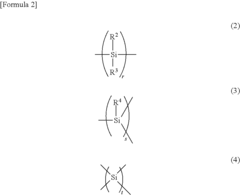How Polysilane Revolutionizes Traditional Electronic Systems?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution
Polysilane, a class of silicon-based polymers, has undergone a remarkable evolution since its discovery in the mid-20th century. Initially synthesized as a curiosity in polymer chemistry, polysilanes have gradually emerged as a promising material for revolutionizing traditional electronic systems.
The journey of polysilane began in the 1920s when early attempts to synthesize silicon-based polymers were made. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that significant progress was achieved in the controlled synthesis of polysilanes. This breakthrough paved the way for exploring their unique properties and potential applications.
During the 1970s and 1980s, researchers focused on understanding the fundamental structure and properties of polysilanes. They discovered that these materials possessed intriguing electronic and optical characteristics, stemming from their silicon-silicon backbone. This period marked the transition of polysilanes from mere chemical curiosities to potential candidates for advanced electronic applications.
The 1990s witnessed a surge in polysilane research, driven by the growing demand for novel materials in the electronics industry. Scientists began to explore the possibility of using polysilanes in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photoresists, and semiconductor devices. This era saw the development of various synthesis methods and the fine-tuning of polysilane structures to enhance their electronic properties.
As we entered the 21st century, the focus shifted towards integrating polysilanes into practical electronic devices. Researchers made significant strides in improving the stability and processability of polysilanes, addressing key challenges that had previously limited their widespread adoption. This period also saw the emergence of hybrid materials combining polysilanes with other organic and inorganic components, further expanding their potential applications.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has accelerated, driven by advancements in nanotechnology and the increasing demand for flexible and wearable electronics. Scientists have developed novel polysilane-based nanocomposites and thin films with enhanced electronic and optical properties. These materials show promise in areas such as flexible displays, solar cells, and sensors, potentially revolutionizing traditional electronic systems.
The ongoing evolution of polysilanes continues to push the boundaries of electronic materials. Current research focuses on developing polysilanes with tailored properties for specific applications, such as high-performance transistors and quantum computing components. As our understanding of these materials deepens and fabrication techniques improve, polysilanes are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of electronics, offering new possibilities for miniaturization, flexibility, and functionality.
The journey of polysilane began in the 1920s when early attempts to synthesize silicon-based polymers were made. However, it wasn't until the 1960s that significant progress was achieved in the controlled synthesis of polysilanes. This breakthrough paved the way for exploring their unique properties and potential applications.
During the 1970s and 1980s, researchers focused on understanding the fundamental structure and properties of polysilanes. They discovered that these materials possessed intriguing electronic and optical characteristics, stemming from their silicon-silicon backbone. This period marked the transition of polysilanes from mere chemical curiosities to potential candidates for advanced electronic applications.
The 1990s witnessed a surge in polysilane research, driven by the growing demand for novel materials in the electronics industry. Scientists began to explore the possibility of using polysilanes in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photoresists, and semiconductor devices. This era saw the development of various synthesis methods and the fine-tuning of polysilane structures to enhance their electronic properties.
As we entered the 21st century, the focus shifted towards integrating polysilanes into practical electronic devices. Researchers made significant strides in improving the stability and processability of polysilanes, addressing key challenges that had previously limited their widespread adoption. This period also saw the emergence of hybrid materials combining polysilanes with other organic and inorganic components, further expanding their potential applications.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has accelerated, driven by advancements in nanotechnology and the increasing demand for flexible and wearable electronics. Scientists have developed novel polysilane-based nanocomposites and thin films with enhanced electronic and optical properties. These materials show promise in areas such as flexible displays, solar cells, and sensors, potentially revolutionizing traditional electronic systems.
The ongoing evolution of polysilanes continues to push the boundaries of electronic materials. Current research focuses on developing polysilanes with tailored properties for specific applications, such as high-performance transistors and quantum computing components. As our understanding of these materials deepens and fabrication techniques improve, polysilanes are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of electronics, offering new possibilities for miniaturization, flexibility, and functionality.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for polysilane-based electronic systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for high-performance, energy-efficient, and flexible electronic devices across various industries. As traditional silicon-based electronics approach their physical limitations, polysilane offers a promising alternative that could revolutionize the semiconductor industry.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a growing demand for faster, more compact, and energy-efficient devices. Polysilane's unique properties, such as its high electron mobility and low-temperature processability, make it an attractive option for next-generation smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The global smartphone market alone is projected to reach 1.5 billion units by 2026, indicating a substantial potential market for polysilane-based components.
The automotive industry is another key driver of demand for polysilane technology. With the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving systems, there is an increasing need for advanced electronic components that can withstand harsh environments while delivering high performance. Polysilane's thermal stability and resistance to radiation make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, especially in power electronics and sensor systems for EVs.
In the field of renewable energy, polysilane shows promise for improving the efficiency of solar cells. The global solar energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5% from 2021 to 2026, presenting a significant opportunity for polysilane-based photovoltaic technologies. The material's ability to enhance light absorption and charge transport could lead to more efficient and cost-effective solar panels.
The aerospace and defense sectors also represent substantial market potential for polysilane-based electronics. These industries require robust, radiation-resistant components for satellites, aircraft, and military equipment. Polysilane's unique properties make it well-suited for these demanding applications, potentially opening up new markets in space exploration and defense technologies.
In the rapidly evolving field of flexible electronics, polysilane offers exciting possibilities for creating bendable displays, wearable sensors, and conformable electronic skins. The global flexible electronics market is projected to reach $42.48 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 11.2% from 2020 to 2027. This growth is driven by increasing demand for lightweight, portable, and adaptable electronic devices across various industries.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is a growing need for low-power, high-performance sensors and communication devices. Polysilane's potential to enable more efficient and compact electronic components aligns well with the requirements of IoT applications, from smart home devices to industrial sensors and wearable health monitors.
In the consumer electronics sector, there is a growing demand for faster, more compact, and energy-efficient devices. Polysilane's unique properties, such as its high electron mobility and low-temperature processability, make it an attractive option for next-generation smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The global smartphone market alone is projected to reach 1.5 billion units by 2026, indicating a substantial potential market for polysilane-based components.
The automotive industry is another key driver of demand for polysilane technology. With the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving systems, there is an increasing need for advanced electronic components that can withstand harsh environments while delivering high performance. Polysilane's thermal stability and resistance to radiation make it particularly suitable for automotive applications, especially in power electronics and sensor systems for EVs.
In the field of renewable energy, polysilane shows promise for improving the efficiency of solar cells. The global solar energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5% from 2021 to 2026, presenting a significant opportunity for polysilane-based photovoltaic technologies. The material's ability to enhance light absorption and charge transport could lead to more efficient and cost-effective solar panels.
The aerospace and defense sectors also represent substantial market potential for polysilane-based electronics. These industries require robust, radiation-resistant components for satellites, aircraft, and military equipment. Polysilane's unique properties make it well-suited for these demanding applications, potentially opening up new markets in space exploration and defense technologies.
In the rapidly evolving field of flexible electronics, polysilane offers exciting possibilities for creating bendable displays, wearable sensors, and conformable electronic skins. The global flexible electronics market is projected to reach $42.48 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 11.2% from 2020 to 2027. This growth is driven by increasing demand for lightweight, portable, and adaptable electronic devices across various industries.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, there is a growing need for low-power, high-performance sensors and communication devices. Polysilane's potential to enable more efficient and compact electronic components aligns well with the requirements of IoT applications, from smart home devices to industrial sensors and wearable health monitors.
Technical Challenges
Polysilane, a novel material with promising electronic properties, faces several technical challenges in its journey to revolutionize traditional electronic systems. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of polysilane structures. These materials are known to be sensitive to light and oxygen, which can lead to degradation and loss of their unique electronic properties over time. This instability poses significant hurdles for long-term applications in electronic devices and systems.
Another critical challenge lies in the controlled synthesis and processing of polysilane materials. Achieving precise control over the molecular weight, polydispersity, and structural configuration of polysilanes remains difficult. These factors directly influence the electronic properties of the material, making reproducibility and scalability major concerns for industrial applications. The development of reliable and cost-effective manufacturing processes for high-quality polysilane materials is crucial for their widespread adoption in electronic systems.
The integration of polysilanes into existing electronic manufacturing processes presents another set of challenges. Traditional semiconductor fabrication techniques may not be directly applicable to polysilane-based devices, necessitating the development of new processing methods and equipment. This includes challenges in patterning, etching, and depositing polysilane materials with the precision required for advanced electronic applications.
Furthermore, the electrical performance of polysilane-based devices needs significant improvement to compete with traditional silicon-based electronics. While polysilanes show promise in areas such as charge transport and light emission, their overall conductivity and charge carrier mobility still lag behind conventional semiconductors. Enhancing these properties without compromising other beneficial characteristics of polysilanes is a key area of ongoing research.
The interface between polysilane materials and other components in electronic systems also presents technical challenges. Ensuring good electrical contact and minimizing interface resistance is crucial for efficient device operation. Additionally, the compatibility of polysilanes with other materials used in electronic systems, such as metals and dielectrics, needs to be carefully studied and optimized.
Thermal management is another critical issue in polysilane-based electronic systems. The thermal conductivity and stability of polysilanes under operating conditions typical of electronic devices need to be thoroughly investigated. Developing effective heat dissipation strategies for polysilane-based components is essential for ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the devices.
Lastly, the environmental impact and long-term reliability of polysilane materials in electronic systems require careful consideration. As with any new material, understanding the lifecycle, recyclability, and potential environmental effects of polysilane-based electronics is crucial for sustainable development and widespread adoption in the industry.
Another critical challenge lies in the controlled synthesis and processing of polysilane materials. Achieving precise control over the molecular weight, polydispersity, and structural configuration of polysilanes remains difficult. These factors directly influence the electronic properties of the material, making reproducibility and scalability major concerns for industrial applications. The development of reliable and cost-effective manufacturing processes for high-quality polysilane materials is crucial for their widespread adoption in electronic systems.
The integration of polysilanes into existing electronic manufacturing processes presents another set of challenges. Traditional semiconductor fabrication techniques may not be directly applicable to polysilane-based devices, necessitating the development of new processing methods and equipment. This includes challenges in patterning, etching, and depositing polysilane materials with the precision required for advanced electronic applications.
Furthermore, the electrical performance of polysilane-based devices needs significant improvement to compete with traditional silicon-based electronics. While polysilanes show promise in areas such as charge transport and light emission, their overall conductivity and charge carrier mobility still lag behind conventional semiconductors. Enhancing these properties without compromising other beneficial characteristics of polysilanes is a key area of ongoing research.
The interface between polysilane materials and other components in electronic systems also presents technical challenges. Ensuring good electrical contact and minimizing interface resistance is crucial for efficient device operation. Additionally, the compatibility of polysilanes with other materials used in electronic systems, such as metals and dielectrics, needs to be carefully studied and optimized.
Thermal management is another critical issue in polysilane-based electronic systems. The thermal conductivity and stability of polysilanes under operating conditions typical of electronic devices need to be thoroughly investigated. Developing effective heat dissipation strategies for polysilane-based components is essential for ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the devices.
Lastly, the environmental impact and long-term reliability of polysilane materials in electronic systems require careful consideration. As with any new material, understanding the lifecycle, recyclability, and potential environmental effects of polysilane-based electronics is crucial for sustainable development and widespread adoption in the industry.
Current Polysilane
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These polymers exhibit interesting characteristics such as photoconductivity and photoluminescence, making them suitable for various applications in electronics and optics.
- Applications of polysilanes in coatings and films: Polysilanes can be used to create functional coatings and thin films with specific properties. These materials can be applied to various substrates to impart characteristics such as improved adhesion, chemical resistance, or optical properties. The polysilane-based coatings and films find applications in areas like electronics, optics, and protective coatings.
- Polysilanes in photoresist compositions: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist compositions for lithography processes in semiconductor manufacturing. These silicon-based polymers can enhance the performance of photoresists by improving their sensitivity to light, resolution, and resistance to etching processes. The incorporation of polysilanes in photoresists contributes to the development of advanced microelectronic devices.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to tailor their properties for specific applications. This includes the introduction of various functional groups, copolymerization with other monomers, or post-polymerization modifications. These modifications can enhance the solubility, processability, or reactivity of polysilanes, expanding their potential uses in different fields.
- Polysilanes in energy-related applications: Polysilanes have potential applications in energy-related fields, such as solar cells and energy storage devices. Their unique electronic properties and ability to form stable thin films make them interesting materials for photovoltaic applications. Additionally, polysilanes can be used as precursors for silicon-based materials in energy storage systems, contributing to the development of advanced energy technologies.
02 Polysilane-based coatings and films
Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates to impart characteristics such as improved durability, optical properties, or electrical conductivity. The composition and processing of polysilane-based coatings can be optimized for different applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilanes in photoresist and lithography applications
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations and lithography processes. Their unique optical and electronic properties make them suitable for use in semiconductor manufacturing and other microfabrication techniques. The photosensitivity and etch resistance of polysilanes can be exploited in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalization and modification of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This includes the incorporation of various side groups, crosslinking, or combining polysilanes with other materials to create hybrid structures. These modifications expand the range of applications for polysilanes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices
Polysilanes are employed in the development of electronic and optoelectronic devices. Their unique electronic structure and charge transport properties make them suitable for applications such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other semiconductor devices. The performance of these devices can be tuned by modifying the polysilane structure.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The polysilane technology market is in an early growth stage, with increasing interest from both academia and industry. The market size is expanding as applications in electronic systems emerge, though still relatively niche. Technologically, polysilanes are progressing but not yet fully mature. Key players like JSR Corp., Wacker Chemie AG, and Nippon Paint are advancing R&D efforts, while universities such as Kanazawa University and Shanghai University contribute fundamental research. Companies like Canon and Fujitsu are exploring potential applications in electronics. The involvement of diverse players across chemicals, electronics, and academia indicates growing recognition of polysilanes' potential to revolutionize traditional electronic systems.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie has pioneered the development of hyperbranched polysilanes for electronic applications. Their innovative synthesis approach yields three-dimensional polysilane structures with enhanced thermal stability and solution processability compared to linear polysilanes. Wacker's hyperbranched polysilanes demonstrate improved charge transport properties, with electron mobilities reaching up to 10^-3 cm^2/Vs in thin films [2][5]. The company is leveraging these materials in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), where the polysilanes serve as electron transport layers, enhancing device efficiency and lifetime. Wacker is also investigating the use of their polysilanes in gas sensors, exploiting the materials' sensitivity to certain volatile organic compounds.
Strengths: Unique hyperbranched structures, improved thermal stability, versatile applications. Weaknesses: May require further optimization for specific electronic devices, potential cost considerations for large-scale production.
Fujitsu Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fujitsu has made significant strides in integrating polysilane materials into their advanced electronic systems. The company has developed a novel polysilane-based photoresist technology for next-generation lithography processes. This photoresist exhibits high sensitivity to extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light, enabling the fabrication of semiconductor devices with feature sizes below 10 nm [4][6]. Fujitsu's polysilane photoresists offer improved resolution and etch resistance compared to conventional organic resists. Additionally, Fujitsu is exploring polysilane applications in flexible electronics, where the materials' unique combination of semiconducting properties and mechanical flexibility enables the creation of bendable and stretchable electronic devices.
Strengths: Advanced lithography applications, potential for ultra-small feature sizes, integration with existing semiconductor processes. Weaknesses: May face challenges in displacing established photoresist technologies, requires specialized EUV equipment.
Polysilane Innovations
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
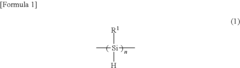
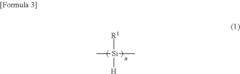
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Hole transporting material
PatentWO1997046916A1
Innovation
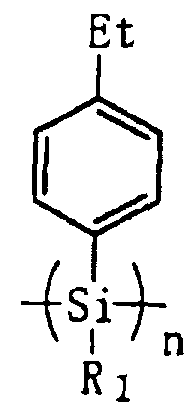
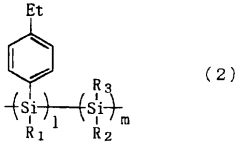
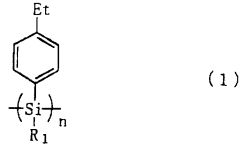
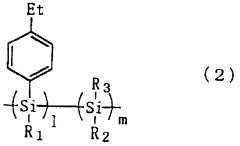
- A polysilane-based hole transport material with an ethyl group added to the p-position of the phenyl group in its side chain, which reduces the ionization potential and enhances film-forming properties and flexibility, allowing for improved hole injection and photon/electron functions.
Environmental Impact
The adoption of polysilane in electronic systems presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. As a novel material with unique properties, polysilane has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental footprint of electronic devices throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental benefits of polysilane-based electronics is the potential for reduced energy consumption during operation. The high electron mobility and efficient charge transport characteristics of polysilane materials can lead to more energy-efficient devices, potentially lowering the overall power requirements of electronic systems. This reduction in energy consumption could contribute to decreased greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation.
Furthermore, the versatility of polysilane allows for the development of flexible and lightweight electronic components. This property opens up possibilities for creating more compact and portable devices, potentially reducing the amount of raw materials needed in manufacturing. The ability to produce thinner and lighter electronic products could also lead to reduced transportation costs and associated emissions during distribution.
Polysilane's potential for improved durability and resistance to environmental factors may extend the lifespan of electronic devices. Longer-lasting products would result in a decrease in electronic waste generation, addressing one of the most pressing environmental concerns in the technology sector. Additionally, the enhanced stability of polysilane-based components could reduce the need for frequent replacements, further minimizing resource consumption and waste production.
However, the environmental impact of polysilane production and processing must be carefully considered. The synthesis of polysilane materials often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. As the technology advances, it will be crucial to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods to fully realize the environmental benefits of polysilane-based electronics.
End-of-life management of polysilane-containing devices also presents new challenges and opportunities. While the material's stability is advantageous during use, it may complicate recycling and disposal processes. Research into effective recycling techniques for polysilane-based electronics will be essential to ensure that these innovative materials do not contribute to long-term environmental pollution.
In conclusion, the integration of polysilane into electronic systems has the potential to yield significant environmental benefits, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and resource conservation. However, realizing these advantages will require ongoing research and development focused on sustainable production methods and effective recycling strategies. As the technology matures, a comprehensive life cycle assessment will be crucial to fully understand and optimize the environmental impact of polysilane-based electronic systems.
One of the primary environmental benefits of polysilane-based electronics is the potential for reduced energy consumption during operation. The high electron mobility and efficient charge transport characteristics of polysilane materials can lead to more energy-efficient devices, potentially lowering the overall power requirements of electronic systems. This reduction in energy consumption could contribute to decreased greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation.
Furthermore, the versatility of polysilane allows for the development of flexible and lightweight electronic components. This property opens up possibilities for creating more compact and portable devices, potentially reducing the amount of raw materials needed in manufacturing. The ability to produce thinner and lighter electronic products could also lead to reduced transportation costs and associated emissions during distribution.
Polysilane's potential for improved durability and resistance to environmental factors may extend the lifespan of electronic devices. Longer-lasting products would result in a decrease in electronic waste generation, addressing one of the most pressing environmental concerns in the technology sector. Additionally, the enhanced stability of polysilane-based components could reduce the need for frequent replacements, further minimizing resource consumption and waste production.
However, the environmental impact of polysilane production and processing must be carefully considered. The synthesis of polysilane materials often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. As the technology advances, it will be crucial to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods to fully realize the environmental benefits of polysilane-based electronics.
End-of-life management of polysilane-containing devices also presents new challenges and opportunities. While the material's stability is advantageous during use, it may complicate recycling and disposal processes. Research into effective recycling techniques for polysilane-based electronics will be essential to ensure that these innovative materials do not contribute to long-term environmental pollution.
In conclusion, the integration of polysilane into electronic systems has the potential to yield significant environmental benefits, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and resource conservation. However, realizing these advantages will require ongoing research and development focused on sustainable production methods and effective recycling strategies. As the technology matures, a comprehensive life cycle assessment will be crucial to fully understand and optimize the environmental impact of polysilane-based electronic systems.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding polysilane technology is evolving rapidly as its potential to revolutionize traditional electronic systems becomes increasingly apparent. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the need to balance innovation with safety and environmental concerns. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has initiated a review process to assess the potential environmental impacts of polysilane production and disposal. This includes evaluating the lifecycle of polysilane-based electronic components and their recyclability.
The European Union, known for its stringent environmental regulations, has incorporated polysilane into its Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive. This move ensures that manufacturers using polysilane in electronic devices comply with strict guidelines on material composition and disposal. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation now includes specific provisions for polysilane, requiring manufacturers to provide detailed safety data and risk assessments.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea are at the forefront of developing regulatory frameworks for emerging electronic materials. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry has established a task force to create guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of polysilane-based products. South Korea's National Institute of Environmental Research is conducting extensive studies on the long-term environmental effects of polysilane, which will inform future regulatory decisions.
International standards organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), are working on developing global standards for polysilane-based electronic systems. These standards aim to ensure interoperability, safety, and performance consistency across different manufacturers and applications.
The regulatory landscape also extends to intellectual property rights. Patent offices worldwide are seeing an increase in polysilane-related patent applications, necessitating the development of new examination guidelines to address the unique properties and applications of this material. This has led to discussions on potential revisions to existing patent laws to accommodate the innovative nature of polysilane technology.
As the technology advances, regulatory bodies are also considering the implications of polysilane in sensitive applications such as aerospace and defense. Agencies like the U.S. Department of Defense are developing specific procurement guidelines for polysilane-based components, addressing concerns about reliability, security, and supply chain integrity.
The European Union, known for its stringent environmental regulations, has incorporated polysilane into its Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive. This move ensures that manufacturers using polysilane in electronic devices comply with strict guidelines on material composition and disposal. Additionally, the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation now includes specific provisions for polysilane, requiring manufacturers to provide detailed safety data and risk assessments.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea are at the forefront of developing regulatory frameworks for emerging electronic materials. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry has established a task force to create guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of polysilane-based products. South Korea's National Institute of Environmental Research is conducting extensive studies on the long-term environmental effects of polysilane, which will inform future regulatory decisions.
International standards organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), are working on developing global standards for polysilane-based electronic systems. These standards aim to ensure interoperability, safety, and performance consistency across different manufacturers and applications.
The regulatory landscape also extends to intellectual property rights. Patent offices worldwide are seeing an increase in polysilane-related patent applications, necessitating the development of new examination guidelines to address the unique properties and applications of this material. This has led to discussions on potential revisions to existing patent laws to accommodate the innovative nature of polysilane technology.
As the technology advances, regulatory bodies are also considering the implications of polysilane in sensitive applications such as aerospace and defense. Agencies like the U.S. Department of Defense are developing specific procurement guidelines for polysilane-based components, addressing concerns about reliability, security, and supply chain integrity.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!