Production of Ethyl Propanoate via Enzymatic Reactions
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Enzymatic Ethyl Propanoate Synthesis Background
Enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate represents a significant advancement in the field of biocatalysis and green chemistry. This process has gained considerable attention in recent years due to its potential to replace traditional chemical synthesis methods with more environmentally friendly and sustainable alternatives.
The development of enzymatic routes for ester production can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first discovered the ability of certain enzymes to catalyze esterification reactions. However, it wasn't until the late 1980s and early 1990s that significant progress was made in applying these enzymes to industrial-scale production of esters, including ethyl propanoate.
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an important ester compound widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry. It is characterized by its fruity odor, reminiscent of pineapple and rum, making it a valuable ingredient in various food and beverage applications. Traditionally, this compound has been produced through chemical synthesis, involving the reaction of propionic acid with ethanol in the presence of strong acid catalysts.
The shift towards enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate has been driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing consumer demand for natural and clean-label products, which has prompted manufacturers to seek bio-based production methods. Secondly, increasing environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have pushed the industry to explore greener alternatives to chemical synthesis.
Lipases, a class of enzymes that naturally catalyze the hydrolysis of fats, have emerged as the primary biocatalysts for the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate. These enzymes can work in reverse to catalyze esterification reactions under controlled conditions. The use of lipases offers several advantages, including mild reaction conditions, high selectivity, and the ability to produce high-purity products without the need for extensive purification steps.
Recent technological advancements have further improved the efficiency and scalability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production. These include the development of immobilized enzyme technologies, which allow for enzyme reuse and continuous production processes, as well as protein engineering techniques that have led to the creation of more stable and active lipase variants.
As research in this field continues to progress, the focus has shifted towards optimizing reaction conditions, exploring novel enzyme sources, and developing more efficient reactor designs. These efforts aim to enhance the economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production and expand its application to larger industrial scales.
The development of enzymatic routes for ester production can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first discovered the ability of certain enzymes to catalyze esterification reactions. However, it wasn't until the late 1980s and early 1990s that significant progress was made in applying these enzymes to industrial-scale production of esters, including ethyl propanoate.
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an important ester compound widely used in the flavor and fragrance industry. It is characterized by its fruity odor, reminiscent of pineapple and rum, making it a valuable ingredient in various food and beverage applications. Traditionally, this compound has been produced through chemical synthesis, involving the reaction of propionic acid with ethanol in the presence of strong acid catalysts.
The shift towards enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate has been driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing consumer demand for natural and clean-label products, which has prompted manufacturers to seek bio-based production methods. Secondly, increasing environmental regulations and sustainability concerns have pushed the industry to explore greener alternatives to chemical synthesis.
Lipases, a class of enzymes that naturally catalyze the hydrolysis of fats, have emerged as the primary biocatalysts for the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate. These enzymes can work in reverse to catalyze esterification reactions under controlled conditions. The use of lipases offers several advantages, including mild reaction conditions, high selectivity, and the ability to produce high-purity products without the need for extensive purification steps.
Recent technological advancements have further improved the efficiency and scalability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production. These include the development of immobilized enzyme technologies, which allow for enzyme reuse and continuous production processes, as well as protein engineering techniques that have led to the creation of more stable and active lipase variants.
As research in this field continues to progress, the focus has shifted towards optimizing reaction conditions, exploring novel enzyme sources, and developing more efficient reactor designs. These efforts aim to enhance the economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production and expand its application to larger industrial scales.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Propanoate
The global market for ethyl propanoate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. This ester compound, also known as ethyl propionate, finds extensive use in flavors and fragrances, solvents, and as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl propanoate is widely utilized as a flavoring agent due to its fruity, rum-like aroma. The increasing demand for natural and artificial fruit flavors in processed foods, beverages, and confectionery products has been a significant factor contributing to market growth. The compound's ability to impart a pineapple-like scent has made it particularly popular in the production of fruit-flavored products.
The cosmetics and personal care sector represents another key market for ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant odor and solvent properties make it a valuable ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other beauty products. As consumer preferences shift towards natural and organic cosmetics, the demand for bio-based ethyl propanoate produced through enzymatic reactions is expected to rise.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl propanoate serves as a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The growing pharmaceutical sector, particularly in emerging economies, is likely to drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in the coming years.
The paint and coatings industry also contributes to the market growth of ethyl propanoate. Its use as a solvent in paints, varnishes, and lacquers is attributed to its low toxicity and favorable evaporation rate. The expanding construction and automotive sectors in developing countries are expected to fuel the demand for paints and coatings, subsequently boosting the ethyl propanoate market.
Geographically, Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl propanoate, owing to the rapid industrialization and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are mature markets with steady demand, primarily driven by the food and beverage and pharmaceutical industries.
The shift towards sustainable production methods has led to increased interest in enzymatic reactions for the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. This eco-friendly approach aligns with the growing consumer preference for green products and stringent environmental regulations. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to optimize enzymatic production processes, potentially reshaping the market landscape in the coming years.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl propanoate is widely utilized as a flavoring agent due to its fruity, rum-like aroma. The increasing demand for natural and artificial fruit flavors in processed foods, beverages, and confectionery products has been a significant factor contributing to market growth. The compound's ability to impart a pineapple-like scent has made it particularly popular in the production of fruit-flavored products.
The cosmetics and personal care sector represents another key market for ethyl propanoate. Its pleasant odor and solvent properties make it a valuable ingredient in perfumes, lotions, and other beauty products. As consumer preferences shift towards natural and organic cosmetics, the demand for bio-based ethyl propanoate produced through enzymatic reactions is expected to rise.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl propanoate serves as a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The growing pharmaceutical sector, particularly in emerging economies, is likely to drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in the coming years.
The paint and coatings industry also contributes to the market growth of ethyl propanoate. Its use as a solvent in paints, varnishes, and lacquers is attributed to its low toxicity and favorable evaporation rate. The expanding construction and automotive sectors in developing countries are expected to fuel the demand for paints and coatings, subsequently boosting the ethyl propanoate market.
Geographically, Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl propanoate, owing to the rapid industrialization and increasing disposable income in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are mature markets with steady demand, primarily driven by the food and beverage and pharmaceutical industries.
The shift towards sustainable production methods has led to increased interest in enzymatic reactions for the synthesis of ethyl propanoate. This eco-friendly approach aligns with the growing consumer preference for green products and stringent environmental regulations. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to optimize enzymatic production processes, potentially reshaping the market landscape in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Enzymatic Esterification
Enzymatic esterification for the production of ethyl propanoate faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread industrial application. One of the primary obstacles is the thermodynamic equilibrium limitation. The reversible nature of the esterification reaction often results in low product yields, necessitating strategies to shift the equilibrium towards product formation.
Water, a byproduct of the esterification reaction, poses another major challenge. Its accumulation in the reaction medium can inhibit enzyme activity and drive the equilibrium towards hydrolysis, reducing the overall yield of ethyl propanoate. Effective water removal techniques are crucial but can be complex to implement on an industrial scale.
Enzyme stability and longevity present ongoing challenges in enzymatic esterification. Lipases, the commonly used enzymes for this reaction, may suffer from deactivation or loss of catalytic efficiency over time, especially in the presence of organic solvents or at elevated temperatures. This necessitates frequent enzyme replacement, increasing production costs.
The choice of reaction medium is another critical factor. While organic solvents can enhance substrate solubility and product extraction, they may also negatively impact enzyme stability and activity. Finding the optimal balance between reaction efficiency and enzyme preservation remains a significant challenge.
Substrate inhibition is an additional hurdle in the enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate. High concentrations of propionic acid or ethanol can inhibit enzyme activity, limiting the reaction rate and overall productivity. Developing strategies to mitigate substrate inhibition while maintaining high substrate concentrations is essential for process optimization.
Mass transfer limitations, particularly in immobilized enzyme systems, can significantly impact reaction kinetics. The diffusion of substrates to and products from the enzyme active sites can become rate-limiting, especially in large-scale operations. Overcoming these mass transfer limitations requires careful reactor design and optimization of reaction conditions.
Scalability and process integration pose challenges when transitioning from laboratory-scale to industrial-scale production. Maintaining enzyme performance, ensuring consistent product quality, and achieving cost-effectiveness at larger scales require significant engineering efforts and process modifications.
Lastly, the high cost of enzymes compared to traditional chemical catalysts remains a significant economic barrier. Developing more efficient and cost-effective enzyme production methods, as well as improving enzyme recyclability and reusability, are crucial for enhancing the economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production.
Water, a byproduct of the esterification reaction, poses another major challenge. Its accumulation in the reaction medium can inhibit enzyme activity and drive the equilibrium towards hydrolysis, reducing the overall yield of ethyl propanoate. Effective water removal techniques are crucial but can be complex to implement on an industrial scale.
Enzyme stability and longevity present ongoing challenges in enzymatic esterification. Lipases, the commonly used enzymes for this reaction, may suffer from deactivation or loss of catalytic efficiency over time, especially in the presence of organic solvents or at elevated temperatures. This necessitates frequent enzyme replacement, increasing production costs.
The choice of reaction medium is another critical factor. While organic solvents can enhance substrate solubility and product extraction, they may also negatively impact enzyme stability and activity. Finding the optimal balance between reaction efficiency and enzyme preservation remains a significant challenge.
Substrate inhibition is an additional hurdle in the enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate. High concentrations of propionic acid or ethanol can inhibit enzyme activity, limiting the reaction rate and overall productivity. Developing strategies to mitigate substrate inhibition while maintaining high substrate concentrations is essential for process optimization.
Mass transfer limitations, particularly in immobilized enzyme systems, can significantly impact reaction kinetics. The diffusion of substrates to and products from the enzyme active sites can become rate-limiting, especially in large-scale operations. Overcoming these mass transfer limitations requires careful reactor design and optimization of reaction conditions.
Scalability and process integration pose challenges when transitioning from laboratory-scale to industrial-scale production. Maintaining enzyme performance, ensuring consistent product quality, and achieving cost-effectiveness at larger scales require significant engineering efforts and process modifications.
Lastly, the high cost of enzymes compared to traditional chemical catalysts remains a significant economic barrier. Developing more efficient and cost-effective enzyme production methods, as well as improving enzyme recyclability and reusability, are crucial for enhancing the economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production.
Existing Enzymatic Esterification Methods
01 Synthesis and production methods of ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions, catalytic processes, and continuous production techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl alcohol with propionyl chloride, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry aromas. The compound is also utilized in perfumery to add sweet, ethereal notes to various fragrances.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an effective solvent for various organic compounds and is used in the production of paints, inks, and coatings. It also acts as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds, playing a crucial role in numerous industrial processes.
- Purification and quality control: Various methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on biodegradability, toxicity, and potential health effects. Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable production methods and safer handling practices for industrial applications.
02 Applications of ethyl propanoate in fragrances and flavors
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, air fresheners, and food flavorings to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use of ethyl propanoate as a solvent or intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent and intermediate in various chemical processes. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other industrial chemicals, offering advantages such as low toxicity and good solvency properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and separation techniques for ethyl propanoate
Various methods for purifying and separating ethyl propanoate from reaction mixtures or other compounds are described. These techniques include distillation, extraction, and chromatography, aimed at obtaining high-purity ethyl propanoate for industrial and research applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations in ethyl propanoate production
Innovations in the production and handling of ethyl propanoate focus on improving environmental sustainability and safety. This includes developing green synthesis methods, reducing waste, and implementing safety measures to minimize risks associated with its flammability and potential health hazards.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Biocatalysis
The production of ethyl propanoate via enzymatic reactions is an emerging field in green chemistry, currently in its early development stage. The market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing demand for sustainable chemical processes. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Fudan University and Nanjing Tech University are conducting foundational research, while companies like Novozymes A/S and Evonik Operations GmbH are at the forefront of industrial applications. Mitsubishi Chemical UK Ltd. and Dow Global Technologies LLC are also exploring this area, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and established chemical companies, indicating a collaborative approach to advancing this technology.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has pioneered a hybrid approach for ethyl propanoate production, combining enzymatic and chemical processes. Their method begins with an enzymatic esterification using a proprietary lipase formulation, followed by a chemical purification step. This two-stage process allows for high conversion rates (>98%) while maintaining product quality[4]. Dow's system operates in a semi-continuous mode, with the enzymatic reaction occurring in a packed bed reactor and the purification step utilizing advanced distillation techniques. The company has also developed a novel enzyme immobilization technique that extends the catalyst's lifetime to over 6 months of continuous operation[5]. Additionally, Dow has implemented process intensification strategies, reducing the overall footprint of the production facility by approximately 30% compared to traditional methods[6].
Strengths: High conversion rates, extended enzyme lifetime, and reduced plant footprint. Weaknesses: Complexity of the hybrid process and potential higher capital costs due to the dual-stage system.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik Operations GmbH has developed an innovative enzymatic process for ethyl propanoate production using their proprietary ENOVA® enzyme technology. This process employs a highly stable esterase enzyme that can withstand temperatures up to 70°C, allowing for increased reaction rates and reduced microbial contamination risks[7]. Evonik's approach includes a unique water removal system that continuously shifts the equilibrium towards product formation, achieving yields of over 99% within 3 hours[8]. The company has also integrated in-situ product recovery (ISPR) techniques, which selectively remove ethyl propanoate from the reaction mixture, further driving the reaction to completion and simplifying downstream processing. Evonik's process is characterized by its flexibility, capable of handling various alcohol and acid substrates for the production of different esters[9].
Strengths: High temperature stability of enzymes, excellent yields, and process flexibility. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with specialized enzyme production and ISPR implementation.
Innovative Enzymes for Ethyl Propanoate Synthesis
Energy efficient methods to produce products
PatentInactiveUS20130189752A1
Innovation
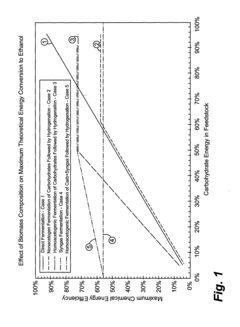
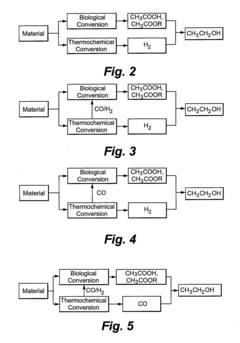
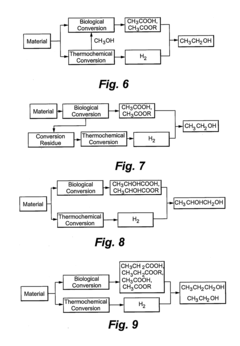
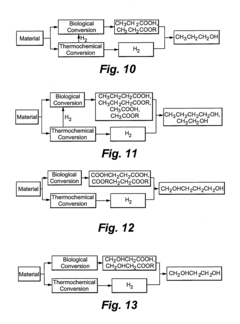
- A method combining biological and thermochemical conversion processes to produce intermediates, where biological processes convert carbohydrate substances and thermochemical processes convert non-carbohydrate substances, then reacting these intermediates to form the final product, thereby enhancing energy and mass transfer efficiency.
Novel propanoate and its production method
PatentActiveJP2012500846A
Innovation
- A novel process for preparing propanoates using a two-step reaction involving 4-hydroxyphenylmethylcarbinol (HPMC) as a starting material.
- The use of an acid-catalyzed displacement reaction to convert HPMC to 4-hydroxyphenylmethylcarbinol methyl ether (HPME) as an intermediate step.
- The development of a new class of propanoates (EHPEPs) with applications in the electronic chemicals market, particularly in photoresist compositions.
Green Chemistry Aspects of Enzymatic Synthesis
The enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate represents a significant advancement in green chemistry, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional chemical processes. This approach aligns with several key principles of green chemistry, including the use of renewable feedstocks, reduced energy consumption, and minimization of waste products.
Enzymes, as biocatalysts, operate under mild conditions, typically at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This characteristic significantly reduces the energy requirements compared to conventional chemical synthesis methods, which often necessitate high temperatures and pressures. The lower energy demand not only decreases operational costs but also contributes to a reduced carbon footprint, making the process more environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, enzymatic reactions exhibit high selectivity and specificity, leading to improved product yields and reduced formation of unwanted by-products. This selectivity minimizes the need for extensive purification steps, thereby reducing solvent usage and waste generation. The ability to conduct reactions in aqueous media or with minimal organic solvents further enhances the green aspects of enzymatic synthesis.
The use of enzymes also allows for the utilization of renewable raw materials. In the case of ethyl propanoate production, both the alcohol (ethanol) and the acid (propionic acid) components can be derived from bio-based sources. This shift towards renewable feedstocks reduces dependence on fossil resources and promotes a more circular economy.
Another significant advantage of enzymatic synthesis is the potential for enzyme immobilization and reuse. Immobilized enzymes can be easily separated from the reaction mixture and reused multiple times, improving process efficiency and reducing enzyme consumption. This recyclability aspect further contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation.
The mild reaction conditions and high selectivity of enzymatic processes also enhance safety aspects. The reduced risk of side reactions and the elimination of harsh chemicals or extreme conditions make enzymatic synthesis a safer alternative for industrial-scale production. This improved safety profile aligns with green chemistry principles that emphasize the design of inherently safer chemical processes.
In conclusion, the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate exemplifies several core tenets of green chemistry. By leveraging the power of biocatalysts, this approach offers a more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally benign route to chemical production, paving the way for greener industrial practices in the future.
Enzymes, as biocatalysts, operate under mild conditions, typically at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This characteristic significantly reduces the energy requirements compared to conventional chemical synthesis methods, which often necessitate high temperatures and pressures. The lower energy demand not only decreases operational costs but also contributes to a reduced carbon footprint, making the process more environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, enzymatic reactions exhibit high selectivity and specificity, leading to improved product yields and reduced formation of unwanted by-products. This selectivity minimizes the need for extensive purification steps, thereby reducing solvent usage and waste generation. The ability to conduct reactions in aqueous media or with minimal organic solvents further enhances the green aspects of enzymatic synthesis.
The use of enzymes also allows for the utilization of renewable raw materials. In the case of ethyl propanoate production, both the alcohol (ethanol) and the acid (propionic acid) components can be derived from bio-based sources. This shift towards renewable feedstocks reduces dependence on fossil resources and promotes a more circular economy.
Another significant advantage of enzymatic synthesis is the potential for enzyme immobilization and reuse. Immobilized enzymes can be easily separated from the reaction mixture and reused multiple times, improving process efficiency and reducing enzyme consumption. This recyclability aspect further contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation.
The mild reaction conditions and high selectivity of enzymatic processes also enhance safety aspects. The reduced risk of side reactions and the elimination of harsh chemicals or extreme conditions make enzymatic synthesis a safer alternative for industrial-scale production. This improved safety profile aligns with green chemistry principles that emphasize the design of inherently safer chemical processes.
In conclusion, the enzymatic synthesis of ethyl propanoate exemplifies several core tenets of green chemistry. By leveraging the power of biocatalysts, this approach offers a more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally benign route to chemical production, paving the way for greener industrial practices in the future.
Scalability and Process Integration
The scalability and process integration of enzymatic production of ethyl propanoate present both challenges and opportunities for industrial implementation. As the demand for this ester grows in various sectors, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, the need for efficient large-scale production becomes increasingly important.
One of the primary considerations in scaling up enzymatic reactions is maintaining optimal reaction conditions across larger volumes. This includes factors such as temperature control, pH stability, and substrate concentration. In the case of ethyl propanoate production, careful monitoring and adjustment of these parameters are crucial to ensure consistent enzyme activity and product yield. Advanced reactor designs, such as continuous stirred-tank reactors (CSTRs) or packed-bed reactors, can help address these challenges by providing better mixing and temperature control.
Process integration plays a vital role in enhancing the overall efficiency and economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production. This involves optimizing the entire production chain, from raw material handling to product purification. For instance, implementing in situ product removal techniques can help overcome potential product inhibition issues and improve reaction kinetics. Membrane-based separation processes or selective adsorption methods could be integrated into the production system to continuously remove ethyl propanoate, driving the reaction equilibrium towards product formation.
Another aspect of process integration is the recycling of enzymes and unreacted substrates. Immobilization techniques, such as enzyme entrapment in alginate beads or covalent attachment to solid supports, can significantly enhance enzyme stability and reusability. This not only reduces production costs but also improves the overall sustainability of the process. Additionally, implementing a closed-loop system for solvent recovery and reuse can further optimize resource utilization and minimize waste generation.
The integration of downstream processing steps is equally important for scalability. This includes efficient product separation, purification, and quality control measures. Advanced separation technologies, such as pervaporation or reactive distillation, can be incorporated to achieve high-purity ethyl propanoate while minimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, the implementation of real-time monitoring and control systems, utilizing process analytical technology (PAT), can ensure consistent product quality and facilitate rapid process optimization.
As the scale of production increases, considerations for waste management and environmental impact become more significant. Integrating waste treatment processes, such as biological treatment of aqueous waste streams or recovery of valuable by-products, can improve the overall sustainability of the production process. Additionally, exploring the use of renewable feedstocks for ethanol and propionic acid production can further enhance the green credentials of enzymatic ethyl propanoate synthesis.
One of the primary considerations in scaling up enzymatic reactions is maintaining optimal reaction conditions across larger volumes. This includes factors such as temperature control, pH stability, and substrate concentration. In the case of ethyl propanoate production, careful monitoring and adjustment of these parameters are crucial to ensure consistent enzyme activity and product yield. Advanced reactor designs, such as continuous stirred-tank reactors (CSTRs) or packed-bed reactors, can help address these challenges by providing better mixing and temperature control.
Process integration plays a vital role in enhancing the overall efficiency and economic viability of enzymatic ethyl propanoate production. This involves optimizing the entire production chain, from raw material handling to product purification. For instance, implementing in situ product removal techniques can help overcome potential product inhibition issues and improve reaction kinetics. Membrane-based separation processes or selective adsorption methods could be integrated into the production system to continuously remove ethyl propanoate, driving the reaction equilibrium towards product formation.
Another aspect of process integration is the recycling of enzymes and unreacted substrates. Immobilization techniques, such as enzyme entrapment in alginate beads or covalent attachment to solid supports, can significantly enhance enzyme stability and reusability. This not only reduces production costs but also improves the overall sustainability of the process. Additionally, implementing a closed-loop system for solvent recovery and reuse can further optimize resource utilization and minimize waste generation.
The integration of downstream processing steps is equally important for scalability. This includes efficient product separation, purification, and quality control measures. Advanced separation technologies, such as pervaporation or reactive distillation, can be incorporated to achieve high-purity ethyl propanoate while minimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, the implementation of real-time monitoring and control systems, utilizing process analytical technology (PAT), can ensure consistent product quality and facilitate rapid process optimization.
As the scale of production increases, considerations for waste management and environmental impact become more significant. Integrating waste treatment processes, such as biological treatment of aqueous waste streams or recovery of valuable by-products, can improve the overall sustainability of the production process. Additionally, exploring the use of renewable feedstocks for ethanol and propionic acid production can further enhance the green credentials of enzymatic ethyl propanoate synthesis.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!