Photo-initiated Reactions of Ethyl Propanoate: A Study
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Background and Objectives
Photo-initiated reactions have gained significant attention in the field of organic chemistry due to their potential for clean, efficient, and selective transformations. The study of photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate represents an important area of research that bridges fundamental photochemistry with practical applications in synthetic organic chemistry and materials science.
The background of this research lies in the growing interest in sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical processes. Photochemical reactions offer a promising avenue for achieving these goals, as they often proceed under mild conditions and can be driven by renewable energy sources such as sunlight. Ethyl propanoate, a common ester with various industrial applications, serves as an excellent model compound for investigating photo-initiated reactions of esters.
The evolution of photochemistry has been marked by several key developments. Early studies in the field focused primarily on understanding the fundamental principles of light-matter interactions. As technology advanced, researchers gained access to more sophisticated light sources and analytical techniques, enabling deeper insights into reaction mechanisms and kinetics. The advent of laser technology in the latter half of the 20th century revolutionized the field, allowing for precise control over wavelength and intensity of light used in photochemical reactions.
In recent years, there has been a surge of interest in applying photochemical principles to organic synthesis. This has led to the development of novel synthetic methodologies, including photoredox catalysis and visible light-mediated transformations. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for selective and efficient chemical transformations, often under milder conditions than traditional thermal processes.
The objectives of studying photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms underlying these photochemical processes. This includes understanding the nature of excited states, identifying reactive intermediates, and mapping out reaction pathways. Such knowledge is crucial for predicting and controlling the outcomes of photo-initiated reactions.
Secondly, the study seeks to explore the potential of ethyl propanoate as a platform for developing new synthetic methodologies. By investigating various reaction conditions, catalysts, and additives, researchers hope to uncover novel transformations that could be applied to a broader range of ester compounds. This could lead to more efficient and selective methods for ester functionalization, with potential applications in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
Another important objective is to assess the sustainability and scalability of these photo-initiated reactions. As the chemical industry moves towards greener processes, understanding how these reactions perform under different conditions and at larger scales becomes crucial. This includes evaluating energy efficiency, product yields, and the potential for continuous flow processes.
The background of this research lies in the growing interest in sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical processes. Photochemical reactions offer a promising avenue for achieving these goals, as they often proceed under mild conditions and can be driven by renewable energy sources such as sunlight. Ethyl propanoate, a common ester with various industrial applications, serves as an excellent model compound for investigating photo-initiated reactions of esters.
The evolution of photochemistry has been marked by several key developments. Early studies in the field focused primarily on understanding the fundamental principles of light-matter interactions. As technology advanced, researchers gained access to more sophisticated light sources and analytical techniques, enabling deeper insights into reaction mechanisms and kinetics. The advent of laser technology in the latter half of the 20th century revolutionized the field, allowing for precise control over wavelength and intensity of light used in photochemical reactions.
In recent years, there has been a surge of interest in applying photochemical principles to organic synthesis. This has led to the development of novel synthetic methodologies, including photoredox catalysis and visible light-mediated transformations. These advancements have opened up new possibilities for selective and efficient chemical transformations, often under milder conditions than traditional thermal processes.
The objectives of studying photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate are multifaceted. Firstly, researchers aim to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms underlying these photochemical processes. This includes understanding the nature of excited states, identifying reactive intermediates, and mapping out reaction pathways. Such knowledge is crucial for predicting and controlling the outcomes of photo-initiated reactions.
Secondly, the study seeks to explore the potential of ethyl propanoate as a platform for developing new synthetic methodologies. By investigating various reaction conditions, catalysts, and additives, researchers hope to uncover novel transformations that could be applied to a broader range of ester compounds. This could lead to more efficient and selective methods for ester functionalization, with potential applications in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.
Another important objective is to assess the sustainability and scalability of these photo-initiated reactions. As the chemical industry moves towards greener processes, understanding how these reactions perform under different conditions and at larger scales becomes crucial. This includes evaluating energy efficiency, product yields, and the potential for continuous flow processes.
Market Analysis
The market for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient chemical processes in various industries. This technology finds applications in polymer synthesis, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where controlled and rapid reactions are crucial.
In the polymer industry, photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate are gaining traction due to their ability to produce high-quality materials with precise control over molecular weight and structure. The coatings sector is also adopting this technology for its fast curing times and energy efficiency, leading to improved productivity and reduced environmental impact.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key market for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate. As drug manufacturers seek more efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis methods, this technology offers advantages in terms of reaction selectivity and yield. The ability to conduct reactions at room temperature and with minimal solvent use aligns well with green chemistry principles, further driving adoption in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate, owing to their well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development.
The market is characterized by a growing emphasis on customized solutions, as end-users seek photo-initiated reaction systems tailored to their specific applications. This trend is creating opportunities for specialized chemical companies and equipment manufacturers to develop innovative products and services.
Challenges in the market include the need for improved photocatalysts with broader spectral sensitivity and higher efficiency. Additionally, there is a demand for more robust and user-friendly reaction systems that can be easily integrated into existing manufacturing processes.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate remains positive. The technology's potential to enable more sustainable and efficient chemical processes aligns well with global trends towards greener manufacturing practices and circular economy principles. As research in this field continues to advance, new applications and market opportunities are likely to emerge, further driving growth in this sector.
In the polymer industry, photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate are gaining traction due to their ability to produce high-quality materials with precise control over molecular weight and structure. The coatings sector is also adopting this technology for its fast curing times and energy efficiency, leading to improved productivity and reduced environmental impact.
The pharmaceutical industry is another key market for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate. As drug manufacturers seek more efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis methods, this technology offers advantages in terms of reaction selectivity and yield. The ability to conduct reactions at room temperature and with minimal solvent use aligns well with green chemistry principles, further driving adoption in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate, owing to their well-established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in research and development.
The market is characterized by a growing emphasis on customized solutions, as end-users seek photo-initiated reaction systems tailored to their specific applications. This trend is creating opportunities for specialized chemical companies and equipment manufacturers to develop innovative products and services.
Challenges in the market include the need for improved photocatalysts with broader spectral sensitivity and higher efficiency. Additionally, there is a demand for more robust and user-friendly reaction systems that can be easily integrated into existing manufacturing processes.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate remains positive. The technology's potential to enable more sustainable and efficient chemical processes aligns well with global trends towards greener manufacturing practices and circular economy principles. As research in this field continues to advance, new applications and market opportunities are likely to emerge, further driving growth in this sector.
Technical Challenges
The photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate present several technical challenges that researchers and industry professionals must address. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of the reaction mechanisms involved. The photochemical behavior of esters, particularly ethyl propanoate, is not fully understood, making it difficult to predict and control reaction outcomes accurately.
The selection of appropriate light sources poses another significant challenge. The wavelength and intensity of light used in these reactions can greatly influence the reaction pathways and product distributions. Finding the optimal light source that can efficiently initiate the desired reactions while minimizing unwanted side reactions requires extensive experimentation and precise control over irradiation conditions.
Controlling the selectivity of photo-initiated reactions is a major hurdle. Ethyl propanoate can undergo various photochemical transformations, including Norrish Type I and Type II reactions, photo-rearrangements, and photo-oxidations. Achieving high selectivity for a specific product or reaction pathway often requires careful tuning of reaction conditions and the use of specialized catalysts or sensitizers.
The stability of reaction intermediates presents another technical challenge. Many photo-initiated reactions involve the formation of highly reactive species such as radicals or excited states. These intermediates can be short-lived and difficult to characterize, making it challenging to elucidate reaction mechanisms and optimize reaction conditions.
Scaling up photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate from laboratory to industrial scale introduces additional complexities. Ensuring uniform light distribution throughout larger reaction volumes and maintaining consistent reaction conditions across batch sizes can be technically demanding. The design of efficient photoreactors that can handle larger quantities of reactants while providing adequate light penetration is an ongoing challenge in this field.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose technical challenges. The use of potentially harmful solvents, the generation of volatile organic compounds, and the handling of photosensitive materials require careful consideration and the development of safer, more sustainable reaction protocols.
Lastly, the analytical techniques required to monitor and characterize photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate can be technically challenging. Real-time monitoring of reaction progress, identification of transient intermediates, and accurate quantification of product distributions often require sophisticated spectroscopic and chromatographic methods. Developing robust analytical protocols that can provide detailed insights into these complex photochemical systems remains an important area of research and development.
The selection of appropriate light sources poses another significant challenge. The wavelength and intensity of light used in these reactions can greatly influence the reaction pathways and product distributions. Finding the optimal light source that can efficiently initiate the desired reactions while minimizing unwanted side reactions requires extensive experimentation and precise control over irradiation conditions.
Controlling the selectivity of photo-initiated reactions is a major hurdle. Ethyl propanoate can undergo various photochemical transformations, including Norrish Type I and Type II reactions, photo-rearrangements, and photo-oxidations. Achieving high selectivity for a specific product or reaction pathway often requires careful tuning of reaction conditions and the use of specialized catalysts or sensitizers.
The stability of reaction intermediates presents another technical challenge. Many photo-initiated reactions involve the formation of highly reactive species such as radicals or excited states. These intermediates can be short-lived and difficult to characterize, making it challenging to elucidate reaction mechanisms and optimize reaction conditions.
Scaling up photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate from laboratory to industrial scale introduces additional complexities. Ensuring uniform light distribution throughout larger reaction volumes and maintaining consistent reaction conditions across batch sizes can be technically demanding. The design of efficient photoreactors that can handle larger quantities of reactants while providing adequate light penetration is an ongoing challenge in this field.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose technical challenges. The use of potentially harmful solvents, the generation of volatile organic compounds, and the handling of photosensitive materials require careful consideration and the development of safer, more sustainable reaction protocols.
Lastly, the analytical techniques required to monitor and characterize photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate can be technically challenging. Real-time monitoring of reaction progress, identification of transient intermediates, and accurate quantification of product distributions often require sophisticated spectroscopic and chromatographic methods. Developing robust analytical protocols that can provide detailed insights into these complex photochemical systems remains an important area of research and development.
Current Methodologies
01 Synthesis of ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various reactions, including the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol. This process typically involves the use of catalysts and specific reaction conditions to promote the formation of the ester. The synthesis can be optimized for improved yield and purity.- Synthesis of ethyl propanoate: Ethyl propanoate can be synthesized through various reactions, including the esterification of propanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of a catalyst. This process typically involves heating the reactants and removing water to drive the equilibrium towards the product. Alternative methods may include the reaction of propanoyl chloride with ethanol or the transesterification of methyl propanoate with ethanol.
- Hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate: Ethyl propanoate can undergo hydrolysis reactions in both acidic and basic conditions. In acidic hydrolysis, water and a strong acid catalyst are used to break the ester bond, producing propanoic acid and ethanol. Basic hydrolysis, also known as saponification, involves the reaction of ethyl propanoate with a strong base like sodium hydroxide, resulting in the formation of the sodium salt of propanoic acid and ethanol.
- Reduction reactions of ethyl propanoate: Ethyl propanoate can be reduced to various products depending on the reducing agent and reaction conditions. Common reduction reactions include the conversion to propanol using strong reducing agents like lithium aluminum hydride or sodium borohydride. Partial reduction can lead to the formation of propanal, while more vigorous conditions may result in the complete reduction to propane.
- Transesterification of ethyl propanoate: Ethyl propanoate can undergo transesterification reactions with other alcohols to form different esters. This process involves the exchange of the ethoxy group with another alkoxy group, typically catalyzed by acids or bases. The reaction is reversible and can be driven to completion by removing one of the products or using an excess of the desired alcohol.
- Applications of ethyl propanoate reactions: Reactions involving ethyl propanoate have various industrial and laboratory applications. These include the production of flavors and fragrances, as ethyl propanoate has a fruity odor reminiscent of pineapple. It is also used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The reactions of ethyl propanoate play a role in the development of new materials and chemical processes across multiple industries.
02 Catalytic reactions involving ethyl propanoate
Ethyl propanoate can participate in various catalytic reactions, such as hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, and transesterification. These reactions often employ metal catalysts or enzymes to facilitate the transformation of ethyl propanoate into other valuable compounds or to modify its structure.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of ethyl propanoate in chemical processes
Ethyl propanoate serves as a versatile reagent or intermediate in various chemical processes. It can be used in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other fine chemicals. The compound's reactivity and functional groups make it suitable for a wide range of transformations and applications in organic synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions04 Reactions for modifying ethyl propanoate
Various reactions can be employed to modify the structure of ethyl propanoate, including alkylation, acylation, and reduction. These modifications can lead to the formation of new compounds with different properties and applications. The selection of appropriate reagents and reaction conditions is crucial for achieving the desired transformations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analysis and characterization of ethyl propanoate reactions
Analytical techniques and methods are employed to study and characterize the reactions involving ethyl propanoate. These may include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and other instrumental analyses to determine reaction kinetics, product distribution, and mechanistic details. Such analyses are crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and understanding the behavior of ethyl propanoate in various chemical transformations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate field is in an early development stage, with growing research interest but limited commercial applications. The market size is relatively small but expanding as new potential uses emerge in areas like green chemistry and materials science. Technologically, it remains at a low to moderate maturity level, with ongoing fundamental research predominating. Key players advancing the technology include academic institutions like Beijing University of Chemical Technology and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, alongside industrial research efforts from companies such as 3M, BASF, and DuPont. These organizations are exploring novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and applications to unlock the potential of photo-initiated reactions involving this ester compound.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a proprietary photo-initiated reaction system for ethyl propanoate, leveraging their expertise in materials science and photochemistry. Their approach utilizes specially designed photoactive polymers that can be easily incorporated into existing manufacturing processes. These polymers act as both photosensitizers and stabilizers, enabling efficient energy transfer and controlled reaction rates[9]. 3M's technology allows for the production of functionalized ethyl propanoate derivatives with applications in adhesives, coatings, and specialty chemicals. The company has also developed novel light delivery systems, including flexible LED arrays and light-guiding materials, to ensure uniform irradiation in complex reactor geometries[10].
Strengths: Extensive materials science expertise, integration with existing manufacturing processes, and diverse potential applications. Weaknesses: Possible limitations in reaction scope due to the use of specific photoactive polymers, and potential intellectual property constraints.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced photo-initiated reaction systems for ethyl propanoate, utilizing their expertise in photochemistry. Their approach involves using specially designed photoinitiators that can efficiently trigger the reaction of ethyl propanoate under specific light conditions. The company has optimized the reaction parameters, including light wavelength, intensity, and exposure time, to achieve high conversion rates and selectivity[1]. BASF's technology also incorporates stabilizers and additives to enhance the shelf life and performance of the final products. They have successfully scaled up this process for industrial applications, particularly in the production of specialty chemicals and polymer precursors[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in industrial-scale chemical processes, strong R&D capabilities, and a wide range of potential applications. Weaknesses: Potential high costs associated with specialized equipment and energy consumption for photo-initiated reactions.
Innovative Approaches
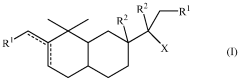
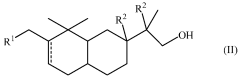
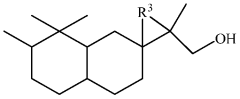
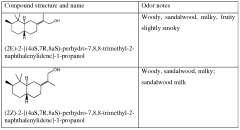
Compounds having sandalwood odors
PatentWO2010061316A2
Innovation
- Development of 2-[perhydro-trialkyl-2-naphthalenylidene]-l-propanol or propanal derivatives that possess a sandalwood odor, featuring a naphthalene skeleton, which can be used as perfuming ingredients to impart sandalwood notes in perfumes and consumer products.
High refractive index composition
PatentWO2011139856A2
Innovation
- Development of processable high refractive index compositions through a reaction product of organic compounds capable of polymerization and sol-gel condensation, combined with UV absorptive compounds, to enhance mechanical properties and UV protection from 290 to 400 nm.
Environmental Impact
The photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. These reactions, when occurring in the atmosphere, can contribute to the formation of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs), which play a crucial role in air quality and climate change. The photolysis of ethyl propanoate leads to the production of various reactive species, including radicals and carbonyl compounds, which can further participate in complex atmospheric chemistry processes.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with these reactions is their potential impact on air quality. The formation of SOAs from ethyl propanoate photolysis can lead to increased particulate matter concentrations in the atmosphere, particularly in urban and industrial areas where this compound may be present in higher concentrations. Elevated levels of particulate matter are known to have adverse effects on human health, including respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
Furthermore, the photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of photochemical smog. Ozone formation occurs through complex reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight. The products of ethyl propanoate photolysis can act as precursors in these reactions, potentially exacerbating ozone pollution in affected areas.
From a climate perspective, the SOAs formed from ethyl propanoate reactions can influence the Earth's radiative balance. These aerosols can scatter or absorb incoming solar radiation, depending on their composition and size, thereby affecting the amount of energy reaching the Earth's surface. Additionally, SOAs can serve as cloud condensation nuclei, altering cloud formation processes and potentially impacting precipitation patterns.
The environmental impact of these reactions extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. Atmospheric deposition of reaction products and SOAs can lead to the introduction of organic compounds into water bodies. This can potentially affect water quality and aquatic life, particularly in sensitive ecosystems. The long-term effects of such deposition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning require further investigation.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate is not limited to direct effects. The products of these reactions can undergo further transformations in the environment, leading to the formation of secondary pollutants with their own set of environmental implications. Understanding these complex reaction pathways and their environmental consequences is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate potential negative impacts.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with these reactions is their potential impact on air quality. The formation of SOAs from ethyl propanoate photolysis can lead to increased particulate matter concentrations in the atmosphere, particularly in urban and industrial areas where this compound may be present in higher concentrations. Elevated levels of particulate matter are known to have adverse effects on human health, including respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
Furthermore, the photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of photochemical smog. Ozone formation occurs through complex reactions involving volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight. The products of ethyl propanoate photolysis can act as precursors in these reactions, potentially exacerbating ozone pollution in affected areas.
From a climate perspective, the SOAs formed from ethyl propanoate reactions can influence the Earth's radiative balance. These aerosols can scatter or absorb incoming solar radiation, depending on their composition and size, thereby affecting the amount of energy reaching the Earth's surface. Additionally, SOAs can serve as cloud condensation nuclei, altering cloud formation processes and potentially impacting precipitation patterns.
The environmental impact of these reactions extends to aquatic ecosystems as well. Atmospheric deposition of reaction products and SOAs can lead to the introduction of organic compounds into water bodies. This can potentially affect water quality and aquatic life, particularly in sensitive ecosystems. The long-term effects of such deposition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning require further investigation.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate is not limited to direct effects. The products of these reactions can undergo further transformations in the environment, leading to the formation of secondary pollutants with their own set of environmental implications. Understanding these complex reaction pathways and their environmental consequences is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate potential negative impacts.
Safety Considerations
When conducting photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate, safety considerations are paramount to ensure the well-being of researchers and the integrity of the experimental setup. The use of ultraviolet (UV) light as an initiator presents specific hazards that must be addressed. Proper eye protection, such as UV-blocking goggles, is essential to prevent potential damage to the retina. Skin exposure to UV radiation should also be minimized through the use of appropriate personal protective equipment, including long-sleeved lab coats and gloves.
The volatile nature of ethyl propanoate necessitates careful handling and storage procedures. This ester has a relatively low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air. Therefore, all experiments should be conducted in a well-ventilated area, preferably under a fume hood, to prevent the accumulation of vapors. Proper grounding of equipment and the use of spark-proof tools are advisable to mitigate the risk of ignition.
Chemical incompatibilities must be considered when designing the experimental setup. Ethyl propanoate can react vigorously with strong oxidizing agents and bases. Researchers should ensure that all materials used in the reaction vessel and surrounding equipment are compatible with the ester and any potential byproducts of the photo-initiated reaction.
The potential for pressure build-up in sealed reaction vessels during photo-initiated reactions is a critical safety concern. Adequate pressure relief mechanisms should be incorporated into the experimental design to prevent the risk of explosion. Regular inspection and maintenance of all pressure-related equipment are essential.
Disposal of reaction products and unused materials requires careful consideration. Ethyl propanoate and its derivatives may have environmental impacts if improperly discharged. A comprehensive waste management plan should be in place, adhering to local regulations and best practices for chemical waste disposal.
Emergency response protocols specific to photo-initiated reactions involving ethyl propanoate should be established and communicated to all laboratory personnel. This includes procedures for dealing with spills, fires, and accidental exposures. Readily accessible safety equipment, such as eye wash stations, safety showers, and appropriate fire extinguishers, must be available in the immediate vicinity of the experimental area.
Lastly, thorough training of all personnel involved in the study is crucial. This should cover not only the general laboratory safety procedures but also the specific risks associated with photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate. Regular safety briefings and updates on any new findings related to the hazards of this particular experimental setup should be conducted to maintain a high level of safety awareness among the research team.
The volatile nature of ethyl propanoate necessitates careful handling and storage procedures. This ester has a relatively low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air. Therefore, all experiments should be conducted in a well-ventilated area, preferably under a fume hood, to prevent the accumulation of vapors. Proper grounding of equipment and the use of spark-proof tools are advisable to mitigate the risk of ignition.
Chemical incompatibilities must be considered when designing the experimental setup. Ethyl propanoate can react vigorously with strong oxidizing agents and bases. Researchers should ensure that all materials used in the reaction vessel and surrounding equipment are compatible with the ester and any potential byproducts of the photo-initiated reaction.
The potential for pressure build-up in sealed reaction vessels during photo-initiated reactions is a critical safety concern. Adequate pressure relief mechanisms should be incorporated into the experimental design to prevent the risk of explosion. Regular inspection and maintenance of all pressure-related equipment are essential.
Disposal of reaction products and unused materials requires careful consideration. Ethyl propanoate and its derivatives may have environmental impacts if improperly discharged. A comprehensive waste management plan should be in place, adhering to local regulations and best practices for chemical waste disposal.
Emergency response protocols specific to photo-initiated reactions involving ethyl propanoate should be established and communicated to all laboratory personnel. This includes procedures for dealing with spills, fires, and accidental exposures. Readily accessible safety equipment, such as eye wash stations, safety showers, and appropriate fire extinguishers, must be available in the immediate vicinity of the experimental area.
Lastly, thorough training of all personnel involved in the study is crucial. This should cover not only the general laboratory safety procedures but also the specific risks associated with photo-initiated reactions of ethyl propanoate. Regular safety briefings and updates on any new findings related to the hazards of this particular experimental setup should be conducted to maintain a high level of safety awareness among the research team.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!