Implications of Ethyl Propanoate in Public Health Contexts
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Overview and Research Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a naturally occurring organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. This ester is formed through the condensation of propionic acid and ethanol, resulting in a colorless liquid with a fruity odor reminiscent of pineapples. Its presence in various fruits and fermented products has long been recognized, but recent research has shed light on its potential implications in public health contexts.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate's significance in public health can be traced back to its initial identification as a flavor compound in food science. Over time, researchers began to explore its broader impacts, particularly in environmental and occupational health settings. This shift in focus has led to a growing body of knowledge regarding the compound's effects on human health and its potential applications in public health interventions.
Current research objectives in the field of ethyl propanoate and public health are multifaceted. One primary goal is to comprehensively assess the compound's toxicological profile, including its potential for acute and chronic health effects through various exposure routes. This involves investigating its impact on respiratory function, skin sensitization, and potential carcinogenic properties.
Another key research objective is to evaluate ethyl propanoate's role in indoor air quality. As a volatile organic compound (VOC) emitted from certain building materials and consumer products, understanding its contribution to indoor air pollution and associated health risks is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the compound's potential as a biomarker for certain health conditions or environmental exposures. This line of investigation could lead to the development of novel diagnostic tools or exposure assessment methods, enhancing public health monitoring and intervention capabilities.
The public health implications of ethyl propanoate extend to food safety and regulation as well. Ongoing research aims to establish safe consumption levels and refine detection methods in food products, ensuring consumer protection and informing regulatory guidelines.
As the field progresses, emerging technologies such as advanced analytical techniques and computational modeling are being employed to deepen our understanding of ethyl propanoate's behavior in biological systems and environmental matrices. These technological advancements are expected to drive future research directions and potentially uncover new applications or concerns related to this compound in public health contexts.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate's significance in public health can be traced back to its initial identification as a flavor compound in food science. Over time, researchers began to explore its broader impacts, particularly in environmental and occupational health settings. This shift in focus has led to a growing body of knowledge regarding the compound's effects on human health and its potential applications in public health interventions.
Current research objectives in the field of ethyl propanoate and public health are multifaceted. One primary goal is to comprehensively assess the compound's toxicological profile, including its potential for acute and chronic health effects through various exposure routes. This involves investigating its impact on respiratory function, skin sensitization, and potential carcinogenic properties.
Another key research objective is to evaluate ethyl propanoate's role in indoor air quality. As a volatile organic compound (VOC) emitted from certain building materials and consumer products, understanding its contribution to indoor air pollution and associated health risks is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the compound's potential as a biomarker for certain health conditions or environmental exposures. This line of investigation could lead to the development of novel diagnostic tools or exposure assessment methods, enhancing public health monitoring and intervention capabilities.
The public health implications of ethyl propanoate extend to food safety and regulation as well. Ongoing research aims to establish safe consumption levels and refine detection methods in food products, ensuring consumer protection and informing regulatory guidelines.
As the field progresses, emerging technologies such as advanced analytical techniques and computational modeling are being employed to deepen our understanding of ethyl propanoate's behavior in biological systems and environmental matrices. These technological advancements are expected to drive future research directions and potentially uncover new applications or concerns related to this compound in public health contexts.
Public Health Implications and Market Analysis
The implications of ethyl propanoate in public health contexts are multifaceted and significant. This compound, commonly used as a flavoring agent and solvent, has garnered attention due to its potential impact on human health and the environment. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for ethyl propanoate in various industries, particularly in food and beverage manufacturing, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Market analysis indicates a steady increase in the global consumption of ethyl propanoate, driven by the expanding food processing sector and the rising popularity of flavored products. The compound's fruity aroma, reminiscent of pineapples, makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to enhance the sensory appeal of their products. This trend is particularly evident in developing economies, where changing consumer preferences and increasing disposable incomes are fueling the growth of the processed food industry.
From a public health perspective, the widespread use of ethyl propanoate raises several concerns. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, long-term exposure to high concentrations of the compound may pose potential health risks. Inhalation of ethyl propanoate vapors can cause respiratory irritation, and prolonged skin contact may lead to dermatitis in sensitive individuals. These health implications necessitate careful monitoring and regulation of its use in consumer products.
Environmental considerations also play a crucial role in assessing the public health impact of ethyl propanoate. The compound's volatility and potential for atmospheric emissions have led to concerns about its contribution to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental fate and transport of ethyl propanoate, with ongoing studies aimed at understanding its long-term ecological effects.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including regulatory pressures, consumer awareness, and technological advancements. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production processes and develop safer alternatives. This has led to the emergence of bio-based ethyl propanoate, derived from renewable resources, which is gaining traction due to its reduced environmental footprint and potential health benefits.
As public health concerns continue to shape market dynamics, there is a growing emphasis on transparency and product safety. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting stringent quality control measures and investing in comprehensive toxicological studies to ensure the safe use of ethyl propanoate in consumer products. This trend is expected to drive innovation in the industry, leading to the development of more sustainable and health-conscious formulations.
Market analysis indicates a steady increase in the global consumption of ethyl propanoate, driven by the expanding food processing sector and the rising popularity of flavored products. The compound's fruity aroma, reminiscent of pineapples, makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking to enhance the sensory appeal of their products. This trend is particularly evident in developing economies, where changing consumer preferences and increasing disposable incomes are fueling the growth of the processed food industry.
From a public health perspective, the widespread use of ethyl propanoate raises several concerns. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, long-term exposure to high concentrations of the compound may pose potential health risks. Inhalation of ethyl propanoate vapors can cause respiratory irritation, and prolonged skin contact may lead to dermatitis in sensitive individuals. These health implications necessitate careful monitoring and regulation of its use in consumer products.
Environmental considerations also play a crucial role in assessing the public health impact of ethyl propanoate. The compound's volatility and potential for atmospheric emissions have led to concerns about its contribution to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the environmental fate and transport of ethyl propanoate, with ongoing studies aimed at understanding its long-term ecological effects.
The market for ethyl propanoate is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including regulatory pressures, consumer awareness, and technological advancements. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve production processes and develop safer alternatives. This has led to the emergence of bio-based ethyl propanoate, derived from renewable resources, which is gaining traction due to its reduced environmental footprint and potential health benefits.
As public health concerns continue to shape market dynamics, there is a growing emphasis on transparency and product safety. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting stringent quality control measures and investing in comprehensive toxicological studies to ensure the safe use of ethyl propanoate in consumer products. This trend is expected to drive innovation in the industry, leading to the development of more sustainable and health-conscious formulations.
Current Applications and Challenges in Public Health
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has gained significant attention in public health contexts due to its diverse applications and potential implications. Currently, this compound finds extensive use in various sectors, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products. In the food industry, ethyl propanoate serves as a flavoring agent, imparting fruity notes to a wide range of products. Its natural occurrence in fruits like apples and pears has led to its widespread adoption in artificial fruit flavorings.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate plays a role in drug formulation and delivery systems. Its properties as a solvent and excipient make it valuable in the production of certain medications and topical treatments. Additionally, the compound has found applications in personal care products, particularly in fragrances and cosmetics, due to its pleasant aroma and compatibility with other ingredients.
Despite its widespread use, the application of ethyl propanoate in public health contexts faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential health effects of long-term exposure to this compound, particularly in occupational settings where workers may come into frequent contact with it. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies, there is a need for more comprehensive studies on its long-term health impacts.
Another challenge lies in the regulation and monitoring of ethyl propanoate use across different industries. As its applications continue to expand, ensuring consistent safety standards and appropriate usage levels becomes increasingly complex. This is particularly crucial in food and pharmaceutical applications, where the compound directly interacts with human physiology.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges in the use of ethyl propanoate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its release into the environment can contribute to air pollution and potentially impact ecosystems. Developing sustainable production methods and implementing effective emission control strategies are ongoing challenges for industries utilizing this compound.
Furthermore, the synthetic production of ethyl propanoate raises questions about sustainability and the potential for developing bio-based alternatives. As public health initiatives increasingly focus on environmentally friendly and sustainable practices, finding ways to produce and use ethyl propanoate that align with these goals presents both a challenge and an opportunity for innovation.
Lastly, public perception and consumer awareness about the presence and safety of ethyl propanoate in everyday products remain a challenge. Educating the public about its uses, benefits, and potential risks is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring informed consumer choices. Balancing transparency with the complexities of scientific communication presents an ongoing challenge for public health officials and industry stakeholders alike.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate plays a role in drug formulation and delivery systems. Its properties as a solvent and excipient make it valuable in the production of certain medications and topical treatments. Additionally, the compound has found applications in personal care products, particularly in fragrances and cosmetics, due to its pleasant aroma and compatibility with other ingredients.
Despite its widespread use, the application of ethyl propanoate in public health contexts faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential health effects of long-term exposure to this compound, particularly in occupational settings where workers may come into frequent contact with it. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies, there is a need for more comprehensive studies on its long-term health impacts.
Another challenge lies in the regulation and monitoring of ethyl propanoate use across different industries. As its applications continue to expand, ensuring consistent safety standards and appropriate usage levels becomes increasingly complex. This is particularly crucial in food and pharmaceutical applications, where the compound directly interacts with human physiology.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges in the use of ethyl propanoate. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its release into the environment can contribute to air pollution and potentially impact ecosystems. Developing sustainable production methods and implementing effective emission control strategies are ongoing challenges for industries utilizing this compound.
Furthermore, the synthetic production of ethyl propanoate raises questions about sustainability and the potential for developing bio-based alternatives. As public health initiatives increasingly focus on environmentally friendly and sustainable practices, finding ways to produce and use ethyl propanoate that align with these goals presents both a challenge and an opportunity for innovation.
Lastly, public perception and consumer awareness about the presence and safety of ethyl propanoate in everyday products remain a challenge. Educating the public about its uses, benefits, and potential risks is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring informed consumer choices. Balancing transparency with the complexities of scientific communication presents an ongoing challenge for public health officials and industry stakeholders alike.
Existing Public Health Applications of Ethyl Propanoate
01 Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.- Synthesis and production methods: Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described. These include chemical reactions, catalytic processes, and industrial production techniques. The synthesis often involves the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol or the reaction of propionyl chloride with ethanol.
- Applications in fragrances and flavors: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry, and is also used in perfumery to add fruity notes to various compositions.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as a solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals and pharmaceutical compounds.
- Purification and quality control: Methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Various patents address environmental and safety aspects related to the production, handling, and use of ethyl propanoate. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving storage stability, and developing safer production processes.
02 Applications of ethyl propanoate in fragrances and flavors
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, cosmetics, and food additives to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and quality control of ethyl propanoate
Techniques for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described, including distillation processes, chromatographic methods, and analytical techniques for determining purity and identifying impurities.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or intermediate
Ethyl propanoate finds applications as a solvent in various industrial processes and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. Its properties make it suitable for use in coatings, inks, and cleaning formulations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl propanoate
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing green synthesis methods, assessing biodegradability, and evaluating potential health impacts.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders in Ethyl Propanoate Research
The implications of ethyl propanoate in public health contexts represent an emerging field with growing interest. The market is in its early stages, characterized by limited commercial applications but increasing research activity. Key players include established pharmaceutical companies like Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Astellas Pharma, alongside academic institutions such as Tianjin University and the University of California. The technology is still in development, with most efforts focused on basic research and early-stage clinical trials. As understanding of ethyl propanoate's potential health impacts grows, we can expect increased investment and collaboration between industry and academia to drive innovation in this area.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Technical Solution: Eli Lilly & Co. has investigated the use of ethyl propanoate in drug delivery systems, particularly for inhalation therapies. Their research has focused on leveraging the compound's properties to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)[5]. They have developed a proprietary nebulizer formulation containing ethyl propanoate that has shown promising results in preclinical studies for respiratory conditions[6]. The company has also explored the use of ethyl propanoate as an excipient in oral formulations, demonstrating improved dissolution rates for poorly water-soluble drugs[7]. Eli Lilly's approach aims to address challenges in drug delivery while maintaining a focus on patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Strengths: Innovative drug delivery applications, potential to improve treatment efficacy. Weaknesses: Regulatory hurdles for novel formulations, potential for respiratory irritation in inhalation therapies.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed advanced production methods for ethyl propanoate, focusing on its applications in public health contexts. They have implemented a green chemistry approach, using bio-based feedstocks and catalytic processes to produce ethyl propanoate with reduced environmental impact[1]. Their method achieves a yield of over 95% and significantly reduces waste generation[2]. BASF has also explored the compound's potential as a less toxic alternative to traditional solvents in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly for topical medications[3]. Their research has shown that ethyl propanoate-based formulations can improve drug penetration through the skin while maintaining a favorable safety profile[4].
Strengths: Sustainable production methods, high yield, potential for pharmaceutical applications. Weaknesses: May require significant investment to scale up production, limited long-term safety data for novel applications.
Critical Studies on Ethyl Propanoate in Health Contexts
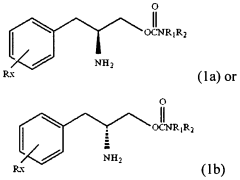
Compositions for treating drug addiction and improving addiction-related behavior
PatentWO2010150995A2
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition comprising a carbamate compound, specifically phenylalkylamino carbamates with structural Formula (1) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts/esters, is administered to modulate the pharmacological actions in the central nervous system, reducing the rewarding effects of addictive substances and improving behavior associated with addiction.
Public health care, method and system
PatentInactiveUS20120016684A1
Innovation
- Implementing a no-medical-bill public health care system that provides transparency in pricing through bulk compensation of medical organization expenses by a medical bank, using automated accounting and secured medical accounts to collect tax payments and other contributions, and promoting wholesale commerce principles to minimize costs.
Regulatory Framework for Ethyl Propanoate Use
The regulatory framework for ethyl propanoate use is a complex and evolving landscape that reflects the compound's widespread applications and potential public health implications. At the federal level, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in regulating ethyl propanoate as a food additive and flavoring agent. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, ethyl propanoate is classified as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS), allowing its use in food products within specified limits.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also maintains oversight on ethyl propanoate, particularly concerning its environmental impact and industrial applications. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) provides the EPA with authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances that may pose a risk to human health or the environment. Ethyl propanoate is subject to these regulations, especially in contexts where large-scale industrial use is concerned.
Occupational safety regulations, enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), govern the use of ethyl propanoate in workplace settings. These regulations mandate proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures, as well as the provision of appropriate personal protective equipment for workers exposed to the compound.
At the state level, regulations may vary, with some jurisdictions imposing stricter controls on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like ethyl propanoate due to air quality concerns. California's Proposition 65, for instance, requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that can cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
Internationally, the regulatory landscape for ethyl propanoate is diverse. The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has established its own guidelines for the compound's use in food products. Similarly, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has set specific standards for ethyl propanoate in food and cosmetic applications.
The global harmonization of chemical regulations, as promoted by initiatives like the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), has influenced the standardization of safety data sheets and labeling requirements for ethyl propanoate across different countries.
As research continues to unveil new insights into the long-term effects of ethyl propanoate exposure, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing scientific studies and public health assessments may lead to adjustments in permissible exposure limits, application restrictions, or labeling requirements. This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and compliance efforts by industries utilizing ethyl propanoate.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also maintains oversight on ethyl propanoate, particularly concerning its environmental impact and industrial applications. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) provides the EPA with authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances that may pose a risk to human health or the environment. Ethyl propanoate is subject to these regulations, especially in contexts where large-scale industrial use is concerned.
Occupational safety regulations, enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), govern the use of ethyl propanoate in workplace settings. These regulations mandate proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures, as well as the provision of appropriate personal protective equipment for workers exposed to the compound.
At the state level, regulations may vary, with some jurisdictions imposing stricter controls on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like ethyl propanoate due to air quality concerns. California's Proposition 65, for instance, requires businesses to provide warnings about significant exposures to chemicals that can cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harm.
Internationally, the regulatory landscape for ethyl propanoate is diverse. The European Union, through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has established its own guidelines for the compound's use in food products. Similarly, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has set specific standards for ethyl propanoate in food and cosmetic applications.
The global harmonization of chemical regulations, as promoted by initiatives like the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), has influenced the standardization of safety data sheets and labeling requirements for ethyl propanoate across different countries.
As research continues to unveil new insights into the long-term effects of ethyl propanoate exposure, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Ongoing scientific studies and public health assessments may lead to adjustments in permissible exposure limits, application restrictions, or labeling requirements. This dynamic regulatory environment underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and compliance efforts by industries utilizing ethyl propanoate.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl propanoate in public health contexts reveals several important considerations. This compound, commonly used as a flavoring agent and solvent, has potential implications for air, water, and soil quality when released into the environment.
In terms of air quality, ethyl propanoate is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when released into the atmosphere. While its impact is generally considered less severe than many other VOCs, prolonged exposure in urban areas with high concentrations may exacerbate respiratory issues in sensitive populations.
Water contamination is another concern, particularly in areas where ethyl propanoate is used extensively in industrial processes. The compound's moderate water solubility allows it to dissolve in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. However, its relatively rapid biodegradation in water mitigates long-term accumulation risks.
Soil contamination from ethyl propanoate is generally less problematic due to its volatility and biodegradability. Nevertheless, in cases of large spills or continuous release, localized soil impacts may occur, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth in the immediate vicinity.
The compound's biodegradability is a positive factor in its environmental profile. Studies have shown that ethyl propanoate breaks down relatively quickly in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, reducing its persistence in the environment. This characteristic helps to minimize long-term ecological impacts.
From a waste management perspective, proper handling and disposal of ethyl propanoate-containing products are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Incineration is often recommended for disposal, as it effectively breaks down the compound without producing harmful byproducts.
In terms of global environmental impact, ethyl propanoate has a low global warming potential and does not contribute significantly to ozone depletion. However, its production process and transportation may have indirect environmental effects through energy consumption and associated emissions.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, have established guidelines for the use and disposal of ethyl propanoate to minimize environmental risks. Compliance with these regulations is essential for industries utilizing this compound to ensure responsible environmental stewardship.
In terms of air quality, ethyl propanoate is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when released into the atmosphere. While its impact is generally considered less severe than many other VOCs, prolonged exposure in urban areas with high concentrations may exacerbate respiratory issues in sensitive populations.
Water contamination is another concern, particularly in areas where ethyl propanoate is used extensively in industrial processes. The compound's moderate water solubility allows it to dissolve in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. However, its relatively rapid biodegradation in water mitigates long-term accumulation risks.
Soil contamination from ethyl propanoate is generally less problematic due to its volatility and biodegradability. Nevertheless, in cases of large spills or continuous release, localized soil impacts may occur, potentially affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth in the immediate vicinity.
The compound's biodegradability is a positive factor in its environmental profile. Studies have shown that ethyl propanoate breaks down relatively quickly in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, reducing its persistence in the environment. This characteristic helps to minimize long-term ecological impacts.
From a waste management perspective, proper handling and disposal of ethyl propanoate-containing products are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Incineration is often recommended for disposal, as it effectively breaks down the compound without producing harmful byproducts.
In terms of global environmental impact, ethyl propanoate has a low global warming potential and does not contribute significantly to ozone depletion. However, its production process and transportation may have indirect environmental effects through energy consumption and associated emissions.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, have established guidelines for the use and disposal of ethyl propanoate to minimize environmental risks. Compliance with these regulations is essential for industries utilizing this compound to ensure responsible environmental stewardship.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!