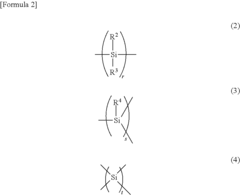How to Implement Polysilane in High-Temperature Applications?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Background and High-Temp Goals
Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers with a backbone consisting of silicon-silicon bonds, have garnered significant attention in materials science and engineering over the past few decades. These unique polymers were first synthesized in the 1920s, but their potential for high-temperature applications has only recently been recognized and explored in depth.
The evolution of polysilane technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, polysilanes were primarily studied for their photochemical and electrical properties. However, as research progressed, their thermal stability and resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures became increasingly apparent, opening up new avenues for their application in high-temperature environments.
The development of polysilanes for high-temperature applications is driven by the growing demand for materials that can withstand extreme conditions in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. As traditional organic polymers often fail under high-temperature stress, polysilanes offer a promising alternative due to their inorganic backbone structure.
One of the primary goals in implementing polysilanes for high-temperature applications is to enhance their thermal stability further. Current research aims to develop polysilane derivatives that can maintain their structural integrity and functional properties at temperatures exceeding 300°C, with some ambitious targets pushing beyond 500°C.
Another critical objective is to improve the processability of polysilanes while maintaining their high-temperature performance. This involves developing new synthesis methods and modifying the polymer structure to achieve better solubility and easier fabrication into various forms such as films, coatings, and composite materials.
Researchers are also focusing on tailoring the electronic and optical properties of polysilanes for specific high-temperature applications. This includes enhancing their conductivity at elevated temperatures for potential use in sensors and electronic components that operate in extreme environments.
The implementation of polysilanes in high-temperature applications also necessitates a thorough understanding of their long-term behavior under prolonged exposure to heat and other environmental factors. Consequently, accelerated aging studies and real-world testing are crucial aspects of the ongoing research and development efforts.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly and cost-effective synthesis methods for polysilanes. This aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable materials and processes in the chemical industry.
The evolution of polysilane technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, polysilanes were primarily studied for their photochemical and electrical properties. However, as research progressed, their thermal stability and resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures became increasingly apparent, opening up new avenues for their application in high-temperature environments.
The development of polysilanes for high-temperature applications is driven by the growing demand for materials that can withstand extreme conditions in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics. As traditional organic polymers often fail under high-temperature stress, polysilanes offer a promising alternative due to their inorganic backbone structure.
One of the primary goals in implementing polysilanes for high-temperature applications is to enhance their thermal stability further. Current research aims to develop polysilane derivatives that can maintain their structural integrity and functional properties at temperatures exceeding 300°C, with some ambitious targets pushing beyond 500°C.
Another critical objective is to improve the processability of polysilanes while maintaining their high-temperature performance. This involves developing new synthesis methods and modifying the polymer structure to achieve better solubility and easier fabrication into various forms such as films, coatings, and composite materials.
Researchers are also focusing on tailoring the electronic and optical properties of polysilanes for specific high-temperature applications. This includes enhancing their conductivity at elevated temperatures for potential use in sensors and electronic components that operate in extreme environments.
The implementation of polysilanes in high-temperature applications also necessitates a thorough understanding of their long-term behavior under prolonged exposure to heat and other environmental factors. Consequently, accelerated aging studies and real-world testing are crucial aspects of the ongoing research and development efforts.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly and cost-effective synthesis methods for polysilanes. This aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable materials and processes in the chemical industry.
Market Demand for High-Temp Materials
The demand for high-temperature materials has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the need for enhanced performance and durability in extreme environments. Polysilane, a class of silicon-based polymers, has emerged as a promising candidate for high-temperature applications due to its unique properties and potential advantages over traditional materials.
In the aerospace and automotive sectors, there is a growing market for materials that can withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining structural integrity. Engine components, exhaust systems, and thermal insulation materials require materials capable of operating at temperatures exceeding 300°C. Polysilane-based composites offer potential solutions to these challenges, with their ability to retain mechanical properties at elevated temperatures and resist thermal degradation.
The electronics industry also presents a significant market opportunity for high-temperature materials. As electronic devices become more compact and powerful, heat management becomes increasingly critical. Polysilane-based materials could find applications in thermal interface materials, circuit boards, and packaging for high-temperature electronics, addressing the industry's need for materials that can operate reliably in harsh thermal environments.
Energy production and storage systems represent another key market for high-temperature materials. Solar thermal power plants, fuel cells, and advanced battery technologies all require materials that can function efficiently at elevated temperatures. Polysilane-based materials could potentially enhance the performance and longevity of these systems, contributing to the growth of renewable energy technologies.
The chemical processing industry has a constant demand for materials that can withstand corrosive environments at high temperatures. Polysilane-based coatings and components could offer improved resistance to chemical attack and thermal stress, extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing maintenance costs in chemical plants and refineries.
Market analysis indicates that the global high-temperature materials market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors driving this growth include increasing industrialization, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and the push for energy efficiency across various sectors. The unique properties of polysilane make it a strong contender in this expanding market, potentially capturing a significant share as research and development efforts continue to improve its performance and cost-effectiveness.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of polysilane in high-temperature applications. These include the need for scalable production methods, optimization of material properties for specific applications, and demonstration of long-term reliability under real-world conditions. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in realizing the full market potential of polysilane-based high-temperature materials.
In the aerospace and automotive sectors, there is a growing market for materials that can withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining structural integrity. Engine components, exhaust systems, and thermal insulation materials require materials capable of operating at temperatures exceeding 300°C. Polysilane-based composites offer potential solutions to these challenges, with their ability to retain mechanical properties at elevated temperatures and resist thermal degradation.
The electronics industry also presents a significant market opportunity for high-temperature materials. As electronic devices become more compact and powerful, heat management becomes increasingly critical. Polysilane-based materials could find applications in thermal interface materials, circuit boards, and packaging for high-temperature electronics, addressing the industry's need for materials that can operate reliably in harsh thermal environments.
Energy production and storage systems represent another key market for high-temperature materials. Solar thermal power plants, fuel cells, and advanced battery technologies all require materials that can function efficiently at elevated temperatures. Polysilane-based materials could potentially enhance the performance and longevity of these systems, contributing to the growth of renewable energy technologies.
The chemical processing industry has a constant demand for materials that can withstand corrosive environments at high temperatures. Polysilane-based coatings and components could offer improved resistance to chemical attack and thermal stress, extending the lifespan of equipment and reducing maintenance costs in chemical plants and refineries.
Market analysis indicates that the global high-temperature materials market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Factors driving this growth include increasing industrialization, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, and the push for energy efficiency across various sectors. The unique properties of polysilane make it a strong contender in this expanding market, potentially capturing a significant share as research and development efforts continue to improve its performance and cost-effectiveness.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of polysilane in high-temperature applications. These include the need for scalable production methods, optimization of material properties for specific applications, and demonstration of long-term reliability under real-world conditions. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in realizing the full market potential of polysilane-based high-temperature materials.
Polysilane Challenges in High-Temp Applications
Polysilanes face significant challenges when applied in high-temperature environments, primarily due to their inherent thermal instability. The silicon-silicon backbone of polysilanes tends to degrade at elevated temperatures, typically above 300°C, leading to chain scission and loss of desired properties. This thermal degradation is a major hurdle in expanding the application scope of polysilanes to high-temperature scenarios.
One of the primary challenges is maintaining the structural integrity of polysilanes at high temperatures. The Si-Si bonds are susceptible to homolytic cleavage, resulting in the formation of silyl radicals. These radicals can initiate various side reactions, leading to crosslinking, chain rearrangement, or complete decomposition of the polymer. Consequently, the unique electronic and optical properties that make polysilanes attractive for many applications are compromised or lost entirely.
Another significant challenge is the oxidation of polysilanes at high temperatures, especially in the presence of oxygen. The Si-Si bonds are prone to oxidation, forming silicon oxides and potentially disrupting the polymer structure. This oxidation process can lead to a dramatic change in the material's properties, affecting its performance in high-temperature applications.
The volatility of low molecular weight silane species formed during thermal degradation poses another challenge. As the polymer chains break down, these volatile compounds can evaporate, leading to mass loss and changes in the material's physical properties. This phenomenon can result in dimensional instability and reduced performance of polysilane-based components in high-temperature environments.
Furthermore, the mechanical properties of polysilanes often deteriorate at elevated temperatures. The softening and potential melting of the polymer can lead to loss of structural integrity, making it challenging to maintain the desired shape and functionality of polysilane-based materials in high-temperature applications.
The incorporation of polysilanes into composite materials for high-temperature use presents additional challenges. Ensuring good interfacial adhesion between polysilanes and other components of the composite at elevated temperatures is crucial for maintaining overall material performance. Thermal expansion mismatches and potential chemical interactions between polysilanes and other materials in the composite can lead to delamination or other structural failures under high-temperature conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in polymer design and synthesis. Strategies such as incorporating thermally stable functional groups, increasing the molecular weight of polysilanes, or developing novel copolymer structures are being explored to enhance the high-temperature stability of polysilanes. Additionally, the development of protective coatings or encapsulation techniques may offer solutions to mitigate the effects of thermal degradation and oxidation in high-temperature environments.
One of the primary challenges is maintaining the structural integrity of polysilanes at high temperatures. The Si-Si bonds are susceptible to homolytic cleavage, resulting in the formation of silyl radicals. These radicals can initiate various side reactions, leading to crosslinking, chain rearrangement, or complete decomposition of the polymer. Consequently, the unique electronic and optical properties that make polysilanes attractive for many applications are compromised or lost entirely.
Another significant challenge is the oxidation of polysilanes at high temperatures, especially in the presence of oxygen. The Si-Si bonds are prone to oxidation, forming silicon oxides and potentially disrupting the polymer structure. This oxidation process can lead to a dramatic change in the material's properties, affecting its performance in high-temperature applications.
The volatility of low molecular weight silane species formed during thermal degradation poses another challenge. As the polymer chains break down, these volatile compounds can evaporate, leading to mass loss and changes in the material's physical properties. This phenomenon can result in dimensional instability and reduced performance of polysilane-based components in high-temperature environments.
Furthermore, the mechanical properties of polysilanes often deteriorate at elevated temperatures. The softening and potential melting of the polymer can lead to loss of structural integrity, making it challenging to maintain the desired shape and functionality of polysilane-based materials in high-temperature applications.
The incorporation of polysilanes into composite materials for high-temperature use presents additional challenges. Ensuring good interfacial adhesion between polysilanes and other components of the composite at elevated temperatures is crucial for maintaining overall material performance. Thermal expansion mismatches and potential chemical interactions between polysilanes and other materials in the composite can lead to delamination or other structural failures under high-temperature conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in polymer design and synthesis. Strategies such as incorporating thermally stable functional groups, increasing the molecular weight of polysilanes, or developing novel copolymer structures are being explored to enhance the high-temperature stability of polysilanes. Additionally, the development of protective coatings or encapsulation techniques may offer solutions to mitigate the effects of thermal degradation and oxidation in high-temperature environments.
Current High-Temp Polysilane Solutions
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
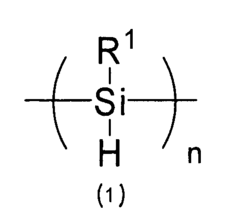
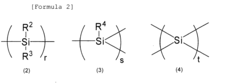
Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These polymers exhibit interesting characteristics such as photoconductivity and photoluminescence, making them suitable for various applications in electronics and optics.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electrical conductivity, photosensitivity, and thermal stability. The synthesis and modification of polysilanes can be tailored to achieve specific properties for different applications.
- Polysilanes as photoresist materials: Polysilanes are utilized as photoresist materials in lithography processes. They exhibit high sensitivity to UV light and can undergo photochemical reactions, making them suitable for pattern formation in semiconductor manufacturing. The photosensitivity of polysilanes can be adjusted by modifying their chemical structure or incorporating additives.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create functional coatings and thin films with various applications. These coatings can provide properties such as water repellency, scratch resistance, and improved adhesion. Polysilane films can be deposited through methods like spin-coating or chemical vapor deposition, offering unique optical and electronic properties.
- Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Polysilanes find applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices due to their semiconducting properties. They can be used as charge transport materials in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and field-effect transistors. The electronic properties of polysilanes can be tuned by modifying their molecular structure or doping with other elements.
- Functionalization and copolymerization of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or copolymerized with other monomers to enhance their properties or create hybrid materials. This approach allows for the development of new materials with combined characteristics of polysilanes and other polymers. Functionalization can introduce specific chemical groups to polysilanes, enabling their use in various applications such as sensors or catalysts.
02 Applications of polysilanes in coatings and films
Polysilanes can be used to create functional coatings and films with specific properties. These materials can be applied to various substrates to impart characteristics such as improved adhesion, chemical resistance, or optical properties. The polysilane-based coatings and films find applications in areas like electronics, optics, and protective coatings.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilanes in photoresist compositions
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist compositions for lithography applications. These silicon-based polymers can enhance the performance of photoresists by improving their sensitivity to light, resolution, and resistance to etching processes. Polysilane-containing photoresists are particularly useful in the fabrication of microelectronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be modified and functionalized to tailor their properties for specific applications. This includes the incorporation of various functional groups, copolymerization with other monomers, or post-polymerization modifications. These modifications can enhance the solubility, processability, or reactivity of polysilanes, expanding their potential uses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in semiconductor applications
Polysilanes have potential applications in semiconductor technology. They can be used as precursors for silicon-based materials, such as amorphous silicon or silicon carbide. Additionally, polysilanes can be employed in the fabrication of thin-film transistors, solar cells, or other electronic devices, leveraging their unique electronic properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Industry
The implementation of polysilane in high-temperature applications is an emerging field within advanced materials science. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing research and development efforts. While the market size is still relatively small, it shows significant potential for expansion due to the unique properties of polysilanes. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with companies like Wacker Chemie AG, Air Liquide SA, and Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. leading the way in developing innovative polysilane-based solutions for high-temperature environments. These companies are investing in research to enhance the thermal stability and performance of polysilanes, aiming to broaden their applications in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and energy.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane formulations for high-temperature applications. Their approach involves synthesizing polysilanes with enhanced thermal stability through the incorporation of phenyl groups and cross-linking agents. The company utilizes a proprietary catalytic dehydrocoupling process to produce high molecular weight polysilanes with improved heat resistance[1]. These materials exhibit thermal stability up to 400°C, making them suitable for use in high-temperature coatings, adhesives, and electronic applications[2]. Wacker's polysilanes also demonstrate excellent oxidation resistance and maintain their electrical properties at elevated temperatures[3].
Strengths: Superior thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and retention of electrical properties at high temperatures. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional polymers, limited commercial availability.
ASM IP Holding BV
Technical Solution: ASM IP Holding BV has developed a novel approach to implementing polysilanes in high-temperature semiconductor processing. Their method involves using polysilanes as precursors for silicon-based thin films in atomic layer deposition (ALD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes[4]. The company has engineered polysilane compounds that decompose at controlled rates at temperatures exceeding 300°C, allowing for precise deposition of silicon-containing layers in advanced microelectronics manufacturing[5]. This technology enables the formation of ultra-thin, conformal silicon nitride and silicon oxide films with excellent step coverage and low impurity levels[6].
Strengths: Precise control over film deposition, compatibility with existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Limited to specific high-temperature semiconductor applications, requires specialized equipment.
Innovations in Polysilane Synthesis
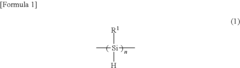
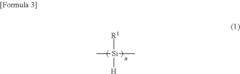
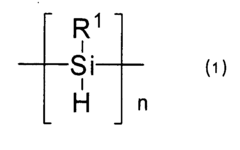
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact of Polysilanes
The implementation of polysilanes in high-temperature applications raises important environmental considerations. Polysilanes, being silicon-based polymers, have unique properties that make them attractive for various industrial uses. However, their environmental impact must be carefully assessed, particularly in high-temperature scenarios.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polysilanes is their potential for decomposition at elevated temperatures. When exposed to high heat, polysilanes can break down into smaller silicon-containing compounds, which may be released into the atmosphere. These decomposition products could contribute to air pollution and potentially affect local ecosystems. The exact nature and extent of these emissions depend on the specific polysilane formulation and the temperature conditions.
Another aspect to consider is the energy consumption required for high-temperature applications involving polysilanes. The production and processing of these materials often demand significant energy inputs, which indirectly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if non-renewable energy sources are used. This energy footprint should be factored into the overall environmental assessment of polysilane implementation.
The disposal of polysilane-containing products after their useful life is another environmental consideration. While silicon-based materials are generally considered less harmful than many organic polymers, improper disposal can still lead to soil and water contamination. High-temperature applications may alter the chemical structure of polysilanes, potentially creating new compounds with unknown environmental impacts.
On a positive note, the durability and heat resistance of polysilanes in high-temperature applications can lead to longer-lasting products. This increased lifespan could reduce the frequency of replacement and, consequently, the overall material consumption and waste generation. Additionally, the ability of polysilanes to withstand extreme conditions may enable more efficient industrial processes, potentially reducing energy consumption and associated emissions in certain applications.
The recyclability of polysilane-based materials used in high-temperature applications is an area that requires further research. If effective recycling methods can be developed, it would significantly mitigate the environmental impact by reducing the need for virgin material production and minimizing waste.
Lastly, the potential for polysilanes to replace more environmentally harmful materials in high-temperature applications should be considered. If polysilanes can substitute materials with higher carbon footprints or those that produce more toxic emissions, their implementation could lead to a net positive environmental impact, despite their own environmental considerations.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with polysilanes is their potential for decomposition at elevated temperatures. When exposed to high heat, polysilanes can break down into smaller silicon-containing compounds, which may be released into the atmosphere. These decomposition products could contribute to air pollution and potentially affect local ecosystems. The exact nature and extent of these emissions depend on the specific polysilane formulation and the temperature conditions.
Another aspect to consider is the energy consumption required for high-temperature applications involving polysilanes. The production and processing of these materials often demand significant energy inputs, which indirectly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if non-renewable energy sources are used. This energy footprint should be factored into the overall environmental assessment of polysilane implementation.
The disposal of polysilane-containing products after their useful life is another environmental consideration. While silicon-based materials are generally considered less harmful than many organic polymers, improper disposal can still lead to soil and water contamination. High-temperature applications may alter the chemical structure of polysilanes, potentially creating new compounds with unknown environmental impacts.
On a positive note, the durability and heat resistance of polysilanes in high-temperature applications can lead to longer-lasting products. This increased lifespan could reduce the frequency of replacement and, consequently, the overall material consumption and waste generation. Additionally, the ability of polysilanes to withstand extreme conditions may enable more efficient industrial processes, potentially reducing energy consumption and associated emissions in certain applications.
The recyclability of polysilane-based materials used in high-temperature applications is an area that requires further research. If effective recycling methods can be developed, it would significantly mitigate the environmental impact by reducing the need for virgin material production and minimizing waste.
Lastly, the potential for polysilanes to replace more environmentally harmful materials in high-temperature applications should be considered. If polysilanes can substitute materials with higher carbon footprints or those that produce more toxic emissions, their implementation could lead to a net positive environmental impact, despite their own environmental considerations.
Safety Regulations for High-Temp Materials
The implementation of polysilane in high-temperature applications necessitates strict adherence to safety regulations for high-temperature materials. These regulations are crucial to ensure the protection of workers, equipment, and the environment during the handling, processing, and use of polysilane in extreme thermal conditions.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have established comprehensive guidelines for high-temperature materials. These guidelines encompass various aspects of safety, including proper storage, handling procedures, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
One of the primary safety concerns when working with polysilane at high temperatures is its potential for thermal decomposition. As temperatures increase, polysilane may release hazardous gases or particulates. To mitigate this risk, regulations mandate the use of appropriate ventilation systems and gas detection equipment in areas where polysilane is processed or stored at elevated temperatures.
Personal protective equipment requirements for handling polysilane in high-temperature applications are stringent. Workers must wear heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and flame-retardant clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary, depending on the specific application and potential for airborne particulates or vapors.
Safety regulations also address the proper design and maintenance of equipment used in high-temperature polysilane applications. This includes specifications for materials of construction, pressure ratings, and temperature monitoring systems. Regular inspections and maintenance schedules are typically mandated to ensure the integrity of equipment exposed to extreme thermal conditions.
Emergency response planning is another critical component of safety regulations. Facilities working with polysilane at high temperatures must have clearly defined procedures for handling spills, fires, or other incidents. This includes the installation of appropriate fire suppression systems, emergency shut-off mechanisms, and evacuation protocols.
Training requirements form a significant part of safety regulations. Personnel involved in high-temperature polysilane applications must receive comprehensive training on the properties of the material, potential hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses are often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Waste management and disposal regulations are also crucial when implementing polysilane in high-temperature applications. Proper procedures must be followed for the disposal of any waste materials, including residues from processing or contaminated PPE. These regulations aim to prevent environmental contamination and protect public health.
In conclusion, the implementation of polysilane in high-temperature applications is subject to a complex web of safety regulations. Adherence to these regulations is essential for ensuring the safe and responsible use of this material in extreme thermal environments. As research and applications of polysilane continue to evolve, it is likely that safety regulations will be periodically updated to address new findings and potential risks.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have established comprehensive guidelines for high-temperature materials. These guidelines encompass various aspects of safety, including proper storage, handling procedures, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols.
One of the primary safety concerns when working with polysilane at high temperatures is its potential for thermal decomposition. As temperatures increase, polysilane may release hazardous gases or particulates. To mitigate this risk, regulations mandate the use of appropriate ventilation systems and gas detection equipment in areas where polysilane is processed or stored at elevated temperatures.
Personal protective equipment requirements for handling polysilane in high-temperature applications are stringent. Workers must wear heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and flame-retardant clothing. Respiratory protection may also be necessary, depending on the specific application and potential for airborne particulates or vapors.
Safety regulations also address the proper design and maintenance of equipment used in high-temperature polysilane applications. This includes specifications for materials of construction, pressure ratings, and temperature monitoring systems. Regular inspections and maintenance schedules are typically mandated to ensure the integrity of equipment exposed to extreme thermal conditions.
Emergency response planning is another critical component of safety regulations. Facilities working with polysilane at high temperatures must have clearly defined procedures for handling spills, fires, or other incidents. This includes the installation of appropriate fire suppression systems, emergency shut-off mechanisms, and evacuation protocols.
Training requirements form a significant part of safety regulations. Personnel involved in high-temperature polysilane applications must receive comprehensive training on the properties of the material, potential hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses are often mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Waste management and disposal regulations are also crucial when implementing polysilane in high-temperature applications. Proper procedures must be followed for the disposal of any waste materials, including residues from processing or contaminated PPE. These regulations aim to prevent environmental contamination and protect public health.
In conclusion, the implementation of polysilane in high-temperature applications is subject to a complex web of safety regulations. Adherence to these regulations is essential for ensuring the safe and responsible use of this material in extreme thermal environments. As research and applications of polysilane continue to evolve, it is likely that safety regulations will be periodically updated to address new findings and potential risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!