How Power Steering Fluids Mitigate Component Friction and Heat
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Power Steering Fluid Evolution and Objectives
Power steering fluid has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the automotive industry. Initially developed to reduce the effort required to steer vehicles, these fluids have become increasingly sophisticated in their ability to mitigate component friction and heat. The primary objective of power steering fluid is to transmit hydraulic pressure within the steering system, enabling smooth and effortless steering control.
Over time, the focus of power steering fluid development has shifted towards enhancing its ability to reduce friction and manage heat generation within the steering system. This evolution has been driven by the need for improved vehicle performance, increased durability of steering components, and enhanced overall efficiency. Modern power steering fluids are engineered to provide superior lubrication, thermal stability, and anti-wear properties.
The technological advancements in power steering fluids have been closely tied to the development of more complex steering systems and the increasing demands of modern vehicles. As vehicles have become heavier and more powerful, the requirements for power steering fluids have grown more stringent. Manufacturers have responded by developing fluids with advanced additive packages that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures while maintaining their protective properties.
One of the key objectives in the evolution of power steering fluids has been to minimize energy loss due to friction. By reducing friction between moving parts in the steering system, these fluids contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced wear on components. This has led to the development of low-viscosity fluids that can maintain their performance characteristics across a wide range of operating temperatures.
Another critical objective has been to enhance the fluid's ability to dissipate heat. As steering systems generate heat during operation, especially under high-load conditions, the fluid plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Advanced power steering fluids are designed to efficiently transfer heat away from critical components, preventing premature degradation and ensuring consistent performance.
The ongoing evolution of power steering fluids also aims to address environmental concerns. Manufacturers are developing more environmentally friendly formulations that are biodegradable and less toxic, without compromising on performance. This trend aligns with broader automotive industry goals of reducing environmental impact and meeting increasingly stringent regulations.
Looking ahead, the objectives for power steering fluid development continue to focus on further improving friction reduction, heat management, and overall system efficiency. As vehicle technologies advance, including the integration of electric power steering systems, the role of specialized fluids in mitigating friction and heat remains crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of steering components.
Over time, the focus of power steering fluid development has shifted towards enhancing its ability to reduce friction and manage heat generation within the steering system. This evolution has been driven by the need for improved vehicle performance, increased durability of steering components, and enhanced overall efficiency. Modern power steering fluids are engineered to provide superior lubrication, thermal stability, and anti-wear properties.
The technological advancements in power steering fluids have been closely tied to the development of more complex steering systems and the increasing demands of modern vehicles. As vehicles have become heavier and more powerful, the requirements for power steering fluids have grown more stringent. Manufacturers have responded by developing fluids with advanced additive packages that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures while maintaining their protective properties.
One of the key objectives in the evolution of power steering fluids has been to minimize energy loss due to friction. By reducing friction between moving parts in the steering system, these fluids contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced wear on components. This has led to the development of low-viscosity fluids that can maintain their performance characteristics across a wide range of operating temperatures.
Another critical objective has been to enhance the fluid's ability to dissipate heat. As steering systems generate heat during operation, especially under high-load conditions, the fluid plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Advanced power steering fluids are designed to efficiently transfer heat away from critical components, preventing premature degradation and ensuring consistent performance.
The ongoing evolution of power steering fluids also aims to address environmental concerns. Manufacturers are developing more environmentally friendly formulations that are biodegradable and less toxic, without compromising on performance. This trend aligns with broader automotive industry goals of reducing environmental impact and meeting increasingly stringent regulations.
Looking ahead, the objectives for power steering fluid development continue to focus on further improving friction reduction, heat management, and overall system efficiency. As vehicle technologies advance, including the integration of electric power steering systems, the role of specialized fluids in mitigating friction and heat remains crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of steering components.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Power Steering Fluids
The market demand for advanced power steering fluids is experiencing significant growth, driven by several key factors in the automotive industry. As vehicles become more sophisticated and performance-oriented, there is an increasing need for high-quality power steering fluids that can effectively mitigate component friction and heat.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the growing automotive industry, particularly in emerging economies. As car ownership rates rise in countries like China and India, the demand for power steering systems and associated fluids is also increasing. This trend is further amplified by the rising consumer preference for comfortable driving experiences, which power steering systems provide.
The shift towards electric power steering (EPS) systems in modern vehicles is also influencing the market for advanced power steering fluids. While EPS systems generally require less fluid than traditional hydraulic systems, they still need specialized fluids to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This transition is creating new opportunities for advanced fluid formulations that cater to the specific needs of EPS systems.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns are another significant factor shaping market demand. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have minimal environmental impact. This trend is particularly strong in regions with strict environmental regulations, such as Europe and North America.
The aftermarket segment represents a substantial portion of the power steering fluid market. As vehicles age, the need for fluid replacement and maintenance increases, driving demand for high-quality, long-lasting fluids. This segment is particularly important in regions with a large existing vehicle fleet.
Technological advancements in power steering systems are also fueling the demand for more sophisticated fluids. Modern power steering systems operate at higher temperatures and pressures, requiring fluids that can withstand these conditions while providing superior protection against wear and corrosion.
The commercial vehicle sector, including trucks and buses, is another significant contributor to market demand. These vehicles often operate under more demanding conditions and require robust power steering fluids that can maintain performance over long periods and under heavy loads.
In terms of market size, the global power steering fluid market is projected to show steady growth over the coming years. While specific figures vary depending on the source and methodology, industry reports consistently indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the range of 3-5% for the forecast period up to 2025.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the growing automotive industry, particularly in emerging economies. As car ownership rates rise in countries like China and India, the demand for power steering systems and associated fluids is also increasing. This trend is further amplified by the rising consumer preference for comfortable driving experiences, which power steering systems provide.
The shift towards electric power steering (EPS) systems in modern vehicles is also influencing the market for advanced power steering fluids. While EPS systems generally require less fluid than traditional hydraulic systems, they still need specialized fluids to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This transition is creating new opportunities for advanced fluid formulations that cater to the specific needs of EPS systems.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns are another significant factor shaping market demand. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have minimal environmental impact. This trend is particularly strong in regions with strict environmental regulations, such as Europe and North America.
The aftermarket segment represents a substantial portion of the power steering fluid market. As vehicles age, the need for fluid replacement and maintenance increases, driving demand for high-quality, long-lasting fluids. This segment is particularly important in regions with a large existing vehicle fleet.
Technological advancements in power steering systems are also fueling the demand for more sophisticated fluids. Modern power steering systems operate at higher temperatures and pressures, requiring fluids that can withstand these conditions while providing superior protection against wear and corrosion.
The commercial vehicle sector, including trucks and buses, is another significant contributor to market demand. These vehicles often operate under more demanding conditions and require robust power steering fluids that can maintain performance over long periods and under heavy loads.
In terms of market size, the global power steering fluid market is projected to show steady growth over the coming years. While specific figures vary depending on the source and methodology, industry reports consistently indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the range of 3-5% for the forecast period up to 2025.
Current Challenges in Power Steering Fluid Technology
Power steering fluid technology, while advanced, still faces several significant challenges in mitigating component friction and heat. One of the primary issues is the degradation of fluid performance over time. As vehicles age and accumulate mileage, the fluid's ability to reduce friction and dissipate heat gradually diminishes, leading to increased wear on steering components and potential system failures.
Another challenge lies in the fluid's sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. Extreme cold can cause the fluid to thicken, reducing its flow and effectiveness, while high temperatures can lead to fluid breakdown and loss of lubricating properties. This temperature sensitivity affects the fluid's ability to maintain consistent performance across diverse operating conditions, particularly in regions with wide temperature variations.
The increasing demand for more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles presents another hurdle. Traditional power steering fluids often contain petroleum-based compounds that may not align with stricter environmental regulations. Developing bio-based or synthetic alternatives that offer comparable or superior performance while meeting environmental standards remains a significant challenge for fluid manufacturers.
Compatibility issues also pose a concern, especially with the introduction of new materials in modern steering systems. Some fluids may interact negatively with certain seals, hoses, or metal components, leading to premature wear or failure. Ensuring broad compatibility across various vehicle makes and models while maintaining optimal performance is an ongoing challenge for fluid developers.
The advent of electric power steering systems has introduced new complexities. While these systems generally require less fluid, they often operate at higher temperatures and place different demands on the fluid's properties. Developing fluids that can meet the specific needs of both traditional hydraulic and newer electric systems adds another layer of complexity to fluid formulation.
Lastly, the challenge of extended fluid life persists. Vehicle manufacturers and consumers alike seek fluids that can maintain their performance characteristics for longer periods, reducing the frequency of fluid changes. However, achieving this extended life while ensuring consistent friction reduction and heat dissipation throughout the fluid's lifespan remains a significant technical hurdle.
These challenges collectively drive ongoing research and development in power steering fluid technology, as manufacturers strive to create more robust, versatile, and long-lasting solutions to meet the evolving demands of modern vehicles and environmental standards.
Another challenge lies in the fluid's sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. Extreme cold can cause the fluid to thicken, reducing its flow and effectiveness, while high temperatures can lead to fluid breakdown and loss of lubricating properties. This temperature sensitivity affects the fluid's ability to maintain consistent performance across diverse operating conditions, particularly in regions with wide temperature variations.
The increasing demand for more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles presents another hurdle. Traditional power steering fluids often contain petroleum-based compounds that may not align with stricter environmental regulations. Developing bio-based or synthetic alternatives that offer comparable or superior performance while meeting environmental standards remains a significant challenge for fluid manufacturers.
Compatibility issues also pose a concern, especially with the introduction of new materials in modern steering systems. Some fluids may interact negatively with certain seals, hoses, or metal components, leading to premature wear or failure. Ensuring broad compatibility across various vehicle makes and models while maintaining optimal performance is an ongoing challenge for fluid developers.
The advent of electric power steering systems has introduced new complexities. While these systems generally require less fluid, they often operate at higher temperatures and place different demands on the fluid's properties. Developing fluids that can meet the specific needs of both traditional hydraulic and newer electric systems adds another layer of complexity to fluid formulation.
Lastly, the challenge of extended fluid life persists. Vehicle manufacturers and consumers alike seek fluids that can maintain their performance characteristics for longer periods, reducing the frequency of fluid changes. However, achieving this extended life while ensuring consistent friction reduction and heat dissipation throughout the fluid's lifespan remains a significant technical hurdle.
These challenges collectively drive ongoing research and development in power steering fluid technology, as manufacturers strive to create more robust, versatile, and long-lasting solutions to meet the evolving demands of modern vehicles and environmental standards.
Existing Friction and Heat Mitigation Solutions
01 Friction reduction in power steering fluids
Power steering fluids are formulated with additives to reduce friction between moving parts in the steering system. These additives create a protective film on metal surfaces, minimizing wear and improving overall system efficiency. Friction reduction helps to maintain smooth steering operation and extends the lifespan of components.- Friction reduction in power steering fluids: Power steering fluids are formulated with additives to reduce friction between moving parts in the steering system. These additives help to minimize wear and tear, improve efficiency, and reduce heat generation. Friction modifiers and anti-wear agents are commonly used to achieve these benefits, resulting in smoother steering operation and extended component life.
- Heat dissipation in power steering systems: Effective heat dissipation is crucial in power steering systems to maintain optimal fluid performance and prevent degradation. Cooling mechanisms, such as heat exchangers or improved fluid circulation, are implemented to manage temperature increases caused by friction and fluid compression. Proper heat management helps maintain fluid viscosity and prevents premature breakdown of the power steering fluid.
- Fluid composition for improved performance: Power steering fluid compositions are designed to optimize performance under various operating conditions. These formulations may include a combination of base oils, viscosity modifiers, and performance-enhancing additives. The goal is to maintain proper viscosity across a wide temperature range, provide excellent lubrication, and protect against corrosion and oxidation, ultimately contributing to reduced friction and heat generation.
- Hydraulic system design for efficiency: The design of power steering hydraulic systems plays a crucial role in minimizing friction and heat generation. Optimized pump designs, flow control valves, and hydraulic circuit layouts can reduce fluid turbulence and pressure drops. These improvements lead to more efficient power transfer, lower operating temperatures, and reduced strain on the power steering fluid.
- Maintenance and fluid monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring of power steering fluid conditions are essential for managing friction and heat issues. This includes periodic fluid replacement, system flushing, and the use of diagnostic tools to assess fluid quality. Proper maintenance practices help prevent the accumulation of contaminants that can increase friction and heat generation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the power steering system.
02 Heat management in power steering systems
Effective heat management is crucial in power steering systems to prevent fluid degradation and component damage. Cooling mechanisms, such as heat exchangers or improved fluid circulation, are implemented to dissipate excess heat generated during operation. This helps maintain optimal fluid viscosity and ensures consistent steering performance under various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fluid composition for improved performance
Power steering fluid compositions are designed to optimize performance under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. These formulations may include synthetic base oils, viscosity modifiers, and anti-wear additives to enhance lubrication properties, reduce friction, and withstand thermal stress. The improved fluid composition contributes to smoother steering operation and increased system longevity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fluid flow control and pressure regulation
Power steering systems incorporate mechanisms to control fluid flow and regulate pressure, ensuring optimal steering assistance while minimizing heat generation. These may include variable-assist pumps, flow control valves, or electronic control systems that adjust fluid pressure based on vehicle speed and steering input. Proper fluid management helps reduce energy losses and heat buildup in the system.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sealing and leak prevention
Effective sealing solutions are implemented in power steering systems to prevent fluid leaks and maintain system integrity. High-quality seals and gaskets are used to withstand high pressures and temperatures, reducing the risk of fluid loss and air infiltration. Proper sealing helps maintain consistent fluid performance and prevents contamination, which can lead to increased friction and heat generation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Power Steering Fluid Industry
The power steering fluid market is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated to reach $1.5 billion by 2025. The technology for mitigating component friction and heat in power steering systems is well-established, with ongoing incremental improvements. Key players like ZF Friedrichshafen, JTEKT, and NSK dominate the market, leveraging their extensive automotive experience. Emerging companies such as Hitachi Automotive Systems and Robert Bosch Automotive Steering are focusing on advanced electronic power steering systems, which require less fluid but more sophisticated friction and heat management solutions. The market is characterized by a balance between traditional hydraulic systems and newer electric power steering technologies, with a gradual shift towards the latter in modern vehicles.
Robert Bosch Automotive Steering GmbH
Technical Solution: Robert Bosch Automotive Steering GmbH has developed advanced power steering fluid technologies to mitigate component friction and heat. Their solution incorporates a high-performance synthetic fluid with enhanced thermal stability and lubricity properties. This fluid maintains its viscosity over a wide temperature range, ensuring consistent steering performance in various operating conditions[1]. The company has also implemented a closed-loop circulation system that continuously filters and cools the fluid, reducing heat buildup and extending the life of steering components[2]. Additionally, Bosch has integrated smart sensors to monitor fluid pressure, temperature, and quality in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimal system performance[3].
Strengths: Superior thermal stability, advanced filtration system, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost and complexity compared to traditional systems.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota Motor Corp. has innovated in power steering fluid technology to address friction and heat issues. Their approach involves a proprietary fluid formulation with nano-scale friction modifiers and anti-wear additives[4]. This advanced fluid significantly reduces friction between moving parts, resulting in lower operating temperatures and improved energy efficiency. Toyota has also developed a variable-flow pump system that adjusts fluid circulation based on steering demand, minimizing unnecessary fluid movement and associated heat generation[5]. Furthermore, the company has implemented a heat exchanger design that efficiently dissipates heat from the power steering fluid, maintaining optimal fluid properties even under extreme conditions[6].
Strengths: Highly efficient fluid formulation, adaptive circulation system, and effective heat management. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology may limit compatibility with other systems.
Innovative Additives for Enhanced Fluid Performance
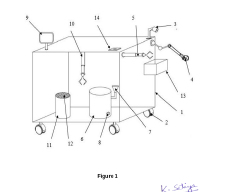
Power steering fluid refining device
PatentPendingIN202211077346A
Innovation
- A power steering fluid refining device equipped with omnidirectional wheels, an AI-based image capturing module, a robotic arm, a telescopic gripper, a viscosity sensor, and a motorized gripper, which autonomously locates the fluid chamber, unfastens it, and determines the fluid's usability, refining the fluid without manual effort and storing it in a filtered receptacle.
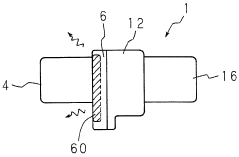
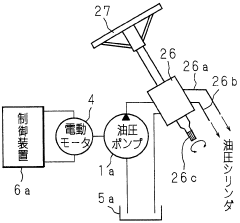
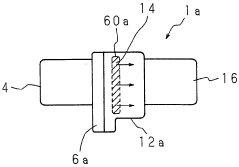
Power steering device
PatentWO1999059859A1
Innovation
- Incorporating a heat-conducting sheet radiator sandwiched between the control device and the hydraulic pump, with a fitting structure having a substantially circular cross-section and crimping spaces for O-rings, to efficiently dissipate heat and ensure water resistance without relying on external air conditions.
Environmental Impact of Power Steering Fluids
Power steering fluids play a crucial role in vehicle operation, but their environmental impact is a growing concern. These fluids, typically composed of mineral or synthetic oils, can have significant consequences when released into the environment. Leaks and improper disposal of power steering fluids contribute to soil and water contamination, posing risks to ecosystems and human health.
When power steering fluid enters the soil, it can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms and affect plant growth. The hydrocarbons present in the fluid can persist in the environment for extended periods, leading to long-term soil degradation. Furthermore, contaminated soil can act as a source of ongoing pollution, as rainwater may carry the contaminants into nearby water bodies.
Water pollution resulting from power steering fluid leaks or improper disposal is particularly problematic. Even small amounts of these fluids can contaminate large volumes of water, affecting aquatic life and potentially entering the food chain. The oil-based nature of power steering fluids creates a film on water surfaces, reducing oxygen transfer and impacting the survival of aquatic organisms.
The production and disposal of power steering fluids also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive operations, while the incineration of used fluids releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. This aspect of their lifecycle adds to the overall carbon footprint of automotive operations.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of power steering fluids include the development of biodegradable alternatives. These eco-friendly options are designed to break down more rapidly in the environment, reducing long-term contamination risks. Additionally, improved recycling programs and stricter regulations on fluid disposal aim to minimize the release of these substances into ecosystems.
The automotive industry is also exploring alternative power steering technologies, such as electric power steering systems, which eliminate the need for hydraulic fluids altogether. These innovations not only reduce the environmental risks associated with fluid leaks but also contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight.
In conclusion, while power steering fluids are essential for vehicle operation, their environmental impact necessitates ongoing research and development of more sustainable alternatives. Balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations remains a key challenge in the automotive sector's pursuit of eco-friendly technologies.
When power steering fluid enters the soil, it can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms and affect plant growth. The hydrocarbons present in the fluid can persist in the environment for extended periods, leading to long-term soil degradation. Furthermore, contaminated soil can act as a source of ongoing pollution, as rainwater may carry the contaminants into nearby water bodies.
Water pollution resulting from power steering fluid leaks or improper disposal is particularly problematic. Even small amounts of these fluids can contaminate large volumes of water, affecting aquatic life and potentially entering the food chain. The oil-based nature of power steering fluids creates a film on water surfaces, reducing oxygen transfer and impacting the survival of aquatic organisms.
The production and disposal of power steering fluids also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive operations, while the incineration of used fluids releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. This aspect of their lifecycle adds to the overall carbon footprint of automotive operations.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of power steering fluids include the development of biodegradable alternatives. These eco-friendly options are designed to break down more rapidly in the environment, reducing long-term contamination risks. Additionally, improved recycling programs and stricter regulations on fluid disposal aim to minimize the release of these substances into ecosystems.
The automotive industry is also exploring alternative power steering technologies, such as electric power steering systems, which eliminate the need for hydraulic fluids altogether. These innovations not only reduce the environmental risks associated with fluid leaks but also contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight.
In conclusion, while power steering fluids are essential for vehicle operation, their environmental impact necessitates ongoing research and development of more sustainable alternatives. Balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations remains a key challenge in the automotive sector's pursuit of eco-friendly technologies.
Regulatory Standards for Automotive Fluids
Regulatory standards for automotive fluids play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, performance, and environmental compatibility of power steering systems. These standards are established and enforced by various regulatory bodies, including the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and government agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States.
The SAE has developed specific standards for power steering fluids, such as SAE J1703 and SAE J1704, which outline the minimum performance requirements for these fluids. These standards address key properties like viscosity, boiling point, and corrosion protection, which are essential for mitigating component friction and heat in power steering systems.
ISO standards, particularly ISO 7308, provide guidelines for the chemical and physical properties of power steering fluids. These standards ensure that fluids meet the necessary criteria for optimal performance across various operating conditions, including extreme temperatures and high-pressure environments.
Environmental regulations also impact the formulation of power steering fluids. Many countries have implemented restrictions on the use of certain chemicals and additives in automotive fluids to reduce environmental impact. For instance, the EPA's Significant New Use Rules (SNURs) under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulate the use of specific chemical substances in automotive products, including power steering fluids.
Manufacturers must adhere to these regulatory standards when developing and producing power steering fluids. Compliance ensures that the fluids effectively reduce friction and heat while meeting safety and environmental requirements. Regular testing and certification processes are typically required to demonstrate ongoing compliance with these standards.
The automotive industry has also established voluntary standards and best practices for power steering fluids. Organizations like the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) provide specifications that often exceed regulatory requirements, driving innovation in fluid technology to enhance performance and durability.
As vehicle technologies evolve, regulatory standards for automotive fluids continue to adapt. The increasing adoption of electric power steering systems has led to the development of new fluid standards that address the unique requirements of these systems, such as compatibility with electronic components and enhanced thermal stability.
Regulatory bodies regularly review and update these standards to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging environmental concerns. This ongoing process ensures that power steering fluids continue to meet the demands of modern automotive systems while minimizing their environmental footprint.
The SAE has developed specific standards for power steering fluids, such as SAE J1703 and SAE J1704, which outline the minimum performance requirements for these fluids. These standards address key properties like viscosity, boiling point, and corrosion protection, which are essential for mitigating component friction and heat in power steering systems.
ISO standards, particularly ISO 7308, provide guidelines for the chemical and physical properties of power steering fluids. These standards ensure that fluids meet the necessary criteria for optimal performance across various operating conditions, including extreme temperatures and high-pressure environments.
Environmental regulations also impact the formulation of power steering fluids. Many countries have implemented restrictions on the use of certain chemicals and additives in automotive fluids to reduce environmental impact. For instance, the EPA's Significant New Use Rules (SNURs) under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulate the use of specific chemical substances in automotive products, including power steering fluids.
Manufacturers must adhere to these regulatory standards when developing and producing power steering fluids. Compliance ensures that the fluids effectively reduce friction and heat while meeting safety and environmental requirements. Regular testing and certification processes are typically required to demonstrate ongoing compliance with these standards.
The automotive industry has also established voluntary standards and best practices for power steering fluids. Organizations like the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) provide specifications that often exceed regulatory requirements, driving innovation in fluid technology to enhance performance and durability.
As vehicle technologies evolve, regulatory standards for automotive fluids continue to adapt. The increasing adoption of electric power steering systems has led to the development of new fluid standards that address the unique requirements of these systems, such as compatibility with electronic components and enhanced thermal stability.
Regulatory bodies regularly review and update these standards to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging environmental concerns. This ongoing process ensures that power steering fluids continue to meet the demands of modern automotive systems while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!