How to Select Proper Equipment for Hydrochloric Acid Handling?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Handling Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) handling is a critical process in various industries, including chemical manufacturing, metal processing, and water treatment. The proper selection of equipment for HCl handling is essential to ensure safety, efficiency, and environmental protection. This technical research report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the background and objectives related to HCl handling equipment selection.
The history of HCl handling can be traced back to the early days of industrial chemistry. As the demand for HCl in various applications grew, so did the need for specialized equipment to handle this corrosive substance. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in materials science, engineering, and safety protocols, leading to the development of more sophisticated and reliable HCl handling equipment.
The primary objective of selecting proper equipment for HCl handling is to minimize risks associated with its corrosive nature while maximizing operational efficiency. This involves addressing several key factors, including material compatibility, containment, transfer mechanisms, and safety features. The equipment must be capable of withstanding the highly corrosive properties of HCl, which can rapidly degrade many common materials.
Another crucial objective is to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and safety standards. As awareness of the potential hazards associated with HCl handling has grown, regulatory bodies have implemented more rigorous guidelines for its storage, transport, and use. Equipment selection must take these regulations into account to avoid legal issues and potential environmental damage.
The technological evolution in HCl handling equipment has been driven by the need for improved safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Recent trends include the development of advanced corrosion-resistant materials, such as specialized plastics and alloys, which offer superior durability and longevity compared to traditional materials. Additionally, there has been a focus on designing equipment with enhanced leak detection and containment features to minimize the risk of accidental releases.
Automation and digital technologies are also playing an increasingly important role in HCl handling equipment. Smart sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance algorithms are being integrated into modern equipment to improve operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of equipment failure. These technological advancements not only enhance safety but also contribute to optimizing overall process performance.
As industries continue to evolve, the objectives for HCl handling equipment selection are expanding to include sustainability considerations. This includes designing equipment that minimizes energy consumption, reduces waste generation, and facilitates the recycling or reuse of HCl where possible. The goal is to develop handling solutions that not only meet immediate operational needs but also align with long-term environmental sustainability goals.
The history of HCl handling can be traced back to the early days of industrial chemistry. As the demand for HCl in various applications grew, so did the need for specialized equipment to handle this corrosive substance. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in materials science, engineering, and safety protocols, leading to the development of more sophisticated and reliable HCl handling equipment.
The primary objective of selecting proper equipment for HCl handling is to minimize risks associated with its corrosive nature while maximizing operational efficiency. This involves addressing several key factors, including material compatibility, containment, transfer mechanisms, and safety features. The equipment must be capable of withstanding the highly corrosive properties of HCl, which can rapidly degrade many common materials.
Another crucial objective is to ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and safety standards. As awareness of the potential hazards associated with HCl handling has grown, regulatory bodies have implemented more rigorous guidelines for its storage, transport, and use. Equipment selection must take these regulations into account to avoid legal issues and potential environmental damage.
The technological evolution in HCl handling equipment has been driven by the need for improved safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Recent trends include the development of advanced corrosion-resistant materials, such as specialized plastics and alloys, which offer superior durability and longevity compared to traditional materials. Additionally, there has been a focus on designing equipment with enhanced leak detection and containment features to minimize the risk of accidental releases.
Automation and digital technologies are also playing an increasingly important role in HCl handling equipment. Smart sensors, real-time monitoring systems, and predictive maintenance algorithms are being integrated into modern equipment to improve operational efficiency and reduce the likelihood of equipment failure. These technological advancements not only enhance safety but also contribute to optimizing overall process performance.
As industries continue to evolve, the objectives for HCl handling equipment selection are expanding to include sustainability considerations. This includes designing equipment that minimizes energy consumption, reduces waste generation, and facilitates the recycling or reuse of HCl where possible. The goal is to develop handling solutions that not only meet immediate operational needs but also align with long-term environmental sustainability goals.
Market Analysis for HCl Handling Equipment
The global market for hydrochloric acid (HCl) handling equipment has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as chemical manufacturing, steel production, and water treatment. The market size for HCl handling equipment is projected to expand significantly over the next five years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall industrial equipment sector average.
Key factors contributing to this growth include the rising adoption of HCl in diverse applications, stringent safety regulations, and the need for efficient and corrosion-resistant equipment. The chemical industry remains the largest consumer of HCl handling equipment, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. However, emerging applications in pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing are expected to create new opportunities for equipment suppliers.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market, led by China and India's robust industrial growth and increasing investments in chemical production facilities. North America and Europe follow, with a focus on upgrading existing infrastructure and implementing advanced safety measures. The Middle East and Africa region is anticipated to witness rapid growth due to expanding petrochemical and desalination projects.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized regional players. Leading companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative materials and designs that enhance equipment durability and safety. There is a growing trend towards the integration of smart technologies and automation in HCl handling systems, improving operational efficiency and reducing human exposure to hazardous materials.
Customer preferences are shifting towards modular and customizable equipment solutions that can be easily adapted to specific process requirements. This trend is driving manufacturers to offer more flexible and scalable product lines. Additionally, there is an increasing demand for turnkey solutions that include installation, maintenance, and operator training services.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are influencing market dynamics, with a growing emphasis on equipment that minimizes HCl emissions and reduces energy consumption. This has led to the development of more efficient pumps, valves, and storage systems designed specifically for HCl applications.
The competitive landscape is intensifying, with players focusing on strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence. Price competition remains fierce in certain segments, particularly for standard equipment, while specialized high-end solutions command premium pricing.
Key factors contributing to this growth include the rising adoption of HCl in diverse applications, stringent safety regulations, and the need for efficient and corrosion-resistant equipment. The chemical industry remains the largest consumer of HCl handling equipment, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. However, emerging applications in pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing are expected to create new opportunities for equipment suppliers.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market, led by China and India's robust industrial growth and increasing investments in chemical production facilities. North America and Europe follow, with a focus on upgrading existing infrastructure and implementing advanced safety measures. The Middle East and Africa region is anticipated to witness rapid growth due to expanding petrochemical and desalination projects.
The market is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized regional players. Leading companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative materials and designs that enhance equipment durability and safety. There is a growing trend towards the integration of smart technologies and automation in HCl handling systems, improving operational efficiency and reducing human exposure to hazardous materials.
Customer preferences are shifting towards modular and customizable equipment solutions that can be easily adapted to specific process requirements. This trend is driving manufacturers to offer more flexible and scalable product lines. Additionally, there is an increasing demand for turnkey solutions that include installation, maintenance, and operator training services.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives are influencing market dynamics, with a growing emphasis on equipment that minimizes HCl emissions and reduces energy consumption. This has led to the development of more efficient pumps, valves, and storage systems designed specifically for HCl applications.
The competitive landscape is intensifying, with players focusing on strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions to expand their product portfolios and geographical presence. Price competition remains fierce in certain segments, particularly for standard equipment, while specialized high-end solutions command premium pricing.
Current Challenges in HCl Equipment Selection
The selection of proper equipment for hydrochloric acid (HCl) handling presents several significant challenges in today's industrial landscape. One of the primary difficulties lies in the highly corrosive nature of HCl, which necessitates the use of specialized materials that can withstand its aggressive properties. This requirement often limits the range of suitable equipment options and increases the complexity of the selection process.
Another major challenge is the variability in HCl concentrations used across different industries and applications. Equipment that is suitable for handling dilute HCl solutions may not be appropriate for more concentrated forms, requiring careful consideration of the specific concentration ranges encountered in each application. This variability also extends to temperature and pressure conditions, further complicating the equipment selection process.
Safety considerations pose additional challenges in HCl equipment selection. The potential for acid leaks, spills, or vapor emissions demands robust containment systems and fail-safe mechanisms. Integrating these safety features while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness can be a delicate balancing act for engineers and facility managers.
The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding hazardous materials handling adds another layer of complexity to equipment selection. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental and safety regulations often requires the incorporation of advanced monitoring and control systems, as well as the use of more sophisticated materials and designs.
Scalability and flexibility present further challenges, particularly for growing or diversifying operations. Selecting equipment that can accommodate potential future changes in production volumes or HCl concentrations without requiring complete system overhauls is a critical consideration that often complicates the decision-making process.
Maintenance and longevity concerns also factor significantly into equipment selection challenges. The aggressive nature of HCl can lead to accelerated wear and corrosion, necessitating careful consideration of maintenance requirements, replacement schedules, and overall equipment lifespan when making selection decisions.
Lastly, the economic aspects of equipment selection for HCl handling cannot be overlooked. Balancing the initial investment costs against long-term operational expenses, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime, presents a significant challenge. This economic calculus is further complicated by the need to factor in the potential costs of equipment failure or safety incidents, which can be catastrophic in HCl handling applications.
Another major challenge is the variability in HCl concentrations used across different industries and applications. Equipment that is suitable for handling dilute HCl solutions may not be appropriate for more concentrated forms, requiring careful consideration of the specific concentration ranges encountered in each application. This variability also extends to temperature and pressure conditions, further complicating the equipment selection process.
Safety considerations pose additional challenges in HCl equipment selection. The potential for acid leaks, spills, or vapor emissions demands robust containment systems and fail-safe mechanisms. Integrating these safety features while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness can be a delicate balancing act for engineers and facility managers.
The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding hazardous materials handling adds another layer of complexity to equipment selection. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental and safety regulations often requires the incorporation of advanced monitoring and control systems, as well as the use of more sophisticated materials and designs.
Scalability and flexibility present further challenges, particularly for growing or diversifying operations. Selecting equipment that can accommodate potential future changes in production volumes or HCl concentrations without requiring complete system overhauls is a critical consideration that often complicates the decision-making process.
Maintenance and longevity concerns also factor significantly into equipment selection challenges. The aggressive nature of HCl can lead to accelerated wear and corrosion, necessitating careful consideration of maintenance requirements, replacement schedules, and overall equipment lifespan when making selection decisions.
Lastly, the economic aspects of equipment selection for HCl handling cannot be overlooked. Balancing the initial investment costs against long-term operational expenses, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime, presents a significant challenge. This economic calculus is further complicated by the need to factor in the potential costs of equipment failure or safety incidents, which can be catastrophic in HCl handling applications.
Existing HCl Equipment Selection Methodologies
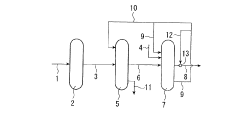
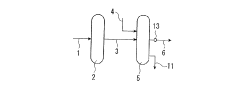
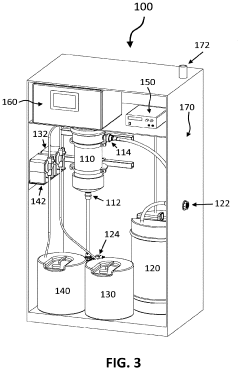
01 Corrosion-resistant storage tanks
Specialized storage tanks designed to withstand the corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid are essential for safe handling. These tanks are typically made of materials such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), polyethylene, or lined steel to prevent degradation and leaks. The design often includes features like double-walled construction and leak detection systems for added safety.- Corrosion-resistant storage tanks: Specialized storage tanks designed to withstand the corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid are essential for safe handling. These tanks are typically made of materials such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), rubber-lined steel, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE) to prevent leaks and ensure long-term durability.
- Acid-resistant pumping systems: Pumps specifically designed for handling hydrochloric acid are crucial for safe transfer and circulation. These pumps often feature materials like PTFE, PFA, or ceramic components to resist corrosion and maintain efficiency when handling the aggressive acid.
- Safety equipment and protective gear: Personal protective equipment (PPE) and safety systems are vital for workers handling hydrochloric acid. This includes acid-resistant suits, gloves, face shields, and emergency eyewash stations. Proper ventilation systems and gas detectors are also essential to prevent exposure to harmful fumes.
- Acid-resistant piping and valves: Specialized piping systems and valves made from corrosion-resistant materials such as PTFE-lined steel, PVC, or high-grade alloys are necessary for the safe transport of hydrochloric acid within a facility. These components must withstand the acid's corrosive properties and maintain integrity over time.
- Neutralization and spill containment systems: Equipment for neutralizing and containing potential spills is crucial for handling hydrochloric acid safely. This includes neutralization tanks, containment berms, and absorbent materials designed to quickly and effectively manage accidental releases and minimize environmental impact.
02 Acid-resistant pumping systems
Pumps used for transferring hydrochloric acid must be constructed with materials that can withstand its corrosive properties. These pumps often utilize components made from materials such as PTFE, PFA, or high-grade stainless steel. The design may include features like mechanical seals or magnetic drive to prevent leaks and ensure safe operation when handling the acid.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety equipment and personal protective gear
Proper safety equipment is crucial when handling hydrochloric acid. This includes personal protective equipment (PPE) such as acid-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and chemical-resistant suits. Additionally, safety showers, eyewash stations, and spill containment systems should be readily available in areas where hydrochloric acid is handled or stored.Expand Specific Solutions04 Acid-resistant piping and valves
Specialized piping and valves are required for the safe transport of hydrochloric acid within a facility. These components are typically made from materials such as PTFE-lined steel, PVC, or high-grade alloys that can resist corrosion. The design often includes features like double containment piping and leak detection systems to prevent and quickly identify any potential leaks.Expand Specific Solutions05 Acid fume scrubbers and ventilation systems
To manage the hazardous fumes produced by hydrochloric acid, specialized scrubbers and ventilation systems are employed. These systems are designed to neutralize or capture acid vapors, ensuring a safe working environment. They may include features such as packed bed scrubbers, mist eliminators, and exhaust fans to effectively remove and treat acid fumes before release into the atmosphere.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers of HCl Handling Equipment
The hydrochloric acid handling equipment market is in a mature stage, with a steady global demand driven by various industries such as chemical processing, steel production, and water treatment. The market size is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars annually. Technologically, the field is well-established, with continuous improvements in materials and safety features. Key players like Baker Hughes Co., Schlumberger, and GEA Systems North America LLC offer advanced solutions, while specialized chemical companies such as Jiangyin Runma Electronic Material Co., Ltd. and Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE provide high-purity acid handling equipment for niche markets. The competition is intense, with companies focusing on innovation in corrosion-resistant materials, automation, and environmental compliance to maintain their market positions.
Baker Hughes Co.
Technical Solution: Baker Hughes has developed advanced equipment for handling hydrochloric acid in oil and gas operations. Their approach includes using corrosion-resistant materials such as high-grade stainless steel and specialized alloys for storage tanks, piping, and pumps. They have implemented a comprehensive safety system with real-time monitoring of acid concentration, temperature, and pressure [1]. Their equipment features double-walled containment systems and automated shut-off valves to prevent leaks. Baker Hughes also utilizes advanced sealing technologies and gasket materials specifically designed to withstand the corrosive nature of hydrochloric acid [3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in oil and gas industry, advanced materials technology, comprehensive safety features. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized materials, may require specialized training for operation.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a range of equipment for hydrochloric acid handling in their refining and petrochemical operations. Their approach focuses on using fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) tanks and piping systems, which offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability [2]. Sinopec has also implemented advanced process control systems to manage acid concentration and flow rates. They utilize specialized pumps with silicon carbide or ceramic internals for acid transfer. Sinopec's equipment design incorporates fail-safe mechanisms and redundant safety systems to minimize risks associated with acid handling [5].
Strengths: Cost-effective solutions, extensive experience in large-scale chemical operations. Weaknesses: May have less advanced automation compared to some Western competitors.
Innovative Materials for HCl Resistance
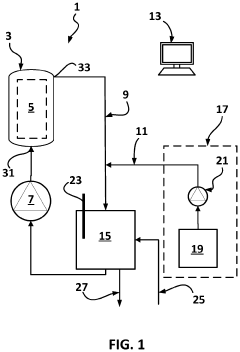
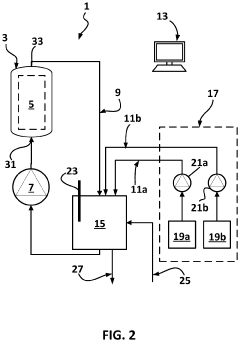
Hydrochloric acid recovering apparatus and method for recovering hydrochloric acid from waste hydrochloric acid solution
PatentActiveJP2009274906A
Innovation
- A two-stage absorption system with a first and second absorption tower, using recycled washing water and dilute hydrochloric acid solution to separate and recover hydrochloric acid, and cleaning the exhaust fan blades with a dilute solution to prevent vibration and corrosion.
Apparatus and method for the electrolytic production of hypochlorous acid
PatentPendingUS20230313389A1
Innovation
- An apparatus and method using electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution with an acidic solution in a reaction loop, controlled by a system that monitors and adjusts pH to produce a stable HOCl solution, allowing for on-demand production with variable scale and remote monitoring.
Safety Regulations for HCl Handling
Safety regulations for handling hydrochloric acid (HCl) are crucial to ensure the protection of workers and the environment. These regulations are typically established by governmental agencies and industry organizations to provide guidelines for the safe storage, transportation, and use of HCl in various industrial applications.
One of the primary safety regulations for HCl handling is the requirement for proper personal protective equipment (PPE). Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, protective clothing, and eye protection when handling HCl. In cases where there is a risk of inhalation, respiratory protection is also mandatory. The specific type of PPE required may vary depending on the concentration of the acid and the nature of the handling process.
Ventilation is another critical aspect of HCl safety regulations. Adequate ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the accumulation of HCl vapors, which can be harmful if inhaled. Local exhaust ventilation is often required in areas where HCl is used or stored to capture and remove any vapors at the source.
Storage regulations for HCl are equally important. The acid must be stored in properly labeled, corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas. Secondary containment is often required to prevent spills from spreading in case of a leak. Incompatible materials, such as certain metals and oxidizing agents, must be kept separate from HCl storage areas to prevent dangerous reactions.
Emergency response procedures are a vital component of HCl safety regulations. Facilities handling HCl must have clearly defined emergency plans, including procedures for spill containment and neutralization. Safety showers and eyewash stations must be readily accessible in areas where HCl is used or stored.
Transportation of HCl is subject to strict regulations, including proper labeling, packaging, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting HCl must be equipped with appropriate safety features and placards indicating the presence of hazardous materials.
Training is a fundamental aspect of HCl safety regulations. All personnel involved in handling HCl must receive comprehensive training on the hazards associated with the acid, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. This training must be documented and regularly updated to ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment used for HCl handling are also mandated by safety regulations. This includes routine checks of storage tanks, piping systems, and transfer equipment to ensure their integrity and prevent leaks or failures.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for protecting human health and the environment. Companies handling HCl must stay informed about updates to these regulations and implement any new requirements promptly to maintain a safe working environment.
One of the primary safety regulations for HCl handling is the requirement for proper personal protective equipment (PPE). Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, protective clothing, and eye protection when handling HCl. In cases where there is a risk of inhalation, respiratory protection is also mandatory. The specific type of PPE required may vary depending on the concentration of the acid and the nature of the handling process.
Ventilation is another critical aspect of HCl safety regulations. Adequate ventilation systems must be in place to prevent the accumulation of HCl vapors, which can be harmful if inhaled. Local exhaust ventilation is often required in areas where HCl is used or stored to capture and remove any vapors at the source.
Storage regulations for HCl are equally important. The acid must be stored in properly labeled, corrosion-resistant containers in well-ventilated areas. Secondary containment is often required to prevent spills from spreading in case of a leak. Incompatible materials, such as certain metals and oxidizing agents, must be kept separate from HCl storage areas to prevent dangerous reactions.
Emergency response procedures are a vital component of HCl safety regulations. Facilities handling HCl must have clearly defined emergency plans, including procedures for spill containment and neutralization. Safety showers and eyewash stations must be readily accessible in areas where HCl is used or stored.
Transportation of HCl is subject to strict regulations, including proper labeling, packaging, and documentation requirements. Vehicles transporting HCl must be equipped with appropriate safety features and placards indicating the presence of hazardous materials.
Training is a fundamental aspect of HCl safety regulations. All personnel involved in handling HCl must receive comprehensive training on the hazards associated with the acid, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. This training must be documented and regularly updated to ensure ongoing compliance with safety standards.
Regular inspections and maintenance of equipment used for HCl handling are also mandated by safety regulations. This includes routine checks of storage tanks, piping systems, and transfer equipment to ensure their integrity and prevent leaks or failures.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for protecting human health and the environment. Companies handling HCl must stay informed about updates to these regulations and implement any new requirements promptly to maintain a safe working environment.
Environmental Impact of HCl Equipment
The selection of proper equipment for hydrochloric acid (HCl) handling has significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered. HCl is a highly corrosive substance, and its improper handling can lead to severe environmental consequences. The equipment used in HCl handling plays a crucial role in preventing leaks, spills, and emissions that could harm ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with HCl equipment is the potential for atmospheric pollution. Inadequate or poorly maintained equipment can result in HCl vapor emissions, which contribute to air pollution and acid rain formation. These emissions can have far-reaching effects on vegetation, soil quality, and aquatic ecosystems. To mitigate this risk, proper ventilation systems and scrubbers must be incorporated into the equipment design to capture and neutralize any escaping vapors.
Water pollution is another critical environmental issue related to HCl handling equipment. Leaks or spills from faulty equipment can contaminate water sources, leading to acidification of aquatic environments and harm to aquatic life. The selection of corrosion-resistant materials and implementation of robust containment systems are essential to prevent such incidents. Additionally, proper drainage and wastewater treatment facilities should be integrated into the overall equipment setup to manage any potential HCl-contaminated water.
The lifecycle environmental impact of HCl equipment is also a significant consideration. The manufacturing process of specialized corrosion-resistant materials used in HCl handling equipment can have its own environmental footprint. Therefore, the selection of equipment should take into account not only its operational efficiency but also the sustainability of its production and eventual disposal or recycling.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the environmental impact of HCl equipment. Pumps, valves, and other components should be selected and designed to minimize energy consumption while maintaining safe and effective operation. This not only reduces operational costs but also lowers the carbon footprint associated with HCl handling processes.
Lastly, the proper selection of HCl equipment can contribute to waste reduction and resource conservation. Well-designed and maintained equipment can minimize product loss through leaks or inefficient transfer processes, thereby reducing the overall consumption of HCl and the associated environmental impacts of its production and transportation.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HCl equipment is multifaceted, encompassing air and water pollution risks, lifecycle considerations, energy efficiency, and resource conservation. Careful selection and implementation of appropriate equipment are crucial for minimizing these impacts and ensuring environmentally responsible HCl handling practices.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with HCl equipment is the potential for atmospheric pollution. Inadequate or poorly maintained equipment can result in HCl vapor emissions, which contribute to air pollution and acid rain formation. These emissions can have far-reaching effects on vegetation, soil quality, and aquatic ecosystems. To mitigate this risk, proper ventilation systems and scrubbers must be incorporated into the equipment design to capture and neutralize any escaping vapors.
Water pollution is another critical environmental issue related to HCl handling equipment. Leaks or spills from faulty equipment can contaminate water sources, leading to acidification of aquatic environments and harm to aquatic life. The selection of corrosion-resistant materials and implementation of robust containment systems are essential to prevent such incidents. Additionally, proper drainage and wastewater treatment facilities should be integrated into the overall equipment setup to manage any potential HCl-contaminated water.
The lifecycle environmental impact of HCl equipment is also a significant consideration. The manufacturing process of specialized corrosion-resistant materials used in HCl handling equipment can have its own environmental footprint. Therefore, the selection of equipment should take into account not only its operational efficiency but also the sustainability of its production and eventual disposal or recycling.
Energy efficiency is another crucial factor in the environmental impact of HCl equipment. Pumps, valves, and other components should be selected and designed to minimize energy consumption while maintaining safe and effective operation. This not only reduces operational costs but also lowers the carbon footprint associated with HCl handling processes.
Lastly, the proper selection of HCl equipment can contribute to waste reduction and resource conservation. Well-designed and maintained equipment can minimize product loss through leaks or inefficient transfer processes, thereby reducing the overall consumption of HCl and the associated environmental impacts of its production and transportation.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HCl equipment is multifaceted, encompassing air and water pollution risks, lifecycle considerations, energy efficiency, and resource conservation. Careful selection and implementation of appropriate equipment are crucial for minimizing these impacts and ensuring environmentally responsible HCl handling practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!