The Interplay Between Power Steering Fluid and Vehicle Electronics
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Power Steering Evolution
Power steering technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, hydraulic power steering systems dominated the automotive industry, providing drivers with enhanced control and maneuverability. These systems relied on a hydraulic pump driven by the engine to pressurize power steering fluid, which assisted in turning the wheels.
As vehicle design progressed, the interplay between power steering fluid and vehicle electronics became increasingly important. The introduction of electronic control units (ECUs) in the 1980s marked a turning point in power steering technology. These ECUs allowed for more precise control over the hydraulic system, improving steering feel and efficiency.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the emergence of electrohydraulic power steering (EHPS) systems. This hybrid technology combined traditional hydraulic components with electric motors and sensors, offering a more responsive and adaptable steering experience. EHPS systems represented a crucial step in the integration of power steering fluid dynamics with vehicle electronics.
The most recent and significant development in power steering evolution is the widespread adoption of electric power steering (EPS) systems. EPS eliminates the need for traditional power steering fluid, relying instead on an electric motor to assist steering. This shift has profound implications for the relationship between steering systems and vehicle electronics, as EPS is fully integrated with the vehicle's electrical architecture.
EPS systems offer several advantages, including improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced compatibility with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The absence of hydraulic components also contributes to weight reduction and simplified vehicle design. However, the transition to EPS has necessitated significant advancements in motor control algorithms, sensor technology, and power management systems.
As vehicles become increasingly electrified and autonomous, the evolution of power steering continues. The latest developments focus on steer-by-wire systems, which completely eliminate the mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels. These systems rely entirely on electronic control and actuators, further blurring the line between steering mechanisms and vehicle electronics.
The ongoing evolution of power steering technology reflects the broader trend of increasing electrification and digitalization in the automotive industry. As vehicles become more complex and interconnected, the integration of steering systems with other vehicle subsystems, such as braking, suspension, and powertrain management, becomes crucial for achieving optimal performance and safety.
As vehicle design progressed, the interplay between power steering fluid and vehicle electronics became increasingly important. The introduction of electronic control units (ECUs) in the 1980s marked a turning point in power steering technology. These ECUs allowed for more precise control over the hydraulic system, improving steering feel and efficiency.
The late 1990s and early 2000s saw the emergence of electrohydraulic power steering (EHPS) systems. This hybrid technology combined traditional hydraulic components with electric motors and sensors, offering a more responsive and adaptable steering experience. EHPS systems represented a crucial step in the integration of power steering fluid dynamics with vehicle electronics.
The most recent and significant development in power steering evolution is the widespread adoption of electric power steering (EPS) systems. EPS eliminates the need for traditional power steering fluid, relying instead on an electric motor to assist steering. This shift has profound implications for the relationship between steering systems and vehicle electronics, as EPS is fully integrated with the vehicle's electrical architecture.
EPS systems offer several advantages, including improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced compatibility with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The absence of hydraulic components also contributes to weight reduction and simplified vehicle design. However, the transition to EPS has necessitated significant advancements in motor control algorithms, sensor technology, and power management systems.
As vehicles become increasingly electrified and autonomous, the evolution of power steering continues. The latest developments focus on steer-by-wire systems, which completely eliminate the mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels. These systems rely entirely on electronic control and actuators, further blurring the line between steering mechanisms and vehicle electronics.
The ongoing evolution of power steering technology reflects the broader trend of increasing electrification and digitalization in the automotive industry. As vehicles become more complex and interconnected, the integration of steering systems with other vehicle subsystems, such as braking, suspension, and powertrain management, becomes crucial for achieving optimal performance and safety.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for power steering fluid and its interaction with vehicle electronics has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing complexity of modern automotive systems. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the integration of electronic components with traditional mechanical systems has created new challenges and opportunities in the automotive industry.
The global power steering fluid market is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising production of vehicles worldwide, particularly in emerging economies. The increasing adoption of electric power steering systems in modern vehicles has also contributed to the demand for specialized power steering fluids that can effectively interact with electronic components.
Consumer preferences for smoother driving experiences and enhanced vehicle handling have further fueled the demand for advanced power steering systems. This, in turn, has led to a greater focus on the development of power steering fluids that can optimize the performance of these systems while ensuring compatibility with vehicle electronics.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles has created new market opportunities for power steering fluid manufacturers. These vehicles often require specialized fluids that can withstand higher operating temperatures and provide improved electrical insulation properties to protect sensitive electronic components.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have also influenced market demand. There is a growing trend towards the development of eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have reduced environmental impact. This shift has prompted manufacturers to invest in research and development of new formulations that meet both performance and environmental standards.
The aftermarket segment for power steering fluids has shown substantial growth potential. As vehicle owners become more aware of the importance of regular maintenance, the demand for high-quality replacement fluids has increased. This trend is particularly evident in regions with aging vehicle fleets, where proper maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of power steering systems and associated electronics.
The interplay between power steering fluid and vehicle electronics has led to the emergence of new market segments. Manufacturers are developing specialized fluids designed to enhance the performance and longevity of electronic power steering systems. These advanced fluids offer improved thermal stability, corrosion protection, and compatibility with a wide range of materials used in modern vehicle electronics.
In conclusion, the market demand for power steering fluid, particularly in relation to vehicle electronics, is driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and the growing complexity of automotive systems. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative power steering fluid solutions that can effectively interact with and protect vehicle electronics is expected to remain strong.
The global power steering fluid market is experiencing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising production of vehicles worldwide, particularly in emerging economies. The increasing adoption of electric power steering systems in modern vehicles has also contributed to the demand for specialized power steering fluids that can effectively interact with electronic components.
Consumer preferences for smoother driving experiences and enhanced vehicle handling have further fueled the demand for advanced power steering systems. This, in turn, has led to a greater focus on the development of power steering fluids that can optimize the performance of these systems while ensuring compatibility with vehicle electronics.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles has created new market opportunities for power steering fluid manufacturers. These vehicles often require specialized fluids that can withstand higher operating temperatures and provide improved electrical insulation properties to protect sensitive electronic components.
Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have also influenced market demand. There is a growing trend towards the development of eco-friendly power steering fluids that are biodegradable and have reduced environmental impact. This shift has prompted manufacturers to invest in research and development of new formulations that meet both performance and environmental standards.
The aftermarket segment for power steering fluids has shown substantial growth potential. As vehicle owners become more aware of the importance of regular maintenance, the demand for high-quality replacement fluids has increased. This trend is particularly evident in regions with aging vehicle fleets, where proper maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of power steering systems and associated electronics.
The interplay between power steering fluid and vehicle electronics has led to the emergence of new market segments. Manufacturers are developing specialized fluids designed to enhance the performance and longevity of electronic power steering systems. These advanced fluids offer improved thermal stability, corrosion protection, and compatibility with a wide range of materials used in modern vehicle electronics.
In conclusion, the market demand for power steering fluid, particularly in relation to vehicle electronics, is driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and the growing complexity of automotive systems. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative power steering fluid solutions that can effectively interact with and protect vehicle electronics is expected to remain strong.
Technical Challenges
The integration of power steering fluid systems with modern vehicle electronics presents several significant technical challenges. One of the primary issues is the potential for electromagnetic interference (EMI) between the power steering system and sensitive electronic components. As vehicles become increasingly reliant on complex electronic systems, the risk of EMI-induced malfunctions or performance degradation grows, necessitating advanced shielding and isolation techniques.
Another challenge lies in the development of adaptive power steering systems that can seamlessly integrate with electronic stability control (ESC) and other driver assistance technologies. These systems require sophisticated algorithms and sensors to accurately interpret driver inputs and road conditions, adjusting steering assistance in real-time. The complexity of such systems increases the potential for software bugs and system failures, which could compromise vehicle safety.
The miniaturization of electronic components in modern vehicles has led to space constraints within the engine compartment. This presents difficulties in designing power steering fluid systems that can efficiently coexist with densely packed electronic modules while maintaining optimal fluid circulation and cooling. Engineers must develop innovative packaging solutions to ensure proper fluid flow and heat dissipation without compromising the integrity of nearby electronic systems.
Durability and longevity of both the power steering fluid and electronic components in harsh automotive environments pose another significant challenge. The constant exposure to heat, vibration, and potential fluid leaks can accelerate the degradation of electronic components. Conversely, the presence of electronic systems near fluid reservoirs and lines increases the risk of fluid contamination, which can lead to reduced performance and increased wear on mechanical components.
The transition towards electric power steering (EPS) systems introduces new challenges in the interplay between steering systems and vehicle electronics. While EPS eliminates the need for traditional power steering fluid, it requires more sophisticated electronic control units and sensors. This shift demands a complete redesign of power distribution systems and cooling strategies to accommodate the increased electrical load and heat generation.
Lastly, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities with steering systems presents complex technical hurdles. These systems require precise control over steering inputs, necessitating highly responsive and accurate communication between the steering system and the vehicle's central electronic control units. Ensuring the reliability and fail-safe operation of these integrated systems under all driving conditions remains a significant engineering challenge.
Another challenge lies in the development of adaptive power steering systems that can seamlessly integrate with electronic stability control (ESC) and other driver assistance technologies. These systems require sophisticated algorithms and sensors to accurately interpret driver inputs and road conditions, adjusting steering assistance in real-time. The complexity of such systems increases the potential for software bugs and system failures, which could compromise vehicle safety.
The miniaturization of electronic components in modern vehicles has led to space constraints within the engine compartment. This presents difficulties in designing power steering fluid systems that can efficiently coexist with densely packed electronic modules while maintaining optimal fluid circulation and cooling. Engineers must develop innovative packaging solutions to ensure proper fluid flow and heat dissipation without compromising the integrity of nearby electronic systems.
Durability and longevity of both the power steering fluid and electronic components in harsh automotive environments pose another significant challenge. The constant exposure to heat, vibration, and potential fluid leaks can accelerate the degradation of electronic components. Conversely, the presence of electronic systems near fluid reservoirs and lines increases the risk of fluid contamination, which can lead to reduced performance and increased wear on mechanical components.
The transition towards electric power steering (EPS) systems introduces new challenges in the interplay between steering systems and vehicle electronics. While EPS eliminates the need for traditional power steering fluid, it requires more sophisticated electronic control units and sensors. This shift demands a complete redesign of power distribution systems and cooling strategies to accommodate the increased electrical load and heat generation.
Lastly, the integration of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities with steering systems presents complex technical hurdles. These systems require precise control over steering inputs, necessitating highly responsive and accurate communication between the steering system and the vehicle's central electronic control units. Ensuring the reliability and fail-safe operation of these integrated systems under all driving conditions remains a significant engineering challenge.
Current Solution Landscape
01 Power steering fluid composition
Power steering fluids are specially formulated to meet the requirements of hydraulic power steering systems. These fluids typically contain base oils, additives for wear protection, anti-foaming agents, and viscosity modifiers to ensure optimal performance across a range of temperatures and operating conditions.- Power steering fluid composition: Power steering fluids are specially formulated to provide optimal performance in power steering systems. These fluids typically contain a base oil, additives for wear protection, anti-foaming agents, and viscosity modifiers to ensure proper function across a range of temperatures and operating conditions.
- Power steering fluid reservoirs and systems: Power steering systems incorporate reservoirs to store and supply fluid to the steering mechanism. These reservoirs are designed to maintain proper fluid levels, prevent contamination, and allow for easy fluid checks and refills. The design of the reservoir and associated components can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the power steering system.
- Power steering pumps and fluid circulation: Power steering pumps are crucial components that circulate fluid through the system, providing the necessary pressure for power assistance. The design and efficiency of these pumps, along with the fluid circulation pathways, play a significant role in the overall performance and energy consumption of the power steering system.
- Power steering fluid maintenance and replacement: Regular maintenance of power steering fluid is essential for optimal system performance and longevity. This includes periodic checks of fluid levels, quality, and replacement intervals. Proper maintenance procedures and tools can help prevent system failures and extend the life of power steering components.
- Power steering fluid in electric and hybrid systems: As automotive technology evolves, power steering systems in electric and hybrid vehicles may require specialized fluids or alternative designs. These systems often integrate electric power steering or electro-hydraulic systems, which can have different fluid requirements or eliminate the need for traditional power steering fluid altogether.
02 Power steering fluid reservoirs and systems
Power steering systems incorporate reservoirs to store and supply fluid to the steering mechanism. These reservoirs are designed to maintain proper fluid levels, prevent contamination, and facilitate easy refilling. The design of the reservoir and associated components can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the power steering system.Expand Specific Solutions03 Power steering pumps and fluid circulation
Power steering pumps are crucial components that circulate fluid through the system, providing the necessary hydraulic pressure for power assistance. The design and efficiency of these pumps, along with the fluid circulation system, play a significant role in the overall performance and energy consumption of power steering systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Power steering fluid maintenance and replacement
Regular maintenance and replacement of power steering fluid are essential for optimal system performance and longevity. This includes periodic checks of fluid levels, inspection for contamination or degradation, and complete fluid changes at recommended intervals. Proper maintenance procedures and tools can help extend the life of power steering components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Power steering fluid in electric and hybrid systems
As automotive technology evolves, power steering systems in electric and hybrid vehicles are being adapted to work with new drivetrain configurations. This has led to the development of specialized power steering fluids and systems that are compatible with electric power steering (EPS) and electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS) setups, focusing on energy efficiency and environmental considerations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The interplay between power steering fluid and vehicle electronics represents a complex technological landscape in the automotive industry. This field is currently in a mature stage of development, with established players like Toyota, GM, and Ford leading the way. The market size is substantial, driven by the increasing integration of electronic systems in modern vehicles. Technologically, the sector is well-developed, with companies like ZF Friedrichshafen, Bosch, and JTEKT offering advanced solutions. However, there's ongoing innovation, particularly in the integration of electronic power steering systems, with emerging players like BYD and LG Electronics entering the market with new approaches to electric and autonomous vehicle technologies.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has developed an advanced Electric Power Steering (EPS) system that integrates seamlessly with vehicle electronics. Their system utilizes a high-precision torque sensor and a microcontroller unit (MCU) to continuously monitor steering input and vehicle conditions[1]. The EPS system adjusts power assistance based on vehicle speed, reducing assistance at higher speeds for improved stability. Toyota has also implemented a fail-safe mechanism that can detect system malfunctions and switch to a mechanical backup mode[2]. To address electromagnetic interference (EMI) concerns, Toyota employs shielded power steering fluid lines and strategically placed EMI filters to protect sensitive electronic components[3].
Strengths: Highly responsive and adaptable system, improved fuel efficiency, advanced safety features. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost, complexity may lead to more expensive repairs.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has pioneered a hybrid power steering system that combines traditional hydraulic assist with electric assist technology. This system uses an electric pump to pressurize the power steering fluid, allowing for variable assistance based on driving conditions[4]. The system incorporates advanced sensors to monitor fluid pressure, temperature, and flow rate, enabling real-time adjustments to optimize performance and efficiency. GM's solution also features a sophisticated electronic control unit (ECU) that interfaces with other vehicle systems, such as stability control and lane-keeping assist, to enhance overall vehicle dynamics[5]. To mitigate potential electromagnetic interference, GM employs specialized fluid formulations with reduced conductivity and implements robust shielding techniques for critical electronic components[6].
Strengths: Combines benefits of hydraulic and electric systems, seamless integration with other vehicle electronics. Weaknesses: More complex than pure electric systems, potential for fluid leaks remains.
Innovative Fluid Designs
Power steering system
PatentInactiveUS7257947B2
Innovation
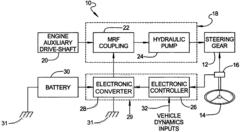
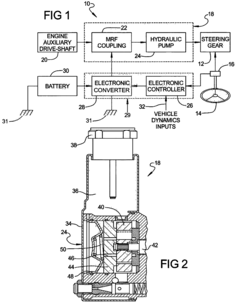
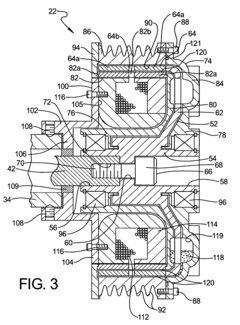
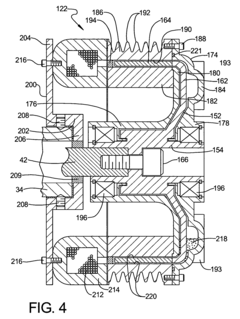
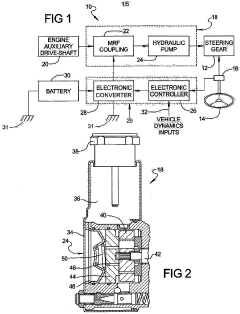
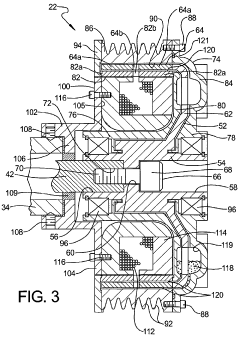
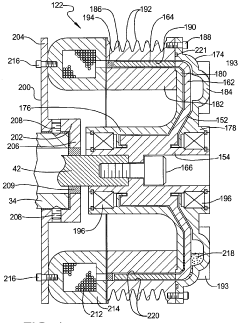
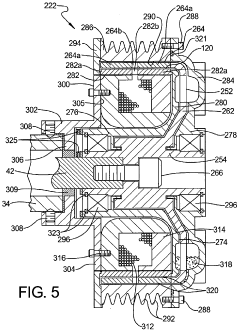
- A magneto-rheological hydraulic power steering system that uses a fluid coupling to directly control the speed of the hydraulic pump, reducing energy losses and costs by eliminating the need for continuous engine-driven operation and high-power electronics, with a controller and power electronic converter managing torque and pressure dynamically.
Power steering system
PatentWO2006107337A2
Innovation
- A power steering system incorporating a magneto-rheological fluid coupling that connects the engine drive shaft with a hydraulic pump, allowing for variable control of torque transmission via an electronic controller, enabling adjustable speed and pressure independent of engine speed, reducing energy losses and costs.
Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory landscape surrounding power steering fluid and vehicle electronics is complex and evolving, reflecting the increasing integration of mechanical and electronic systems in modern vehicles. Compliance with safety standards and environmental regulations is paramount for manufacturers and suppliers in the automotive industry.
Safety regulations, such as those set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, mandate specific performance criteria for power steering systems. These regulations often include requirements for fluid integrity, system reliability, and fail-safe mechanisms. As electronic power steering systems become more prevalent, regulatory bodies are adapting their guidelines to address the unique challenges posed by these advanced technologies.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the development and use of power steering fluids. Many jurisdictions have implemented strict guidelines on the composition and disposal of automotive fluids to minimize environmental impact. Manufacturers must ensure that their power steering fluids meet these environmental standards while maintaining optimal performance and compatibility with vehicle electronics.
The European Union's End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive is a prime example of regulatory influence on automotive fluid design. This directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of vehicles at the end of their lifecycle, including the proper handling and recycling of fluids. Consequently, power steering fluid formulations must be designed with recyclability and reduced toxicity in mind.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations are becoming increasingly relevant as vehicle electronics become more sophisticated. Power steering systems, particularly those with electronic components, must comply with EMC standards to prevent interference with other vehicle systems and external electronic devices. This requires careful design and testing to ensure that power steering fluids and associated electronic components do not emit or are susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
The global nature of the automotive industry necessitates compliance with a diverse array of regional and international standards. Manufacturers must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure their products meet the requirements of various markets. This often involves extensive testing and certification processes, as well as ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and updates.
As autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles gain traction, new regulatory challenges are emerging. The interplay between power steering systems and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is subject to evolving safety standards. Regulators are working to develop frameworks that address the unique safety considerations of these integrated systems, including the reliability and performance of power steering in various autonomous driving scenarios.
Safety regulations, such as those set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, mandate specific performance criteria for power steering systems. These regulations often include requirements for fluid integrity, system reliability, and fail-safe mechanisms. As electronic power steering systems become more prevalent, regulatory bodies are adapting their guidelines to address the unique challenges posed by these advanced technologies.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping the development and use of power steering fluids. Many jurisdictions have implemented strict guidelines on the composition and disposal of automotive fluids to minimize environmental impact. Manufacturers must ensure that their power steering fluids meet these environmental standards while maintaining optimal performance and compatibility with vehicle electronics.
The European Union's End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive is a prime example of regulatory influence on automotive fluid design. This directive aims to reduce the environmental impact of vehicles at the end of their lifecycle, including the proper handling and recycling of fluids. Consequently, power steering fluid formulations must be designed with recyclability and reduced toxicity in mind.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations are becoming increasingly relevant as vehicle electronics become more sophisticated. Power steering systems, particularly those with electronic components, must comply with EMC standards to prevent interference with other vehicle systems and external electronic devices. This requires careful design and testing to ensure that power steering fluids and associated electronic components do not emit or are susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
The global nature of the automotive industry necessitates compliance with a diverse array of regional and international standards. Manufacturers must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure their products meet the requirements of various markets. This often involves extensive testing and certification processes, as well as ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and updates.
As autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles gain traction, new regulatory challenges are emerging. The interplay between power steering systems and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is subject to evolving safety standards. Regulators are working to develop frameworks that address the unique safety considerations of these integrated systems, including the reliability and performance of power steering in various autonomous driving scenarios.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of power steering fluid and its interaction with vehicle electronics is a critical consideration in the automotive industry. As vehicles become increasingly electrified and autonomous, the traditional hydraulic power steering systems are being phased out in favor of electric power steering (EPS) systems. This shift has significant implications for the environment.
Traditional power steering fluid, typically a petroleum-based product, poses several environmental risks. When leaked or improperly disposed of, it can contaminate soil and water sources, potentially harming ecosystems and wildlife. The production and disposal of these fluids also contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion. In contrast, EPS systems eliminate the need for hydraulic fluid, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and the associated disposal challenges.
However, the transition to EPS is not without environmental concerns. The production of electric motors and control units for EPS systems requires rare earth elements and other materials with complex supply chains and extraction processes. These processes can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the increased reliance on electronics in vehicles raises concerns about electronic waste (e-waste) management at the end of a vehicle's life cycle.
The interplay between power steering systems and vehicle electronics also affects overall vehicle efficiency and, consequently, environmental impact. EPS systems generally improve fuel efficiency compared to hydraulic systems, as they only draw power when steering input is required. This efficiency gain translates to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions in internal combustion engine vehicles. In electric vehicles, the efficiency improvements contribute to extended range and reduced energy consumption.
As vehicle electronics become more sophisticated, the integration of power steering systems with other vehicle systems offers opportunities for further environmental benefits. For instance, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies can optimize steering inputs for improved energy efficiency and reduced tire wear, indirectly benefiting the environment through reduced resource consumption and particulate emissions.
The lifecycle environmental impact of power steering systems and vehicle electronics must be considered holistically. While EPS systems offer clear advantages in terms of operational environmental impact, the production and end-of-life phases present new challenges. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainable design principles, such as designing for recyclability and using recycled materials in production. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives to rare earth elements and to improve the recycling processes for electronic components.
In conclusion, the shift from hydraulic to electric power steering systems, driven by the increasing integration of electronics in vehicles, presents both environmental benefits and challenges. While immediate operational impacts are generally positive, the industry must continue to address the environmental concerns associated with the production and disposal of electronic components to ensure a truly sustainable transition in automotive technology.
Traditional power steering fluid, typically a petroleum-based product, poses several environmental risks. When leaked or improperly disposed of, it can contaminate soil and water sources, potentially harming ecosystems and wildlife. The production and disposal of these fluids also contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion. In contrast, EPS systems eliminate the need for hydraulic fluid, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and the associated disposal challenges.
However, the transition to EPS is not without environmental concerns. The production of electric motors and control units for EPS systems requires rare earth elements and other materials with complex supply chains and extraction processes. These processes can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the increased reliance on electronics in vehicles raises concerns about electronic waste (e-waste) management at the end of a vehicle's life cycle.
The interplay between power steering systems and vehicle electronics also affects overall vehicle efficiency and, consequently, environmental impact. EPS systems generally improve fuel efficiency compared to hydraulic systems, as they only draw power when steering input is required. This efficiency gain translates to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions in internal combustion engine vehicles. In electric vehicles, the efficiency improvements contribute to extended range and reduced energy consumption.
As vehicle electronics become more sophisticated, the integration of power steering systems with other vehicle systems offers opportunities for further environmental benefits. For instance, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies can optimize steering inputs for improved energy efficiency and reduced tire wear, indirectly benefiting the environment through reduced resource consumption and particulate emissions.
The lifecycle environmental impact of power steering systems and vehicle electronics must be considered holistically. While EPS systems offer clear advantages in terms of operational environmental impact, the production and end-of-life phases present new challenges. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on sustainable design principles, such as designing for recyclability and using recycled materials in production. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives to rare earth elements and to improve the recycling processes for electronic components.
In conclusion, the shift from hydraulic to electric power steering systems, driven by the increasing integration of electronics in vehicles, presents both environmental benefits and challenges. While immediate operational impacts are generally positive, the industry must continue to address the environmental concerns associated with the production and disposal of electronic components to ensure a truly sustainable transition in automotive technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!