Power Steering Fluid and Its Interaction with Rubber Seals
JUL 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Power Steering Fluid Evolution and Objectives
Power steering fluid has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the automotive industry. Initially developed in the 1950s, these fluids were primarily mineral oil-based and designed to provide basic lubrication and pressure transfer within power steering systems. As vehicle technology advanced, so did the demands placed on power steering fluids, leading to continuous improvements in their formulation and performance characteristics.
The evolution of power steering fluids has been driven by several key factors. Firstly, the need for enhanced durability and longevity to match the increasing lifespan of modern vehicles. Secondly, the requirement for improved thermal stability to withstand higher operating temperatures in more compact engine compartments. Thirdly, the demand for better compatibility with a wide range of materials used in power steering systems, particularly rubber seals.
In response to these challenges, synthetic-based power steering fluids were introduced in the 1980s. These fluids offered superior thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and improved low-temperature performance compared to their mineral oil-based predecessors. The synthetic formulations also provided better protection against wear and corrosion, contributing to extended component life.
A significant milestone in power steering fluid development was the introduction of multi-vehicle formulations in the 1990s. These universal fluids were designed to be compatible with a broad range of vehicle makes and models, simplifying inventory management for service centers and reducing the risk of incorrect fluid usage.
The primary objectives of modern power steering fluid development focus on several key areas. Enhancing the fluid's ability to maintain its viscosity and lubricating properties under extreme temperature conditions is crucial for consistent steering performance. Improving the fluid's compatibility with various seal materials, particularly rubber seals, is essential to prevent leaks and extend system longevity.
Another critical objective is to develop environmentally friendly formulations that reduce the impact of potential leaks and disposal. This includes the use of biodegradable base oils and additives that minimize environmental harm. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on creating fluids that can operate effectively in hybrid and electric vehicles, which may have different thermal and chemical requirements compared to traditional combustion engine vehicles.
Looking ahead, the evolution of power steering fluids is likely to continue, driven by advancements in vehicle technology and increasing environmental regulations. Future objectives may include the development of smart fluids that can adapt their properties based on operating conditions, as well as formulations specifically designed for autonomous vehicles with advanced steering systems.
The evolution of power steering fluids has been driven by several key factors. Firstly, the need for enhanced durability and longevity to match the increasing lifespan of modern vehicles. Secondly, the requirement for improved thermal stability to withstand higher operating temperatures in more compact engine compartments. Thirdly, the demand for better compatibility with a wide range of materials used in power steering systems, particularly rubber seals.
In response to these challenges, synthetic-based power steering fluids were introduced in the 1980s. These fluids offered superior thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and improved low-temperature performance compared to their mineral oil-based predecessors. The synthetic formulations also provided better protection against wear and corrosion, contributing to extended component life.
A significant milestone in power steering fluid development was the introduction of multi-vehicle formulations in the 1990s. These universal fluids were designed to be compatible with a broad range of vehicle makes and models, simplifying inventory management for service centers and reducing the risk of incorrect fluid usage.
The primary objectives of modern power steering fluid development focus on several key areas. Enhancing the fluid's ability to maintain its viscosity and lubricating properties under extreme temperature conditions is crucial for consistent steering performance. Improving the fluid's compatibility with various seal materials, particularly rubber seals, is essential to prevent leaks and extend system longevity.
Another critical objective is to develop environmentally friendly formulations that reduce the impact of potential leaks and disposal. This includes the use of biodegradable base oils and additives that minimize environmental harm. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on creating fluids that can operate effectively in hybrid and electric vehicles, which may have different thermal and chemical requirements compared to traditional combustion engine vehicles.
Looking ahead, the evolution of power steering fluids is likely to continue, driven by advancements in vehicle technology and increasing environmental regulations. Future objectives may include the development of smart fluids that can adapt their properties based on operating conditions, as well as formulations specifically designed for autonomous vehicles with advanced steering systems.
Market Analysis for Power Steering Systems
The power steering system market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for comfortable and effortless driving experiences. As vehicles become more advanced and heavier, the need for power steering systems has become paramount across various vehicle segments. The global power steering market size was valued at approximately $26.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $38.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period.
The market is segmented into hydraulic power steering (HPS), electric power steering (EPS), and electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS) systems. While HPS has been the traditional choice, EPS is rapidly gaining market share due to its improved fuel efficiency, reduced complexity, and compatibility with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The EPS segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate, with a CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to 2027.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the power steering market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the high vehicle production volumes in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow closely, with growing adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles driving the demand for advanced power steering systems.
The passenger car segment holds the largest market share, owing to the increasing production of compact and mid-sized vehicles. However, the commercial vehicle segment is expected to grow at a faster rate, driven by the rising demand for heavy-duty trucks and buses in developing economies.
Key market players include JTEKT Corporation, Robert Bosch GmbH, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, NSK Ltd., and Nexteer Automotive. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative power steering solutions that offer improved performance, durability, and compatibility with autonomous driving technologies.
The power steering fluid market, a crucial component of hydraulic and electro-hydraulic systems, is also witnessing steady growth. The global power steering fluid market size was valued at $2.1 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $2.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%. The increasing vehicle parc and growing awareness about regular maintenance of power steering systems are driving this market segment.
In conclusion, the power steering systems market is poised for substantial growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing vehicle production, and the shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles. The interaction between power steering fluid and rubber seals remains a critical aspect of system performance and longevity, highlighting the need for ongoing research and development in this area.
The market is segmented into hydraulic power steering (HPS), electric power steering (EPS), and electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS) systems. While HPS has been the traditional choice, EPS is rapidly gaining market share due to its improved fuel efficiency, reduced complexity, and compatibility with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The EPS segment is expected to witness the highest growth rate, with a CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to 2027.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the power steering market, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the high vehicle production volumes in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. North America and Europe follow closely, with growing adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles driving the demand for advanced power steering systems.
The passenger car segment holds the largest market share, owing to the increasing production of compact and mid-sized vehicles. However, the commercial vehicle segment is expected to grow at a faster rate, driven by the rising demand for heavy-duty trucks and buses in developing economies.
Key market players include JTEKT Corporation, Robert Bosch GmbH, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, NSK Ltd., and Nexteer Automotive. These companies are focusing on research and development to introduce innovative power steering solutions that offer improved performance, durability, and compatibility with autonomous driving technologies.
The power steering fluid market, a crucial component of hydraulic and electro-hydraulic systems, is also witnessing steady growth. The global power steering fluid market size was valued at $2.1 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $2.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%. The increasing vehicle parc and growing awareness about regular maintenance of power steering systems are driving this market segment.
In conclusion, the power steering systems market is poised for substantial growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing vehicle production, and the shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles. The interaction between power steering fluid and rubber seals remains a critical aspect of system performance and longevity, highlighting the need for ongoing research and development in this area.
Current Challenges in Fluid-Seal Compatibility
The compatibility between power steering fluid and rubber seals presents significant challenges in the automotive industry. One of the primary issues is the degradation of rubber seals over time due to prolonged exposure to power steering fluid. This degradation can lead to leaks, reduced system efficiency, and potential safety hazards.
The chemical composition of power steering fluid plays a crucial role in its interaction with rubber seals. Traditional mineral-based fluids tend to cause swelling and softening of certain rubber compounds, particularly those used in older vehicle models. This swelling can compromise the seal's integrity, leading to fluid leakage and reduced steering performance.
Conversely, some synthetic power steering fluids may cause excessive shrinkage or hardening of rubber seals, resulting in poor sealing properties and increased wear. The challenge lies in finding the right balance between fluid performance and seal compatibility across a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
Temperature fluctuations further complicate the fluid-seal interaction. Extreme heat generated during vehicle operation can accelerate the degradation of both the fluid and the seals, while cold temperatures may cause the fluid to thicken, potentially damaging seals during startup.
Another significant challenge is the varying composition of rubber seals used by different manufacturers. The diversity in rubber compounds makes it difficult to develop a universal power steering fluid that is compatible with all seal types. This variability necessitates extensive testing and validation processes for fluid manufacturers.
The increasing use of electric power steering systems in modern vehicles introduces new challenges in fluid-seal compatibility. While these systems generally require less fluid, they often operate at higher temperatures, placing additional stress on the seals and fluid.
Environmental concerns and regulations also impact fluid-seal compatibility. The push for more environmentally friendly fluids may require changes in seal materials or designs to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Lastly, the long-term effects of fluid-seal interactions remain a concern. As vehicles are designed for longer lifespans, the durability of seals and the stability of power steering fluids over extended periods become critical factors. This necessitates ongoing research into advanced materials and fluid formulations that can withstand the test of time while maintaining optimal performance and safety standards.
The chemical composition of power steering fluid plays a crucial role in its interaction with rubber seals. Traditional mineral-based fluids tend to cause swelling and softening of certain rubber compounds, particularly those used in older vehicle models. This swelling can compromise the seal's integrity, leading to fluid leakage and reduced steering performance.
Conversely, some synthetic power steering fluids may cause excessive shrinkage or hardening of rubber seals, resulting in poor sealing properties and increased wear. The challenge lies in finding the right balance between fluid performance and seal compatibility across a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
Temperature fluctuations further complicate the fluid-seal interaction. Extreme heat generated during vehicle operation can accelerate the degradation of both the fluid and the seals, while cold temperatures may cause the fluid to thicken, potentially damaging seals during startup.
Another significant challenge is the varying composition of rubber seals used by different manufacturers. The diversity in rubber compounds makes it difficult to develop a universal power steering fluid that is compatible with all seal types. This variability necessitates extensive testing and validation processes for fluid manufacturers.
The increasing use of electric power steering systems in modern vehicles introduces new challenges in fluid-seal compatibility. While these systems generally require less fluid, they often operate at higher temperatures, placing additional stress on the seals and fluid.
Environmental concerns and regulations also impact fluid-seal compatibility. The push for more environmentally friendly fluids may require changes in seal materials or designs to maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Lastly, the long-term effects of fluid-seal interactions remain a concern. As vehicles are designed for longer lifespans, the durability of seals and the stability of power steering fluids over extended periods become critical factors. This necessitates ongoing research into advanced materials and fluid formulations that can withstand the test of time while maintaining optimal performance and safety standards.
Existing Fluid Formulations and Seal Materials
01 Fluid composition and properties
Power steering fluid composition and properties are crucial for optimal system performance. This includes the development of specific formulations to enhance lubrication, reduce wear, and improve overall efficiency of the power steering system. The fluid's viscosity, thermal stability, and compatibility with system components are key factors considered in its design.- Power steering fluid composition: Specialized fluid compositions are developed for power steering systems to optimize performance and reduce wear. These fluids often contain additives to improve lubrication, reduce friction, and protect against corrosion. The composition may include base oils, viscosity modifiers, and anti-wear agents to ensure smooth operation of the power steering system.
- Fluid interaction with power steering components: The interaction between power steering fluid and system components is crucial for optimal performance. This includes the fluid's compatibility with seals, hoses, and metal parts. Proper fluid interaction helps prevent leaks, reduces wear on moving parts, and ensures efficient power transfer within the steering system.
- Power steering fluid circulation and flow control: Efficient circulation and flow control of power steering fluid are essential for system performance. This involves the design of fluid passages, valves, and pumps to ensure proper fluid distribution and pressure regulation. Optimized fluid flow helps maintain steering responsiveness and reduces power losses in the system.
- Temperature management of power steering fluid: Managing the temperature of power steering fluid is crucial for maintaining its properties and system performance. This includes cooling mechanisms to prevent fluid degradation at high temperatures and ensuring proper viscosity across a range of operating conditions. Effective temperature management extends the life of both the fluid and the power steering components.
- Power steering fluid maintenance and replacement: Regular maintenance and timely replacement of power steering fluid are important for system longevity. This includes procedures for flushing the system, removing contaminants, and refilling with fresh fluid. Proper maintenance helps prevent issues such as fluid breakdown, component wear, and system failure.
02 Fluid circulation and flow control
Effective circulation and flow control of power steering fluid is essential for system operation. This involves the design of pumps, valves, and channels to ensure proper fluid distribution throughout the steering system. Innovations in this area focus on optimizing fluid flow rates, pressure regulation, and minimizing energy losses.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fluid-component interaction
The interaction between power steering fluid and various system components is a critical aspect of steering system design. This includes studying the effects of fluid on seals, hoses, and metal surfaces, as well as developing materials and coatings that are resistant to fluid-induced degradation. Compatibility between the fluid and system components is essential for long-term reliability and performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fluid maintenance and monitoring
Maintaining and monitoring power steering fluid quality is crucial for system longevity. This involves developing methods for fluid condition assessment, filtration systems to remove contaminants, and strategies for fluid replacement or replenishment. Advanced monitoring techniques may include sensors to detect fluid degradation or leaks in real-time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Environmental and safety aspects of power steering fluid are increasingly important. This includes developing eco-friendly fluid formulations, improving fluid containment to prevent leaks, and ensuring safe handling and disposal practices. Innovations in this area aim to reduce the environmental impact of power steering systems while maintaining or improving performance and safety standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers in Automotive Fluid Industry
The power steering fluid and rubber seal interaction market is in a mature stage, with established players and well-defined technologies. The global market size for automotive power steering systems is substantial, driven by increasing vehicle production and demand for enhanced driving comfort. Technologically, the field is relatively stable, with incremental improvements rather than disruptive innovations. Key players like NSK Ltd., JTEKT Europe SAS, and ZF Friedrichshafen AG have developed advanced solutions, focusing on improving fluid-seal compatibility, reducing wear, and enhancing overall system performance. Companies such as Tianjin Pengling Group Co. Ltd. and Qingdao Sunsong Co., Ltd. are contributing to the market with specialized rubber hose and seal products, while major automotive suppliers like Robert Bosch GmbH and Hitachi Ltd. integrate these components into their broader power steering system offerings.
NSK Ltd.
Technical Solution: NSK Ltd. has focused on developing power steering fluids that are specifically tailored for use in electric power steering (EPS) systems. Their fluid technology emphasizes low viscosity to improve energy efficiency while maintaining adequate lubrication and seal protection. NSK's formulation includes advanced polymer additives that create a protective film on seal surfaces, reducing friction and preventing seal degradation[5]. The company has also incorporated anti-oxidation agents to extend fluid life and maintain consistent performance over time, even in high-temperature environments common in EPS systems[6].
Strengths: Optimized for modern EPS systems, energy-efficient formulation, and excellent oxidation resistance. Weaknesses: May not be as suitable for traditional hydraulic power steering systems.
Hitachi Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hitachi Ltd. has developed an innovative power steering fluid technology that focuses on enhancing the fluid's electrical properties to improve compatibility with modern steering systems. Their approach involves incorporating nano-scale conductive particles into the fluid formulation, which helps dissipate static charges that can build up and potentially damage rubber seals[7]. Hitachi's fluid also features a unique blend of synthetic base oils that provide excellent low-temperature fluidity while maintaining proper viscosity at high temperatures, ensuring consistent seal protection across a wide range of operating conditions[8].
Strengths: Enhanced electrical properties, excellent temperature range performance, and improved seal protection from static charge. Weaknesses: Higher production costs due to specialized nano-particles and synthetic base oils.
Innovations in Fluid-Seal Interface Technology
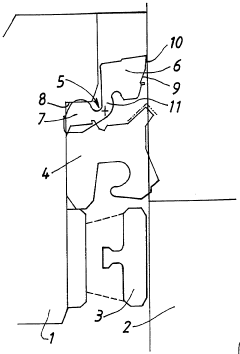
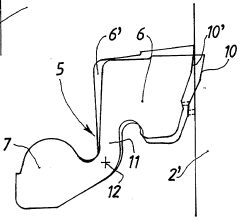
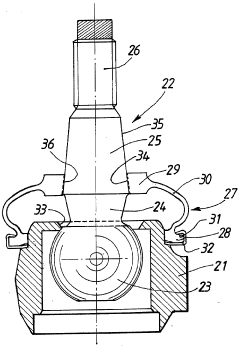
Rubber Composition of Oil Seal for Power steering System
PatentInactiveKR1020110041291A
Innovation
- A composition comprising hydrogenated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber with a blend of FEF and SRF carbon blacks, along with crosslinking agents and additives, reduces modulus and surface smoothness to prevent dry friction and noise, while maintaining heat and oil resistance.
Ring shaped seal protects case of power steering system
PatentInactiveDE19845205A1
Innovation
- The seal design incorporates two distinct materials: heavy rubber for end sections and soft membrane for the center, allowing for both stability and flexibility.
- The soft membrane center of the seal absorbs the movement between the axle and housing, reducing wear and extending the seal's lifespan.
- The ring-shaped design provides comprehensive protection for the power steering system case, effectively sealing the interface between the valve housing and axle.
Environmental Impact of Power Steering Fluids
Power steering fluids, while essential for the smooth operation of vehicle steering systems, have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. These fluids, typically composed of mineral oils or synthetic compounds, can pose substantial risks to ecosystems when improperly disposed of or leaked into the environment. When released into soil or water bodies, power steering fluids can contaminate groundwater, disrupt aquatic ecosystems, and harm plant and animal life.
The persistence of these fluids in the environment is a major concern. Many power steering fluids are not readily biodegradable, meaning they can remain in ecosystems for extended periods, potentially causing long-term damage. This persistence can lead to bioaccumulation in food chains, affecting not only immediate wildlife but also higher-order consumers, including humans.
Leaks and spills during vehicle maintenance or accidents are common sources of environmental contamination. Even small, chronic leaks can accumulate over time, leading to significant pollution in urban areas where vehicle density is high. Runoff from roads and parking lots can carry these contaminants into storm drains and eventually into natural water bodies, impacting aquatic life and water quality.
The production and disposal of power steering fluids also contribute to their environmental footprint. The manufacturing process involves the extraction and processing of petroleum products, which has its own set of environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and potential for oil spills. End-of-life disposal presents additional challenges, as improper handling can lead to direct environmental contamination.
In response to these concerns, there has been a push towards developing more environmentally friendly power steering fluids. Bio-based fluids derived from renewable resources are emerging as potential alternatives, offering improved biodegradability and reduced toxicity. Additionally, synthetic fluids with enhanced longevity are being developed to reduce the frequency of fluid changes and, consequently, the volume of waste generated.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the environmental risks associated with power steering fluids. Stricter regulations on disposal and handling are being implemented in many jurisdictions, alongside incentives for the development and adoption of more sustainable alternatives. These measures aim to mitigate the environmental impact of power steering fluids throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
As the automotive industry shifts towards electric and hybrid vehicles, which often use electric power steering systems, the reliance on traditional hydraulic power steering fluids is expected to decrease. This transition could significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with these fluids in the long term. However, the large existing fleet of vehicles with hydraulic systems ensures that the environmental management of power steering fluids will remain a relevant issue for years to come.
The persistence of these fluids in the environment is a major concern. Many power steering fluids are not readily biodegradable, meaning they can remain in ecosystems for extended periods, potentially causing long-term damage. This persistence can lead to bioaccumulation in food chains, affecting not only immediate wildlife but also higher-order consumers, including humans.
Leaks and spills during vehicle maintenance or accidents are common sources of environmental contamination. Even small, chronic leaks can accumulate over time, leading to significant pollution in urban areas where vehicle density is high. Runoff from roads and parking lots can carry these contaminants into storm drains and eventually into natural water bodies, impacting aquatic life and water quality.
The production and disposal of power steering fluids also contribute to their environmental footprint. The manufacturing process involves the extraction and processing of petroleum products, which has its own set of environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and potential for oil spills. End-of-life disposal presents additional challenges, as improper handling can lead to direct environmental contamination.
In response to these concerns, there has been a push towards developing more environmentally friendly power steering fluids. Bio-based fluids derived from renewable resources are emerging as potential alternatives, offering improved biodegradability and reduced toxicity. Additionally, synthetic fluids with enhanced longevity are being developed to reduce the frequency of fluid changes and, consequently, the volume of waste generated.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the environmental risks associated with power steering fluids. Stricter regulations on disposal and handling are being implemented in many jurisdictions, alongside incentives for the development and adoption of more sustainable alternatives. These measures aim to mitigate the environmental impact of power steering fluids throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
As the automotive industry shifts towards electric and hybrid vehicles, which often use electric power steering systems, the reliance on traditional hydraulic power steering fluids is expected to decrease. This transition could significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with these fluids in the long term. However, the large existing fleet of vehicles with hydraulic systems ensures that the environmental management of power steering fluids will remain a relevant issue for years to come.
Regulatory Standards for Automotive Fluids
Regulatory standards for automotive fluids play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, performance, and environmental compatibility of power steering systems. These standards are established and enforced by various regulatory bodies, including the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and government agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States.
The SAE has developed specific standards for power steering fluids, such as SAE J1703 and SAE J1704, which define the minimum performance requirements for these fluids. These standards cover aspects like viscosity, boiling point, corrosion protection, and compatibility with rubber seals. The ISO has also established standards, including ISO 4925, which specifies the requirements for brake fluids used in hydraulic brake and clutch systems of road vehicles.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of automotive fluids. The EPA, for instance, has implemented regulations to control the disposal and recycling of used power steering fluids, as well as to limit the volatile organic compound (VOC) content in these fluids. These regulations aim to reduce air and water pollution associated with automotive fluid production and use.
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on the development of environmentally friendly power steering fluids. This has led to the introduction of biodegradable and non-toxic formulations that meet or exceed existing regulatory standards. Manufacturers are now required to provide detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for their power steering fluids, outlining the chemical composition, potential hazards, and proper handling procedures.
The interaction between power steering fluids and rubber seals is a critical aspect addressed by regulatory standards. These standards typically require that power steering fluids do not cause excessive swelling, shrinkage, or degradation of rubber seals over time. Manufacturers must conduct extensive compatibility tests to ensure that their fluids meet these requirements across a wide range of operating temperatures and conditions.
Regulatory bodies also set standards for the labeling and packaging of power steering fluids. These standards ensure that consumers have access to accurate information about the fluid's specifications, intended use, and any potential hazards. Additionally, there are regulations governing the transportation and storage of these fluids to prevent spills and contamination.
As automotive technology continues to evolve, regulatory standards for power steering fluids are also adapting. With the increasing adoption of electric power steering systems, new standards are being developed to address the specific requirements of these systems, including their interaction with electronic components and their overall environmental impact.
The SAE has developed specific standards for power steering fluids, such as SAE J1703 and SAE J1704, which define the minimum performance requirements for these fluids. These standards cover aspects like viscosity, boiling point, corrosion protection, and compatibility with rubber seals. The ISO has also established standards, including ISO 4925, which specifies the requirements for brake fluids used in hydraulic brake and clutch systems of road vehicles.
Regulatory bodies also focus on the environmental impact of automotive fluids. The EPA, for instance, has implemented regulations to control the disposal and recycling of used power steering fluids, as well as to limit the volatile organic compound (VOC) content in these fluids. These regulations aim to reduce air and water pollution associated with automotive fluid production and use.
In recent years, there has been an increased emphasis on the development of environmentally friendly power steering fluids. This has led to the introduction of biodegradable and non-toxic formulations that meet or exceed existing regulatory standards. Manufacturers are now required to provide detailed safety data sheets (SDS) for their power steering fluids, outlining the chemical composition, potential hazards, and proper handling procedures.
The interaction between power steering fluids and rubber seals is a critical aspect addressed by regulatory standards. These standards typically require that power steering fluids do not cause excessive swelling, shrinkage, or degradation of rubber seals over time. Manufacturers must conduct extensive compatibility tests to ensure that their fluids meet these requirements across a wide range of operating temperatures and conditions.
Regulatory bodies also set standards for the labeling and packaging of power steering fluids. These standards ensure that consumers have access to accurate information about the fluid's specifications, intended use, and any potential hazards. Additionally, there are regulations governing the transportation and storage of these fluids to prevent spills and contamination.
As automotive technology continues to evolve, regulatory standards for power steering fluids are also adapting. With the increasing adoption of electric power steering systems, new standards are being developed to address the specific requirements of these systems, including their interaction with electronic components and their overall environmental impact.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!