Polysilane's Contribution to Advanced Catalytic Processes
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Catalysis Evolution and Objectives
Polysilanes have emerged as a significant contributor to advanced catalytic processes, marking a new era in the field of catalysis. The evolution of polysilane catalysis can be traced back to the early 1980s when researchers first recognized the unique electronic properties of these silicon-based polymers. Initially, polysilanes were primarily studied for their photophysical and photochemical properties, but their potential in catalysis remained largely unexplored.
The turning point came in the late 1990s when scientists discovered that polysilanes could act as efficient electron donors in various chemical reactions. This revelation opened up new avenues for their application in catalysis, particularly in redox-driven processes. The subsequent decades witnessed a rapid expansion of research into polysilane-based catalytic systems, with a focus on enhancing their stability, selectivity, and efficiency.
One of the key objectives in polysilane catalysis research has been to develop more environmentally friendly and sustainable catalytic processes. Polysilanes offer several advantages in this regard, including their relatively low toxicity, ease of synthesis, and potential for recyclability. Researchers have been working towards creating polysilane catalysts that can operate under milder conditions, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation in industrial processes.
Another important goal has been to expand the scope of reactions that can be catalyzed by polysilanes. While initial applications were limited to simple redox reactions, recent efforts have focused on developing polysilane catalysts for more complex transformations, including C-C bond formation, hydrogenation, and polymerization reactions. This broadening of applicability aims to position polysilanes as versatile catalysts across various sectors of the chemical industry.
The pursuit of structure-activity relationships in polysilane catalysis has been a crucial objective. Scientists have been systematically investigating how the molecular structure of polysilanes influences their catalytic performance. This includes studying the effects of different substituents on the silicon backbone, varying the chain length, and exploring branched and cyclic polysilane structures. The ultimate goal is to establish design principles that will enable the rational development of tailored polysilane catalysts for specific applications.
Looking ahead, the field of polysilane catalysis is poised for further advancements. Researchers are exploring the integration of polysilanes with other catalytic systems, such as metal nanoparticles and enzymes, to create hybrid catalysts with enhanced performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing stimuli-responsive polysilane catalysts that can be activated or deactivated on demand, offering unprecedented control over catalytic processes. These ongoing efforts underscore the continued evolution and expanding potential of polysilanes in advanced catalytic applications.
The turning point came in the late 1990s when scientists discovered that polysilanes could act as efficient electron donors in various chemical reactions. This revelation opened up new avenues for their application in catalysis, particularly in redox-driven processes. The subsequent decades witnessed a rapid expansion of research into polysilane-based catalytic systems, with a focus on enhancing their stability, selectivity, and efficiency.
One of the key objectives in polysilane catalysis research has been to develop more environmentally friendly and sustainable catalytic processes. Polysilanes offer several advantages in this regard, including their relatively low toxicity, ease of synthesis, and potential for recyclability. Researchers have been working towards creating polysilane catalysts that can operate under milder conditions, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation in industrial processes.
Another important goal has been to expand the scope of reactions that can be catalyzed by polysilanes. While initial applications were limited to simple redox reactions, recent efforts have focused on developing polysilane catalysts for more complex transformations, including C-C bond formation, hydrogenation, and polymerization reactions. This broadening of applicability aims to position polysilanes as versatile catalysts across various sectors of the chemical industry.
The pursuit of structure-activity relationships in polysilane catalysis has been a crucial objective. Scientists have been systematically investigating how the molecular structure of polysilanes influences their catalytic performance. This includes studying the effects of different substituents on the silicon backbone, varying the chain length, and exploring branched and cyclic polysilane structures. The ultimate goal is to establish design principles that will enable the rational development of tailored polysilane catalysts for specific applications.
Looking ahead, the field of polysilane catalysis is poised for further advancements. Researchers are exploring the integration of polysilanes with other catalytic systems, such as metal nanoparticles and enzymes, to create hybrid catalysts with enhanced performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing stimuli-responsive polysilane catalysts that can be activated or deactivated on demand, offering unprecedented control over catalytic processes. These ongoing efforts underscore the continued evolution and expanding potential of polysilanes in advanced catalytic applications.
Market Demand for Advanced Catalytic Processes
The market demand for advanced catalytic processes has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing need for more efficient and sustainable chemical production methods. This demand is particularly pronounced in industries such as petrochemicals, fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and environmental technologies. The global catalysis market, which encompasses a wide range of catalytic processes, is expected to expand significantly in the coming years.
In the petrochemical sector, there is a strong push for catalytic processes that can improve the efficiency of refining operations and reduce energy consumption. This is partly due to stricter environmental regulations and the need to process heavier crude oil feedstocks. The fine chemicals and pharmaceutical industries are seeking catalytic solutions that can enable more selective and environmentally friendly synthesis routes, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Environmental concerns are also driving demand for advanced catalytic processes in pollution control and renewable energy applications. Catalytic converters for automotive emissions, catalysts for industrial exhaust treatment, and processes for the production of biofuels are all areas experiencing growth. The shift towards a circular economy is further fueling interest in catalytic technologies that can enable the recycling and upcycling of waste materials.
The emergence of new materials and nanotechnology has opened up possibilities for novel catalytic systems, including those based on polysilanes. These advanced materials offer potential advantages in terms of selectivity, activity, and stability compared to traditional catalysts. As industries seek to improve their processes and meet sustainability goals, the demand for innovative catalytic solutions incorporating materials like polysilanes is likely to increase.
In the context of polysilane's contribution to advanced catalytic processes, there is growing interest in their unique electronic and optical properties. These properties make polysilanes potentially valuable in photocatalysis and electrocatalysis applications. Industries are exploring the use of polysilane-based catalysts for reactions such as water splitting for hydrogen production, CO2 reduction, and organic transformations under mild conditions.
The market is also showing interest in the potential of polysilanes to act as supports or modifiers for existing catalytic systems. Their ability to form stable, well-defined structures at the nanoscale could lead to improved catalyst performance and longevity. This is particularly relevant in high-value applications where catalyst efficiency and recyclability are crucial factors.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that the demand for polysilane-based catalytic processes will grow, especially if they can demonstrate clear advantages over current technologies in terms of efficiency, selectivity, or environmental impact. However, the market adoption will depend on factors such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to integrate these new catalytic systems into existing industrial processes.
In the petrochemical sector, there is a strong push for catalytic processes that can improve the efficiency of refining operations and reduce energy consumption. This is partly due to stricter environmental regulations and the need to process heavier crude oil feedstocks. The fine chemicals and pharmaceutical industries are seeking catalytic solutions that can enable more selective and environmentally friendly synthesis routes, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Environmental concerns are also driving demand for advanced catalytic processes in pollution control and renewable energy applications. Catalytic converters for automotive emissions, catalysts for industrial exhaust treatment, and processes for the production of biofuels are all areas experiencing growth. The shift towards a circular economy is further fueling interest in catalytic technologies that can enable the recycling and upcycling of waste materials.
The emergence of new materials and nanotechnology has opened up possibilities for novel catalytic systems, including those based on polysilanes. These advanced materials offer potential advantages in terms of selectivity, activity, and stability compared to traditional catalysts. As industries seek to improve their processes and meet sustainability goals, the demand for innovative catalytic solutions incorporating materials like polysilanes is likely to increase.
In the context of polysilane's contribution to advanced catalytic processes, there is growing interest in their unique electronic and optical properties. These properties make polysilanes potentially valuable in photocatalysis and electrocatalysis applications. Industries are exploring the use of polysilane-based catalysts for reactions such as water splitting for hydrogen production, CO2 reduction, and organic transformations under mild conditions.
The market is also showing interest in the potential of polysilanes to act as supports or modifiers for existing catalytic systems. Their ability to form stable, well-defined structures at the nanoscale could lead to improved catalyst performance and longevity. This is particularly relevant in high-value applications where catalyst efficiency and recyclability are crucial factors.
As research in this field progresses, it is anticipated that the demand for polysilane-based catalytic processes will grow, especially if they can demonstrate clear advantages over current technologies in terms of efficiency, selectivity, or environmental impact. However, the market adoption will depend on factors such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to integrate these new catalytic systems into existing industrial processes.
Polysilane Catalysis: Current State and Challenges
Polysilanes have emerged as a promising class of materials in advanced catalytic processes, offering unique properties that contribute to enhanced catalytic performance. However, the current state of polysilane catalysis faces several challenges that need to be addressed for wider industrial adoption.
The use of polysilanes in catalysis has gained significant attention due to their ability to act as both catalysts and catalyst supports. Their unique electronic properties, stemming from σ-conjugation along the silicon backbone, allow for efficient electron transfer processes, making them particularly suitable for redox reactions. Additionally, the structural versatility of polysilanes enables the incorporation of various functional groups, further expanding their catalytic applications.
One of the primary challenges in polysilane catalysis is the stability of these materials under harsh reaction conditions. While polysilanes exhibit excellent thermal stability, their susceptibility to oxidation and hydrolysis can limit their long-term performance in certain catalytic processes. Researchers are actively working on developing strategies to enhance the chemical stability of polysilanes, such as incorporating protective groups or creating hybrid materials with inorganic components.
Another significant challenge lies in controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of polysilanes. The catalytic activity and selectivity of polysilanes are closely related to their molecular structure, and achieving precise control over these parameters remains a key focus area. Advanced polymerization techniques, such as living anionic polymerization and controlled radical polymerization, are being explored to address this challenge and produce well-defined polysilane catalysts.
The heterogeneity of polysilane catalysts presents both opportunities and challenges. While heterogeneous catalysts offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and recyclability, achieving uniform catalytic sites and preventing leaching of active species are ongoing concerns. Researchers are investigating various immobilization techniques and developing novel support materials to overcome these limitations.
Furthermore, the scalability of polysilane synthesis and catalyst preparation remains a significant hurdle for industrial applications. Current synthetic methods often involve complex procedures and expensive reagents, limiting large-scale production. Efforts are underway to develop more efficient and cost-effective synthetic routes, including the exploration of alternative precursors and catalytic polymerization methods.
Despite these challenges, the potential of polysilanes in advanced catalytic processes continues to drive research and development in this field. Recent advancements, such as the development of chiral polysilanes for asymmetric catalysis and the integration of polysilanes with other catalytic materials, demonstrate the ongoing progress in addressing these challenges and expanding the scope of polysilane catalysis.
The use of polysilanes in catalysis has gained significant attention due to their ability to act as both catalysts and catalyst supports. Their unique electronic properties, stemming from σ-conjugation along the silicon backbone, allow for efficient electron transfer processes, making them particularly suitable for redox reactions. Additionally, the structural versatility of polysilanes enables the incorporation of various functional groups, further expanding their catalytic applications.
One of the primary challenges in polysilane catalysis is the stability of these materials under harsh reaction conditions. While polysilanes exhibit excellent thermal stability, their susceptibility to oxidation and hydrolysis can limit their long-term performance in certain catalytic processes. Researchers are actively working on developing strategies to enhance the chemical stability of polysilanes, such as incorporating protective groups or creating hybrid materials with inorganic components.
Another significant challenge lies in controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of polysilanes. The catalytic activity and selectivity of polysilanes are closely related to their molecular structure, and achieving precise control over these parameters remains a key focus area. Advanced polymerization techniques, such as living anionic polymerization and controlled radical polymerization, are being explored to address this challenge and produce well-defined polysilane catalysts.
The heterogeneity of polysilane catalysts presents both opportunities and challenges. While heterogeneous catalysts offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and recyclability, achieving uniform catalytic sites and preventing leaching of active species are ongoing concerns. Researchers are investigating various immobilization techniques and developing novel support materials to overcome these limitations.
Furthermore, the scalability of polysilane synthesis and catalyst preparation remains a significant hurdle for industrial applications. Current synthetic methods often involve complex procedures and expensive reagents, limiting large-scale production. Efforts are underway to develop more efficient and cost-effective synthetic routes, including the exploration of alternative precursors and catalytic polymerization methods.
Despite these challenges, the potential of polysilanes in advanced catalytic processes continues to drive research and development in this field. Recent advancements, such as the development of chiral polysilanes for asymmetric catalysis and the integration of polysilanes with other catalytic materials, demonstrate the ongoing progress in addressing these challenges and expanding the scope of polysilane catalysis.
Current Polysilane-based Catalytic Solutions
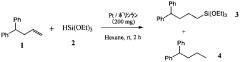
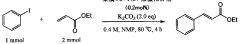
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
Polysilanes are silicon-based polymers with unique electronic and optical properties. They can be synthesized through various methods, including Wurtz coupling of dichlorosilanes. These polymers exhibit interesting characteristics such as photoconductivity and photoluminescence, making them suitable for various applications in electronics and optics.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These silicon-based polymers have applications in electronics, optics, and materials science due to their electronic and optical characteristics. The synthesis methods and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications.
- Polysilane-based coatings and films: Polysilanes are used to create coatings and films with specific properties. These coatings can be applied to various substrates and may offer benefits such as improved durability, optical properties, or electronic characteristics. The composition and application methods of these coatings can be optimized for different purposes.
- Polysilanes in photoresist applications: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations for semiconductor manufacturing. These materials can be designed to have specific photosensitive properties, allowing for precise patterning in lithography processes. The development of polysilane-based photoresists contributes to advancements in microelectronics fabrication.
- Functionalization and modification of polysilanes: Polysilanes can be functionalized or modified to enhance their properties or introduce new functionalities. This may involve the incorporation of specific side groups, crosslinking, or the creation of copolymers. These modifications allow for the tailoring of polysilanes for specific applications or to improve their performance in existing uses.
- Polysilanes in energy and electronic applications: Polysilanes have potential applications in energy-related technologies and electronic devices. Their unique electronic properties make them suitable for use in solar cells, light-emitting diodes, and other optoelectronic devices. Research in this area focuses on optimizing polysilane structures and compositions for improved performance in these applications.
02 Applications of polysilanes in coatings and films
Polysilanes can be used to create functional coatings and films with specific properties. These materials can be applied to various substrates to impart characteristics such as improved adhesion, chemical resistance, or optical properties. The polysilane-based coatings and films find applications in areas like electronics, optics, and protective coatings.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilanes in photoresist compositions
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist compositions for lithography applications. These silicon-based polymers can enhance the performance of photoresists by improving their sensitivity to light, resolution, and resistance to etching processes. Polysilane-containing photoresists are particularly useful in the fabrication of semiconductor devices and other microelectronic components.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of polysilanes
Polysilanes can be modified and functionalized to tailor their properties for specific applications. This includes the incorporation of various functional groups, copolymerization with other monomers, or post-polymerization modifications. These modifications can enhance the solubility, processability, or specific functional properties of the polysilanes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilanes in electronic and optoelectronic devices
Polysilanes have potential applications in electronic and optoelectronic devices due to their unique electronic structure and optical properties. They can be used as active materials in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photovoltaic cells, and other electronic components. The silicon-based backbone of polysilanes contributes to their interesting electronic and optical behavior.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Catalysis Research
The polysilane market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced catalytic processes across various industries. The global market size is expanding, with significant potential in petrochemicals, electronics, and materials science. Technologically, polysilanes are advancing rapidly, with major players like Evonik Operations GmbH, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and SINOPEC Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry leading innovation. Companies such as Wacker Chemie AG and Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. are also contributing to the development of novel applications. The technology's maturity varies across different sectors, with some areas reaching commercial viability while others remain in the research and development stage.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant strides in utilizing polysilanes for advanced catalytic processes in the petrochemical industry. Their research has focused on developing polysilane-based catalysts for hydrocracking and hydrogenation reactions[1]. Sinopec's polysilane catalysts have shown improved activity and stability in heavy oil upgrading processes, leading to higher yields of valuable light fractions[2]. The company has also explored the use of polysilane-modified zeolites for catalytic cracking, resulting in enhanced selectivity towards high-value olefins[3]. Additionally, Sinopec has developed novel polysilane-metal hybrid catalysts that demonstrate superior performance in hydrodesulfurization reactions, addressing the increasing demand for cleaner fuels[4]. Their continuous research efforts have led to the implementation of polysilane-based catalytic technologies in several of their refineries, showcasing the practical application of these advanced materials[5].
Strengths: Improved catalytic activity in petrochemical processes, enhanced selectivity for high-value products, practical implementation in large-scale operations. Weaknesses: Potential high costs associated with catalyst synthesis, possible limitations in catalyst regeneration and longevity.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed advanced polysilane-based catalytic processes for various applications. Their technology involves the synthesis of high-purity polysilanes through controlled polymerization of silane monomers[1]. These polysilanes are then used as precursors in catalytic reactions, particularly in the production of silicon-based materials. Wacker's polysilane catalysts have shown exceptional performance in cross-coupling reactions, hydrosilylation, and dehydrogenative coupling[2]. The company has also developed novel methods for incorporating functional groups into polysilane structures, enhancing their catalytic properties and expanding their application range[3]. Wacker's polysilane catalysts have demonstrated improved selectivity and yield in various organic transformations, making them valuable in fine chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical production[4].
Strengths: High catalytic activity, improved selectivity in organic transformations, versatility in applications. Weaknesses: Potentially high production costs, sensitivity to moisture and air, limited scalability for some applications.
Innovative Polysilane Catalytic Mechanisms
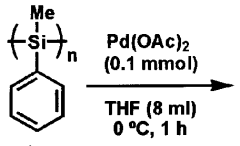
Polysilane-Supported Transition Metal Catalyst
PatentInactiveUS20090143607A1
Innovation
- The development of polysilane-supported transition metal catalysts, where transition metals are immobilized on polysilane compounds with aryl groups, allowing for high catalytic activity, easy handling, and scalability, using a method involving solvent mixing and phase separation to achieve stable and reusable catalysts.
Polysilane-supported transition metal catalyst
PatentWO2007102334A1
Innovation
- A polysilane-supported transition metal catalyst is developed, where transition metals are immobilized on a polysilane compound with an aryl group-containing main chain, allowing for high catalytic activity, easy handling, and efficient recovery and reuse, using a method involving solvent phase separation and cross-linking to stabilize the catalyst.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Catalysts
The environmental impact of polysilane catalysts is a critical consideration in their application to advanced catalytic processes. These catalysts have shown promising potential in various industrial applications, but their effects on the environment must be carefully evaluated to ensure sustainable and responsible use.
Polysilane catalysts offer several environmental advantages compared to traditional catalysts. They often require lower reaction temperatures and pressures, leading to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This energy efficiency contributes to a smaller carbon footprint for industrial processes utilizing polysilane catalysts. Additionally, the high selectivity of polysilane catalysts can result in fewer unwanted by-products, minimizing waste generation and the need for extensive purification steps.
However, the production and disposal of polysilane catalysts present environmental challenges. The synthesis of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. Proper handling and disposal of these materials are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Furthermore, the long-term stability and degradation products of polysilane catalysts in the environment are not yet fully understood, necessitating ongoing research to assess their potential ecological impacts.
The recyclability of polysilane catalysts is an important factor in their environmental profile. Many polysilane catalysts can be recovered and reused multiple times, reducing the overall material consumption and waste generation associated with catalytic processes. However, the efficiency of recycling methods and the potential for catalyst degradation over multiple cycles require further investigation to optimize their environmental performance.
Water pollution is another concern related to polysilane catalysts. While these catalysts often exhibit good stability in aqueous environments, the potential leaching of silicon-based compounds or other components into water systems must be carefully monitored and controlled. Implementing effective wastewater treatment strategies is essential to mitigate any potential negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of polysilane catalysts is an essential tool for comprehensively evaluating their environmental impact. LCA studies can provide valuable insights into the overall sustainability of polysilane-based catalytic processes, considering factors such as raw material extraction, synthesis, use phase, and end-of-life management. These assessments can guide the development of more environmentally friendly polysilane catalysts and inform decision-making regarding their implementation in industrial applications.
As research in this field progresses, efforts are being made to develop greener synthesis methods for polysilane catalysts, such as using renewable resources or less toxic precursors. Additionally, the design of more efficient and longer-lasting polysilane catalysts can further reduce their environmental footprint by decreasing the frequency of catalyst replacement and associated waste generation.
Polysilane catalysts offer several environmental advantages compared to traditional catalysts. They often require lower reaction temperatures and pressures, leading to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This energy efficiency contributes to a smaller carbon footprint for industrial processes utilizing polysilane catalysts. Additionally, the high selectivity of polysilane catalysts can result in fewer unwanted by-products, minimizing waste generation and the need for extensive purification steps.
However, the production and disposal of polysilane catalysts present environmental challenges. The synthesis of polysilanes typically involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. Proper handling and disposal of these materials are crucial to prevent environmental contamination. Furthermore, the long-term stability and degradation products of polysilane catalysts in the environment are not yet fully understood, necessitating ongoing research to assess their potential ecological impacts.
The recyclability of polysilane catalysts is an important factor in their environmental profile. Many polysilane catalysts can be recovered and reused multiple times, reducing the overall material consumption and waste generation associated with catalytic processes. However, the efficiency of recycling methods and the potential for catalyst degradation over multiple cycles require further investigation to optimize their environmental performance.
Water pollution is another concern related to polysilane catalysts. While these catalysts often exhibit good stability in aqueous environments, the potential leaching of silicon-based compounds or other components into water systems must be carefully monitored and controlled. Implementing effective wastewater treatment strategies is essential to mitigate any potential negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of polysilane catalysts is an essential tool for comprehensively evaluating their environmental impact. LCA studies can provide valuable insights into the overall sustainability of polysilane-based catalytic processes, considering factors such as raw material extraction, synthesis, use phase, and end-of-life management. These assessments can guide the development of more environmentally friendly polysilane catalysts and inform decision-making regarding their implementation in industrial applications.
As research in this field progresses, efforts are being made to develop greener synthesis methods for polysilane catalysts, such as using renewable resources or less toxic precursors. Additionally, the design of more efficient and longer-lasting polysilane catalysts can further reduce their environmental footprint by decreasing the frequency of catalyst replacement and associated waste generation.
Scalability of Polysilane Catalytic Processes
The scalability of polysilane catalytic processes is a critical factor in determining their potential for widespread industrial adoption. As polysilanes continue to demonstrate promising catalytic properties in various chemical reactions, the ability to scale up these processes becomes increasingly important.
One of the key advantages of polysilane catalysts is their potential for high efficiency and selectivity in catalytic reactions. However, translating these benefits from laboratory-scale experiments to large-scale industrial applications presents several challenges. The primary concern is maintaining the catalytic activity and selectivity of polysilanes when increasing reaction volumes and throughput.
To address this challenge, researchers are exploring various approaches to optimize the scalability of polysilane catalytic processes. One strategy involves the development of supported polysilane catalysts, where the polysilane molecules are immobilized on a solid support material. This approach can enhance the stability and recyclability of the catalyst, making it more suitable for large-scale operations.
Another important aspect of scalability is the synthesis of polysilanes themselves. As the demand for these materials increases, efficient and cost-effective production methods become crucial. Recent advancements in synthetic routes, such as the use of electrochemical methods or novel precursors, show promise in improving the scalability of polysilane production.
The reactor design also plays a crucial role in scaling up polysilane catalytic processes. Continuous flow reactors, for instance, offer advantages in terms of heat and mass transfer, which can be particularly beneficial when dealing with the unique properties of polysilanes. These reactor types allow for better control of reaction conditions and can potentially lead to improved yields and product quality at larger scales.
Furthermore, the economic viability of scaled-up polysilane catalytic processes must be carefully evaluated. This includes considerations such as raw material costs, energy requirements, and potential environmental impacts. As polysilanes are often silicon-based materials, their production and use must be assessed in terms of sustainability and long-term availability of resources.
In conclusion, while polysilanes show great promise in advanced catalytic processes, their successful implementation on an industrial scale requires overcoming several technical and economic challenges. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, paving the way for the potential widespread adoption of polysilane-based catalytic technologies in various industrial sectors.
One of the key advantages of polysilane catalysts is their potential for high efficiency and selectivity in catalytic reactions. However, translating these benefits from laboratory-scale experiments to large-scale industrial applications presents several challenges. The primary concern is maintaining the catalytic activity and selectivity of polysilanes when increasing reaction volumes and throughput.
To address this challenge, researchers are exploring various approaches to optimize the scalability of polysilane catalytic processes. One strategy involves the development of supported polysilane catalysts, where the polysilane molecules are immobilized on a solid support material. This approach can enhance the stability and recyclability of the catalyst, making it more suitable for large-scale operations.
Another important aspect of scalability is the synthesis of polysilanes themselves. As the demand for these materials increases, efficient and cost-effective production methods become crucial. Recent advancements in synthetic routes, such as the use of electrochemical methods or novel precursors, show promise in improving the scalability of polysilane production.
The reactor design also plays a crucial role in scaling up polysilane catalytic processes. Continuous flow reactors, for instance, offer advantages in terms of heat and mass transfer, which can be particularly beneficial when dealing with the unique properties of polysilanes. These reactor types allow for better control of reaction conditions and can potentially lead to improved yields and product quality at larger scales.
Furthermore, the economic viability of scaled-up polysilane catalytic processes must be carefully evaluated. This includes considerations such as raw material costs, energy requirements, and potential environmental impacts. As polysilanes are often silicon-based materials, their production and use must be assessed in terms of sustainability and long-term availability of resources.
In conclusion, while polysilanes show great promise in advanced catalytic processes, their successful implementation on an industrial scale requires overcoming several technical and economic challenges. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, paving the way for the potential widespread adoption of polysilane-based catalytic technologies in various industrial sectors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!