Refine Protocols for Precise FTIR Surface Analysis
SEP 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
FTIR Surface Analysis Background and Objectives
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century, becoming an indispensable analytical technique for surface characterization across multiple industries. The development trajectory of FTIR surface analysis has been marked by continuous improvements in instrumentation sensitivity, data processing capabilities, and sampling methodologies. Initially limited to bulk material analysis, FTIR has progressively advanced to enable precise surface-specific measurements at micro and nano scales, revolutionizing material science and quality control processes.
The current technological landscape demands increasingly sophisticated protocols for FTIR surface analysis to address emerging challenges in semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical development, polymer science, and nanotechnology. These industries require non-destructive analytical methods capable of providing molecular-level information about surface compositions, contaminants, and chemical modifications with unprecedented precision and reproducibility.
Recent advancements in FTIR technology, including the integration of attenuated total reflection (ATR), grazing angle reflection-absorption, and photoacoustic sampling techniques, have significantly enhanced surface sensitivity. Complementary developments in computational algorithms and chemometric approaches have further improved data interpretation capabilities. However, standardization of protocols remains a critical bottleneck limiting the full potential of these technological improvements.
The primary objective of refining FTIR surface analysis protocols is to establish standardized methodologies that ensure consistent, reliable, and quantifiable results across different laboratory environments and instrument configurations. This includes optimizing sample preparation techniques, defining appropriate measurement parameters, implementing robust calibration procedures, and developing validated data processing workflows tailored to specific surface analysis applications.
Additionally, this technical exploration aims to address existing limitations in spatial resolution, detection sensitivity, and quantitative accuracy that currently constrain FTIR surface analysis applications. By systematically evaluating and refining each component of the analytical workflow, we seek to expand the applicability of FTIR for characterizing increasingly complex material surfaces and interfaces at molecular scales.
The ultimate goal is to develop a comprehensive framework of best practices and protocols that can be readily adopted across research and industrial settings, facilitating more efficient quality control processes, accelerating materials development cycles, and enabling new discoveries in surface science. These refined protocols will serve as the foundation for next-generation FTIR surface analysis capabilities, supporting innovation across multiple technology sectors while ensuring measurement traceability and reproducibility.
The current technological landscape demands increasingly sophisticated protocols for FTIR surface analysis to address emerging challenges in semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical development, polymer science, and nanotechnology. These industries require non-destructive analytical methods capable of providing molecular-level information about surface compositions, contaminants, and chemical modifications with unprecedented precision and reproducibility.
Recent advancements in FTIR technology, including the integration of attenuated total reflection (ATR), grazing angle reflection-absorption, and photoacoustic sampling techniques, have significantly enhanced surface sensitivity. Complementary developments in computational algorithms and chemometric approaches have further improved data interpretation capabilities. However, standardization of protocols remains a critical bottleneck limiting the full potential of these technological improvements.
The primary objective of refining FTIR surface analysis protocols is to establish standardized methodologies that ensure consistent, reliable, and quantifiable results across different laboratory environments and instrument configurations. This includes optimizing sample preparation techniques, defining appropriate measurement parameters, implementing robust calibration procedures, and developing validated data processing workflows tailored to specific surface analysis applications.
Additionally, this technical exploration aims to address existing limitations in spatial resolution, detection sensitivity, and quantitative accuracy that currently constrain FTIR surface analysis applications. By systematically evaluating and refining each component of the analytical workflow, we seek to expand the applicability of FTIR for characterizing increasingly complex material surfaces and interfaces at molecular scales.
The ultimate goal is to develop a comprehensive framework of best practices and protocols that can be readily adopted across research and industrial settings, facilitating more efficient quality control processes, accelerating materials development cycles, and enabling new discoveries in surface science. These refined protocols will serve as the foundation for next-generation FTIR surface analysis capabilities, supporting innovation across multiple technology sectors while ensuring measurement traceability and reproducibility.
Market Applications and Demand for Precise FTIR Analysis
The global market for precise FTIR surface analysis has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demands across multiple industries for advanced material characterization and quality control. The pharmaceutical sector represents one of the largest market segments, where precise FTIR analysis enables researchers to identify molecular structures, verify drug formulations, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This application alone accounts for a substantial portion of the market demand, with pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in advanced analytical technologies to streamline drug development processes.
In the semiconductor and electronics manufacturing industry, precise FTIR surface analysis has become indispensable for quality control and failure analysis. As device dimensions continue to shrink and performance requirements become more stringent, manufacturers require increasingly sensitive analytical techniques to detect surface contaminants and characterize thin films. This sector's demand is projected to grow substantially as the electronics industry continues its rapid expansion and miniaturization trends.
Environmental monitoring represents another significant market driver, with governmental agencies and private organizations utilizing FTIR analysis for detecting and identifying pollutants in air, water, and soil samples. The growing emphasis on environmental protection and sustainability has led to stricter regulations worldwide, necessitating more precise analytical methods for compliance verification and environmental impact assessments.
The automotive and aerospace industries have also emerged as key consumers of precise FTIR analysis technologies, particularly for material testing and development of advanced composites. These sectors require detailed surface characterization to ensure material performance under extreme conditions, driving demand for more sophisticated analytical protocols.
Academic and research institutions constitute a stable market segment, utilizing FTIR surface analysis for fundamental research across chemistry, materials science, biology, and physics. The continuous pursuit of scientific advancement ensures ongoing demand for refined analytical protocols in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for precise FTIR analysis technologies, owing to their established research infrastructure and strong presence of pharmaceutical and technology companies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing R&D investments, and growing adoption of advanced analytical techniques in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Market analysts have identified a clear trend toward integrated analytical solutions that combine FTIR with complementary techniques, offering comprehensive material characterization capabilities. This integration trend is reshaping market demands, with customers increasingly seeking versatile systems rather than standalone FTIR instruments.
In the semiconductor and electronics manufacturing industry, precise FTIR surface analysis has become indispensable for quality control and failure analysis. As device dimensions continue to shrink and performance requirements become more stringent, manufacturers require increasingly sensitive analytical techniques to detect surface contaminants and characterize thin films. This sector's demand is projected to grow substantially as the electronics industry continues its rapid expansion and miniaturization trends.
Environmental monitoring represents another significant market driver, with governmental agencies and private organizations utilizing FTIR analysis for detecting and identifying pollutants in air, water, and soil samples. The growing emphasis on environmental protection and sustainability has led to stricter regulations worldwide, necessitating more precise analytical methods for compliance verification and environmental impact assessments.
The automotive and aerospace industries have also emerged as key consumers of precise FTIR analysis technologies, particularly for material testing and development of advanced composites. These sectors require detailed surface characterization to ensure material performance under extreme conditions, driving demand for more sophisticated analytical protocols.
Academic and research institutions constitute a stable market segment, utilizing FTIR surface analysis for fundamental research across chemistry, materials science, biology, and physics. The continuous pursuit of scientific advancement ensures ongoing demand for refined analytical protocols in this sector.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for precise FTIR analysis technologies, owing to their established research infrastructure and strong presence of pharmaceutical and technology companies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing R&D investments, and growing adoption of advanced analytical techniques in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Market analysts have identified a clear trend toward integrated analytical solutions that combine FTIR with complementary techniques, offering comprehensive material characterization capabilities. This integration trend is reshaping market demands, with customers increasingly seeking versatile systems rather than standalone FTIR instruments.
Current Limitations and Challenges in FTIR Surface Techniques
Despite significant advancements in Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy for surface analysis, several critical limitations continue to challenge researchers and industry professionals. The primary obstacle remains the signal-to-noise ratio when examining extremely thin films or monolayers on surfaces. Current commercial FTIR systems typically require sample thicknesses of at least several nanometers to produce reliable spectra, limiting their application in emerging nanomaterial and semiconductor industries where atomic-level precision is increasingly demanded.
Environmental interference presents another significant challenge, as atmospheric water vapor and carbon dioxide strongly absorb in the infrared region, potentially masking important sample features. While purging systems exist, they add complexity and cost to experimental setups, and complete elimination of these interferences remains difficult to achieve consistently across different laboratory environments.
Sample preparation protocols for FTIR surface analysis lack standardization across industries and research institutions. This inconsistency creates difficulties in comparing results between different laboratories and impedes the development of automated analysis systems. The variability in sample mounting, cleaning procedures, and background correction methods introduces systematic errors that are difficult to quantify and correct.
Spatial resolution limitations restrict the applicability of FTIR for heterogeneous surfaces or microstructures. Conventional FTIR systems are diffraction-limited to approximately 10-20 micrometers, which is inadequate for many modern microelectronic components and nanomaterials. While synchrotron-based and near-field techniques offer improved resolution, they remain specialized tools with limited accessibility and high operational costs.
Quantitative analysis presents persistent challenges, particularly for complex multi-component surfaces. Current calibration methods often rely on idealized models that fail to account for matrix effects, surface roughness, and molecular orientation at interfaces. This leads to significant uncertainties in concentration measurements, especially for trace components below 1% surface coverage.
Data interpretation frameworks remain largely semi-empirical, with limited integration of advanced computational methods. Machine learning and artificial intelligence approaches, which have revolutionized other analytical fields, are only beginning to be applied to FTIR surface analysis. The lack of comprehensive spectral databases specifically for surface-bound species further complicates automated interpretation efforts.
Temporal resolution constraints limit the study of dynamic surface processes. Most FTIR surface techniques require several minutes to acquire high-quality spectra, making them unsuitable for monitoring rapid surface reactions or transformations occurring on sub-second timescales. This temporal limitation particularly affects catalysis research and semiconductor processing studies where surface chemistry changes rapidly.
Environmental interference presents another significant challenge, as atmospheric water vapor and carbon dioxide strongly absorb in the infrared region, potentially masking important sample features. While purging systems exist, they add complexity and cost to experimental setups, and complete elimination of these interferences remains difficult to achieve consistently across different laboratory environments.
Sample preparation protocols for FTIR surface analysis lack standardization across industries and research institutions. This inconsistency creates difficulties in comparing results between different laboratories and impedes the development of automated analysis systems. The variability in sample mounting, cleaning procedures, and background correction methods introduces systematic errors that are difficult to quantify and correct.
Spatial resolution limitations restrict the applicability of FTIR for heterogeneous surfaces or microstructures. Conventional FTIR systems are diffraction-limited to approximately 10-20 micrometers, which is inadequate for many modern microelectronic components and nanomaterials. While synchrotron-based and near-field techniques offer improved resolution, they remain specialized tools with limited accessibility and high operational costs.
Quantitative analysis presents persistent challenges, particularly for complex multi-component surfaces. Current calibration methods often rely on idealized models that fail to account for matrix effects, surface roughness, and molecular orientation at interfaces. This leads to significant uncertainties in concentration measurements, especially for trace components below 1% surface coverage.
Data interpretation frameworks remain largely semi-empirical, with limited integration of advanced computational methods. Machine learning and artificial intelligence approaches, which have revolutionized other analytical fields, are only beginning to be applied to FTIR surface analysis. The lack of comprehensive spectral databases specifically for surface-bound species further complicates automated interpretation efforts.
Temporal resolution constraints limit the study of dynamic surface processes. Most FTIR surface techniques require several minutes to acquire high-quality spectra, making them unsuitable for monitoring rapid surface reactions or transformations occurring on sub-second timescales. This temporal limitation particularly affects catalysis research and semiconductor processing studies where surface chemistry changes rapidly.
State-of-the-Art FTIR Surface Analysis Protocols
01 Advanced FTIR techniques for surface analysis precision
Advanced Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy techniques have been developed to enhance precision in surface analysis. These techniques include specialized sampling methods, improved optical configurations, and advanced data processing algorithms that allow for more accurate characterization of surface properties. These advancements enable higher resolution measurements and better discrimination between surface features, leading to more precise analysis of material surfaces across various applications.- FTIR spectroscopy techniques for surface analysis: Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is widely used for surface analysis with high precision. These techniques involve the use of infrared radiation to analyze the chemical composition of surfaces by measuring the absorption of specific wavelengths. Advanced FTIR methods can detect and identify molecular structures, functional groups, and chemical bonds present on material surfaces, providing detailed characterization of surface properties.
- Precision enhancement methods in FTIR surface analysis: Various methods have been developed to enhance the precision of FTIR surface analysis. These include advanced data processing algorithms, calibration techniques, and reference standards that improve measurement accuracy. Signal processing techniques such as noise reduction, baseline correction, and spectral deconvolution help to extract more accurate information from FTIR spectra, resulting in higher precision surface characterization.
- Integration of FTIR with other analytical techniques: Combining FTIR with other analytical techniques enhances surface analysis precision. Hybrid systems that integrate FTIR with techniques such as microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, or mass spectrometry provide complementary data that improves the overall accuracy of surface characterization. These integrated approaches allow for more comprehensive analysis of surface properties, including chemical composition, morphology, and molecular structure.
- Automated FTIR surface analysis systems: Automated systems for FTIR surface analysis improve precision through consistent measurement protocols and reduced human error. These systems incorporate automated sample handling, data collection, and analysis processes that ensure reproducibility and reliability. Software solutions for automated peak identification, quantification, and reporting further enhance the precision of surface analysis results.
- Real-time monitoring and in-situ FTIR surface analysis: Real-time monitoring and in-situ FTIR techniques allow for surface analysis during processes or reactions, providing dynamic information about surface changes. These approaches enable the observation of surface modifications as they occur, offering insights into reaction mechanisms and kinetics. Advanced in-situ FTIR methods can achieve high precision by continuously tracking surface properties under actual operating conditions.
02 Calibration methods for improving FTIR surface measurement accuracy
Various calibration methodologies have been developed to improve the accuracy of FTIR surface measurements. These include reference standard techniques, algorithmic correction approaches, and automated calibration systems that compensate for environmental variations and instrument drift. Proper calibration ensures that surface analysis results are reproducible and reliable, minimizing systematic errors and enhancing the precision of quantitative measurements across different sample types.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of FTIR with complementary analytical techniques
The integration of FTIR spectroscopy with complementary analytical techniques has significantly improved surface analysis precision. By combining FTIR with techniques such as microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, or mass spectrometry, researchers can obtain more comprehensive and accurate characterization of surface properties. These integrated approaches provide multi-dimensional data that enhances the reliability of surface analysis and enables more precise identification of surface components and structures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sample preparation and handling protocols for enhanced precision
Specialized sample preparation and handling protocols have been developed to enhance the precision of FTIR surface analysis. These protocols include surface cleaning procedures, controlled environmental conditions during measurement, and standardized mounting techniques that minimize contamination and interference. Proper sample preparation ensures that the measured FTIR signals accurately represent the true surface characteristics, leading to more precise and reproducible analysis results.Expand Specific Solutions05 Data processing algorithms for improving FTIR surface analysis
Advanced data processing algorithms have been developed to improve the precision of FTIR surface analysis. These include noise reduction techniques, spectral deconvolution methods, chemometric approaches, and machine learning algorithms that enhance signal quality and extract meaningful information from complex spectral data. These computational methods enable more accurate interpretation of FTIR spectra, leading to higher precision in surface characterization and more reliable identification of surface components.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in FTIR Technology
FTIR surface analysis technology is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market adoption across industrial and research sectors. The market size is expanding steadily, driven by demand for precise material characterization in semiconductor, automotive, and pharmaceutical industries. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels among key players. Bruker Optik and Bruker Nano demonstrate advanced capabilities with specialized instrumentation, while DENSO Corp. and Toyota Motor Corp. are applying FTIR analysis in automotive materials research. Academic institutions like Heriot-Watt University and Xidian University are pushing methodological innovations. Industrial players including Smiths Detection and Schlumberger are refining protocols for security and energy applications respectively. The competitive landscape shows a healthy balance between established instrumentation providers and industry-specific implementation experts working to enhance surface analysis precision.
Smiths Detection Ltd.
Technical Solution: Smiths Detection has developed specialized FTIR surface analysis protocols optimized for security and defense applications. Their technology focuses on rapid, high-sensitivity detection of trace substances on various surfaces. The company's protocols incorporate proprietary sampling techniques using specialized swabs and direct surface probes that maximize analyte collection efficiency. Their analytical approach employs machine learning algorithms trained on extensive threat substance libraries to rapidly identify compounds of interest even in complex matrices. Smiths' protocols feature automated background subtraction methods that account for common environmental interferents, significantly reducing false positive rates. The company has also developed portable FTIR systems with simplified protocols for field deployment, enabling non-specialist operators to conduct precise surface analysis in challenging environments. Their technology includes real-time alert systems that flag the presence of specific chemical signatures based on predefined threshold values[4][7].
Strengths: Exceptional sensitivity for trace detection; rapid analysis capabilities suitable for high-throughput screening; robust performance in field conditions. Weaknesses: Protocols primarily optimized for specific threat substances rather than general analytical applications; less emphasis on spatial resolution compared to research-oriented systems; proprietary nature limits customization options.
Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: Halliburton has developed specialized FTIR surface analysis protocols for the oil and gas industry, focusing on wellbore material characterization and formation evaluation. Their approach combines attenuated total reflectance (ATR) FTIR with custom sampling fixtures designed for analyzing irregular core samples and drill cuttings. The company's protocols incorporate advanced spectral preprocessing techniques that compensate for scattering effects and baseline variations common in heterogeneous geological samples. Halliburton has implemented automated mineral identification algorithms that can quantify complex mineral assemblages based on characteristic absorption bands. Their protocols include specialized calibration procedures using certified reference materials that match the matrix composition of downhole samples. The company has also developed protocols for analyzing organic contaminants on equipment surfaces, helping to identify potential sources of wellbore instability or production issues. Their approach integrates FTIR data with other analytical techniques through proprietary software platforms that enable comprehensive surface characterization[6][8].
Strengths: Protocols specifically optimized for challenging geological samples; robust performance in high-pressure/high-temperature conditions; seamless integration with other oilfield analytical techniques. Weaknesses: Limited applicability outside petroleum industry applications; protocols prioritize practical field utility over maximum analytical sensitivity; specialized equipment requirements increase implementation costs.
Critical Patents and Innovations in FTIR Surface Characterization
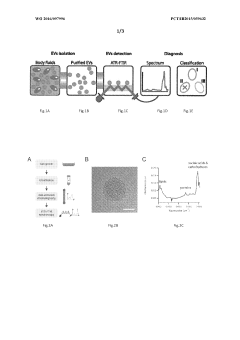
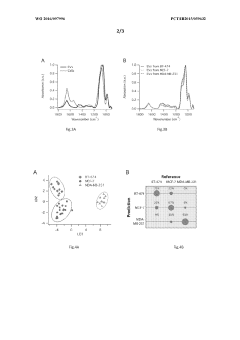
Use of fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis of extracellular vesicles isolated from body fluids for diagnosing, prognosing and monitoring pathophysiological states and method therfor
PatentWO2016097996A1
Innovation
- The use of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) to analyze extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from body fluids, combined with multivariate analysis, provides a non-invasive and label-free method for classifying EVs based on their molecular composition, enabling early diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of cancer and other proliferative diseases.
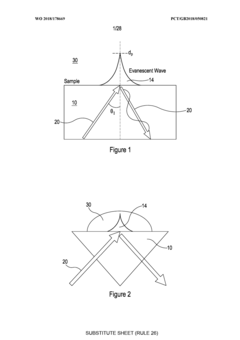
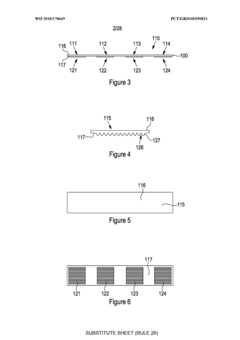
Infra-red spectroscopy system
PatentWO2018178669A2
Innovation
- A sample slide with multiple sample-receiving portions and integrated beam-receiving portions acting as internal reflection elements, allowing for multiple measurements without removing and replacing the slide, and the use of a disposable silicon slide to reduce costs and eliminate cleaning and drying requirements.
Standardization and Quality Control in FTIR Surface Analysis
Standardization and quality control represent critical components in the advancement of FTIR surface analysis methodologies. The inherent variability in sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data interpretation necessitates robust standardization protocols to ensure reproducibility and reliability across different laboratories and research environments.
Current standardization efforts in FTIR surface analysis face significant challenges due to the diverse nature of sample surfaces and the sensitivity of measurements to environmental factors. Industry standards such as ASTM E1252 and ISO 15472 provide general guidelines for FTIR analysis, but specialized protocols for surface-specific applications remain inconsistent across different sectors.
Quality control measures in FTIR surface analysis typically involve the use of reference materials with known spectral characteristics. These standards serve as benchmarks for instrument performance verification and method validation. However, the availability of certified reference materials specifically designed for surface analysis applications is limited, creating obstacles for comprehensive quality assurance programs.
Statistical process control methods are increasingly being integrated into FTIR surface analysis workflows. These approaches employ statistical tools to monitor measurement stability and detect deviations from established parameters. Techniques such as control charts, capability indices, and measurement system analysis (MSA) provide quantitative frameworks for assessing analytical performance and identifying sources of variability.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have emerged as valuable tools for validating standardization efforts. These collaborative exercises involve multiple laboratories performing identical analyses on the same samples, allowing for the assessment of method reproducibility and the identification of systematic biases. Recent studies have demonstrated that even with standardized protocols, interlaboratory variability in FTIR surface analysis can exceed 10% for certain applications.
Automation and digital standardization represent promising avenues for enhancing quality control in FTIR surface analysis. Machine learning algorithms can identify spectral artifacts, correct baseline inconsistencies, and flag anomalous results with minimal human intervention. Additionally, digital repositories of reference spectra facilitate more consistent interpretation of results across different research groups and analytical platforms.
The development of comprehensive standard operating procedures (SOPs) that address sample preparation, instrument setup, data acquisition, and spectral processing is essential for advancing standardization efforts. These SOPs must balance the need for methodological rigor with practical considerations of implementation across diverse research and industrial settings.
Current standardization efforts in FTIR surface analysis face significant challenges due to the diverse nature of sample surfaces and the sensitivity of measurements to environmental factors. Industry standards such as ASTM E1252 and ISO 15472 provide general guidelines for FTIR analysis, but specialized protocols for surface-specific applications remain inconsistent across different sectors.
Quality control measures in FTIR surface analysis typically involve the use of reference materials with known spectral characteristics. These standards serve as benchmarks for instrument performance verification and method validation. However, the availability of certified reference materials specifically designed for surface analysis applications is limited, creating obstacles for comprehensive quality assurance programs.
Statistical process control methods are increasingly being integrated into FTIR surface analysis workflows. These approaches employ statistical tools to monitor measurement stability and detect deviations from established parameters. Techniques such as control charts, capability indices, and measurement system analysis (MSA) provide quantitative frameworks for assessing analytical performance and identifying sources of variability.
Interlaboratory comparison studies have emerged as valuable tools for validating standardization efforts. These collaborative exercises involve multiple laboratories performing identical analyses on the same samples, allowing for the assessment of method reproducibility and the identification of systematic biases. Recent studies have demonstrated that even with standardized protocols, interlaboratory variability in FTIR surface analysis can exceed 10% for certain applications.
Automation and digital standardization represent promising avenues for enhancing quality control in FTIR surface analysis. Machine learning algorithms can identify spectral artifacts, correct baseline inconsistencies, and flag anomalous results with minimal human intervention. Additionally, digital repositories of reference spectra facilitate more consistent interpretation of results across different research groups and analytical platforms.
The development of comprehensive standard operating procedures (SOPs) that address sample preparation, instrument setup, data acquisition, and spectral processing is essential for advancing standardization efforts. These SOPs must balance the need for methodological rigor with practical considerations of implementation across diverse research and industrial settings.
Environmental Factors Affecting FTIR Surface Measurements
Environmental factors play a crucial role in the accuracy and reliability of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) surface analysis measurements. Ambient humidity represents one of the most significant challenges, as water vapor absorption bands can overlap with sample spectra in key regions, particularly around 3500-3200 cm⁻¹ and 1800-1600 cm⁻¹. These interferences can mask important functional group identifications and lead to misinterpretation of surface chemistry data.
Temperature fluctuations during measurement sessions introduce additional complications by affecting both the instrument stability and sample characteristics. Even minor temperature variations can cause thermal drift in optical components, resulting in baseline shifts and reduced spectral resolution. For temperature-sensitive materials, phase transitions or structural changes may occur during analysis, fundamentally altering the surface properties being measured.
Atmospheric contaminants present another significant challenge for precise FTIR surface analysis. Carbon dioxide absorption at approximately 2350 cm⁻¹ and various volatile organic compounds can contribute to background noise and create misleading spectral features. In industrial environments, airborne particulates may deposit on sample surfaces during preparation or analysis, introducing extraneous chemical signatures.
Light exposure conditions must be carefully controlled, particularly for photosensitive materials where UV or visible light exposure can trigger surface chemical reactions. Such photochemical alterations may significantly change the surface composition between sample preparation and measurement completion, leading to non-representative results.
Vibration interference from nearby equipment or building systems can degrade spectral quality by introducing noise and reducing the signal-to-noise ratio. This is particularly problematic for high-resolution measurements where subtle spectral features are critical for accurate interpretation. Modern FTIR systems incorporate vibration isolation mechanisms, but environmental vibrations can still impact measurement precision in suboptimal laboratory settings.
Sample handling protocols themselves introduce environmental variables, as exposure time to ambient conditions before and during analysis can significantly alter surface characteristics. Materials that readily adsorb atmospheric components or undergo oxidation require specialized handling procedures to maintain surface integrity throughout the analytical process.
Purge gas quality represents a final critical environmental factor, as impurities in nitrogen or argon purge systems can introduce contaminants directly onto sample surfaces or create background spectral artifacts. High-purity gases and properly maintained delivery systems are essential for minimizing these interferences in sensitive surface analysis applications.
Temperature fluctuations during measurement sessions introduce additional complications by affecting both the instrument stability and sample characteristics. Even minor temperature variations can cause thermal drift in optical components, resulting in baseline shifts and reduced spectral resolution. For temperature-sensitive materials, phase transitions or structural changes may occur during analysis, fundamentally altering the surface properties being measured.
Atmospheric contaminants present another significant challenge for precise FTIR surface analysis. Carbon dioxide absorption at approximately 2350 cm⁻¹ and various volatile organic compounds can contribute to background noise and create misleading spectral features. In industrial environments, airborne particulates may deposit on sample surfaces during preparation or analysis, introducing extraneous chemical signatures.
Light exposure conditions must be carefully controlled, particularly for photosensitive materials where UV or visible light exposure can trigger surface chemical reactions. Such photochemical alterations may significantly change the surface composition between sample preparation and measurement completion, leading to non-representative results.
Vibration interference from nearby equipment or building systems can degrade spectral quality by introducing noise and reducing the signal-to-noise ratio. This is particularly problematic for high-resolution measurements where subtle spectral features are critical for accurate interpretation. Modern FTIR systems incorporate vibration isolation mechanisms, but environmental vibrations can still impact measurement precision in suboptimal laboratory settings.
Sample handling protocols themselves introduce environmental variables, as exposure time to ambient conditions before and during analysis can significantly alter surface characteristics. Materials that readily adsorb atmospheric components or undergo oxidation require specialized handling procedures to maintain surface integrity throughout the analytical process.
Purge gas quality represents a final critical environmental factor, as impurities in nitrogen or argon purge systems can introduce contaminants directly onto sample surfaces or create background spectral artifacts. High-purity gases and properly maintained delivery systems are essential for minimizing these interferences in sensitive surface analysis applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!