Ethyl Propanoate as a Precursor in Polymer Synthesis
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
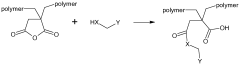
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. This ester has gained significant attention in the field of polymer synthesis due to its unique properties and potential applications. The compound's structure, consisting of an ethyl group and a propanoate group, provides it with versatile chemical reactivity, making it an attractive precursor for various polymer synthesis processes.
The development of ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative starting materials for sustainable polymer production. As environmental concerns grew, the need for bio-based and biodegradable polymers became more pressing, leading to increased interest in renewable precursors like ethyl propanoate.
Over the past two decades, the use of ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis has evolved from experimental studies to practical applications. Its low toxicity, biodegradability, and potential for renewable sourcing have made it an attractive option for green chemistry initiatives. The compound's ability to participate in various polymerization reactions, including condensation and ring-opening polymerizations, has expanded its utility across different polymer classes.
The primary objective of research on ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor is to develop novel, sustainable polymeric materials with enhanced properties. This includes the creation of biodegradable plastics, high-performance coatings, and specialized polymers for medical applications. Researchers aim to optimize reaction conditions, explore new catalytic systems, and investigate the structure-property relationships of the resulting polymers.
Another key goal is to establish efficient and scalable production methods for ethyl propanoate-based polymers. This involves developing cost-effective synthesis routes, improving reaction yields, and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, there is a focus on understanding the degradation mechanisms of these polymers to ensure their environmental compatibility and to design materials with controlled lifespans.
The research landscape surrounding ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis is characterized by interdisciplinary collaboration, combining expertise from organic chemistry, polymer science, materials engineering, and environmental studies. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing the complex challenges associated with developing sustainable polymeric materials that can compete with traditional petroleum-based plastics in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness.
The development of ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative starting materials for sustainable polymer production. As environmental concerns grew, the need for bio-based and biodegradable polymers became more pressing, leading to increased interest in renewable precursors like ethyl propanoate.
Over the past two decades, the use of ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis has evolved from experimental studies to practical applications. Its low toxicity, biodegradability, and potential for renewable sourcing have made it an attractive option for green chemistry initiatives. The compound's ability to participate in various polymerization reactions, including condensation and ring-opening polymerizations, has expanded its utility across different polymer classes.
The primary objective of research on ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor is to develop novel, sustainable polymeric materials with enhanced properties. This includes the creation of biodegradable plastics, high-performance coatings, and specialized polymers for medical applications. Researchers aim to optimize reaction conditions, explore new catalytic systems, and investigate the structure-property relationships of the resulting polymers.
Another key goal is to establish efficient and scalable production methods for ethyl propanoate-based polymers. This involves developing cost-effective synthesis routes, improving reaction yields, and minimizing waste generation. Additionally, there is a focus on understanding the degradation mechanisms of these polymers to ensure their environmental compatibility and to design materials with controlled lifespans.
The research landscape surrounding ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis is characterized by interdisciplinary collaboration, combining expertise from organic chemistry, polymer science, materials engineering, and environmental studies. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing the complex challenges associated with developing sustainable polymeric materials that can compete with traditional petroleum-based plastics in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Market Analysis for Polymer Precursors
The polymer precursor market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced materials across various industries. Ethyl propanoate, as a potential precursor in polymer synthesis, is gaining attention due to its versatile properties and potential applications. The global market for polymer precursors is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be in the high single digits over the next five years.
The demand for ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor is primarily fueled by the growing need for sustainable and high-performance materials in industries such as automotive, electronics, packaging, and construction. As manufacturers seek to improve the properties of their products while reducing environmental impact, the use of novel precursors like ethyl propanoate is becoming increasingly attractive.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Polymers derived from ethyl propanoate have the potential to offer enhanced mechanical properties while maintaining a low weight profile. This aligns well with the industry's shift towards electric vehicles and stricter environmental regulations.
The electronics industry is another key driver for the polymer precursor market. With the rapid advancement of technology and the miniaturization of devices, there is a growing need for materials that can withstand high temperatures and offer excellent electrical insulation properties. Ethyl propanoate-based polymers show promise in meeting these requirements, potentially opening up new opportunities in the production of advanced electronic components.
In the packaging industry, there is an increasing focus on sustainable and biodegradable materials. Ethyl propanoate, being derived from renewable resources, could play a crucial role in developing eco-friendly packaging solutions. This aligns with the global trend towards reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles.
The construction industry is also showing interest in advanced polymer materials for improved durability, energy efficiency, and fire resistance. Ethyl propanoate-based polymers could potentially address these needs, leading to new applications in building materials and insulation.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the polymer precursor market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing investments in research and development. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a focus on high-value applications and technological innovations.
The demand for ethyl propanoate as a polymer precursor is primarily fueled by the growing need for sustainable and high-performance materials in industries such as automotive, electronics, packaging, and construction. As manufacturers seek to improve the properties of their products while reducing environmental impact, the use of novel precursors like ethyl propanoate is becoming increasingly attractive.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Polymers derived from ethyl propanoate have the potential to offer enhanced mechanical properties while maintaining a low weight profile. This aligns well with the industry's shift towards electric vehicles and stricter environmental regulations.
The electronics industry is another key driver for the polymer precursor market. With the rapid advancement of technology and the miniaturization of devices, there is a growing need for materials that can withstand high temperatures and offer excellent electrical insulation properties. Ethyl propanoate-based polymers show promise in meeting these requirements, potentially opening up new opportunities in the production of advanced electronic components.
In the packaging industry, there is an increasing focus on sustainable and biodegradable materials. Ethyl propanoate, being derived from renewable resources, could play a crucial role in developing eco-friendly packaging solutions. This aligns with the global trend towards reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles.
The construction industry is also showing interest in advanced polymer materials for improved durability, energy efficiency, and fire resistance. Ethyl propanoate-based polymers could potentially address these needs, leading to new applications in building materials and insulation.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the polymer precursor market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing investments in research and development. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a focus on high-value applications and technological innovations.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Propanoate Utilization
Despite the promising potential of ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis, several challenges currently hinder its widespread utilization. One of the primary obstacles is the limited availability of high-purity ethyl propanoate at industrial scales. The production process often results in impurities that can negatively impact polymer quality and consistency, necessitating additional purification steps that increase costs and complexity.
Another significant challenge lies in the reactivity control of ethyl propanoate during polymerization processes. The ester group's susceptibility to hydrolysis under certain conditions can lead to unwanted side reactions, affecting the polymer's molecular weight distribution and overall properties. This reactivity issue requires careful optimization of reaction conditions and the development of specialized catalysts to ensure controlled polymerization.
The incorporation of ethyl propanoate into existing polymer production lines presents technical hurdles. Many current industrial setups are not optimized for handling this precursor, requiring significant modifications to equipment and processes. This adaptation can be both time-consuming and capital-intensive, deterring some manufacturers from adopting ethyl propanoate-based polymer synthesis methods.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the widespread use of ethyl propanoate. While it is considered less harmful than some alternative precursors, there are still concerns about its potential environmental impact, particularly in terms of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Addressing these concerns requires the development of more efficient capture and recycling systems, as well as improved life cycle assessments to quantify its environmental footprint accurately.
The economic viability of ethyl propanoate-based polymer synthesis remains a significant challenge. Current production costs for high-quality ethyl propanoate are relatively high compared to some traditional precursors. This cost differential makes it difficult for manufacturers to justify the switch, especially in price-sensitive markets. Overcoming this challenge requires advancements in production efficiency and economies of scale to reduce costs.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the full potential of ethyl propanoate in diverse polymer applications. While its use has shown promise in certain areas, such as biodegradable plastics, its potential in other high-performance polymer applications remains underexplored. This lack of comprehensive research and development across various polymer types limits its adoption and integration into new product lines.
Another significant challenge lies in the reactivity control of ethyl propanoate during polymerization processes. The ester group's susceptibility to hydrolysis under certain conditions can lead to unwanted side reactions, affecting the polymer's molecular weight distribution and overall properties. This reactivity issue requires careful optimization of reaction conditions and the development of specialized catalysts to ensure controlled polymerization.
The incorporation of ethyl propanoate into existing polymer production lines presents technical hurdles. Many current industrial setups are not optimized for handling this precursor, requiring significant modifications to equipment and processes. This adaptation can be both time-consuming and capital-intensive, deterring some manufacturers from adopting ethyl propanoate-based polymer synthesis methods.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the widespread use of ethyl propanoate. While it is considered less harmful than some alternative precursors, there are still concerns about its potential environmental impact, particularly in terms of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Addressing these concerns requires the development of more efficient capture and recycling systems, as well as improved life cycle assessments to quantify its environmental footprint accurately.
The economic viability of ethyl propanoate-based polymer synthesis remains a significant challenge. Current production costs for high-quality ethyl propanoate are relatively high compared to some traditional precursors. This cost differential makes it difficult for manufacturers to justify the switch, especially in price-sensitive markets. Overcoming this challenge requires advancements in production efficiency and economies of scale to reduce costs.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the full potential of ethyl propanoate in diverse polymer applications. While its use has shown promise in certain areas, such as biodegradable plastics, its potential in other high-performance polymer applications remains underexplored. This lack of comprehensive research and development across various polymer types limits its adoption and integration into new product lines.
Existing Ethyl Propanoate Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate
Various methods are employed to synthesize ethyl propanoate, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of propionyl chloride with ethanol, and catalytic processes using different catalysts. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce reaction time, and enhance product purity.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions between propionic acid and ethanol, as well as catalytic processes using different catalysts and reaction conditions. These methods aim to improve yield, selectivity, and efficiency in the production of ethyl propanoate.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, cosmetics, and food flavorings to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.
- Use in agricultural formulations: Ethyl propanoate is utilized in agricultural formulations, particularly as a solvent or carrier for pesticides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators. Its properties make it suitable for enhancing the effectiveness and stability of various agrochemical products.
- Industrial applications and processes: Ethyl propanoate finds applications in various industrial processes, including as a solvent in paints, coatings, and cleaning solutions. It is also used in the production of polymers and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals.
- Purification and quality control methods: Various techniques for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These methods include distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic analysis to remove impurities and maintain the desired purity levels for different applications.
02 Applications in fragrance and flavor industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is incorporated into various products such as perfumes, cosmetics, and food additives to impart a pleasant aroma and taste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial processes and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and other organic compounds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and separation techniques
Various purification and separation techniques are employed to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate. These include distillation, extraction, and chromatographic methods, which aim to remove impurities and achieve the desired product quality for different applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly production methods for ethyl propanoate, as well as improving its handling and storage safety. This includes the use of green solvents, catalysts, and processes to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polymer Synthesis Industry
The research on Ethyl Propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis is in a developing stage, with the market showing potential for growth. The technology's maturity is moderate, with key players like BASF Corp., Dow Global Technologies LLC, and Evonik Operations GmbH leading the way in research and development. These companies are leveraging their expertise in chemical synthesis and polymer science to explore the applications of Ethyl Propanoate in various industries. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies and specialized polymer manufacturers, indicating a growing interest in this field. As the demand for sustainable and high-performance polymers increases, the market for Ethyl Propanoate-based polymers is expected to expand, driving further innovation and competition among industry players.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed an innovative process for utilizing ethyl propanoate in the synthesis of high-performance polymers for industrial applications. Their method involves a controlled copolymerization reaction that incorporates ethyl propanoate alongside other monomers, resulting in polymers with enhanced chemical resistance and improved processing characteristics[7]. Evonik's research has particularly focused on the development of ethyl propanoate-based polymers for use in automotive and aerospace industries, where lightweight and durable materials are in high demand[9]. The company has also explored the potential of these polymers in 3D printing applications, demonstrating their ability to produce complex structures with excellent mechanical properties[11].
Strengths: High-performance materials, diverse industrial applications. Weaknesses: Potentially higher raw material costs, limited availability of ethyl propanoate at industrial scales.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel approach for using ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis, focusing on sustainable and eco-friendly processes. Their method involves a catalytic transesterification reaction to incorporate ethyl propanoate into polymer chains, resulting in biodegradable polyesters with improved thermal and mechanical properties[1]. The company has also explored the use of ethyl propanoate in the production of high-performance coatings and adhesives, leveraging its low toxicity and good solvent properties[3]. BASF's research has shown that polymers synthesized using ethyl propanoate as a precursor exhibit enhanced flexibility and durability compared to conventional alternatives[5].
Strengths: Sustainable process, improved polymer properties, versatile applications. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, limited scalability for some applications.
Innovative Applications in Polymer Chemistry
Polymer, process and composition
PatentWO2013113933A1
Innovation
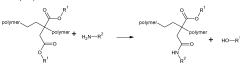
- The method involves polymerizing itaconic anhydride monomers to form itaconate polymers, which are then post-modified by reacting anhydride groups with nucleophiles to introduce mono-functional itaconate groups, enabling the creation of polymers with desirable properties such as high Tg values.
Process of producing a supported mixed catalyst system and polyolefins therefrom
PatentInactiveUS20040132933A1
Innovation
- A mixed catalyst system is developed by combining a High Melt Flow Rate (MFR) cyclic bridged metallocene with a Low MFR bridged metallocene, supported on an inorganic oxide, using a specific process involving activators and diluents like mineral or silicon oil to expand the range of bimodal polyethylene properties.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of using ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis is a crucial aspect to consider in the development and implementation of this technology. The production and use of ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis can have both positive and negative effects on the environment, which need to be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during the synthesis process. Ethyl propanoate is a volatile ester that can contribute to air pollution if not properly contained and managed. This may lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. To mitigate these risks, proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies must be implemented in production facilities.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact that requires attention. The synthesis process may generate wastewater containing residual ethyl propanoate or other chemical byproducts. If not properly treated, this wastewater could contaminate local water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Implementing effective wastewater treatment systems and adhering to strict disposal regulations are essential to minimize this risk.
On the positive side, the use of ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis may offer some environmental benefits compared to traditional methods. For instance, it may enable the production of polymers with improved biodegradability or recyclability, potentially reducing long-term environmental impacts associated with plastic waste. Additionally, if the synthesis process is optimized for efficiency, it could lead to reduced energy consumption and lower overall carbon footprint compared to conventional polymer production methods.
The sourcing of raw materials for ethyl propanoate production is another important consideration. If derived from renewable resources, such as biomass or agricultural waste, it could contribute to a more sustainable supply chain. However, this must be balanced against potential land-use changes or competition with food crops if large-scale production is required.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are crucial for comprehensively evaluating the environmental impacts of using ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis. These assessments should consider all stages of the product life cycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. LCA results can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable production processes.
Regulatory compliance is a key aspect of environmental impact assessment. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations governing chemical production and use. This includes obtaining necessary permits, conducting regular environmental monitoring, and reporting emissions and waste management practices to relevant authorities.
In conclusion, while the use of ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis shows promise for innovative polymer development, careful consideration of its environmental impacts is essential. Balancing the potential benefits with the risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies will be crucial for the sustainable development and adoption of this technology in the polymer industry.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during the synthesis process. Ethyl propanoate is a volatile ester that can contribute to air pollution if not properly contained and managed. This may lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, which can have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems. To mitigate these risks, proper ventilation systems and emission control technologies must be implemented in production facilities.
Water pollution is another potential environmental impact that requires attention. The synthesis process may generate wastewater containing residual ethyl propanoate or other chemical byproducts. If not properly treated, this wastewater could contaminate local water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Implementing effective wastewater treatment systems and adhering to strict disposal regulations are essential to minimize this risk.
On the positive side, the use of ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis may offer some environmental benefits compared to traditional methods. For instance, it may enable the production of polymers with improved biodegradability or recyclability, potentially reducing long-term environmental impacts associated with plastic waste. Additionally, if the synthesis process is optimized for efficiency, it could lead to reduced energy consumption and lower overall carbon footprint compared to conventional polymer production methods.
The sourcing of raw materials for ethyl propanoate production is another important consideration. If derived from renewable resources, such as biomass or agricultural waste, it could contribute to a more sustainable supply chain. However, this must be balanced against potential land-use changes or competition with food crops if large-scale production is required.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are crucial for comprehensively evaluating the environmental impacts of using ethyl propanoate in polymer synthesis. These assessments should consider all stages of the product life cycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal or recycling. LCA results can help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable production processes.
Regulatory compliance is a key aspect of environmental impact assessment. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations governing chemical production and use. This includes obtaining necessary permits, conducting regular environmental monitoring, and reporting emissions and waste management practices to relevant authorities.
In conclusion, while the use of ethyl propanoate as a precursor in polymer synthesis shows promise for innovative polymer development, careful consideration of its environmental impacts is essential. Balancing the potential benefits with the risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies will be crucial for the sustainable development and adoption of this technology in the polymer industry.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Precursors
The regulatory framework for chemical precursors in polymer synthesis, particularly for ethyl propanoate, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international organizations have established various regulations to control the production, distribution, and use of chemical precursors due to their potential dual-use nature in both legitimate industrial applications and illicit drug manufacturing.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) maintains a list of controlled substance precursors, which includes chemicals that can be used in the synthesis of controlled substances. While ethyl propanoate is not currently listed as a controlled substance precursor, its use in polymer synthesis is subject to general chemical safety regulations enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals, including precursors used in polymer synthesis. Under REACH, ethyl propanoate must be registered if manufactured or imported in quantities of one tonne or more per year per company.
Internationally, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has established guidelines for the control of precursor chemicals under the 1988 United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. While ethyl propanoate is not specifically listed, the convention provides a framework for monitoring and controlling chemicals that could be diverted for illicit purposes.
In the context of polymer synthesis research, laboratories and industrial facilities must adhere to strict safety protocols and reporting requirements when handling chemical precursors. This includes maintaining detailed records of chemical inventories, implementing proper storage and disposal procedures, and ensuring that personnel are adequately trained in handling these materials.
Many countries have implemented export control regulations that may affect the international trade of chemical precursors used in polymer synthesis. Researchers and manufacturers must be aware of these regulations when sourcing or shipping materials across borders, as violations can result in severe penalties.
As the field of polymer synthesis advances, regulatory bodies continue to assess and update their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new chemical compounds. Researchers working with ethyl propanoate and similar precursors must stay informed about changes in regulations and ensure compliance with all applicable laws and guidelines to maintain the integrity of their research and avoid potential legal issues.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) maintains a list of controlled substance precursors, which includes chemicals that can be used in the synthesis of controlled substances. While ethyl propanoate is not currently listed as a controlled substance precursor, its use in polymer synthesis is subject to general chemical safety regulations enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
The European Union has implemented the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals, including precursors used in polymer synthesis. Under REACH, ethyl propanoate must be registered if manufactured or imported in quantities of one tonne or more per year per company.
Internationally, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has established guidelines for the control of precursor chemicals under the 1988 United Nations Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. While ethyl propanoate is not specifically listed, the convention provides a framework for monitoring and controlling chemicals that could be diverted for illicit purposes.
In the context of polymer synthesis research, laboratories and industrial facilities must adhere to strict safety protocols and reporting requirements when handling chemical precursors. This includes maintaining detailed records of chemical inventories, implementing proper storage and disposal procedures, and ensuring that personnel are adequately trained in handling these materials.
Many countries have implemented export control regulations that may affect the international trade of chemical precursors used in polymer synthesis. Researchers and manufacturers must be aware of these regulations when sourcing or shipping materials across borders, as violations can result in severe penalties.
As the field of polymer synthesis advances, regulatory bodies continue to assess and update their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new chemical compounds. Researchers working with ethyl propanoate and similar precursors must stay informed about changes in regulations and ensure compliance with all applicable laws and guidelines to maintain the integrity of their research and avoid potential legal issues.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!