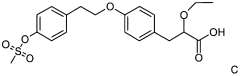
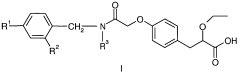
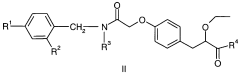
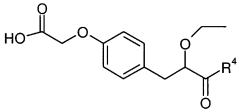
Impact of Ethyl Propanoate on Aqueous-Phase Reaction Kinetics
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Kinetics Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an ester compound that has gained significant attention in the field of chemical kinetics, particularly in aqueous-phase reactions. The study of its impact on reaction kinetics has become increasingly important due to its widespread use in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. This research aims to comprehensively examine the influence of ethyl propanoate on the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions occurring in aqueous environments.
The historical development of this field can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began investigating the behavior of organic compounds in water. However, it was not until the 1950s that the specific effects of esters on aqueous-phase reactions started to gain traction. The advent of more sophisticated analytical techniques in the following decades allowed for more precise measurements and deeper insights into the kinetic processes involved.
Recent technological advancements, particularly in spectroscopic methods and computational chemistry, have revolutionized our ability to study these reactions at a molecular level. This has led to a surge in research activities focused on understanding the intricate details of how ethyl propanoate interacts with water molecules and other reactants in solution.
The primary objective of this investigation is to elucidate the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate influences reaction rates in aqueous systems. This includes examining its role as a potential catalyst, inhibitor, or reactant in various chemical processes. Additionally, we aim to quantify the kinetic parameters associated with these reactions, such as rate constants, activation energies, and reaction orders.
Another crucial goal is to explore the environmental implications of ethyl propanoate in natural water systems. As this compound is frequently released into the environment through industrial processes and consumer products, understanding its impact on aqueous ecosystems is of paramount importance. This research seeks to provide valuable insights that can inform environmental regulations and guide the development of more sustainable industrial practices.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in controlling reaction rates in aqueous media. By manipulating the concentration and conditions under which this compound is present, it may be possible to fine-tune reaction kinetics for specific industrial or laboratory processes. This could lead to more efficient chemical syntheses, improved product yields, and reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, this research into the impact of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reaction kinetics represents a critical step forward in our understanding of complex chemical systems. The findings from this study are expected to have far-reaching implications across multiple scientific disciplines and industrial sectors, paving the way for innovative applications and more sustainable chemical processes.
The historical development of this field can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers began investigating the behavior of organic compounds in water. However, it was not until the 1950s that the specific effects of esters on aqueous-phase reactions started to gain traction. The advent of more sophisticated analytical techniques in the following decades allowed for more precise measurements and deeper insights into the kinetic processes involved.
Recent technological advancements, particularly in spectroscopic methods and computational chemistry, have revolutionized our ability to study these reactions at a molecular level. This has led to a surge in research activities focused on understanding the intricate details of how ethyl propanoate interacts with water molecules and other reactants in solution.
The primary objective of this investigation is to elucidate the mechanisms by which ethyl propanoate influences reaction rates in aqueous systems. This includes examining its role as a potential catalyst, inhibitor, or reactant in various chemical processes. Additionally, we aim to quantify the kinetic parameters associated with these reactions, such as rate constants, activation energies, and reaction orders.
Another crucial goal is to explore the environmental implications of ethyl propanoate in natural water systems. As this compound is frequently released into the environment through industrial processes and consumer products, understanding its impact on aqueous ecosystems is of paramount importance. This research seeks to provide valuable insights that can inform environmental regulations and guide the development of more sustainable industrial practices.
Furthermore, this study aims to investigate the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in controlling reaction rates in aqueous media. By manipulating the concentration and conditions under which this compound is present, it may be possible to fine-tune reaction kinetics for specific industrial or laboratory processes. This could lead to more efficient chemical syntheses, improved product yields, and reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, this research into the impact of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reaction kinetics represents a critical step forward in our understanding of complex chemical systems. The findings from this study are expected to have far-reaching implications across multiple scientific disciplines and industrial sectors, paving the way for innovative applications and more sustainable chemical processes.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Propanoate Applications
The market for ethyl propanoate applications has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by its versatile properties and increasing demand across various industries. As a key ester compound, ethyl propanoate finds extensive use in flavors and fragrances, solvents, and as a chemical intermediate in pharmaceutical and agrochemical production.
In the flavor and fragrance industry, ethyl propanoate is highly valued for its fruity, rum-like aroma, making it a popular choice in food and beverage applications. The compound is widely used in the production of artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry notes. The growing consumer preference for natural and organic products has also led to an increased demand for ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources.
The solvent market represents another significant application area for ethyl propanoate. Its low toxicity, high solvency power, and rapid evaporation rate make it an attractive option for various industrial processes. The compound is particularly useful in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives, where it serves as an effective solvent for resins and polymers.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate plays a crucial role as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its reactivity and compatibility with other compounds make it valuable in organic synthesis processes. The ongoing research and development in the pharmaceutical industry are expected to further drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector.
The agrochemical industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate in the production of pesticides and herbicides. Its ability to enhance the effectiveness of certain active ingredients and improve the overall formulation of agrochemical products contributes to its growing adoption in this sector.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by the rapid industrialization and growth of end-use industries in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also maintain significant market shares, primarily due to the well-established flavor and fragrance industries in these regions.
The market for ethyl propanoate is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the mid-single digits. Factors such as increasing disposable income, changing consumer preferences, and technological advancements in production processes are likely to fuel this growth.
In the flavor and fragrance industry, ethyl propanoate is highly valued for its fruity, rum-like aroma, making it a popular choice in food and beverage applications. The compound is widely used in the production of artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry notes. The growing consumer preference for natural and organic products has also led to an increased demand for ethyl propanoate derived from natural sources.
The solvent market represents another significant application area for ethyl propanoate. Its low toxicity, high solvency power, and rapid evaporation rate make it an attractive option for various industrial processes. The compound is particularly useful in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives, where it serves as an effective solvent for resins and polymers.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate plays a crucial role as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its reactivity and compatibility with other compounds make it valuable in organic synthesis processes. The ongoing research and development in the pharmaceutical industry are expected to further drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in this sector.
The agrochemical industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate in the production of pesticides and herbicides. Its ability to enhance the effectiveness of certain active ingredients and improve the overall formulation of agrochemical products contributes to its growing adoption in this sector.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key market for ethyl propanoate, driven by the rapid industrialization and growth of end-use industries in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also maintain significant market shares, primarily due to the well-established flavor and fragrance industries in these regions.
The market for ethyl propanoate is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the mid-single digits. Factors such as increasing disposable income, changing consumer preferences, and technological advancements in production processes are likely to fuel this growth.
Current Challenges in Aqueous-Phase Reaction Kinetics
The field of aqueous-phase reaction kinetics faces several significant challenges, particularly when considering the impact of organic compounds like ethyl propanoate. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of multi-phase systems, where the presence of organic molecules in an aqueous environment creates intricate interactions that are difficult to model accurately.
The solubility and partitioning behavior of ethyl propanoate in water introduce complications in understanding reaction rates and mechanisms. Researchers struggle to develop comprehensive models that account for the distribution of the compound between the aqueous and organic phases, as well as its potential to form micelles or other aggregates that can influence reaction kinetics.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement of reaction rates in such heterogeneous systems. Traditional kinetic measurement techniques may not be suitable for capturing the nuanced effects of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reactions. This necessitates the development of new analytical methods and instruments capable of real-time, in situ monitoring of reaction progress in multi-phase environments.
The potential catalytic or inhibitory effects of ethyl propanoate on various aqueous-phase reactions present another layer of complexity. Understanding how this organic compound interacts with reactants, intermediates, and catalysts in water is crucial for predicting and controlling reaction outcomes. However, elucidating these interactions at a molecular level remains a significant challenge.
Environmental factors, such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength, can dramatically influence the behavior of ethyl propanoate in aqueous systems. Researchers face difficulties in isolating and quantifying the individual contributions of these factors to overall reaction kinetics. This challenge is compounded by the potential synergistic or antagonistic effects between environmental variables and the organic compound.
The formation of by-products and intermediates in the presence of ethyl propanoate adds another dimension to the complexity of aqueous-phase reaction kinetics. Identifying and characterizing these species, as well as understanding their roles in reaction pathways, requires advanced analytical techniques and sophisticated data interpretation methods.
Scaling up laboratory findings to industrial processes presents its own set of challenges. The behavior of ethyl propanoate in large-scale aqueous reactions may differ significantly from small-scale experiments, necessitating the development of robust scaling laws and predictive models that can bridge this gap.
The solubility and partitioning behavior of ethyl propanoate in water introduce complications in understanding reaction rates and mechanisms. Researchers struggle to develop comprehensive models that account for the distribution of the compound between the aqueous and organic phases, as well as its potential to form micelles or other aggregates that can influence reaction kinetics.
Another challenge lies in the accurate measurement of reaction rates in such heterogeneous systems. Traditional kinetic measurement techniques may not be suitable for capturing the nuanced effects of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reactions. This necessitates the development of new analytical methods and instruments capable of real-time, in situ monitoring of reaction progress in multi-phase environments.
The potential catalytic or inhibitory effects of ethyl propanoate on various aqueous-phase reactions present another layer of complexity. Understanding how this organic compound interacts with reactants, intermediates, and catalysts in water is crucial for predicting and controlling reaction outcomes. However, elucidating these interactions at a molecular level remains a significant challenge.
Environmental factors, such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength, can dramatically influence the behavior of ethyl propanoate in aqueous systems. Researchers face difficulties in isolating and quantifying the individual contributions of these factors to overall reaction kinetics. This challenge is compounded by the potential synergistic or antagonistic effects between environmental variables and the organic compound.
The formation of by-products and intermediates in the presence of ethyl propanoate adds another dimension to the complexity of aqueous-phase reaction kinetics. Identifying and characterizing these species, as well as understanding their roles in reaction pathways, requires advanced analytical techniques and sophisticated data interpretation methods.
Scaling up laboratory findings to industrial processes presents its own set of challenges. The behavior of ethyl propanoate in large-scale aqueous reactions may differ significantly from small-scale experiments, necessitating the development of robust scaling laws and predictive models that can bridge this gap.
Existing Methodologies for Kinetic Analysis
01 Reaction kinetics modeling and simulation
Advanced computational methods are used to model and simulate the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These techniques help in understanding the reaction mechanisms, predicting reaction rates, and optimizing process conditions. The models take into account various factors such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst properties to provide accurate kinetic data.- Reaction kinetics modeling and simulation: Advanced computational methods are used to model and simulate the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These techniques help in understanding the reaction mechanisms, predicting reaction rates, and optimizing process conditions for improved yield and efficiency.
- Catalytic processes for ethyl propanoate production: Various catalytic processes are employed to enhance the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These include heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts, which can significantly increase reaction rates, improve selectivity, and reduce energy requirements.
- Continuous flow reactors for ethyl propanoate synthesis: Continuous flow reactors are utilized to study and optimize the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate production. These systems allow for better control of reaction parameters, improved heat and mass transfer, and enhanced overall process efficiency.
- Kinetic studies of side reactions and impurities: Research focuses on understanding the kinetics of side reactions and impurity formation during ethyl propanoate synthesis. This knowledge is crucial for developing strategies to minimize unwanted by-products and improve the purity of the final product.
- Process intensification techniques: Various process intensification techniques are applied to enhance the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate production. These may include microreactor technology, ultrasound-assisted reactions, and other innovative approaches to improve mass and heat transfer, leading to faster reaction rates and higher yields.
02 Catalytic processes for ethyl propanoate production
Various catalytic processes are employed to enhance the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These include heterogeneous catalysts, enzyme catalysts, and novel catalyst designs that improve selectivity and yield. The catalysts are optimized to reduce activation energy, increase reaction rates, and minimize side reactions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Continuous flow reactors for improved kinetics
Continuous flow reactors are utilized to improve the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis. These systems offer better heat and mass transfer, controlled residence times, and enhanced mixing, leading to improved reaction rates and product quality. The design of these reactors is optimized based on kinetic studies to maximize efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Kinetic studies of side reactions and impurities
Detailed kinetic studies are conducted to understand and control side reactions and impurity formation during ethyl propanoate synthesis. These studies help in developing strategies to minimize unwanted products, improve selectivity, and enhance overall reaction efficiency. The kinetic data is used to optimize reaction conditions and purification processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature and pressure effects on reaction kinetics
The influence of temperature and pressure on the reaction kinetics of ethyl propanoate synthesis is extensively studied. These parameters significantly affect reaction rates, equilibrium constants, and product distribution. Kinetic models are developed to predict optimal temperature and pressure conditions for maximizing yield and selectivity while minimizing energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Propanoate Research
The impact of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reaction kinetics represents an emerging field of study in chemical engineering. The competitive landscape is characterized by early-stage research and development, with potential applications across various industries. While the market size remains relatively small, it is expected to grow as understanding of the compound's effects improves. Leading research institutions like the Chinese Academy of Science and Tianjin University are at the forefront of academic studies, while companies such as BASF, Dow, and AstraZeneca are exploring industrial applications. The technology is still in its infancy, with ongoing efforts to elucidate mechanisms and optimize processes for practical use.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced catalytic systems for studying the impact of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reaction kinetics. Their approach utilizes in-situ spectroscopic techniques, including ATR-FTIR and Raman spectroscopy, to monitor real-time changes in reaction rates and intermediate formation[1]. BASF's research has shown that ethyl propanoate can act as both a reactant and a solvent in aqueous systems, influencing reaction pathways and product distributions. They have observed that increasing ethyl propanoate concentration can lead to a non-linear effect on reaction rates, with optimal concentrations varying depending on the specific reaction system[2]. BASF has also developed computational models to predict the influence of ethyl propanoate on reaction kinetics, allowing for more efficient process design and optimization in industrial applications[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive analytical techniques, advanced modeling capabilities, and extensive experience in industrial-scale applications. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in studying extremely dilute systems or ultra-fast reactions.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has pioneered a microfluidic platform for investigating the impact of ethyl propanoate on aqueous-phase reaction kinetics. This innovative approach allows for precise control of reaction conditions and rapid screening of multiple parameters. Dow's system incorporates online analytics, including UV-Vis spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, enabling real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product formation[4]. Their research has revealed that ethyl propanoate can significantly alter the polarity and hydrogen-bonding characteristics of the reaction medium, leading to changes in reaction rates and selectivity. Dow has also explored the use of ethyl propanoate as a co-solvent in biphasic systems, demonstrating its potential to enhance mass transfer and accelerate interfacial reactions[5]. Furthermore, Dow has developed predictive models that account for the non-ideal behavior of ethyl propanoate in aqueous mixtures, improving the accuracy of kinetic predictions in complex reaction environments[6].
Strengths: High-throughput screening capabilities, advanced analytical integration, and expertise in multiphase systems. Weaknesses: Potential scalability challenges when translating microfluidic results to larger-scale processes.
Innovative Approaches in Reaction Kinetics
Therapeutic agents
PatentWO2004056748A1
Innovation
- Development of novel (2S)-3-(4-{2-[amino]-2-oxoethoxy}phenyl)-2-ethoxypropanoic acid derivatives as selective PPAR modulators, which include specific compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, and prodrugs, to enhance insulin sensitivity and treat lipid disorders.
Device allowing improved reaction monitoring of gas phase reactions in mass spectrometers using an auto ejection ion trap
PatentActiveGB2512474B
Innovation
- The use of broadband excitation with frequency notches to selectively eject product ions while retaining precursor and reagent ions in the collision/reaction cell.
- Determination of reaction times by measuring the ejection times of product ions, allowing differentiation of precursor ions based on their reaction kinetics.
- Application of this technique to an auto ejection ion trap, enabling improved monitoring of gas phase reactions in mass spectrometers.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Propanoate Use
The environmental impact of ethyl propanoate use is a critical consideration in assessing its overall sustainability and safety profile. As a widely used ester in various industries, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, ethyl propanoate's potential effects on ecosystems and human health warrant careful examination.
In aquatic environments, the introduction of ethyl propanoate can lead to significant alterations in water chemistry. The compound's moderate solubility in water allows it to disperse readily, potentially affecting pH levels and dissolved oxygen content. These changes can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems, impacting flora and fauna at various trophic levels.
Biodegradation of ethyl propanoate in natural water bodies is an important factor in its environmental fate. Studies have shown that the compound undergoes relatively rapid biodegradation under aerobic conditions, with half-lives typically ranging from a few days to a few weeks. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary significantly depending on environmental factors such as temperature, microbial populations, and the presence of other organic compounds.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms is generally considered low for ethyl propanoate due to its relatively low octanol-water partition coefficient. This suggests that the compound is unlikely to concentrate in the food chain, reducing long-term ecological risks. Nevertheless, short-term exposure to high concentrations may still pose acute toxicity risks to sensitive aquatic species.
Atmospheric emissions of ethyl propanoate contribute to the formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the troposphere. These VOCs can participate in photochemical reactions, potentially leading to the formation of ground-level ozone and other secondary air pollutants. While the ozone-forming potential of ethyl propanoate is lower than that of many other VOCs, its cumulative impact in urban and industrial areas should not be overlooked.
Soil contamination by ethyl propanoate, though less common than aquatic or atmospheric pollution, can occur through spills or improper disposal. In soil environments, the compound's mobility is influenced by factors such as organic matter content and soil pH. Leaching into groundwater is a potential concern, particularly in areas with high water tables or permeable soil structures.
Human exposure to ethyl propanoate through environmental routes is generally considered to be of low risk at typical environmental concentrations. However, occupational exposure in manufacturing or processing facilities may require specific safety measures to prevent adverse health effects, particularly related to respiratory and dermal irritation.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate's environmental impact is moderated by its relatively rapid biodegradation and low bioaccumulation potential, its widespread use necessitates ongoing monitoring and assessment of potential ecological and health risks. Sustainable management practices and proper handling protocols are essential to minimize its environmental footprint and ensure its continued safe use across various applications.
In aquatic environments, the introduction of ethyl propanoate can lead to significant alterations in water chemistry. The compound's moderate solubility in water allows it to disperse readily, potentially affecting pH levels and dissolved oxygen content. These changes can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems, impacting flora and fauna at various trophic levels.
Biodegradation of ethyl propanoate in natural water bodies is an important factor in its environmental fate. Studies have shown that the compound undergoes relatively rapid biodegradation under aerobic conditions, with half-lives typically ranging from a few days to a few weeks. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary significantly depending on environmental factors such as temperature, microbial populations, and the presence of other organic compounds.
The potential for bioaccumulation in aquatic organisms is generally considered low for ethyl propanoate due to its relatively low octanol-water partition coefficient. This suggests that the compound is unlikely to concentrate in the food chain, reducing long-term ecological risks. Nevertheless, short-term exposure to high concentrations may still pose acute toxicity risks to sensitive aquatic species.
Atmospheric emissions of ethyl propanoate contribute to the formation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the troposphere. These VOCs can participate in photochemical reactions, potentially leading to the formation of ground-level ozone and other secondary air pollutants. While the ozone-forming potential of ethyl propanoate is lower than that of many other VOCs, its cumulative impact in urban and industrial areas should not be overlooked.
Soil contamination by ethyl propanoate, though less common than aquatic or atmospheric pollution, can occur through spills or improper disposal. In soil environments, the compound's mobility is influenced by factors such as organic matter content and soil pH. Leaching into groundwater is a potential concern, particularly in areas with high water tables or permeable soil structures.
Human exposure to ethyl propanoate through environmental routes is generally considered to be of low risk at typical environmental concentrations. However, occupational exposure in manufacturing or processing facilities may require specific safety measures to prevent adverse health effects, particularly related to respiratory and dermal irritation.
In conclusion, while ethyl propanoate's environmental impact is moderated by its relatively rapid biodegradation and low bioaccumulation potential, its widespread use necessitates ongoing monitoring and assessment of potential ecological and health risks. Sustainable management practices and proper handling protocols are essential to minimize its environmental footprint and ensure its continued safe use across various applications.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Kinetics Research
The regulatory framework for chemical kinetics research involving ethyl propanoate in aqueous-phase reactions is governed by a complex interplay of national and international guidelines. These regulations aim to ensure the safety, ethical conduct, and environmental responsibility of research activities while promoting scientific advancement.
At the national level, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States play crucial roles. The EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulates the production, importation, and use of chemical substances, including ethyl propanoate. Researchers must comply with TSCA reporting requirements and safety standards when conducting experiments involving this compound.
OSHA's Laboratory Standard (29 CFR 1910.1450) sets forth guidelines for occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals in laboratories. This standard mandates the implementation of Chemical Hygiene Plans, which include procedures for safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals used in kinetics research.
Internationally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union impacts research involving ethyl propanoate. REACH requires registration of substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, which may affect large-scale kinetics studies.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Researchers must adhere to GHS guidelines when labeling and handling ethyl propanoate and other chemicals used in aqueous-phase reaction kinetics experiments.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping research practices. The Clean Water Act in the United States and similar legislation in other countries set limits on the discharge of chemicals into water bodies. Researchers must consider these regulations when designing experiments and disposing of reaction products containing ethyl propanoate.
Institutional review boards (IRBs) and ethics committees provide additional oversight for research involving human subjects or potential environmental impacts. While chemical kinetics studies may not directly involve human subjects, IRB approval may be necessary if the research has broader implications for human health or the environment.
Funding agencies often impose their own regulatory requirements on research projects. Compliance with these agency-specific guidelines is crucial for securing and maintaining research grants in the field of chemical kinetics.
As the field of chemical kinetics evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. Researchers must stay informed about changes in regulations and best practices to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of their work. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of ongoing collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and regulatory bodies to balance scientific progress with safety and environmental concerns.
At the national level, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States play crucial roles. The EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) regulates the production, importation, and use of chemical substances, including ethyl propanoate. Researchers must comply with TSCA reporting requirements and safety standards when conducting experiments involving this compound.
OSHA's Laboratory Standard (29 CFR 1910.1450) sets forth guidelines for occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals in laboratories. This standard mandates the implementation of Chemical Hygiene Plans, which include procedures for safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals used in kinetics research.
Internationally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union impacts research involving ethyl propanoate. REACH requires registration of substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, which may affect large-scale kinetics studies.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Researchers must adhere to GHS guidelines when labeling and handling ethyl propanoate and other chemicals used in aqueous-phase reaction kinetics experiments.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in shaping research practices. The Clean Water Act in the United States and similar legislation in other countries set limits on the discharge of chemicals into water bodies. Researchers must consider these regulations when designing experiments and disposing of reaction products containing ethyl propanoate.
Institutional review boards (IRBs) and ethics committees provide additional oversight for research involving human subjects or potential environmental impacts. While chemical kinetics studies may not directly involve human subjects, IRB approval may be necessary if the research has broader implications for human health or the environment.
Funding agencies often impose their own regulatory requirements on research projects. Compliance with these agency-specific guidelines is crucial for securing and maintaining research grants in the field of chemical kinetics.
As the field of chemical kinetics evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. Researchers must stay informed about changes in regulations and best practices to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of their work. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of ongoing collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and regulatory bodies to balance scientific progress with safety and environmental concerns.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!