How to Process PA11 for Injection Molding: Temperature, Drying and Cycle Time Guidelines
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PA11 Injection Molding Background and Objectives
Polyamide 11 (PA11), also known as Nylon 11, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that has gained significant attention in the injection molding industry. This biobased polymer, derived from castor oil, offers a unique combination of properties that make it suitable for various applications in automotive, electronics, and industrial sectors.
The development of PA11 can be traced back to the 1940s when it was first synthesized by Wallace Carothers at DuPont. Since then, the material has undergone continuous improvements in its processing techniques and formulations. The evolution of PA11 has been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials in manufacturing processes.
In recent years, the focus on environmental sustainability and the push for bio-based materials have further accelerated the adoption of PA11 in injection molding applications. Its renewable source and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional petroleum-based polyamides have made it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to reduce their environmental impact.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide comprehensive guidelines for processing PA11 in injection molding applications. Specifically, we aim to explore the optimal temperature settings, drying requirements, and cycle time parameters that ensure the production of high-quality PA11 parts. By understanding these critical factors, manufacturers can maximize the potential of PA11 and overcome common processing challenges.
The injection molding of PA11 presents unique challenges due to its specific material properties. These include its sensitivity to moisture, thermal stability requirements, and the need for precise temperature control throughout the molding process. Addressing these challenges is crucial for achieving consistent part quality and optimizing production efficiency.
Furthermore, this report seeks to examine the latest advancements in PA11 processing technologies and their impact on injection molding practices. We will explore innovative techniques and equipment designed to enhance the processing of PA11, such as advanced drying systems, precise temperature control mechanisms, and optimized screw designs for better plasticization.
By providing a comprehensive analysis of PA11 injection molding techniques, this report aims to bridge the knowledge gap between material science and practical manufacturing applications. The insights gained from this research will enable manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding the implementation of PA11 in their injection molding processes, ultimately leading to improved product quality, increased production efficiency, and enhanced sustainability in manufacturing operations.
The development of PA11 can be traced back to the 1940s when it was first synthesized by Wallace Carothers at DuPont. Since then, the material has undergone continuous improvements in its processing techniques and formulations. The evolution of PA11 has been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials in manufacturing processes.
In recent years, the focus on environmental sustainability and the push for bio-based materials have further accelerated the adoption of PA11 in injection molding applications. Its renewable source and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional petroleum-based polyamides have made it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to reduce their environmental impact.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to provide comprehensive guidelines for processing PA11 in injection molding applications. Specifically, we aim to explore the optimal temperature settings, drying requirements, and cycle time parameters that ensure the production of high-quality PA11 parts. By understanding these critical factors, manufacturers can maximize the potential of PA11 and overcome common processing challenges.
The injection molding of PA11 presents unique challenges due to its specific material properties. These include its sensitivity to moisture, thermal stability requirements, and the need for precise temperature control throughout the molding process. Addressing these challenges is crucial for achieving consistent part quality and optimizing production efficiency.
Furthermore, this report seeks to examine the latest advancements in PA11 processing technologies and their impact on injection molding practices. We will explore innovative techniques and equipment designed to enhance the processing of PA11, such as advanced drying systems, precise temperature control mechanisms, and optimized screw designs for better plasticization.
By providing a comprehensive analysis of PA11 injection molding techniques, this report aims to bridge the knowledge gap between material science and practical manufacturing applications. The insights gained from this research will enable manufacturers to make informed decisions regarding the implementation of PA11 in their injection molding processes, ultimately leading to improved product quality, increased production efficiency, and enhanced sustainability in manufacturing operations.
Market Demand for PA11 Injection Molded Products
The market demand for PA11 injection molded products has been steadily growing due to the material's unique properties and versatile applications. PA11, also known as nylon 11, is a bio-based polyamide derived from castor oil, offering a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This eco-friendly aspect has significantly contributed to its increasing popularity across various industries.
In the automotive sector, PA11 injection molded parts are gaining traction for their excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. These properties make PA11 ideal for under-the-hood components, fuel system parts, and interior trim elements. The automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has further boosted the demand for PA11 injection molded products.
The aerospace industry has also shown a growing interest in PA11 injection molded components. The material's low moisture absorption, high dimensional stability, and resistance to fatigue make it suitable for various aircraft applications, including interior panels, ducting systems, and structural components. As the aerospace sector continues to focus on weight reduction and fuel efficiency, the demand for PA11 injection molded parts is expected to rise.
In the consumer goods market, PA11 injection molded products are finding applications in sporting goods, electronics housings, and household appliances. The material's durability, aesthetic appeal, and ability to be processed into complex shapes have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to create high-quality, long-lasting products.
The medical device industry has also recognized the potential of PA11 injection molded parts. The material's biocompatibility, sterilization resistance, and ability to maintain its properties over time make it suitable for various medical applications, including surgical instruments, implants, and drug delivery devices. As the healthcare sector continues to innovate, the demand for PA11 injection molded products in this field is projected to grow significantly.
The global push for sustainability and circular economy practices has further amplified the market demand for PA11 injection molded products. Companies across industries are increasingly seeking bio-based materials to reduce their carbon footprint and meet stringent environmental regulations. PA11's renewable source and recyclability align well with these sustainability goals, driving its adoption in various applications.
As manufacturers continue to explore new applications and optimize processing techniques for PA11 injection molding, the market demand is expected to expand further. The material's unique combination of performance, sustainability, and processability positions it as a promising solution for addressing the evolving needs of diverse industries in the coming years.
In the automotive sector, PA11 injection molded parts are gaining traction for their excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. These properties make PA11 ideal for under-the-hood components, fuel system parts, and interior trim elements. The automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has further boosted the demand for PA11 injection molded products.
The aerospace industry has also shown a growing interest in PA11 injection molded components. The material's low moisture absorption, high dimensional stability, and resistance to fatigue make it suitable for various aircraft applications, including interior panels, ducting systems, and structural components. As the aerospace sector continues to focus on weight reduction and fuel efficiency, the demand for PA11 injection molded parts is expected to rise.
In the consumer goods market, PA11 injection molded products are finding applications in sporting goods, electronics housings, and household appliances. The material's durability, aesthetic appeal, and ability to be processed into complex shapes have made it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to create high-quality, long-lasting products.
The medical device industry has also recognized the potential of PA11 injection molded parts. The material's biocompatibility, sterilization resistance, and ability to maintain its properties over time make it suitable for various medical applications, including surgical instruments, implants, and drug delivery devices. As the healthcare sector continues to innovate, the demand for PA11 injection molded products in this field is projected to grow significantly.
The global push for sustainability and circular economy practices has further amplified the market demand for PA11 injection molded products. Companies across industries are increasingly seeking bio-based materials to reduce their carbon footprint and meet stringent environmental regulations. PA11's renewable source and recyclability align well with these sustainability goals, driving its adoption in various applications.
As manufacturers continue to explore new applications and optimize processing techniques for PA11 injection molding, the market demand is expected to expand further. The material's unique combination of performance, sustainability, and processability positions it as a promising solution for addressing the evolving needs of diverse industries in the coming years.
Current Challenges in PA11 Injection Molding
Despite the numerous advantages of PA11 in injection molding, several challenges persist in its processing. One of the primary issues is moisture sensitivity. PA11, like other polyamides, is hygroscopic and can absorb moisture from the atmosphere. This absorbed moisture can lead to hydrolysis during processing, resulting in reduced mechanical properties and surface defects in the final product. Proper drying of PA11 before processing is crucial, but determining the optimal drying conditions and maintaining them consistently can be challenging.
Temperature control presents another significant challenge in PA11 injection molding. The material requires precise temperature management throughout the molding process, from the feed zone to the nozzle. Insufficient heating can lead to incomplete melting and poor flow, while excessive temperatures can cause material degradation. Achieving and maintaining the ideal temperature profile across different zones of the injection molding machine is often difficult, especially when dealing with complex part geometries or varying wall thicknesses.
Cycle time optimization is a persistent challenge in PA11 injection molding. The material's relatively high melting point and specific cooling requirements can lead to longer cycle times compared to some other thermoplastics. Balancing the need for adequate cooling to ensure dimensional stability and surface quality with the desire for faster production cycles is a constant struggle for manufacturers.
The flow behavior of PA11 during injection can also be problematic. Its viscosity characteristics and melt flow index can vary depending on the specific grade and processing conditions. This variability can lead to issues such as short shots, weld lines, or inconsistent part filling, particularly in complex mold designs or thin-walled sections.
Thermal degradation is another concern in PA11 processing. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which can occur during extended residence times in the barrel or hot runner systems, can lead to molecular weight reduction and deterioration of mechanical properties. This necessitates careful control of processing parameters and may limit the use of PA11 in certain applications requiring extended hot runner residence times.
Lastly, the relatively high cost of PA11 compared to some other engineering plastics can pose economic challenges, particularly in high-volume production scenarios. This cost factor often necessitates a delicate balance between material performance, processing efficiency, and economic viability, adding another layer of complexity to the injection molding process.
Temperature control presents another significant challenge in PA11 injection molding. The material requires precise temperature management throughout the molding process, from the feed zone to the nozzle. Insufficient heating can lead to incomplete melting and poor flow, while excessive temperatures can cause material degradation. Achieving and maintaining the ideal temperature profile across different zones of the injection molding machine is often difficult, especially when dealing with complex part geometries or varying wall thicknesses.
Cycle time optimization is a persistent challenge in PA11 injection molding. The material's relatively high melting point and specific cooling requirements can lead to longer cycle times compared to some other thermoplastics. Balancing the need for adequate cooling to ensure dimensional stability and surface quality with the desire for faster production cycles is a constant struggle for manufacturers.
The flow behavior of PA11 during injection can also be problematic. Its viscosity characteristics and melt flow index can vary depending on the specific grade and processing conditions. This variability can lead to issues such as short shots, weld lines, or inconsistent part filling, particularly in complex mold designs or thin-walled sections.
Thermal degradation is another concern in PA11 processing. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which can occur during extended residence times in the barrel or hot runner systems, can lead to molecular weight reduction and deterioration of mechanical properties. This necessitates careful control of processing parameters and may limit the use of PA11 in certain applications requiring extended hot runner residence times.
Lastly, the relatively high cost of PA11 compared to some other engineering plastics can pose economic challenges, particularly in high-volume production scenarios. This cost factor often necessitates a delicate balance between material performance, processing efficiency, and economic viability, adding another layer of complexity to the injection molding process.
Existing PA11 Injection Molding Guidelines
01 Drying temperature and time for PA11
Proper drying of PA11 is crucial for processing. The material typically requires drying at temperatures between 80°C to 100°C for 4 to 8 hours to remove moisture. This step is essential to prevent hydrolysis and maintain the polymer's properties during processing.- Drying process for PA11: The drying process for Polyamide 11 (PA11) is crucial for optimal performance. It typically involves exposing the material to controlled temperatures for specific durations to remove moisture. Proper drying helps prevent hydrolysis and maintains the polymer's mechanical properties during processing.
- Temperature control in PA11 processing: Temperature control is essential when processing PA11. The material requires specific temperature ranges for different stages, including melting, molding, and cooling. Maintaining appropriate temperatures ensures proper flow, prevents degradation, and achieves desired physical properties in the final product.
- Cycle time optimization for PA11 production: Optimizing cycle time in PA11 production involves balancing various factors such as heating, cooling, and holding times. Efficient cycle times can be achieved through precise control of process parameters, equipment design, and material handling techniques, leading to improved productivity and consistent product quality.
- Moisture management in PA11: Effective moisture management is critical for PA11 processing. This involves not only initial drying but also maintaining low moisture levels during storage and handling. Techniques such as using dry air systems, moisture-proof packaging, and controlled environment storage are employed to prevent moisture absorption and maintain material integrity.
- Thermal stability and degradation prevention of PA11: Ensuring thermal stability and preventing degradation of PA11 during processing is crucial. This involves careful control of processing temperatures, minimizing exposure to high temperatures for extended periods, and potentially using stabilizers or additives. These measures help maintain the polymer's molecular weight and mechanical properties.
02 Processing temperature range for PA11
PA11 is typically processed at temperatures ranging from 220°C to 260°C. The exact temperature depends on the specific grade and application. Maintaining the correct temperature is crucial for achieving optimal melt viscosity and preventing thermal degradation of the polymer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cycle time optimization for PA11 processing
Optimizing cycle time for PA11 processing involves balancing cooling time, injection speed, and hold pressure. Rapid cooling can be achieved using mold temperature control systems. Proper cycle time management ensures efficient production while maintaining product quality and dimensional stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Moisture control and its impact on PA11 properties
Controlling moisture content in PA11 is critical for maintaining its mechanical and thermal properties. Excessive moisture can lead to hydrolysis during processing, reducing molecular weight and compromising the material's performance. Proper storage and handling procedures are essential to prevent moisture absorption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-processing treatments for PA11 parts
Post-processing treatments such as annealing or heat stabilization can improve the dimensional stability and mechanical properties of PA11 parts. These treatments typically involve holding the parts at elevated temperatures below the melting point for a specified time, allowing for stress relaxation and crystallization.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PA11 and Injection Molding Industry
The processing of PA11 for injection molding is in a mature stage of development, with established guidelines for temperature, drying, and cycle time. The market for PA11 injection molding is growing steadily, driven by its unique properties and applications in various industries. Technologically, the process is well-understood, with companies like Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd., Evonik Operations GmbH, and Eastman Chemical Co. leading the way in developing advanced formulations and processing techniques. These companies, along with others such as Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. and DSM IP Assets BV, continue to innovate in areas like improved thermal stability, enhanced mechanical properties, and optimized processing parameters for PA11 injection molding.
Evonik Specialty Chemicals (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed advanced processing techniques for PA11 injection molding. They recommend precise temperature control, with melt temperatures ranging from 220-260°C depending on the specific grade[1]. Pre-drying is crucial, typically at 80°C for 4-6 hours to achieve moisture content below 0.1%[2]. Evonik's optimized cycle times involve rapid injection (1-2 seconds), moderate holding pressure (30-60 MPa), and cooling times of 10-20 seconds for thin-walled parts[3]. They've also introduced additives to enhance flow properties and reduce cycle times by up to 15%[4].
Strengths: Extensive experience with PA11, tailored additives for improved processing. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal results, potentially higher material costs.
Eastman Chemical Co.
Technical Solution: Eastman Chemical has developed a comprehensive approach to PA11 injection molding. They recommend a barrel temperature profile of 230-260°C, with the feed zone at the lower end and the nozzle at the higher end[1]. Drying is performed at 80°C for 4-6 hours in a desiccant dryer to reach a moisture content below 0.05%[2]. Eastman's cycle time optimization includes rapid injection speeds (50-100 mm/s), moderate holding pressures (40-60 MPa), and cooling times tailored to part thickness, typically 12-25 seconds for parts up to 3mm thick[3]. They've also introduced nucleating agents that can reduce cycle times by up to 20% while improving dimensional stability[4].
Strengths: Holistic approach to processing parameters, innovative additives for cycle time reduction. Weaknesses: May require fine-tuning for specific part geometries, potential color limitations with some additives.
Critical Parameters for PA11 Injection Molding
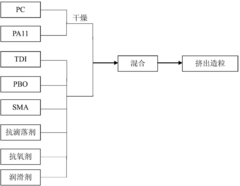
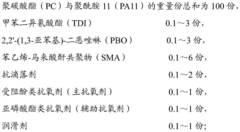
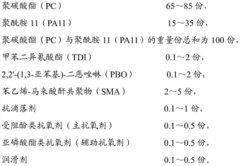
PC/PA 11 (polycarbonate/polyamide 11) composition and preparation method thereof
PatentActiveCN103937192A
Innovation
- Using an in-situ reaction compatibilization method, polycarbonate and polyamide 11 are melt-blended with monomers containing dual reactive functional groups in a parallel twin-screw extruder to generate compatibilizers, improve compatibility, and prepare PC/PA11 composition with good mechanical properties, high flame retardancy, chemical resistance and good processing performance.
Molding technology combining PA11 with metal embedding pieces
PatentActiveCN102689395A
Innovation
- By preheating the metal insert before injection molding, its surface temperature reaches 185℃-340℃, and monitoring the temperature in real time during the injection molding process to ensure that the temperature of the PA11 material and metal insert is between 185℃-340℃. time, use an injection pressure of 60-80MPa, a holding time of 10-15s and a cooling time of 25-30s when combining to avoid excessive internal stress.
Sustainability Aspects of PA11 Injection Molding
Sustainability has become a crucial aspect of manufacturing processes, and PA11 injection molding is no exception. The use of PA11, a bio-based polyamide derived from castor oil, already contributes to sustainability efforts by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. However, there are several additional aspects to consider when evaluating the sustainability of PA11 injection molding processes.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in sustainable manufacturing. PA11 typically requires lower processing temperatures compared to some other engineering plastics, which can lead to reduced energy consumption during the injection molding process. This not only decreases the carbon footprint but also contributes to cost savings for manufacturers.
Material efficiency is another important consideration. PA11's excellent mechanical properties and durability allow for the production of lightweight yet strong parts, potentially reducing material usage and improving fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace applications. Additionally, the ability to recycle PA11 scrap and reuse it in the molding process further enhances material efficiency and reduces waste.
Water usage in PA11 injection molding is relatively low compared to some other manufacturing processes. However, proper water management systems can be implemented to minimize consumption and treat any wastewater generated during cooling or cleaning processes.
The bio-based nature of PA11 contributes to a circular economy approach. As it is derived from renewable resources, it helps reduce the overall environmental impact compared to petroleum-based alternatives. Furthermore, end-of-life considerations for PA11 products are generally favorable, as the material can be recycled or biodegraded under certain conditions.
Emissions control is another aspect of sustainability in PA11 injection molding. While the process generally produces fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than some other plastics, implementing proper ventilation and filtration systems can further reduce any potential air quality impacts.
In terms of social sustainability, the production of PA11 from castor oil can provide economic opportunities for farmers in regions where castor plants are grown. This can contribute to rural development and diversification of agricultural economies.
Lastly, the long-term durability of PA11 products can lead to extended product lifecycles, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby conserving resources over time. This aligns with sustainability principles of product longevity and reduced consumption.
Energy efficiency is a key factor in sustainable manufacturing. PA11 typically requires lower processing temperatures compared to some other engineering plastics, which can lead to reduced energy consumption during the injection molding process. This not only decreases the carbon footprint but also contributes to cost savings for manufacturers.
Material efficiency is another important consideration. PA11's excellent mechanical properties and durability allow for the production of lightweight yet strong parts, potentially reducing material usage and improving fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace applications. Additionally, the ability to recycle PA11 scrap and reuse it in the molding process further enhances material efficiency and reduces waste.
Water usage in PA11 injection molding is relatively low compared to some other manufacturing processes. However, proper water management systems can be implemented to minimize consumption and treat any wastewater generated during cooling or cleaning processes.
The bio-based nature of PA11 contributes to a circular economy approach. As it is derived from renewable resources, it helps reduce the overall environmental impact compared to petroleum-based alternatives. Furthermore, end-of-life considerations for PA11 products are generally favorable, as the material can be recycled or biodegraded under certain conditions.
Emissions control is another aspect of sustainability in PA11 injection molding. While the process generally produces fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than some other plastics, implementing proper ventilation and filtration systems can further reduce any potential air quality impacts.
In terms of social sustainability, the production of PA11 from castor oil can provide economic opportunities for farmers in regions where castor plants are grown. This can contribute to rural development and diversification of agricultural economies.
Lastly, the long-term durability of PA11 products can lead to extended product lifecycles, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby conserving resources over time. This aligns with sustainability principles of product longevity and reduced consumption.
Quality Control in PA11 Injection Molding
Quality control is a critical aspect of PA11 injection molding, ensuring consistent product quality and optimal performance. Effective quality control measures begin with proper material handling and preparation. PA11 is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the environment, which can significantly impact the molding process and final product quality. Therefore, implementing a rigorous drying protocol is essential. This typically involves drying PA11 at temperatures between 80°C and 100°C for 4-6 hours, or until the moisture content is below 0.1%.
During the injection molding process, maintaining precise temperature control is crucial. The melt temperature for PA11 should be carefully monitored and maintained within the range of 220°C to 260°C. Exceeding these temperatures can lead to material degradation, while insufficient heat may result in poor flow and incomplete mold filling. Implementing real-time temperature monitoring systems and closed-loop control mechanisms can help ensure temperature stability throughout the molding cycle.
Mold temperature control is equally important for achieving consistent part quality. For PA11, mold temperatures typically range from 40°C to 80°C, depending on the specific grade and part requirements. Uniform mold heating and cooling are essential to prevent warpage, sink marks, and other defects. Advanced mold temperature control systems, such as those utilizing conformal cooling channels, can significantly improve temperature uniformity and cycle times.
Process parameter monitoring and adjustment are key components of quality control in PA11 injection molding. This includes tracking injection pressure, holding pressure, screw speed, and cycle time. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques can be employed to identify trends and variations in these parameters, allowing for proactive adjustments to maintain optimal processing conditions.
In-process quality checks are vital for detecting and addressing issues promptly. These may include visual inspections for surface defects, dimensional measurements, and weight checks to ensure consistent part filling. Advanced inspection technologies, such as in-mold sensors or infrared cameras, can provide real-time data on part quality and process stability.
Post-molding quality control measures are equally important. This includes conducting mechanical property tests, such as tensile strength and impact resistance, to verify that the molded parts meet specified requirements. Additionally, thermal analysis techniques like differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) can be used to assess the degree of crystallinity and thermal properties of the molded parts, which are critical factors in determining the final performance of PA11 components.
Implementing a comprehensive quality management system, such as ISO 9001, can provide a structured approach to quality control in PA11 injection molding. This includes establishing clear quality objectives, documenting procedures, and continuously monitoring and improving processes. Regular training of operators and quality control personnel is essential to ensure proper implementation of quality control measures and to keep up with evolving best practices in PA11 processing.
During the injection molding process, maintaining precise temperature control is crucial. The melt temperature for PA11 should be carefully monitored and maintained within the range of 220°C to 260°C. Exceeding these temperatures can lead to material degradation, while insufficient heat may result in poor flow and incomplete mold filling. Implementing real-time temperature monitoring systems and closed-loop control mechanisms can help ensure temperature stability throughout the molding cycle.
Mold temperature control is equally important for achieving consistent part quality. For PA11, mold temperatures typically range from 40°C to 80°C, depending on the specific grade and part requirements. Uniform mold heating and cooling are essential to prevent warpage, sink marks, and other defects. Advanced mold temperature control systems, such as those utilizing conformal cooling channels, can significantly improve temperature uniformity and cycle times.
Process parameter monitoring and adjustment are key components of quality control in PA11 injection molding. This includes tracking injection pressure, holding pressure, screw speed, and cycle time. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques can be employed to identify trends and variations in these parameters, allowing for proactive adjustments to maintain optimal processing conditions.
In-process quality checks are vital for detecting and addressing issues promptly. These may include visual inspections for surface defects, dimensional measurements, and weight checks to ensure consistent part filling. Advanced inspection technologies, such as in-mold sensors or infrared cameras, can provide real-time data on part quality and process stability.
Post-molding quality control measures are equally important. This includes conducting mechanical property tests, such as tensile strength and impact resistance, to verify that the molded parts meet specified requirements. Additionally, thermal analysis techniques like differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) can be used to assess the degree of crystallinity and thermal properties of the molded parts, which are critical factors in determining the final performance of PA11 components.
Implementing a comprehensive quality management system, such as ISO 9001, can provide a structured approach to quality control in PA11 injection molding. This includes establishing clear quality objectives, documenting procedures, and continuously monitoring and improving processes. Regular training of operators and quality control personnel is essential to ensure proper implementation of quality control measures and to keep up with evolving best practices in PA11 processing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!