccumulation of all components, including ethyl propanoate. This information is crucial for assessing the long-term environmental impact of the formulation and determining appropriate use restrictions or mitigation measures.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!