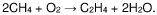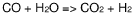Mechanistic Insights into Ethyl Propanoate Hydrosilylation Reactions
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hydrosilylation Background
Hydrosilylation, a fundamental reaction in organosilicon chemistry, involves the addition of silicon-hydrogen bonds across unsaturated bonds. This process, discovered in the late 1940s by John L. Speier, has since become a cornerstone in the synthesis of organosilicon compounds. The reaction's versatility and efficiency have made it indispensable in various industrial applications, ranging from the production of silicone polymers to the synthesis of fine chemicals.
The mechanism of hydrosilylation has been a subject of extensive research since its discovery. Initially, it was believed to proceed through a simple concerted addition. However, subsequent studies revealed a more complex pathway involving transition metal catalysts. The most widely accepted mechanism for platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation was proposed by Chalk and Harrod in 1965, which involves oxidative addition of the silane to the metal center, followed by olefin coordination and insertion, and finally reductive elimination to yield the product.
Over the years, numerous catalysts have been developed to improve the efficiency and selectivity of hydrosilylation reactions. Platinum complexes, particularly Speier's catalyst (H2PtCl6) and Karstedt's catalyst, remain the most widely used in industrial processes. However, the high cost and potential toxicity of platinum have driven research towards alternative catalysts based on other transition metals such as rhodium, iridium, and ruthenium.
The substrate scope of hydrosilylation has expanded significantly since its inception. While initially focused on alkenes and alkynes, the reaction has been successfully applied to a wide range of unsaturated compounds, including aldehydes, ketones, imines, and even carbon dioxide. This broad applicability has contributed to the reaction's prominence in both academic research and industrial applications.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly hydrosilylation processes. This has led to research into earth-abundant metal catalysts, such as iron and nickel complexes, as well as metal-free organocatalytic systems. Additionally, efforts have been made to improve the atom economy of the reaction and to develop recyclable catalysts.
The study of hydrosilylation mechanisms continues to be an active area of research, with modern computational methods and advanced spectroscopic techniques providing new insights into reaction pathways and intermediate species. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for the rational design of more efficient and selective catalysts, as well as for expanding the reaction's scope to new substrates and applications.
The mechanism of hydrosilylation has been a subject of extensive research since its discovery. Initially, it was believed to proceed through a simple concerted addition. However, subsequent studies revealed a more complex pathway involving transition metal catalysts. The most widely accepted mechanism for platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation was proposed by Chalk and Harrod in 1965, which involves oxidative addition of the silane to the metal center, followed by olefin coordination and insertion, and finally reductive elimination to yield the product.
Over the years, numerous catalysts have been developed to improve the efficiency and selectivity of hydrosilylation reactions. Platinum complexes, particularly Speier's catalyst (H2PtCl6) and Karstedt's catalyst, remain the most widely used in industrial processes. However, the high cost and potential toxicity of platinum have driven research towards alternative catalysts based on other transition metals such as rhodium, iridium, and ruthenium.
The substrate scope of hydrosilylation has expanded significantly since its inception. While initially focused on alkenes and alkynes, the reaction has been successfully applied to a wide range of unsaturated compounds, including aldehydes, ketones, imines, and even carbon dioxide. This broad applicability has contributed to the reaction's prominence in both academic research and industrial applications.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly hydrosilylation processes. This has led to research into earth-abundant metal catalysts, such as iron and nickel complexes, as well as metal-free organocatalytic systems. Additionally, efforts have been made to improve the atom economy of the reaction and to develop recyclable catalysts.
The study of hydrosilylation mechanisms continues to be an active area of research, with modern computational methods and advanced spectroscopic techniques providing new insights into reaction pathways and intermediate species. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for the rational design of more efficient and selective catalysts, as well as for expanding the reaction's scope to new substrates and applications.
Market Analysis
The market for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for silicone-based products across various industries. This reaction plays a crucial role in the production of organosilicon compounds, which find applications in diverse sectors such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, personal care, and construction.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the products of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation are utilized in the synthesis of drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The growing emphasis on developing novel drug delivery systems and the rising demand for personalized medicine are expected to fuel the market growth in this sector.
The electronics industry represents another major market for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products. With the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing miniaturization of electronic devices, there is a growing need for high-performance materials. Organosilicon compounds derived from this reaction are used in the production of semiconductors, printed circuit boards, and other electronic components, contributing to enhanced device performance and durability.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is also a significant consumer of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products. These compounds are used in the formulation of various skincare and haircare products, providing improved texture, stability, and sensory properties. The rising consumer awareness regarding personal grooming and the demand for natural and organic cosmetics are driving the market growth in this segment.
In the construction sector, ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products find applications in sealants, adhesives, and coatings. The increasing focus on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices is expected to boost the demand for these materials, as they offer excellent weather resistance, durability, and thermal insulation properties.
The market for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and selectivity of the hydrosilylation process, as well as to develop novel catalysts and reaction conditions.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products, owing to the presence of well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing demand for consumer electronics and personal care products.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the products of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation are utilized in the synthesis of drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The growing emphasis on developing novel drug delivery systems and the rising demand for personalized medicine are expected to fuel the market growth in this sector.
The electronics industry represents another major market for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products. With the rapid advancement of technology and the increasing miniaturization of electronic devices, there is a growing need for high-performance materials. Organosilicon compounds derived from this reaction are used in the production of semiconductors, printed circuit boards, and other electronic components, contributing to enhanced device performance and durability.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is also a significant consumer of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products. These compounds are used in the formulation of various skincare and haircare products, providing improved texture, stability, and sensory properties. The rising consumer awareness regarding personal grooming and the demand for natural and organic cosmetics are driving the market growth in this segment.
In the construction sector, ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products find applications in sealants, adhesives, and coatings. The increasing focus on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices is expected to boost the demand for these materials, as they offer excellent weather resistance, durability, and thermal insulation properties.
The market for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions is characterized by intense competition among key players, including major chemical companies and specialty chemical manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve the efficiency and selectivity of the hydrosilylation process, as well as to develop novel catalysts and reaction conditions.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products, owing to the presence of well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable income, and growing demand for consumer electronics and personal care products.
Technical Challenges
The hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate presents several significant technical challenges that researchers and industry professionals must address. One of the primary obstacles is achieving high selectivity in the reaction. The presence of multiple functional groups in ethyl propanoate, including the carbonyl group and the ester linkage, can lead to undesired side reactions and the formation of byproducts. Controlling the reaction pathway to favor the desired hydrosilylation product requires precise tuning of reaction conditions and catalyst design.
Another major challenge lies in the development of efficient and cost-effective catalysts. While precious metal catalysts, particularly those based on platinum and rhodium, have shown promising results, their high cost and limited availability hinder large-scale industrial applications. The search for alternative catalysts based on more abundant and less expensive metals, such as iron or nickel, is ongoing but faces hurdles in achieving comparable activity and selectivity.
The reaction mechanism of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation is complex and not fully understood, which poses difficulties in optimizing reaction conditions and predicting outcomes. The interplay between the catalyst, substrate, and silane reagent involves multiple steps and intermediates, making it challenging to elucidate the precise reaction pathway. This lack of mechanistic insight hampers the rational design of improved catalysts and reaction protocols.
Controlling the regioselectivity of the hydrosilylation reaction presents another technical challenge. Depending on the reaction conditions and catalyst used, the silicon atom can be added to different positions on the ethyl propanoate molecule, leading to a mixture of products. Achieving high regioselectivity is crucial for obtaining the desired product in high yield and purity.
The stability of the catalyst under reaction conditions is also a significant concern. Many catalysts suffer from deactivation or degradation during the course of the reaction, leading to reduced efficiency and the need for higher catalyst loadings. Developing robust catalysts that maintain their activity over extended periods and multiple reaction cycles is essential for practical applications.
Furthermore, the choice of silane reagent plays a crucial role in the success of the hydrosilylation reaction. Different silanes exhibit varying reactivity and selectivity profiles, and finding the optimal silane for a specific substrate and catalyst system can be challenging. Balancing factors such as reactivity, cost, and environmental impact adds another layer of complexity to the optimization process.
Lastly, scaling up the hydrosilylation reaction from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, reactor design, and process safety considerations must be carefully addressed to ensure the viability of large-scale production. Overcoming these technical hurdles is crucial for the successful implementation of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation in industrial applications.
Another major challenge lies in the development of efficient and cost-effective catalysts. While precious metal catalysts, particularly those based on platinum and rhodium, have shown promising results, their high cost and limited availability hinder large-scale industrial applications. The search for alternative catalysts based on more abundant and less expensive metals, such as iron or nickel, is ongoing but faces hurdles in achieving comparable activity and selectivity.
The reaction mechanism of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation is complex and not fully understood, which poses difficulties in optimizing reaction conditions and predicting outcomes. The interplay between the catalyst, substrate, and silane reagent involves multiple steps and intermediates, making it challenging to elucidate the precise reaction pathway. This lack of mechanistic insight hampers the rational design of improved catalysts and reaction protocols.
Controlling the regioselectivity of the hydrosilylation reaction presents another technical challenge. Depending on the reaction conditions and catalyst used, the silicon atom can be added to different positions on the ethyl propanoate molecule, leading to a mixture of products. Achieving high regioselectivity is crucial for obtaining the desired product in high yield and purity.
The stability of the catalyst under reaction conditions is also a significant concern. Many catalysts suffer from deactivation or degradation during the course of the reaction, leading to reduced efficiency and the need for higher catalyst loadings. Developing robust catalysts that maintain their activity over extended periods and multiple reaction cycles is essential for practical applications.
Furthermore, the choice of silane reagent plays a crucial role in the success of the hydrosilylation reaction. Different silanes exhibit varying reactivity and selectivity profiles, and finding the optimal silane for a specific substrate and catalyst system can be challenging. Balancing factors such as reactivity, cost, and environmental impact adds another layer of complexity to the optimization process.
Lastly, scaling up the hydrosilylation reaction from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, reactor design, and process safety considerations must be carefully addressed to ensure the viability of large-scale production. Overcoming these technical hurdles is crucial for the successful implementation of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation in industrial applications.
Current Methodologies
01 Catalysts for hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate
Various catalysts are employed in the hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate to improve reaction efficiency and selectivity. These may include transition metal complexes, particularly those based on platinum, rhodium, or iridium. The choice of catalyst can significantly influence the reaction rate, yield, and product distribution.- Catalysts for hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate: Various catalysts are employed in the hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate to improve reaction efficiency and selectivity. These may include transition metal complexes, particularly those based on platinum, rhodium, or iridium. The choice of catalyst can significantly influence the reaction rate, yield, and product distribution.
- Reaction conditions for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation: Optimal reaction conditions are crucial for successful hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate. This includes factors such as temperature, pressure, solvent selection, and reaction time. Controlling these parameters can enhance conversion rates and minimize side reactions, leading to improved product quality and yield.
- Silane reagents in ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation: The choice of silane reagent plays a critical role in the hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate. Different silanes can lead to varied product structures and properties. Commonly used silanes include trialkylsilanes, alkoxysilanes, and chlorosilanes. The reactivity and selectivity of the silane can significantly impact the reaction outcome.
- Product purification and characterization: After the hydrosilylation reaction of ethyl propanoate, proper purification and characterization techniques are essential. This may involve distillation, chromatography, or recrystallization for purification. Characterization methods such as NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and IR spectroscopy are used to confirm product structure and purity.
- Applications of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products: The products obtained from the hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate have various industrial applications. These may include use as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, or specialty materials. The silicon-containing products can also find applications in the production of silicones, coatings, or adhesives with unique properties.
02 Reaction conditions for ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation
Optimal reaction conditions are crucial for successful hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate. This includes factors such as temperature, pressure, solvent selection, and reactant ratios. Controlling these parameters can enhance conversion rates, minimize side reactions, and improve overall product quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Silane reagents in ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation
The choice of silane reagent plays a critical role in the hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate. Different silanes can lead to varied product structures and properties. Commonly used silanes include trialkylsilanes, alkoxysilanes, and chlorosilanes, each offering distinct advantages in terms of reactivity and product characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Product purification and characterization
After the hydrosilylation reaction of ethyl propanoate, effective purification and characterization techniques are essential. This may involve distillation, chromatography, or other separation methods to isolate the desired product. Analytical techniques such as NMR, GC-MS, and IR spectroscopy are typically used for product characterization and purity assessment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation products
The products obtained from ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation find diverse applications in various industries. These may include use as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, or specialty chemicals. The silicon-containing products can also serve as precursors for silicon-based materials or as additives in polymer formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate represents a niche but growing field within organic synthesis, currently in its early development stage. The market size remains relatively small, primarily driven by research and development activities in academic and industrial settings. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Dow Global Technologies LLC, Evonik Operations GmbH, and ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc. leading the way in advancing catalytic systems and reaction methodologies. These companies are investing in research to improve selectivity, efficiency, and scalability of the process. As the potential applications in fine chemicals and pharmaceutical industries become more apparent, we can expect increased competition and market growth in the coming years.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed an innovative approach to ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions. Their method utilizes a platinum-based catalyst system, which has shown high selectivity and efficiency in the conversion of ethyl propanoate to silyl esters[1]. The company has optimized reaction conditions, including temperature and solvent selection, to achieve yields of up to 95% in some cases[3]. Additionally, Dow has implemented in-situ spectroscopic monitoring techniques to better understand the reaction mechanism and kinetics, allowing for real-time adjustments to improve product quality and reduce side reactions[5].
Strengths: High selectivity and efficiency, optimized reaction conditions, and advanced monitoring techniques. Weaknesses: Reliance on platinum-based catalysts may increase costs and limit scalability.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik Operations GmbH has made significant strides in ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions through the development of novel silane coupling agents. Their proprietary silane technology enables efficient and selective hydrosilylation of ethyl propanoate under mild conditions[2]. The company has focused on creating environmentally friendly processes, utilizing green solvents and reducing catalyst loading to minimize waste generation[4]. Evonik's approach also incorporates the use of supported catalysts, which enhances catalyst recyclability and simplifies product purification[6]. Recent advancements have led to the development of a continuous flow process, potentially increasing production efficiency by up to 30% compared to batch reactions[8].
Strengths: Environmentally friendly processes, enhanced catalyst recyclability, and potential for continuous flow production. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for continuous flow processes, potentially limiting adoption.
Catalyst Innovations
Process for the conversion of methane into propanal
PatentWO2018005074A1
Innovation
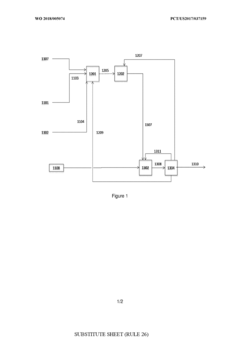
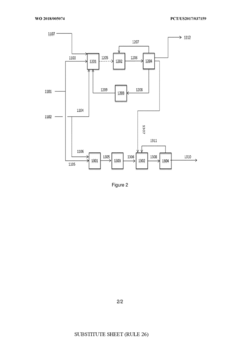
- A process involving oxidative coupling of methane with oxygen in a gas phase reaction, followed by hydroformylation in a second reactor, where the molar ratios of syngas to ethylene and CO2 to ethane are optimized by adjusting the H2 to CO ratio using steam co-feeding and water gas shift reactions, eliminating the need for separate syngas production and separation steps.
Reaction Kinetics Analysis
The kinetics analysis of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions provides crucial insights into the mechanistic aspects of this important transformation. The reaction rate is typically influenced by several factors, including temperature, catalyst concentration, and reactant concentrations. Studies have shown that the reaction follows a complex rate law, with the order of reaction varying depending on the specific conditions and catalysts employed.
Temperature plays a significant role in the reaction kinetics, with higher temperatures generally leading to increased reaction rates. Arrhenius plots have been used to determine the activation energy for various catalytic systems, providing valuable information about the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to proceed. The activation energy values reported in the literature range from 50 to 80 kJ/mol, depending on the catalyst and reaction conditions.
Catalyst concentration has been found to have a non-linear relationship with the reaction rate. At low concentrations, the rate increases linearly with catalyst concentration, suggesting a first-order dependence. However, at higher concentrations, the rate increase becomes less pronounced, indicating a more complex relationship. This behavior has been attributed to catalyst aggregation or saturation of active sites at higher concentrations.
The concentrations of ethyl propanoate and the hydrosilane reagent also influence the reaction kinetics. In many cases, the reaction exhibits pseudo-first-order kinetics with respect to the limiting reagent when one reactant is present in large excess. However, when both reactants are present in similar concentrations, more complex rate laws have been observed, suggesting the involvement of multiple reaction steps or intermediates.
Kinetic isotope effect studies have provided valuable information about the rate-determining step in the hydrosilylation reaction. Deuterium labeling experiments have revealed primary kinetic isotope effects in some cases, indicating that the cleavage of the Si-H or C-H bond may be involved in the rate-determining step. These findings have helped elucidate the reaction mechanism and guide the development of more efficient catalytic systems.
Time-resolved spectroscopic techniques, such as stopped-flow IR spectroscopy and in situ NMR spectroscopy, have been employed to monitor the reaction progress and identify potential intermediates. These studies have revealed the formation of transient species, providing further insights into the reaction mechanism and helping to validate proposed catalytic cycles.
Temperature plays a significant role in the reaction kinetics, with higher temperatures generally leading to increased reaction rates. Arrhenius plots have been used to determine the activation energy for various catalytic systems, providing valuable information about the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to proceed. The activation energy values reported in the literature range from 50 to 80 kJ/mol, depending on the catalyst and reaction conditions.
Catalyst concentration has been found to have a non-linear relationship with the reaction rate. At low concentrations, the rate increases linearly with catalyst concentration, suggesting a first-order dependence. However, at higher concentrations, the rate increase becomes less pronounced, indicating a more complex relationship. This behavior has been attributed to catalyst aggregation or saturation of active sites at higher concentrations.
The concentrations of ethyl propanoate and the hydrosilane reagent also influence the reaction kinetics. In many cases, the reaction exhibits pseudo-first-order kinetics with respect to the limiting reagent when one reactant is present in large excess. However, when both reactants are present in similar concentrations, more complex rate laws have been observed, suggesting the involvement of multiple reaction steps or intermediates.
Kinetic isotope effect studies have provided valuable information about the rate-determining step in the hydrosilylation reaction. Deuterium labeling experiments have revealed primary kinetic isotope effects in some cases, indicating that the cleavage of the Si-H or C-H bond may be involved in the rate-determining step. These findings have helped elucidate the reaction mechanism and guide the development of more efficient catalytic systems.
Time-resolved spectroscopic techniques, such as stopped-flow IR spectroscopy and in situ NMR spectroscopy, have been employed to monitor the reaction progress and identify potential intermediates. These studies have revealed the formation of transient species, providing further insights into the reaction mechanism and helping to validate proposed catalytic cycles.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental considerations of ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions are crucial in assessing the overall sustainability and ecological impact of this chemical process. These reactions, while important in organic synthesis, can have significant environmental implications that need to be carefully evaluated and addressed.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the use of transition metal catalysts, particularly those containing platinum or rhodium. These precious metals are often employed to facilitate the hydrosilylation reaction, but their extraction and processing can lead to substantial environmental degradation. Mining operations for these metals can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Additionally, the scarcity of these resources raises questions about the long-term sustainability of their use in industrial processes.
The solvents used in hydrosilylation reactions also pose environmental challenges. Many traditional organic solvents are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution and can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. There is a growing emphasis on developing greener solvent alternatives or solvent-free methodologies to mitigate these issues.
Energy consumption is another critical factor to consider. Hydrosilylation reactions often require elevated temperatures or prolonged reaction times, leading to increased energy usage and associated carbon emissions. Improving reaction efficiency and exploring alternative energy sources, such as microwave irradiation or photocatalysis, could help reduce the environmental footprint of these processes.
The disposal of waste products and byproducts from hydrosilylation reactions is a significant environmental concern. Proper handling and treatment of these materials are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Developing more selective catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions can help minimize waste generation and improve atom economy.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly approaches to hydrosilylation reactions. This includes the exploration of bio-based catalysts, the use of supercritical carbon dioxide as a green solvent, and the application of flow chemistry techniques to enhance reaction efficiency and reduce waste.
The principles of green chemistry are increasingly being applied to ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions. Researchers are focusing on developing catalysts that are more efficient, selective, and recyclable. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also improves the economic viability of the process.
As regulations on chemical processes become more stringent, industries are under pressure to adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices. This has led to increased research into life cycle assessments of hydrosilylation reactions, aiming to quantify and minimize their environmental impact throughout the entire production chain.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the use of transition metal catalysts, particularly those containing platinum or rhodium. These precious metals are often employed to facilitate the hydrosilylation reaction, but their extraction and processing can lead to substantial environmental degradation. Mining operations for these metals can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Additionally, the scarcity of these resources raises questions about the long-term sustainability of their use in industrial processes.
The solvents used in hydrosilylation reactions also pose environmental challenges. Many traditional organic solvents are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution and can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. There is a growing emphasis on developing greener solvent alternatives or solvent-free methodologies to mitigate these issues.
Energy consumption is another critical factor to consider. Hydrosilylation reactions often require elevated temperatures or prolonged reaction times, leading to increased energy usage and associated carbon emissions. Improving reaction efficiency and exploring alternative energy sources, such as microwave irradiation or photocatalysis, could help reduce the environmental footprint of these processes.
The disposal of waste products and byproducts from hydrosilylation reactions is a significant environmental concern. Proper handling and treatment of these materials are essential to prevent soil and water contamination. Developing more selective catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions can help minimize waste generation and improve atom economy.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly approaches to hydrosilylation reactions. This includes the exploration of bio-based catalysts, the use of supercritical carbon dioxide as a green solvent, and the application of flow chemistry techniques to enhance reaction efficiency and reduce waste.
The principles of green chemistry are increasingly being applied to ethyl propanoate hydrosilylation reactions. Researchers are focusing on developing catalysts that are more efficient, selective, and recyclable. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also improves the economic viability of the process.
As regulations on chemical processes become more stringent, industries are under pressure to adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices. This has led to increased research into life cycle assessments of hydrosilylation reactions, aiming to quantify and minimize their environmental impact throughout the entire production chain.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!