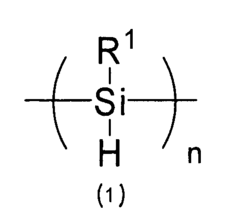
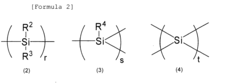
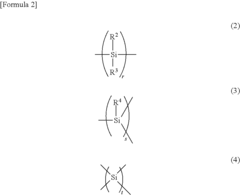Polysilane’s Application to High-Resolution Display Technology
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Display Tech Evolution
The evolution of polysilane display technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers first began exploring the potential of polysilanes as organic semiconductors. Initially, polysilanes were primarily studied for their photoconductivity and photoluminescence properties, which made them promising candidates for optoelectronic applications.
In the mid-2000s, scientists discovered that certain polysilanes exhibited excellent charge transport properties, particularly for hole mobility. This breakthrough led to increased interest in their potential use in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and other display technologies. The unique electronic structure of polysilanes, with their delocalized σ-electrons along the silicon backbone, contributed to their favorable optoelectronic characteristics.
By the late 2000s, researchers had successfully demonstrated the first polysilane-based OLEDs, albeit with relatively low efficiency and stability compared to traditional organic materials. These early prototypes served as proof-of-concept devices and sparked further investigation into optimizing polysilane structures for display applications.
The early 2010s saw significant advancements in polysilane synthesis and processing techniques. Scientists developed new methods to control the molecular weight, polydispersity, and side-chain functionalization of polysilanes, leading to improved charge transport and luminescence properties. These developments enabled the creation of more efficient and stable polysilane-based display devices.
Around 2015, researchers began exploring the potential of polysilanes in quantum dot displays. The unique electronic properties of polysilanes made them excellent candidates for charge transport layers in quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs). This application opened up new avenues for high-resolution display technologies, as QLEDs offered superior color purity and brightness compared to traditional OLEDs.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing polysilane-based materials for flexible and stretchable displays. The inherent flexibility of polysilane chains, combined with their optoelectronic properties, makes them ideal candidates for next-generation display technologies that can be bent, folded, or stretched without compromising performance.
The most recent developments in polysilane display technology involve the integration of nanostructured polysilanes into hybrid organic-inorganic display architectures. These advanced materials combine the benefits of polysilanes with those of inorganic semiconductors, potentially leading to displays with enhanced resolution, color accuracy, and energy efficiency.
In the mid-2000s, scientists discovered that certain polysilanes exhibited excellent charge transport properties, particularly for hole mobility. This breakthrough led to increased interest in their potential use in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and other display technologies. The unique electronic structure of polysilanes, with their delocalized σ-electrons along the silicon backbone, contributed to their favorable optoelectronic characteristics.
By the late 2000s, researchers had successfully demonstrated the first polysilane-based OLEDs, albeit with relatively low efficiency and stability compared to traditional organic materials. These early prototypes served as proof-of-concept devices and sparked further investigation into optimizing polysilane structures for display applications.
The early 2010s saw significant advancements in polysilane synthesis and processing techniques. Scientists developed new methods to control the molecular weight, polydispersity, and side-chain functionalization of polysilanes, leading to improved charge transport and luminescence properties. These developments enabled the creation of more efficient and stable polysilane-based display devices.
Around 2015, researchers began exploring the potential of polysilanes in quantum dot displays. The unique electronic properties of polysilanes made them excellent candidates for charge transport layers in quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs). This application opened up new avenues for high-resolution display technologies, as QLEDs offered superior color purity and brightness compared to traditional OLEDs.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing polysilane-based materials for flexible and stretchable displays. The inherent flexibility of polysilane chains, combined with their optoelectronic properties, makes them ideal candidates for next-generation display technologies that can be bent, folded, or stretched without compromising performance.
The most recent developments in polysilane display technology involve the integration of nanostructured polysilanes into hybrid organic-inorganic display architectures. These advanced materials combine the benefits of polysilanes with those of inorganic semiconductors, potentially leading to displays with enhanced resolution, color accuracy, and energy efficiency.
High-Res Display Market Analysis
The high-resolution display market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for superior visual experiences across various sectors. This market segment encompasses a wide range of display technologies, including OLED, QLED, and micro-LED, with applications spanning from smartphones and tablets to large-format televisions and professional monitors.
Consumer electronics remain the primary driver of the high-resolution display market, with smartphones leading the charge. The proliferation of 4K and even 8K displays in premium smartphones has set new standards for visual clarity and color accuracy. Simultaneously, the gaming industry has emerged as a substantial contributor to market growth, with gamers seeking higher refresh rates and resolutions for immersive experiences.
In the professional sector, high-resolution displays have become indispensable in fields such as graphic design, video editing, and medical imaging. The demand for precise color reproduction and exceptional detail has led to the development of specialized monitors catering to these niche markets.
The automotive industry represents an emerging frontier for high-resolution displays. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the integration of high-quality displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays is becoming increasingly common. This trend is expected to accelerate with the rise of autonomous vehicles, which will likely incorporate multiple high-resolution displays for passenger entertainment and information.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the high-resolution display market, with countries like South Korea, Japan, and China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by strong demand in the consumer electronics and professional sectors.
The market faces challenges, including high production costs and technical limitations in achieving ever-higher pixel densities. However, ongoing research and development in materials science, including the exploration of novel compounds like polysilanes, offer promising avenues for overcoming these obstacles.
Looking ahead, the high-resolution display market is poised for continued growth. Emerging technologies such as foldable and rollable displays are expected to create new product categories and use cases. Additionally, the increasing adoption of augmented and virtual reality technologies is likely to drive demand for high-resolution microdisplays, opening up new opportunities for market expansion and technological innovation.
Consumer electronics remain the primary driver of the high-resolution display market, with smartphones leading the charge. The proliferation of 4K and even 8K displays in premium smartphones has set new standards for visual clarity and color accuracy. Simultaneously, the gaming industry has emerged as a substantial contributor to market growth, with gamers seeking higher refresh rates and resolutions for immersive experiences.
In the professional sector, high-resolution displays have become indispensable in fields such as graphic design, video editing, and medical imaging. The demand for precise color reproduction and exceptional detail has led to the development of specialized monitors catering to these niche markets.
The automotive industry represents an emerging frontier for high-resolution displays. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the integration of high-quality displays for infotainment systems, digital dashboards, and heads-up displays is becoming increasingly common. This trend is expected to accelerate with the rise of autonomous vehicles, which will likely incorporate multiple high-resolution displays for passenger entertainment and information.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the high-resolution display market, with countries like South Korea, Japan, and China leading in both production and consumption. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by strong demand in the consumer electronics and professional sectors.
The market faces challenges, including high production costs and technical limitations in achieving ever-higher pixel densities. However, ongoing research and development in materials science, including the exploration of novel compounds like polysilanes, offer promising avenues for overcoming these obstacles.
Looking ahead, the high-resolution display market is poised for continued growth. Emerging technologies such as foldable and rollable displays are expected to create new product categories and use cases. Additionally, the increasing adoption of augmented and virtual reality technologies is likely to drive demand for high-resolution microdisplays, opening up new opportunities for market expansion and technological innovation.
Polysilane Tech Challenges
Polysilane technology, while promising for high-resolution display applications, faces several significant challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of polysilane materials under various environmental conditions. Polysilanes are known to be sensitive to UV light and oxygen, which can lead to degradation of their optical and electrical properties over time. This instability poses a major hurdle for the long-term reliability of displays utilizing polysilane technology.
Another critical challenge lies in the synthesis and processing of polysilane materials. Current methods for producing high-quality polysilanes with consistent molecular weights and structures are often complex and costly. The need for precise control over the polymerization process and the subsequent purification steps adds to the manufacturing complexity, potentially limiting large-scale production capabilities.
The integration of polysilane materials into existing display manufacturing processes presents additional technical difficulties. Compatibility issues with other materials used in display fabrication, such as electrodes and encapsulation layers, need to be carefully addressed. Furthermore, the deposition of uniform polysilane films with the required thickness and optical properties on large-area substrates remains a significant engineering challenge.
Achieving the desired optoelectronic properties consistently across different batches of polysilane materials is another area of concern. The performance of polysilane-based displays, including color purity, brightness, and efficiency, is highly dependent on the molecular structure and organization of the polysilane chains. Controlling these factors at the nanoscale level during manufacturing is crucial but technically demanding.
The development of efficient and stable charge transport mechanisms within polysilane layers is also a key challenge. While polysilanes exhibit promising charge carrier mobility, optimizing this property for high-performance display applications requires further research and innovation. This includes understanding and controlling the interface between polysilane layers and other functional materials in the display stack.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane materials and their production processes need to be thoroughly evaluated. As with any new technology, ensuring that polysilane-based displays meet stringent environmental and health standards is essential for their commercial viability and public acceptance.
Another critical challenge lies in the synthesis and processing of polysilane materials. Current methods for producing high-quality polysilanes with consistent molecular weights and structures are often complex and costly. The need for precise control over the polymerization process and the subsequent purification steps adds to the manufacturing complexity, potentially limiting large-scale production capabilities.
The integration of polysilane materials into existing display manufacturing processes presents additional technical difficulties. Compatibility issues with other materials used in display fabrication, such as electrodes and encapsulation layers, need to be carefully addressed. Furthermore, the deposition of uniform polysilane films with the required thickness and optical properties on large-area substrates remains a significant engineering challenge.
Achieving the desired optoelectronic properties consistently across different batches of polysilane materials is another area of concern. The performance of polysilane-based displays, including color purity, brightness, and efficiency, is highly dependent on the molecular structure and organization of the polysilane chains. Controlling these factors at the nanoscale level during manufacturing is crucial but technically demanding.
The development of efficient and stable charge transport mechanisms within polysilane layers is also a key challenge. While polysilanes exhibit promising charge carrier mobility, optimizing this property for high-performance display applications requires further research and innovation. This includes understanding and controlling the interface between polysilane layers and other functional materials in the display stack.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety considerations of polysilane materials and their production processes need to be thoroughly evaluated. As with any new technology, ensuring that polysilane-based displays meet stringent environmental and health standards is essential for their commercial viability and public acceptance.
Current Polysilane Display Solutions
01 Synthesis and preparation of polysilanes
Various methods for synthesizing and preparing polysilanes are described. These include techniques for controlling molecular weight, improving yield, and enhancing purity. The processes often involve the use of specific catalysts, solvents, and reaction conditions to achieve desired properties in the resulting polysilanes.- Synthesis and preparation of polysilanes: Various methods for synthesizing and preparing polysilanes are described. These include techniques for controlling molecular weight, improving yield, and enhancing purity. The processes often involve the use of specific catalysts, solvents, and reaction conditions to achieve desired properties in the resulting polysilanes.
- Optical and electronic applications of polysilanes: Polysilanes exhibit unique optical and electronic properties, making them suitable for various applications. These include their use in photoresists, optical materials, and electronic devices. The resolution and performance of polysilanes in these applications are discussed, along with methods to enhance their functionality.
- Chemical modification and functionalization of polysilanes: Techniques for modifying and functionalizing polysilanes are explored. These include the introduction of specific side groups, cross-linking, and surface modifications. Such modifications can enhance the properties and expand the potential applications of polysilanes in various fields.
- Polysilane-based composite materials: The development of composite materials incorporating polysilanes is discussed. These composites often combine the unique properties of polysilanes with other materials to create novel functionalities. Applications in areas such as coatings, films, and nanocomposites are explored.
- Characterization and analysis of polysilanes: Methods for characterizing and analyzing polysilanes are presented. These include techniques for determining molecular weight, structure, and purity. Advanced analytical tools and approaches for studying the properties and behavior of polysilanes in various environments are discussed.
02 Optical and electronic applications of polysilanes
Polysilanes exhibit unique optical and electronic properties, making them suitable for various applications. These include their use in photoresists, optical materials, and electronic devices. The resolution and performance of polysilanes in these applications are discussed, along with methods to enhance their functionality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Chemical modification and functionalization of polysilanes
Techniques for modifying and functionalizing polysilanes are explored. These include the introduction of specific side groups, cross-linking methods, and surface modifications. Such modifications can enhance the properties and expand the potential applications of polysilanes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Polysilane-based composite materials
The development of composite materials incorporating polysilanes is discussed. These composites often combine the unique properties of polysilanes with those of other materials, resulting in enhanced performance characteristics. Applications in areas such as coatings, films, and nanocomposites are explored.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and resolution techniques for polysilanes
Various methods for purifying and resolving polysilanes are described. These include techniques such as fractional precipitation, chromatography, and thermal treatments. The focus is on improving the purity, molecular weight distribution, and stereochemical properties of polysilanes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Displays
The application of polysilane to high-resolution display technology is in an early development stage, with a growing market potential driven by the increasing demand for advanced display solutions. The market size is expanding as major players invest in research and development to leverage polysilane's unique properties. Companies like Toray Industries, JSR Corp., and Merck Patent GmbH are at the forefront of this technology, with varying degrees of technical maturity. While some firms have made significant progress in developing polysilane-based materials for displays, others are still in the experimental phase, indicating a diverse competitive landscape with opportunities for innovation and market differentiation.
Toray Industries, Inc.
Technical Solution: Toray Industries has developed advanced polysilane materials for high-resolution display applications. Their proprietary synthesis method produces ultra-pure polysilane with controlled molecular weight and narrow polydispersity[1]. This results in polysilane films with excellent optical properties, including high transparency and low haze. Toray's polysilane formulations incorporate side-chain engineering to optimize solubility and film-forming properties[2]. The company has demonstrated polysilane-based color filters with enhanced color purity and contrast ratio compared to conventional pigment-based filters[3]. Toray is also exploring polysilane as an electron transport layer in OLED displays, leveraging its high electron mobility.
Strengths: Superior optical properties, established manufacturing capabilities, versatile applications in displays. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some alternatives, potential stability issues under prolonged UV exposure.
JSR Corp.
Technical Solution: JSR Corporation has developed novel polysilane-based photoresist materials for high-resolution patterning in display manufacturing. Their polysilane resists offer excellent sensitivity to deep UV light, enabling fine pattern formation below 100 nm linewidth[4]. JSR's polysilane formulations incorporate crosslinking agents to improve thermal and chemical resistance after patterning. The company has demonstrated the use of their polysilane resists in the fabrication of high-resolution OLED displays, achieving pixel densities over 1000 ppi[5]. JSR is also investigating polysilane as a host material for quantum dot color conversion layers in next-generation displays.
Strengths: High-resolution patterning capability, established presence in display materials market. Weaknesses: Limited to specific manufacturing steps, may require specialized processing equipment.
Polysilane Display Innovations
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
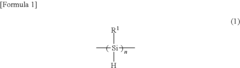
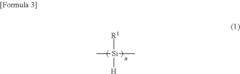
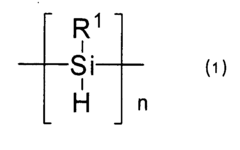
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Polysilane and resin composition containing polysilane
PatentInactiveEP1958979A1
Innovation
- Introducing a Si-H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane
The environmental impact of polysilane in high-resolution display technology is a critical consideration as the industry moves towards more advanced and efficient display solutions. Polysilane, a silicon-based polymer, offers promising applications in display technology due to its unique optical and electrical properties. However, its production, use, and disposal present several environmental challenges that must be carefully addressed.
The manufacturing process of polysilane involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive procedures. The synthesis of polysilane typically requires the use of organosilicon compounds and catalysts, which can potentially lead to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants if not properly managed. Additionally, the energy consumption during production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in regions where the energy grid relies heavily on fossil fuels.
During the operational phase of high-resolution displays incorporating polysilane, the environmental impact is generally lower compared to traditional display technologies. Polysilane-based displays have the potential to be more energy-efficient, which can lead to reduced power consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the device. This efficiency gain is particularly significant in large-scale applications such as public displays or in consumer electronics where energy savings can accumulate substantially.
End-of-life considerations for polysilane-based displays present both challenges and opportunities. The complex nature of these displays, which often combine polysilane with other materials, can make recycling difficult. Proper disposal and recycling processes need to be developed to prevent polysilane and associated materials from ending up in landfills, where they could potentially leach harmful substances into the environment. However, the silicon-based nature of polysilane offers potential for recycling and recovery of valuable materials, which could contribute to a more circular economy in the electronics industry.
Water usage and potential contamination are also important factors to consider in the environmental impact assessment of polysilane production. The synthesis and purification processes may require significant amounts of water, and there is a risk of water pollution if wastewater is not treated adequately before release. Implementing closed-loop water systems and advanced treatment technologies can help mitigate these risks.
As the adoption of polysilane in high-resolution display technology increases, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and quantify its environmental impacts. This will enable the industry to develop more sustainable production methods, improve energy efficiency in device operation, and create effective recycling and disposal strategies. Regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders must work together to establish guidelines and standards that ensure the responsible development and use of polysilane technology, balancing technological advancement with environmental stewardship.
The manufacturing process of polysilane involves the use of various chemicals and energy-intensive procedures. The synthesis of polysilane typically requires the use of organosilicon compounds and catalysts, which can potentially lead to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants if not properly managed. Additionally, the energy consumption during production contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in regions where the energy grid relies heavily on fossil fuels.
During the operational phase of high-resolution displays incorporating polysilane, the environmental impact is generally lower compared to traditional display technologies. Polysilane-based displays have the potential to be more energy-efficient, which can lead to reduced power consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the device. This efficiency gain is particularly significant in large-scale applications such as public displays or in consumer electronics where energy savings can accumulate substantially.
End-of-life considerations for polysilane-based displays present both challenges and opportunities. The complex nature of these displays, which often combine polysilane with other materials, can make recycling difficult. Proper disposal and recycling processes need to be developed to prevent polysilane and associated materials from ending up in landfills, where they could potentially leach harmful substances into the environment. However, the silicon-based nature of polysilane offers potential for recycling and recovery of valuable materials, which could contribute to a more circular economy in the electronics industry.
Water usage and potential contamination are also important factors to consider in the environmental impact assessment of polysilane production. The synthesis and purification processes may require significant amounts of water, and there is a risk of water pollution if wastewater is not treated adequately before release. Implementing closed-loop water systems and advanced treatment technologies can help mitigate these risks.
As the adoption of polysilane in high-resolution display technology increases, it is crucial to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and quantify its environmental impacts. This will enable the industry to develop more sustainable production methods, improve energy efficiency in device operation, and create effective recycling and disposal strategies. Regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders must work together to establish guidelines and standards that ensure the responsible development and use of polysilane technology, balancing technological advancement with environmental stewardship.
Polysilane Display Manufacturing
Polysilane display manufacturing represents a cutting-edge approach in the realm of high-resolution display technology. This innovative process leverages the unique properties of polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers, to create advanced display components with superior performance characteristics.
The manufacturing process begins with the synthesis of polysilane materials, typically through the Wurtz coupling reaction of dichlorosilanes. This step is crucial as it determines the molecular structure and properties of the resulting polymer. The synthesized polysilanes are then purified and processed into a form suitable for thin-film deposition, often involving dissolution in organic solvents.
Thin-film deposition is a critical stage in polysilane display manufacturing. Various techniques can be employed, including spin-coating, vapor deposition, or solution-based methods. The choice of deposition technique significantly influences the film's uniformity, thickness, and overall quality. Post-deposition treatments, such as thermal annealing or UV irradiation, are often applied to optimize the film's electronic and optical properties.
The patterning of polysilane films is achieved through photolithographic techniques, taking advantage of the material's photosensitivity. This allows for precise definition of pixel structures and other display elements. The photopatterning process typically involves exposure to UV light through a mask, followed by development to remove unexposed areas.
Integration of the patterned polysilane layer into the display structure is a complex process. It involves the deposition of additional layers, such as electrodes, insulating materials, and protective coatings. The compatibility of polysilanes with other display components and manufacturing processes is crucial for successful integration.
Quality control and testing are integral parts of the manufacturing process. This includes optical and electrical characterization of the polysilane films, as well as performance testing of the completed display units. Factors such as luminescence efficiency, color purity, and response time are carefully evaluated.
Scaling up polysilane display manufacturing for mass production presents several challenges. These include maintaining consistent material quality across large batches, ensuring uniform film deposition over large areas, and optimizing process parameters for high throughput. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the commercial viability of polysilane-based displays.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in display manufacturing. The polysilane process offers potential advantages in terms of reduced energy consumption and lower use of toxic materials compared to some conventional display technologies. However, proper handling and disposal of chemical precursors and waste products remain important considerations.
The manufacturing process begins with the synthesis of polysilane materials, typically through the Wurtz coupling reaction of dichlorosilanes. This step is crucial as it determines the molecular structure and properties of the resulting polymer. The synthesized polysilanes are then purified and processed into a form suitable for thin-film deposition, often involving dissolution in organic solvents.
Thin-film deposition is a critical stage in polysilane display manufacturing. Various techniques can be employed, including spin-coating, vapor deposition, or solution-based methods. The choice of deposition technique significantly influences the film's uniformity, thickness, and overall quality. Post-deposition treatments, such as thermal annealing or UV irradiation, are often applied to optimize the film's electronic and optical properties.
The patterning of polysilane films is achieved through photolithographic techniques, taking advantage of the material's photosensitivity. This allows for precise definition of pixel structures and other display elements. The photopatterning process typically involves exposure to UV light through a mask, followed by development to remove unexposed areas.
Integration of the patterned polysilane layer into the display structure is a complex process. It involves the deposition of additional layers, such as electrodes, insulating materials, and protective coatings. The compatibility of polysilanes with other display components and manufacturing processes is crucial for successful integration.
Quality control and testing are integral parts of the manufacturing process. This includes optical and electrical characterization of the polysilane films, as well as performance testing of the completed display units. Factors such as luminescence efficiency, color purity, and response time are carefully evaluated.
Scaling up polysilane display manufacturing for mass production presents several challenges. These include maintaining consistent material quality across large batches, ensuring uniform film deposition over large areas, and optimizing process parameters for high throughput. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the commercial viability of polysilane-based displays.
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in display manufacturing. The polysilane process offers potential advantages in terms of reduced energy consumption and lower use of toxic materials compared to some conventional display technologies. However, proper handling and disposal of chemical precursors and waste products remain important considerations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!