How Ethyl Propanoate Enhances Flavor in Food Industry
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a naturally occurring ester compound found in various fruits and fermented products. Its history in the food industry dates back to the early 20th century when synthetic flavor compounds began to be widely used. The evolution of this compound's application in food flavoring has been closely tied to advancements in organic chemistry and food science.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl propanoate in the food industry is to enhance and modify flavor profiles in a wide range of products. This compound is particularly valued for its fruity, rum-like aroma with sweet and ethereal notes, making it a versatile ingredient in flavor formulations. Its use aims to improve the overall sensory experience of food products, potentially increasing consumer appeal and satisfaction.
From a technical perspective, ethyl propanoate belongs to the family of short-chain esters, which are known for their strong flavor impact even at low concentrations. This characteristic makes it an efficient and cost-effective flavoring agent. The compound's molecular structure, consisting of an ethyl group and a propanoate group, contributes to its unique sensory properties and its ability to interact with other flavor compounds synergistically.
In recent years, the food industry has seen a growing trend towards natural and clean label products. This has led to increased interest in naturally derived ethyl propanoate, obtained through biotechnological processes or extraction from natural sources. The development of such natural production methods represents a significant technological goal in the field, aiming to meet consumer demands while maintaining the compound's flavor-enhancing capabilities.
Another important objective in the use of ethyl propanoate is to achieve flavor stability and consistency across different food matrices. This involves understanding how the compound interacts with various food components, such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, and how these interactions affect flavor perception and retention over time. Research in this area focuses on optimizing formulations and processing techniques to ensure the desired flavor profile is maintained throughout the product's shelf life.
The application of ethyl propanoate also extends to the development of novel flavor combinations and the creation of unique taste experiences. Food scientists and flavorists are continuously exploring new ways to incorporate this compound into complex flavor systems, pushing the boundaries of traditional flavor profiles and catering to evolving consumer preferences.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl propanoate in the food industry is to enhance and modify flavor profiles in a wide range of products. This compound is particularly valued for its fruity, rum-like aroma with sweet and ethereal notes, making it a versatile ingredient in flavor formulations. Its use aims to improve the overall sensory experience of food products, potentially increasing consumer appeal and satisfaction.
From a technical perspective, ethyl propanoate belongs to the family of short-chain esters, which are known for their strong flavor impact even at low concentrations. This characteristic makes it an efficient and cost-effective flavoring agent. The compound's molecular structure, consisting of an ethyl group and a propanoate group, contributes to its unique sensory properties and its ability to interact with other flavor compounds synergistically.
In recent years, the food industry has seen a growing trend towards natural and clean label products. This has led to increased interest in naturally derived ethyl propanoate, obtained through biotechnological processes or extraction from natural sources. The development of such natural production methods represents a significant technological goal in the field, aiming to meet consumer demands while maintaining the compound's flavor-enhancing capabilities.
Another important objective in the use of ethyl propanoate is to achieve flavor stability and consistency across different food matrices. This involves understanding how the compound interacts with various food components, such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, and how these interactions affect flavor perception and retention over time. Research in this area focuses on optimizing formulations and processing techniques to ensure the desired flavor profile is maintained throughout the product's shelf life.
The application of ethyl propanoate also extends to the development of novel flavor combinations and the creation of unique taste experiences. Food scientists and flavorists are continuously exploring new ways to incorporate this compound into complex flavor systems, pushing the boundaries of traditional flavor profiles and catering to evolving consumer preferences.
Market Demand Analysis for Flavor Enhancers
The flavor enhancer market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for processed and convenience foods. As consumers seek more flavorful and diverse culinary experiences, the food industry has responded by incorporating a wide range of flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate, to meet these evolving preferences.
Market research indicates that the global flavor enhancer market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of ready-to-eat meals, the expansion of the food and beverage industry, and the growing consumer interest in exotic and unique flavors.
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a key player in the flavor enhancer market due to its versatile applications and desirable organoleptic properties. Its fruity, rum-like aroma and sweet taste profile make it particularly suitable for use in a wide range of food products, including baked goods, confectionery, beverages, and dairy products.
The demand for natural flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources, has been particularly strong. This trend aligns with the broader consumer shift towards clean label products and natural ingredients. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing natural flavor enhancers to cater to this growing market segment.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate. This is largely due to the region's rapidly growing food processing industry, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe also remain significant markets, driven by the demand for innovative and premium food products.
In terms of application sectors, the beverage industry has shown particularly strong demand for ethyl propanoate and similar flavor enhancers. The compound's ability to impart fruity notes makes it ideal for use in fruit-flavored drinks, alcoholic beverages, and dairy-based beverages. The bakery and confectionery sectors have also demonstrated substantial growth in the use of ethyl propanoate, leveraging its ability to enhance and round out flavor profiles in a variety of sweet treats.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate and other flavor enhancers is expected to be influenced by several emerging trends. These include the growing popularity of plant-based and alternative protein products, which often require flavor enhancement to improve palatability, as well as the increasing focus on reduced sugar and salt formulations in processed foods, where flavor enhancers can help maintain taste appeal.
Market research indicates that the global flavor enhancer market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising popularity of ready-to-eat meals, the expansion of the food and beverage industry, and the growing consumer interest in exotic and unique flavors.
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a key player in the flavor enhancer market due to its versatile applications and desirable organoleptic properties. Its fruity, rum-like aroma and sweet taste profile make it particularly suitable for use in a wide range of food products, including baked goods, confectionery, beverages, and dairy products.
The demand for natural flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources, has been particularly strong. This trend aligns with the broader consumer shift towards clean label products and natural ingredients. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing natural flavor enhancers to cater to this growing market segment.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate. This is largely due to the region's rapidly growing food processing industry, changing dietary habits, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe also remain significant markets, driven by the demand for innovative and premium food products.
In terms of application sectors, the beverage industry has shown particularly strong demand for ethyl propanoate and similar flavor enhancers. The compound's ability to impart fruity notes makes it ideal for use in fruit-flavored drinks, alcoholic beverages, and dairy-based beverages. The bakery and confectionery sectors have also demonstrated substantial growth in the use of ethyl propanoate, leveraging its ability to enhance and round out flavor profiles in a variety of sweet treats.
Looking ahead, the market for ethyl propanoate and other flavor enhancers is expected to be influenced by several emerging trends. These include the growing popularity of plant-based and alternative protein products, which often require flavor enhancement to improve palatability, as well as the increasing focus on reduced sugar and salt formulations in processed foods, where flavor enhancers can help maintain taste appeal.
Current Status and Challenges in Flavor Enhancement
The current status of flavor enhancement in the food industry is characterized by a growing demand for natural and clean label ingredients. Ethyl propanoate, a naturally occurring ester, has gained significant attention due to its fruity aroma and potential to enhance flavors in various food products. This compound is widely used in the production of artificial fruit flavors, particularly in beverages, confectionery, and baked goods.
One of the primary challenges in flavor enhancement using ethyl propanoate is achieving the right balance and concentration to create a desirable taste profile without overpowering other flavors. Food scientists and flavor chemists are continuously working on optimizing the use of this compound in different food matrices, considering factors such as pH, temperature, and interactions with other ingredients.
Another significant challenge is the stability of ethyl propanoate during food processing and storage. The compound can be susceptible to hydrolysis, especially in acidic conditions or at high temperatures, which may lead to flavor degradation over time. Researchers are exploring various encapsulation techniques and stabilization methods to improve the shelf life and maintain the flavor integrity of products containing ethyl propanoate.
The regulatory landscape surrounding flavor enhancers presents additional challenges. While ethyl propanoate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, there is an increasing consumer demand for transparency in food labeling. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulations and labeling requirements when using flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate, in their products.
Sustainability and sourcing of flavor compounds have also become important considerations in the industry. There is a growing interest in developing bio-based production methods for ethyl propanoate, moving away from traditional petrochemical-based synthesis. Biotechnological approaches, such as fermentation using engineered microorganisms, are being explored to produce ethyl propanoate more sustainably and cost-effectively.
The application of ethyl propanoate in novel food products and categories is an ongoing area of research and development. Food technologists are investigating its potential use in functional foods, plant-based alternatives, and reduced-sugar formulations. The challenge lies in adapting the flavor-enhancing properties of ethyl propanoate to these new applications while maintaining product quality and consumer acceptance.
Lastly, the food industry faces the challenge of meeting diverse consumer preferences and cultural tastes when using flavor enhancers like ethyl propanoate. Developing globally appealing flavors while catering to regional preferences requires extensive sensory research and consumer testing, adding complexity to the product development process.
One of the primary challenges in flavor enhancement using ethyl propanoate is achieving the right balance and concentration to create a desirable taste profile without overpowering other flavors. Food scientists and flavor chemists are continuously working on optimizing the use of this compound in different food matrices, considering factors such as pH, temperature, and interactions with other ingredients.
Another significant challenge is the stability of ethyl propanoate during food processing and storage. The compound can be susceptible to hydrolysis, especially in acidic conditions or at high temperatures, which may lead to flavor degradation over time. Researchers are exploring various encapsulation techniques and stabilization methods to improve the shelf life and maintain the flavor integrity of products containing ethyl propanoate.
The regulatory landscape surrounding flavor enhancers presents additional challenges. While ethyl propanoate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, there is an increasing consumer demand for transparency in food labeling. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulations and labeling requirements when using flavor enhancers, including ethyl propanoate, in their products.
Sustainability and sourcing of flavor compounds have also become important considerations in the industry. There is a growing interest in developing bio-based production methods for ethyl propanoate, moving away from traditional petrochemical-based synthesis. Biotechnological approaches, such as fermentation using engineered microorganisms, are being explored to produce ethyl propanoate more sustainably and cost-effectively.
The application of ethyl propanoate in novel food products and categories is an ongoing area of research and development. Food technologists are investigating its potential use in functional foods, plant-based alternatives, and reduced-sugar formulations. The challenge lies in adapting the flavor-enhancing properties of ethyl propanoate to these new applications while maintaining product quality and consumer acceptance.
Lastly, the food industry faces the challenge of meeting diverse consumer preferences and cultural tastes when using flavor enhancers like ethyl propanoate. Developing globally appealing flavors while catering to regional preferences requires extensive sensory research and consumer testing, adding complexity to the product development process.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate Applications
01 Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions between propionic acid and ethanol, as well as catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield and purity of the compound for use in flavor enhancement applications.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of this flavor compound.
- Flavor enhancement applications: Ethyl propanoate is used as a flavor enhancer in various food and beverage products. Its fruity, rum-like aroma can be utilized to improve the overall flavor profile of products such as baked goods, dairy items, and confectioneries.
- Formulation techniques for improved flavor delivery: Techniques for incorporating ethyl propanoate into food and beverage formulations are explored. These may include encapsulation methods, emulsion systems, or controlled release mechanisms to optimize flavor delivery and stability.
- Combination with other flavor compounds: Ethyl propanoate is often used in combination with other flavor compounds to create complex flavor profiles. Synergistic effects and optimal ratios of different flavor components are investigated to enhance overall taste and aroma.
- Analytical methods for quality control: Various analytical techniques are employed to assess the quality, purity, and concentration of ethyl propanoate in flavor formulations. These methods may include gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, or spectroscopic techniques to ensure consistent flavor enhancement.
02 Flavor composition formulations
Ethyl propanoate is incorporated into flavor compositions to enhance fruity and sweet notes. These formulations may include other esters, aldehydes, or ketones to create complex flavor profiles for use in food, beverages, and fragrances.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release of ethyl propanoate
Technologies for the controlled release of ethyl propanoate in food and beverage applications are developed. These may include encapsulation techniques or matrix systems to prolong flavor perception and enhance overall sensory experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Natural production of ethyl propanoate
Methods for natural production of ethyl propanoate through fermentation or enzymatic processes are explored. These approaches aim to meet consumer demand for natural flavoring ingredients and may involve the use of specific microorganisms or biocatalysts.Expand Specific Solutions05 Flavor enhancement in specific food applications
The use of ethyl propanoate for flavor enhancement in specific food applications is investigated. This includes optimizing concentrations and combinations with other flavor compounds to improve taste profiles in products such as dairy, baked goods, and confectionery items.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Food Flavoring Industry
The market for ethyl propanoate in the food industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural and synthetic flavoring agents. The global flavor enhancers market, which includes ethyl propanoate, is projected to reach significant market size in the coming years. Technologically, the production and application of ethyl propanoate are relatively mature, with established players like Givaudan SA, International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc., and Firmenich SA leading the way. These companies have extensive R&D capabilities and global distribution networks, allowing them to maintain a competitive edge. Emerging players and regional manufacturers are also entering the market, potentially disrupting the existing competitive landscape.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto Co., Inc. has leveraged its expertise in amino acid technology to develop novel applications of ethyl propanoate in savory food products. The company has created a proprietary process that combines ethyl propanoate with specific amino acids to enhance umami flavors in processed meats and snack foods[8]. This innovative approach not only improves the overall taste profile but also allows for sodium reduction in these products. Ajinomoto has also developed a thermal-stable form of ethyl propanoate that can withstand high-temperature cooking processes, making it suitable for use in retorted and canned foods[10]. The company's research has shown that their ethyl propanoate-based flavor enhancers can improve the perception of freshness and quality in processed foods, particularly in ready-to-eat meals and convenience foods[12].
Strengths: Unique applications in savory foods, sodium reduction capabilities, and thermal stability for processed food applications. Weaknesses: Limited focus on sweet applications and potential challenges in consumer acceptance of flavor-enhanced processed foods.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé has developed a comprehensive approach to incorporating ethyl propanoate in its diverse product portfolio. The company has created a proprietary flavor system that utilizes ethyl propanoate in combination with other natural flavor compounds to enhance the fruity notes in dairy products, particularly yogurts and flavored milk drinks[13]. Nestlé's research has also focused on the application of ethyl propanoate in coffee-based beverages, where it has been shown to enhance the perception of sweetness and reduce the need for added sugars[15]. Additionally, the company has invested in green chemistry initiatives to produce ethyl propanoate through sustainable methods, including the use of agricultural waste as a feedstock for fermentation processes[17].
Strengths: Wide-ranging applications across product categories, focus on sugar reduction, and sustainable production methods. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in maintaining consistent flavor profiles across different product lines and regions.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate Usage
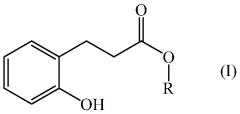
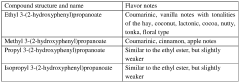
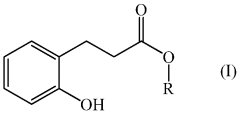
Flavoring compound
PatentWO2013000595A1
Innovation
- The use of ester compounds, such as ethyl 3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate, which provide sweetness, extend vanilla character, and add complexity to flavor compositions, allowing for the enhancement of coumarine and vanilla tonalities.
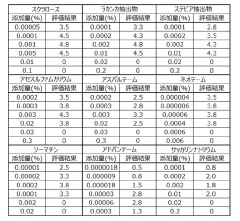
Method for enhancing aroma of flavor component
PatentPendingJP2023172121A
Innovation
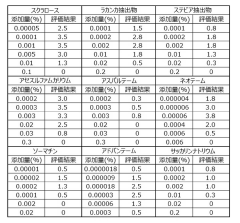
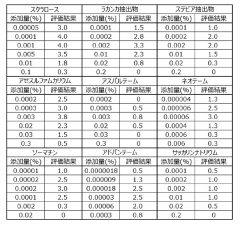
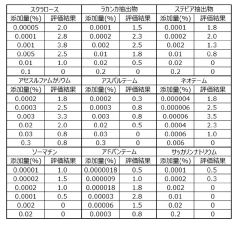
- A method involving a combination of sucralose, Lakanka extract, stevia extract, acesulfame potassium, aspartame, neotame, thaumatin, advantame, and saccharin and its salts is used to enhance the aroma of these components by coexistence in food and beverage formulations.
Regulatory Framework for Food Additives
The regulatory framework for food additives plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of food products enhanced with ethyl propanoate. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of food additives, including ethyl propanoate, under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA). This act establishes the legal basis for the evaluation and approval of food additives, setting stringent standards for their use in food products.
Ethyl propanoate is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance by the FDA, which means it has been deemed safe for its intended use in food based on scientific evidence and expert consensus. This classification allows for its use in food products without the need for premarket approval, provided it meets certain criteria and is used in accordance with good manufacturing practices.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. Ethyl propanoate is listed in the EU Flavouring Substances Register and is authorized for use in food products under Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008. This regulation sets out the conditions for the use of flavorings and food ingredients with flavoring properties in foods.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives, including ethyl propanoate. JECFA has evaluated the safety of ethyl propanoate and established acceptable daily intake (ADI) levels, which are used as a reference by many countries in developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Manufacturers using ethyl propanoate in food products must adhere to labeling requirements set forth by regulatory bodies. In the United States, the FDA requires that ethyl propanoate be listed as an ingredient on food labels when used as a flavoring agent. Similarly, in the EU, Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 mandates the declaration of flavorings on food labels.
The regulatory framework also addresses the purity and quality standards for ethyl propanoate used in food applications. Specifications for food-grade ethyl propanoate are outlined in various pharmacopeias and industry standards, ensuring that only high-quality, contaminant-free substances are used in food production.
As the food industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies regularly review and update their guidelines to address emerging concerns and new scientific evidence. This ongoing process ensures that the use of ethyl propanoate and other flavor enhancers remains safe and compliant with current food safety standards.
Ethyl propanoate is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance by the FDA, which means it has been deemed safe for its intended use in food based on scientific evidence and expert consensus. This classification allows for its use in food products without the need for premarket approval, provided it meets certain criteria and is used in accordance with good manufacturing practices.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food additives. Ethyl propanoate is listed in the EU Flavouring Substances Register and is authorized for use in food products under Regulation (EC) No 1334/2008. This regulation sets out the conditions for the use of flavorings and food ingredients with flavoring properties in foods.
The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) provides international standards for food additives, including ethyl propanoate. JECFA has evaluated the safety of ethyl propanoate and established acceptable daily intake (ADI) levels, which are used as a reference by many countries in developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Manufacturers using ethyl propanoate in food products must adhere to labeling requirements set forth by regulatory bodies. In the United States, the FDA requires that ethyl propanoate be listed as an ingredient on food labels when used as a flavoring agent. Similarly, in the EU, Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 mandates the declaration of flavorings on food labels.
The regulatory framework also addresses the purity and quality standards for ethyl propanoate used in food applications. Specifications for food-grade ethyl propanoate are outlined in various pharmacopeias and industry standards, ensuring that only high-quality, contaminant-free substances are used in food production.
As the food industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies regularly review and update their guidelines to address emerging concerns and new scientific evidence. This ongoing process ensures that the use of ethyl propanoate and other flavor enhancers remains safe and compliant with current food safety standards.
Sensory Evaluation Methodologies
Sensory evaluation methodologies play a crucial role in assessing the impact of ethyl propanoate on flavor enhancement in the food industry. These methods provide objective and subjective data on how this compound affects the sensory properties of various food products.
One of the primary techniques used is descriptive sensory analysis. Trained panelists evaluate the intensity of specific flavor attributes in food samples containing ethyl propanoate. This method allows for a detailed profile of the compound's impact on aroma, taste, and overall flavor perception. Panelists typically use standardized scales to rate attributes such as fruitiness, sweetness, and overall flavor intensity.
Difference testing is another valuable approach in evaluating ethyl propanoate's effects. Triangle tests, for instance, can determine if consumers can detect differences between products with and without the compound. This method helps establish the threshold at which ethyl propanoate's flavor-enhancing properties become noticeable to consumers.
Preference testing and consumer acceptance studies are essential for understanding the market potential of ethyl propanoate-enhanced products. These methods involve larger groups of untrained consumers who rate their liking or preference for products containing different concentrations of the compound. Such studies provide insights into the optimal levels of ethyl propanoate for consumer acceptance.
Instrumental analysis techniques complement sensory evaluations. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and electronic nose systems can quantify the presence and concentration of ethyl propanoate in food products. These methods offer objective data that can be correlated with sensory panel results, providing a comprehensive understanding of the compound's flavor-enhancing effects.
Time-intensity studies are particularly useful for understanding how ethyl propanoate influences flavor perception over time. Panelists rate the intensity of specific attributes at regular intervals during consumption, allowing researchers to map the temporal aspects of flavor enhancement.
Cross-modal sensory evaluations examine how ethyl propanoate affects not only taste and smell but also other sensory modalities such as texture perception. This holistic approach provides a more complete picture of the compound's overall impact on the sensory experience of food products.
Lastly, sensory evaluation methodologies often incorporate statistical analysis techniques to ensure the reliability and validity of results. Methods such as analysis of variance (ANOVA) and principal component analysis (PCA) are commonly used to interpret data from sensory panels and identify significant trends in flavor enhancement due to ethyl propanoate.
One of the primary techniques used is descriptive sensory analysis. Trained panelists evaluate the intensity of specific flavor attributes in food samples containing ethyl propanoate. This method allows for a detailed profile of the compound's impact on aroma, taste, and overall flavor perception. Panelists typically use standardized scales to rate attributes such as fruitiness, sweetness, and overall flavor intensity.
Difference testing is another valuable approach in evaluating ethyl propanoate's effects. Triangle tests, for instance, can determine if consumers can detect differences between products with and without the compound. This method helps establish the threshold at which ethyl propanoate's flavor-enhancing properties become noticeable to consumers.
Preference testing and consumer acceptance studies are essential for understanding the market potential of ethyl propanoate-enhanced products. These methods involve larger groups of untrained consumers who rate their liking or preference for products containing different concentrations of the compound. Such studies provide insights into the optimal levels of ethyl propanoate for consumer acceptance.
Instrumental analysis techniques complement sensory evaluations. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and electronic nose systems can quantify the presence and concentration of ethyl propanoate in food products. These methods offer objective data that can be correlated with sensory panel results, providing a comprehensive understanding of the compound's flavor-enhancing effects.
Time-intensity studies are particularly useful for understanding how ethyl propanoate influences flavor perception over time. Panelists rate the intensity of specific attributes at regular intervals during consumption, allowing researchers to map the temporal aspects of flavor enhancement.
Cross-modal sensory evaluations examine how ethyl propanoate affects not only taste and smell but also other sensory modalities such as texture perception. This holistic approach provides a more complete picture of the compound's overall impact on the sensory experience of food products.
Lastly, sensory evaluation methodologies often incorporate statistical analysis techniques to ensure the reliability and validity of results. Methods such as analysis of variance (ANOVA) and principal component analysis (PCA) are commonly used to interpret data from sensory panels and identify significant trends in flavor enhancement due to ethyl propanoate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!