How to Enhance Lithium Nitrate Thermal Storage Density
OCT 9, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Nitrate Thermal Storage Background and Objectives
Thermal energy storage (TES) systems have emerged as a critical component in the global transition towards renewable energy, with lithium nitrate (LiNO3) standing out as a promising material for high-temperature applications. The evolution of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring molten salt mixtures for concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. Over the past two decades, significant advancements have been made in understanding the thermophysical properties and performance characteristics of lithium nitrate, both as a single component and in eutectic mixtures.
The current technological trajectory indicates a growing interest in enhancing the energy density of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage systems, driven by the need for more compact and efficient energy storage solutions. Recent research has focused on improving the specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and phase change properties of lithium nitrate through various modification techniques, including nanoparticle addition, encapsulation methods, and composite material development.
The primary technical objective in this field is to significantly increase the thermal storage density of lithium nitrate-based systems while maintaining or improving other critical parameters such as cycling stability, cost-effectiveness, and operational safety. Specifically, the industry aims to achieve a 30-50% improvement in energy density compared to conventional molten salt systems, which would revolutionize the economics and practicality of thermal energy storage applications.
Current technical targets include developing lithium nitrate formulations with specific heat capacities exceeding 2 J/g·K in the liquid phase, melting points optimized for specific applications (typically between 250-350°C), and thermal conductivities above 1 W/m·K. Additionally, there is a focus on extending the operational temperature range to enable broader application potential across various industrial sectors.
The evolution of this technology is closely aligned with global sustainability goals, as enhanced thermal storage systems can significantly improve the dispatchability and reliability of renewable energy sources, particularly solar thermal power. The development of high-density lithium nitrate thermal storage also intersects with broader trends in materials science, including the exploration of nanomaterials, composite structures, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for lithium nitrate thermal storage is expected to incorporate innovations from adjacent fields such as battery technology, advanced ceramics, and computational materials science. These cross-disciplinary influences may accelerate the development of next-generation thermal storage solutions with unprecedented energy densities and performance characteristics.
The current technological trajectory indicates a growing interest in enhancing the energy density of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage systems, driven by the need for more compact and efficient energy storage solutions. Recent research has focused on improving the specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and phase change properties of lithium nitrate through various modification techniques, including nanoparticle addition, encapsulation methods, and composite material development.
The primary technical objective in this field is to significantly increase the thermal storage density of lithium nitrate-based systems while maintaining or improving other critical parameters such as cycling stability, cost-effectiveness, and operational safety. Specifically, the industry aims to achieve a 30-50% improvement in energy density compared to conventional molten salt systems, which would revolutionize the economics and practicality of thermal energy storage applications.
Current technical targets include developing lithium nitrate formulations with specific heat capacities exceeding 2 J/g·K in the liquid phase, melting points optimized for specific applications (typically between 250-350°C), and thermal conductivities above 1 W/m·K. Additionally, there is a focus on extending the operational temperature range to enable broader application potential across various industrial sectors.
The evolution of this technology is closely aligned with global sustainability goals, as enhanced thermal storage systems can significantly improve the dispatchability and reliability of renewable energy sources, particularly solar thermal power. The development of high-density lithium nitrate thermal storage also intersects with broader trends in materials science, including the exploration of nanomaterials, composite structures, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Looking forward, the technological roadmap for lithium nitrate thermal storage is expected to incorporate innovations from adjacent fields such as battery technology, advanced ceramics, and computational materials science. These cross-disciplinary influences may accelerate the development of next-generation thermal storage solutions with unprecedented energy densities and performance characteristics.
Market Analysis for High-Density Thermal Storage Solutions
The global thermal energy storage market is experiencing significant growth, projected to reach $7.5 billion by 2025 with a CAGR of 10.2% from 2020. High-density thermal storage solutions, particularly those utilizing lithium nitrate, are positioned as critical components in this expanding market due to their superior energy density capabilities compared to conventional materials.
The renewable energy sector represents the largest demand driver for advanced thermal storage technologies. As solar and wind power installations continue to increase globally, the need for efficient energy storage solutions to address intermittency issues grows proportionally. Lithium nitrate-based thermal storage systems offer particular value in concentrated solar power (CSP) applications, where the market is expected to double in capacity by 2026.
Industrial process heat applications constitute another substantial market segment, valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2021. Manufacturing sectors requiring high-temperature processes, including metallurgy, glass production, and chemical processing, are actively seeking more efficient thermal storage solutions to reduce operational costs and carbon emissions. Enhanced lithium nitrate systems could capture up to 15% of this market within five years.
The building sector presents a growing opportunity for high-density thermal storage technologies. Commercial and residential heating systems increasingly incorporate thermal storage to optimize energy consumption and reduce peak demand charges. This market segment is projected to grow at 12.8% annually through 2027, with particular strength in regions with variable electricity pricing structures.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows concentration in regions with high renewable energy penetration and ambitious decarbonization targets. Europe leads adoption with approximately 38% market share, followed by North America (27%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). China's recent policy shifts toward renewable energy integration have created a rapidly expanding market for advanced thermal storage technologies, with annual growth rates exceeding 15%.
Pricing sensitivity analysis indicates that enhanced lithium nitrate storage systems must achieve a levelized cost of storage below $0.15/kWh to remain competitive with alternative technologies. Current costs average $0.22/kWh, highlighting the need for density improvements to drive down material requirements and system costs.
Market forecasts suggest that high-density thermal storage solutions could capture 22% of the overall thermal storage market by 2028, representing a significant opportunity for technologies that successfully enhance lithium nitrate's thermal storage density. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing regulatory pressure for clean energy solutions and the continuing decline in renewable generation costs.
The renewable energy sector represents the largest demand driver for advanced thermal storage technologies. As solar and wind power installations continue to increase globally, the need for efficient energy storage solutions to address intermittency issues grows proportionally. Lithium nitrate-based thermal storage systems offer particular value in concentrated solar power (CSP) applications, where the market is expected to double in capacity by 2026.
Industrial process heat applications constitute another substantial market segment, valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2021. Manufacturing sectors requiring high-temperature processes, including metallurgy, glass production, and chemical processing, are actively seeking more efficient thermal storage solutions to reduce operational costs and carbon emissions. Enhanced lithium nitrate systems could capture up to 15% of this market within five years.
The building sector presents a growing opportunity for high-density thermal storage technologies. Commercial and residential heating systems increasingly incorporate thermal storage to optimize energy consumption and reduce peak demand charges. This market segment is projected to grow at 12.8% annually through 2027, with particular strength in regions with variable electricity pricing structures.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows concentration in regions with high renewable energy penetration and ambitious decarbonization targets. Europe leads adoption with approximately 38% market share, followed by North America (27%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). China's recent policy shifts toward renewable energy integration have created a rapidly expanding market for advanced thermal storage technologies, with annual growth rates exceeding 15%.
Pricing sensitivity analysis indicates that enhanced lithium nitrate storage systems must achieve a levelized cost of storage below $0.15/kWh to remain competitive with alternative technologies. Current costs average $0.22/kWh, highlighting the need for density improvements to drive down material requirements and system costs.
Market forecasts suggest that high-density thermal storage solutions could capture 22% of the overall thermal storage market by 2028, representing a significant opportunity for technologies that successfully enhance lithium nitrate's thermal storage density. This growth trajectory is supported by increasing regulatory pressure for clean energy solutions and the continuing decline in renewable generation costs.
Current Limitations and Technical Challenges in Lithium Nitrate Systems
Despite the promising attributes of lithium nitrate (LiNO3) as a thermal energy storage material, several significant limitations and technical challenges impede its widespread application and optimal performance. The primary constraint is its relatively modest thermal storage density compared to other molten salt systems. While LiNO3 offers advantages in terms of lower melting point (253°C) and good thermal stability, its volumetric and gravimetric energy storage capacities remain insufficient for many high-density applications, particularly in space-constrained environments.
The thermal conductivity of lithium nitrate presents another substantial challenge. Like many molten salt systems, LiNO3 exhibits relatively low thermal conductivity (approximately 0.5-0.6 W/m·K in liquid phase), which restricts heat transfer rates during charging and discharging cycles. This limitation significantly impacts system response times and overall efficiency, necessitating complex heat exchanger designs that increase system complexity and cost.
Corrosion issues constitute a persistent technical barrier in LiNO3 systems. At elevated temperatures, lithium nitrate demonstrates aggressive corrosive behavior toward common containment materials, particularly certain metal alloys. This corrosivity accelerates during thermal cycling and in the presence of impurities, leading to reduced system longevity and potential safety concerns. The selection of appropriate containment materials that balance corrosion resistance with cost-effectiveness remains challenging.
Phase separation and salt segregation during repeated thermal cycling represent another significant technical hurdle. Over multiple charge-discharge cycles, LiNO3 systems can experience compositional changes and phase segregation, leading to altered melting points, reduced thermal performance, and potential system failure. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in systems utilizing lithium nitrate in eutectic mixtures with other nitrate salts.
Supercooling effects in lithium nitrate systems further complicate their practical implementation. LiNO3 often exhibits significant supercooling behavior, where the material remains in liquid state below its theoretical crystallization temperature. This unpredictable crystallization behavior creates challenges for system control and reliable energy recovery, particularly in applications requiring precise thermal management.
The economic viability of lithium nitrate systems faces challenges due to raw material costs and processing requirements. With increasing demand for lithium compounds in battery applications, price volatility and supply chain constraints affect the cost-effectiveness of large-scale LiNO3 thermal storage implementations. Additionally, the high purity requirements for optimal thermal performance necessitate costly purification processes.
Environmental and safety considerations also present limitations. While generally considered less hazardous than some alternative thermal storage materials, lithium nitrate still poses environmental concerns related to disposal and potential water contamination. Safety protocols for handling, particularly at elevated temperatures, require careful system design and operational procedures.
The thermal conductivity of lithium nitrate presents another substantial challenge. Like many molten salt systems, LiNO3 exhibits relatively low thermal conductivity (approximately 0.5-0.6 W/m·K in liquid phase), which restricts heat transfer rates during charging and discharging cycles. This limitation significantly impacts system response times and overall efficiency, necessitating complex heat exchanger designs that increase system complexity and cost.
Corrosion issues constitute a persistent technical barrier in LiNO3 systems. At elevated temperatures, lithium nitrate demonstrates aggressive corrosive behavior toward common containment materials, particularly certain metal alloys. This corrosivity accelerates during thermal cycling and in the presence of impurities, leading to reduced system longevity and potential safety concerns. The selection of appropriate containment materials that balance corrosion resistance with cost-effectiveness remains challenging.
Phase separation and salt segregation during repeated thermal cycling represent another significant technical hurdle. Over multiple charge-discharge cycles, LiNO3 systems can experience compositional changes and phase segregation, leading to altered melting points, reduced thermal performance, and potential system failure. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in systems utilizing lithium nitrate in eutectic mixtures with other nitrate salts.
Supercooling effects in lithium nitrate systems further complicate their practical implementation. LiNO3 often exhibits significant supercooling behavior, where the material remains in liquid state below its theoretical crystallization temperature. This unpredictable crystallization behavior creates challenges for system control and reliable energy recovery, particularly in applications requiring precise thermal management.
The economic viability of lithium nitrate systems faces challenges due to raw material costs and processing requirements. With increasing demand for lithium compounds in battery applications, price volatility and supply chain constraints affect the cost-effectiveness of large-scale LiNO3 thermal storage implementations. Additionally, the high purity requirements for optimal thermal performance necessitate costly purification processes.
Environmental and safety considerations also present limitations. While generally considered less hazardous than some alternative thermal storage materials, lithium nitrate still poses environmental concerns related to disposal and potential water contamination. Safety protocols for handling, particularly at elevated temperatures, require careful system design and operational procedures.
Current Approaches to Enhance Lithium Nitrate Storage Density
01 Lithium nitrate as phase change material for thermal energy storage
Lithium nitrate is utilized as a phase change material (PCM) in thermal energy storage systems due to its high thermal storage density. When used alone or in mixtures, lithium nitrate undergoes phase transitions that allow it to store and release large amounts of thermal energy. The high latent heat of fusion and specific heat capacity of lithium nitrate make it particularly effective for applications requiring high energy density storage in relatively compact systems.- Lithium nitrate as a thermal energy storage material: Lithium nitrate is used as a thermal energy storage material due to its high energy storage density. It has a high heat of fusion and can store significant amounts of thermal energy during phase transitions. When incorporated into thermal storage systems, lithium nitrate can efficiently store and release heat, making it valuable for various energy storage applications. Its high thermal storage density makes it particularly suitable for compact thermal energy storage systems.
- Lithium nitrate in molten salt mixtures for thermal storage: Lithium nitrate can be combined with other salts to form molten salt mixtures with enhanced thermal storage properties. These mixtures often have lower melting points and higher thermal stability than single-component systems. The addition of lithium nitrate to salt mixtures can increase the overall thermal storage density and improve heat transfer characteristics. These molten salt mixtures are commonly used in concentrated solar power plants and other high-temperature thermal storage applications.
- Lithium nitrate in battery thermal management systems: Lithium nitrate is utilized in thermal management systems for batteries to regulate temperature and enhance performance. The high thermal storage density of lithium nitrate allows it to absorb excess heat during battery operation and discharge cycles. This helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, extend battery life, and improve safety. The integration of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage materials in battery systems is particularly valuable for high-power applications where thermal management is critical.
- Encapsulation techniques for lithium nitrate thermal storage: Various encapsulation methods are employed to contain lithium nitrate for thermal storage applications. These techniques include microencapsulation, macroencapsulation, and composite formation with supporting materials. Encapsulation helps prevent leakage during the molten phase, improves thermal cycling stability, and enhances heat transfer characteristics. These containment strategies allow for more efficient utilization of lithium nitrate's high thermal storage density while mitigating potential issues related to corrosion and material compatibility.
- Enhancement of lithium nitrate thermal properties through additives: The thermal storage density and performance of lithium nitrate can be enhanced through the addition of various additives. These additives may include nanoparticles, other salts, or specialized compounds that modify the thermal properties. Such enhancements can increase the specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity, or phase change characteristics of lithium nitrate-based storage materials. Research in this area focuses on optimizing formulations to achieve maximum thermal storage density while maintaining long-term stability and performance.
02 Lithium nitrate in molten salt mixtures for enhanced thermal storage
Incorporating lithium nitrate into molten salt mixtures significantly enhances thermal storage density. These mixtures, often containing other nitrate salts such as sodium, potassium, or calcium nitrates, demonstrate improved thermal properties compared to single-component systems. The eutectic compositions containing lithium nitrate typically offer lower melting points while maintaining high thermal energy storage capacity, making them suitable for concentrated solar power plants and other high-temperature thermal storage applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Battery applications utilizing lithium nitrate thermal properties
Lithium nitrate is incorporated into battery systems to manage thermal energy and improve performance. The high thermal storage density of lithium nitrate helps regulate temperature within battery cells, preventing overheating while enhancing efficiency and safety. In certain lithium-sulfur and lithium-ion battery designs, lithium nitrate serves dual purposes: as an electrolyte additive and as a thermal management component, contributing to higher energy density and longer cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions04 Encapsulation and composite materials for lithium nitrate thermal storage
Encapsulation techniques and composite material formulations enhance the practical application of lithium nitrate for thermal storage. By incorporating lithium nitrate into supporting matrices or encapsulating it within protective shells, these approaches prevent leakage during the molten phase while maintaining high thermal storage density. These composites often combine the high energy density of lithium nitrate with improved mechanical stability, thermal conductivity, and cycle stability, making them suitable for building materials, textiles, and industrial heat storage applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced manufacturing and processing methods for lithium nitrate thermal storage systems
Innovative manufacturing and processing methods are being developed to optimize lithium nitrate-based thermal storage systems. These include specialized techniques for producing nanostructured lithium nitrate materials, precise control of crystallization processes, and advanced coating technologies. Such methods aim to maximize thermal storage density while addressing challenges related to corrosion, thermal cycling stability, and heat transfer efficiency. The resulting high-performance thermal storage materials offer improved energy density, faster charging/discharging rates, and longer operational lifetimes.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Thermal Storage
The lithium nitrate thermal storage density enhancement market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by renewable energy integration and grid stability needs. The market size is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant value by 2030 due to clean energy transitions globally. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovations. Key players include established chemical giants like BASF, LG Chem, and Wacker Chemie who bring extensive materials expertise, alongside battery technology specialists such as Contemporary Amperex Technology, Samsung SDI, and Panasonic Holdings who contribute advanced energy storage knowledge. Academic institutions including Hunan University and Fuzhou University are advancing fundamental research, while companies like Applied Materials and Siemens provide engineering solutions for implementation. The competitive landscape features collaboration between research institutions and industrial partners to overcome technical challenges in thermal conductivity and cycling stability.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced phase change materials (PCMs) incorporating lithium nitrate to enhance thermal storage density. Their approach involves creating eutectic mixtures of lithium nitrate with other nitrate salts (such as potassium and sodium nitrates) to optimize melting points and increase energy storage capacity. BASF's technology utilizes nanostructured additives to improve the thermal conductivity of lithium nitrate-based storage materials, addressing one of the key limitations of pure lithium nitrate systems. Their research has demonstrated that incorporating carbon-based nanomaterials into lithium nitrate mixtures can enhance thermal conductivity by up to 40%, while maintaining high energy storage density. BASF has also developed encapsulation techniques to prevent leakage and segregation during phase change cycles, significantly improving the long-term stability of lithium nitrate thermal storage systems.
Strengths: Superior thermal conductivity enhancement through proprietary nanomaterial additives; excellent cycling stability through advanced encapsulation techniques; established manufacturing infrastructure for commercial scaling. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional thermal storage materials; potential environmental concerns with some nanomaterial additives; limited performance data in extreme temperature conditions.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem has pioneered a composite material approach to enhance lithium nitrate thermal storage density. Their technology combines lithium nitrate with specialized ceramic matrices to create a stable, high-density thermal storage medium. The company's proprietary manufacturing process involves the precise control of lithium nitrate crystal formation within porous ceramic structures, which prevents salt migration during thermal cycling and maintains consistent performance over thousands of cycles. LG Chem's research has shown that their composite materials can achieve thermal storage densities up to 30% higher than conventional salt mixtures while maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures. Additionally, they've developed surface modification techniques for the ceramic matrices that enhance wetting by molten lithium nitrate, improving heat transfer characteristics and charge/discharge rates. The company has also integrated these materials into modular thermal storage units designed for grid-scale energy storage applications.
Strengths: Exceptional cycling stability (>5000 cycles with minimal degradation); higher thermal storage density than conventional materials; modular design approach enables scalable deployment. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process increases production costs; ceramic components add weight to storage systems; potential for thermal stress fractures in large-scale implementations.
Key Patents and Research on Lithium Nitrate Density Enhancement
Heat-storage means
PatentInactiveEP1501908A1
Innovation
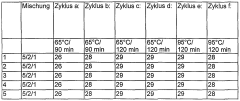
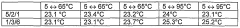
- A mixture of lithium nitrate trihydrate with magnesium nitrate, nickel nitrate, strontium nitrate, magnesium acetate, nickel acetate, or strontium acetate, along with their hydrates, is used as a nucleating agent to enhance crystallization, allowing for reliable nucleation up to 95°C without needing cooling below room temperature, and optionally adding alkali or alkaline earth metal nitrates to adjust the melting point.
Heat-storage means
PatentWO2003095584A1
Innovation
- A mixture of lithium nitrate trihydrate with nucleating agents such as magnesium nitrate, nickel nitrate, strontium nitrate, magnesium acetate, and strontium acetate, or their hydrates, is used to enhance nucleation, allowing reliable crystallization up to 95°C without cooling below room temperature, with the nucleating agents being mixed with lithium nitrate trihydrate and annealed to achieve improved thermal stability.
Material Science Advancements for Thermal Storage Applications
Recent advancements in material science have significantly contributed to enhancing thermal storage capabilities, particularly for lithium nitrate-based systems. The development of novel composite materials has been instrumental in addressing the inherent limitations of traditional thermal storage media. By incorporating nanostructured materials such as carbon nanotubes and graphene into lithium nitrate matrices, researchers have achieved remarkable improvements in thermal conductivity while maintaining high energy density.
Engineered microstructures represent another frontier in material science for thermal storage applications. Through precise control of crystallization processes, scientists have developed methods to create optimized pore structures within lithium nitrate compounds. These controlled microstructures facilitate better heat transfer characteristics while minimizing volume expansion issues during phase transitions, resulting in more stable and efficient thermal storage systems.
Surface modification techniques have emerged as effective approaches to enhance the thermal properties of lithium nitrate. By applying specialized coatings or chemical treatments to lithium nitrate particles, researchers have successfully reduced corrosion issues and improved compatibility with containment materials. These modifications have extended the operational lifespan of thermal storage systems while maintaining high energy density characteristics.
Doping strategies involving the introduction of carefully selected elements into lithium nitrate structures have yielded promising results. Elements such as calcium, potassium, and certain transition metals have been shown to lower melting points while increasing specific heat capacity. These compositional adjustments enable more efficient energy storage and release cycles, particularly in concentrated solar power applications where temperature management is critical.
Encapsulation technologies represent a significant breakthrough in addressing containment challenges. Advanced polymer shells and ceramic microencapsulation techniques have been developed to contain lithium nitrate compounds effectively during phase changes. These encapsulation methods prevent leakage and segregation issues while facilitating better heat transfer characteristics through increased surface area to volume ratios.
Computational materials science has accelerated the discovery and optimization of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage materials. Machine learning algorithms coupled with high-throughput screening methods have enabled researchers to predict promising material combinations and structural configurations without extensive experimental testing. These computational approaches have significantly reduced development timelines and identified non-intuitive material combinations with superior thermal storage properties.
Engineered microstructures represent another frontier in material science for thermal storage applications. Through precise control of crystallization processes, scientists have developed methods to create optimized pore structures within lithium nitrate compounds. These controlled microstructures facilitate better heat transfer characteristics while minimizing volume expansion issues during phase transitions, resulting in more stable and efficient thermal storage systems.
Surface modification techniques have emerged as effective approaches to enhance the thermal properties of lithium nitrate. By applying specialized coatings or chemical treatments to lithium nitrate particles, researchers have successfully reduced corrosion issues and improved compatibility with containment materials. These modifications have extended the operational lifespan of thermal storage systems while maintaining high energy density characteristics.
Doping strategies involving the introduction of carefully selected elements into lithium nitrate structures have yielded promising results. Elements such as calcium, potassium, and certain transition metals have been shown to lower melting points while increasing specific heat capacity. These compositional adjustments enable more efficient energy storage and release cycles, particularly in concentrated solar power applications where temperature management is critical.
Encapsulation technologies represent a significant breakthrough in addressing containment challenges. Advanced polymer shells and ceramic microencapsulation techniques have been developed to contain lithium nitrate compounds effectively during phase changes. These encapsulation methods prevent leakage and segregation issues while facilitating better heat transfer characteristics through increased surface area to volume ratios.
Computational materials science has accelerated the discovery and optimization of lithium nitrate-based thermal storage materials. Machine learning algorithms coupled with high-throughput screening methods have enabled researchers to predict promising material combinations and structural configurations without extensive experimental testing. These computational approaches have significantly reduced development timelines and identified non-intuitive material combinations with superior thermal storage properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of enhancing lithium nitrate thermal storage density extends beyond mere technical considerations, encompassing broader sustainability implications. Lithium nitrate-based thermal energy storage systems offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional fossil fuel alternatives. By enabling more efficient renewable energy integration, these systems contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and decreased reliance on carbon-intensive power generation methods. The enhanced storage density directly correlates with smaller physical footprints for energy storage facilities, minimizing land use requirements and associated ecosystem disruption.
However, the environmental lifecycle assessment reveals several challenges. Mining and processing lithium resources can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial water consumption in extraction regions. The production process of high-purity lithium nitrate is energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits if powered by non-renewable energy sources. These environmental costs must be carefully weighed against the long-term sustainability benefits of improved thermal storage systems.
Recycling and end-of-life management represent critical sustainability considerations. Current recycling rates for lithium compounds remain suboptimal, with technological and economic barriers limiting widespread recovery. Developing closed-loop systems for lithium nitrate thermal storage materials could significantly enhance the sustainability profile of these technologies, reducing primary resource demands and minimizing waste generation.
Water usage presents another important environmental dimension. Traditional lithium extraction can consume between 500,000 to 2 million gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. Enhancing storage density could potentially reduce the total material requirements, thereby decreasing associated water footprints, but process improvements in lithium production remain essential for comprehensive sustainability.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize environmental performance metrics for energy storage technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive and similar regulations worldwide are evolving to include thermal storage materials, establishing standards for resource efficiency, carbon footprints, and recycling requirements. Future enhancements to lithium nitrate storage density must align with these emerging regulatory landscapes to ensure market viability.
The sustainability equation must also consider the enabling effect of improved thermal storage on renewable energy deployment. Enhanced lithium nitrate storage systems can increase solar thermal plant efficiency by 15-20%, potentially avoiding 0.6-0.8 kg CO₂ emissions per kWh compared to fossil fuel alternatives. This multiplicative environmental benefit often outweighs the direct impacts of material production when assessed on a full lifecycle basis.
However, the environmental lifecycle assessment reveals several challenges. Mining and processing lithium resources can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and substantial water consumption in extraction regions. The production process of high-purity lithium nitrate is energy-intensive, potentially offsetting some of the environmental benefits if powered by non-renewable energy sources. These environmental costs must be carefully weighed against the long-term sustainability benefits of improved thermal storage systems.
Recycling and end-of-life management represent critical sustainability considerations. Current recycling rates for lithium compounds remain suboptimal, with technological and economic barriers limiting widespread recovery. Developing closed-loop systems for lithium nitrate thermal storage materials could significantly enhance the sustainability profile of these technologies, reducing primary resource demands and minimizing waste generation.
Water usage presents another important environmental dimension. Traditional lithium extraction can consume between 500,000 to 2 million gallons of water per ton of lithium produced. Enhancing storage density could potentially reduce the total material requirements, thereby decreasing associated water footprints, but process improvements in lithium production remain essential for comprehensive sustainability.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize environmental performance metrics for energy storage technologies. The European Union's Battery Directive and similar regulations worldwide are evolving to include thermal storage materials, establishing standards for resource efficiency, carbon footprints, and recycling requirements. Future enhancements to lithium nitrate storage density must align with these emerging regulatory landscapes to ensure market viability.
The sustainability equation must also consider the enabling effect of improved thermal storage on renewable energy deployment. Enhanced lithium nitrate storage systems can increase solar thermal plant efficiency by 15-20%, potentially avoiding 0.6-0.8 kg CO₂ emissions per kWh compared to fossil fuel alternatives. This multiplicative environmental benefit often outweighs the direct impacts of material production when assessed on a full lifecycle basis.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!