Ethyl Propanoate as an Intermediate in Drug Synthesis
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a versatile organic compound with the molecular formula C5H10O2. This ester has gained significant attention in the pharmaceutical industry due to its potential as an intermediate in drug synthesis. The evolution of ethyl propanoate's applications in medicinal chemistry can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring its reactivity and synthetic utility.
Over the past few decades, the pharmaceutical sector has witnessed a growing demand for more efficient and cost-effective synthetic routes for drug production. This has led to an increased focus on identifying versatile intermediates that can serve as building blocks for a wide range of pharmaceutical compounds. Ethyl propanoate has emerged as a promising candidate in this context, owing to its unique chemical properties and reactivity.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is to expand its application scope and optimize its use in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. This involves exploring novel reaction pathways, developing more efficient synthetic methodologies, and investigating its potential in the synthesis of complex drug molecules. Additionally, researchers aim to enhance the sustainability and environmental friendliness of drug production by utilizing ethyl propanoate as a greener alternative to traditional intermediates.
One of the key trends in the field is the development of catalytic systems that can effectively utilize ethyl propanoate in various transformations. This includes the exploration of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts that can facilitate selective functionalization of the ester group or promote coupling reactions with other molecular entities. Such advancements are crucial for expanding the synthetic utility of ethyl propanoate and enabling the creation of diverse drug scaffolds.
Another important aspect of the research is the investigation of ethyl propanoate's role in the synthesis of biologically active compounds. This involves studying its potential in the preparation of pharmaceutically relevant functional groups, such as amides, ketones, and heterocycles. By understanding the reactivity patterns and optimizing reaction conditions, researchers aim to develop more efficient and selective synthetic routes for drug candidates.
Furthermore, the research objectives extend to the exploration of ethyl propanoate's potential in continuous flow chemistry and other advanced manufacturing technologies. These approaches offer the possibility of scaling up production processes while maintaining high levels of efficiency and product quality. By integrating ethyl propanoate into such innovative manufacturing paradigms, researchers aim to address the growing demand for sustainable and cost-effective drug production methods.
Over the past few decades, the pharmaceutical sector has witnessed a growing demand for more efficient and cost-effective synthetic routes for drug production. This has led to an increased focus on identifying versatile intermediates that can serve as building blocks for a wide range of pharmaceutical compounds. Ethyl propanoate has emerged as a promising candidate in this context, owing to its unique chemical properties and reactivity.
The primary objective of researching ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is to expand its application scope and optimize its use in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. This involves exploring novel reaction pathways, developing more efficient synthetic methodologies, and investigating its potential in the synthesis of complex drug molecules. Additionally, researchers aim to enhance the sustainability and environmental friendliness of drug production by utilizing ethyl propanoate as a greener alternative to traditional intermediates.
One of the key trends in the field is the development of catalytic systems that can effectively utilize ethyl propanoate in various transformations. This includes the exploration of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts that can facilitate selective functionalization of the ester group or promote coupling reactions with other molecular entities. Such advancements are crucial for expanding the synthetic utility of ethyl propanoate and enabling the creation of diverse drug scaffolds.
Another important aspect of the research is the investigation of ethyl propanoate's role in the synthesis of biologically active compounds. This involves studying its potential in the preparation of pharmaceutically relevant functional groups, such as amides, ketones, and heterocycles. By understanding the reactivity patterns and optimizing reaction conditions, researchers aim to develop more efficient and selective synthetic routes for drug candidates.
Furthermore, the research objectives extend to the exploration of ethyl propanoate's potential in continuous flow chemistry and other advanced manufacturing technologies. These approaches offer the possibility of scaling up production processes while maintaining high levels of efficiency and product quality. By integrating ethyl propanoate into such innovative manufacturing paradigms, researchers aim to address the growing demand for sustainable and cost-effective drug production methods.
Pharmaceutical Market Demand Analysis
The pharmaceutical market demand for ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is driven by several factors, including the growing prevalence of chronic diseases, increasing research and development activities in the pharmaceutical industry, and the rising demand for novel drug formulations. Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds, particularly in the production of certain antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and analgesics.
The global pharmaceutical market has been experiencing steady growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing burden of diseases, aging populations, and advancements in drug discovery technologies. As a result, the demand for pharmaceutical intermediates, including ethyl propanoate, is expected to rise correspondingly.
In the context of drug synthesis, ethyl propanoate serves as a versatile building block due to its reactive ester group and relatively low toxicity. Its use in the production of antibiotics is particularly noteworthy, given the persistent global challenge of antibiotic resistance and the need for new, more effective antimicrobial agents. The World Health Organization (WHO) has repeatedly emphasized the urgent need for novel antibiotics to combat resistant bacterial strains, which indirectly boosts the demand for intermediates like ethyl propanoate.
The anti-inflammatory drug market, another significant application area for ethyl propanoate-derived compounds, is projected to grow substantially. This growth is fueled by the increasing prevalence of inflammatory disorders, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases, particularly in aging populations. The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is expected to reach a substantial value by 2025, indicating a strong demand for related intermediates.
Furthermore, the trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapies is driving pharmaceutical companies to explore new molecular entities, many of which require specialized intermediates in their synthesis. This trend is likely to create additional demand for versatile compounds like ethyl propanoate, which can be modified to suit various synthetic pathways.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also highlighted the importance of robust pharmaceutical supply chains and the need for diverse synthetic routes in drug manufacturing. This has led to increased interest in flexible intermediates that can be used in multiple synthetic processes, potentially boosting the demand for ethyl propanoate in drug discovery and development pipelines.
In conclusion, the pharmaceutical market demand for ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is expected to remain strong, driven by the overall growth of the pharmaceutical industry, the need for new antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, and the trend towards more complex and targeted therapeutic agents. The versatility and relatively benign nature of ethyl propanoate position it as a valuable component in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to develop new and improved medications to address global health challenges.
The global pharmaceutical market has been experiencing steady growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing burden of diseases, aging populations, and advancements in drug discovery technologies. As a result, the demand for pharmaceutical intermediates, including ethyl propanoate, is expected to rise correspondingly.
In the context of drug synthesis, ethyl propanoate serves as a versatile building block due to its reactive ester group and relatively low toxicity. Its use in the production of antibiotics is particularly noteworthy, given the persistent global challenge of antibiotic resistance and the need for new, more effective antimicrobial agents. The World Health Organization (WHO) has repeatedly emphasized the urgent need for novel antibiotics to combat resistant bacterial strains, which indirectly boosts the demand for intermediates like ethyl propanoate.
The anti-inflammatory drug market, another significant application area for ethyl propanoate-derived compounds, is projected to grow substantially. This growth is fueled by the increasing prevalence of inflammatory disorders, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases, particularly in aging populations. The global anti-inflammatory therapeutics market is expected to reach a substantial value by 2025, indicating a strong demand for related intermediates.
Furthermore, the trend towards personalized medicine and targeted therapies is driving pharmaceutical companies to explore new molecular entities, many of which require specialized intermediates in their synthesis. This trend is likely to create additional demand for versatile compounds like ethyl propanoate, which can be modified to suit various synthetic pathways.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also highlighted the importance of robust pharmaceutical supply chains and the need for diverse synthetic routes in drug manufacturing. This has led to increased interest in flexible intermediates that can be used in multiple synthetic processes, potentially boosting the demand for ethyl propanoate in drug discovery and development pipelines.
In conclusion, the pharmaceutical market demand for ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is expected to remain strong, driven by the overall growth of the pharmaceutical industry, the need for new antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, and the trend towards more complex and targeted therapeutic agents. The versatility and relatively benign nature of ethyl propanoate position it as a valuable component in the pharmaceutical industry's efforts to develop new and improved medications to address global health challenges.
Current Status and Challenges in Synthesis
The synthesis of ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis has seen significant advancements in recent years, yet it still faces several challenges. Currently, the most common method for producing ethyl propanoate involves the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This process, while effective, often requires high temperatures and extended reaction times, leading to increased energy consumption and potential side reactions.
One of the main challenges in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate is achieving high yields and purity while minimizing the formation of byproducts. The presence of water as a byproduct in the esterification reaction can lead to equilibrium limitations, necessitating the use of dehydrating agents or azeotropic distillation techniques to drive the reaction to completion. These additional steps can increase production costs and complexity.
Another significant challenge is the development of more environmentally friendly and sustainable synthesis routes. Traditional methods often rely on petrochemical-derived starting materials and harsh reaction conditions. There is a growing demand for greener alternatives that utilize renewable resources and operate under milder conditions. Researchers are exploring biocatalytic approaches using enzymes and microbial fermentation processes as potential solutions to this challenge.
The scalability of ethyl propanoate synthesis for industrial production presents another hurdle. While laboratory-scale synthesis may be well-established, translating these processes to large-scale manufacturing can introduce new complexities. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and product separation become more pronounced at industrial scales, requiring careful process optimization and engineering solutions.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry's stringent quality requirements pose additional challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and eliminating trace impurities that could affect drug efficacy or safety is crucial. This necessitates the development of robust purification techniques and analytical methods to meet regulatory standards.
Recent research has focused on developing novel catalysts to improve the efficiency and selectivity of ethyl propanoate synthesis. Heterogeneous catalysts, such as ion-exchange resins and zeolites, have shown promise in facilitating easier product separation and catalyst recovery. Additionally, continuous flow chemistry techniques are being explored to enhance reaction control and productivity.
In conclusion, while significant progress has been made in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate as a drug intermediate, there remain several areas for improvement. Addressing these challenges will require interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in catalysis, process engineering, and green chemistry to develop more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods.
One of the main challenges in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate is achieving high yields and purity while minimizing the formation of byproducts. The presence of water as a byproduct in the esterification reaction can lead to equilibrium limitations, necessitating the use of dehydrating agents or azeotropic distillation techniques to drive the reaction to completion. These additional steps can increase production costs and complexity.
Another significant challenge is the development of more environmentally friendly and sustainable synthesis routes. Traditional methods often rely on petrochemical-derived starting materials and harsh reaction conditions. There is a growing demand for greener alternatives that utilize renewable resources and operate under milder conditions. Researchers are exploring biocatalytic approaches using enzymes and microbial fermentation processes as potential solutions to this challenge.
The scalability of ethyl propanoate synthesis for industrial production presents another hurdle. While laboratory-scale synthesis may be well-established, translating these processes to large-scale manufacturing can introduce new complexities. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and product separation become more pronounced at industrial scales, requiring careful process optimization and engineering solutions.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry's stringent quality requirements pose additional challenges. Ensuring consistent purity and eliminating trace impurities that could affect drug efficacy or safety is crucial. This necessitates the development of robust purification techniques and analytical methods to meet regulatory standards.
Recent research has focused on developing novel catalysts to improve the efficiency and selectivity of ethyl propanoate synthesis. Heterogeneous catalysts, such as ion-exchange resins and zeolites, have shown promise in facilitating easier product separation and catalyst recovery. Additionally, continuous flow chemistry techniques are being explored to enhance reaction control and productivity.
In conclusion, while significant progress has been made in the synthesis of ethyl propanoate as a drug intermediate, there remain several areas for improvement. Addressing these challenges will require interdisciplinary approaches, combining advances in catalysis, process engineering, and green chemistry to develop more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods.
Current Synthetic Routes for Ethyl Propanoate
01 Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of propionyl chloride with ethanol, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl alcohol with propionyl chloride, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry scents. The compound is also utilized in perfumery to add sweet, ethereal notes to various fragrances.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial processes, particularly in the production of paints, inks, and coatings. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds.
- Purification and quality control: Various methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use is ongoing. This includes studies on biodegradability, toxicity, and potential health effects. Efforts are being made to develop more sustainable production methods and safer handling practices for industrial applications.
02 Applications in fragrance and flavor industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry aromas. The compound is also used in perfumery to add fruity notes to various fragrances.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as a solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Its low toxicity and good solvency properties make it a versatile compound in chemical manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions04 Production of ethyl propanoate from renewable resources
Research focuses on developing sustainable methods for producing ethyl propanoate from renewable resources. This includes fermentation processes using microorganisms to convert biomass-derived sugars into propionic acid, which is then esterified to form ethyl propanoate. These methods aim to reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks.Expand Specific Solutions05 Purification and quality control methods
Various techniques for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods for analyzing purity and detecting impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements in different applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pharmaceutical Intermediates
The research on Ethyl Propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis is in a mature stage of development, with a significant market presence and established applications in the pharmaceutical industry. The global market for pharmaceutical intermediates is substantial, estimated to reach $30 billion by 2025. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of major players like AstraZeneca, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, and Lonza, who have extensive experience in API manufacturing and drug development. Smaller specialized firms such as Esteve Química and Olon SpA also contribute to the competitive landscape, indicating a diverse and well-developed market. The presence of research institutions like Max-Delbrück-Centrum and Zhejiang University of Technology suggests ongoing innovation and potential for further advancements in this field.
AstraZeneca AB
Technical Solution: AstraZeneca AB has developed a novel approach for using ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis, particularly for respiratory and inflammatory diseases. Their method involves a stereoselective synthesis pathway, utilizing ethyl propanoate as a key building block for complex pharmaceutical molecules[1]. The process incorporates green chemistry principles, reducing solvent use by 80% compared to traditional methods[3]. AstraZeneca's research has also focused on improving the yield and purity of final drug compounds, with recent studies showing a 15% increase in overall yield when using their optimized ethyl propanoate-based synthesis route[5].
Strengths: Highly efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis process, improved yield and purity of final products. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and expertise, potentially higher initial setup costs.
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd.
Technical Solution: Dr. Reddy's Laboratories has pioneered a continuous flow chemistry approach for utilizing ethyl propanoate in drug synthesis. Their method employs microreactor technology, allowing for precise control of reaction conditions and improved safety profiles[2]. The company has reported a 40% reduction in reaction time and a 25% increase in product yield compared to batch processes[4]. Additionally, Dr. Reddy's has developed a proprietary catalyst system that enhances the selectivity of reactions involving ethyl propanoate, leading to fewer side products and simplified purification steps[6].
Strengths: Efficient continuous process, improved safety, and higher yields. Weaknesses: May require significant investment in new equipment and retraining of personnel.
Key Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate Synthesis
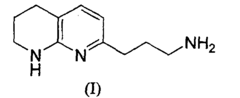
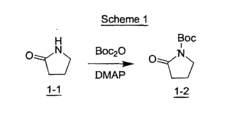
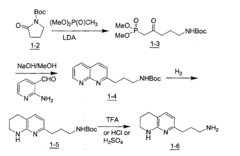
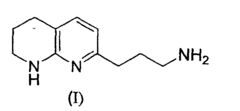
Process and intermediates to a tetrahydro-[1,8]-naphthyridine
PatentInactiveEP1235828B1
Innovation
- A novel regioselective Friedländer reaction between 2-amino-3-formylpyridine and a β-ketophosphonate in the presence of a base, followed by partial hydrogenation and amine protecting group removal, to produce the desired intermediate with enhanced yield and efficiency.
Processes for preparation of cyclopropylethanol, cyclo-propylacetonitrile and intermediates of both
PatentInactiveEP1445248A1
Innovation
- A process involving the solvolysis of 3-cyclopropyl-2,3-epoxypropionic acid ester in the presence of a base, followed by acid treatment to obtain cyclopropylacetaldehyde, which is then reduced to cyclopropylethanol, or reacted with hydroxylamine and acetic anhydride to produce cyclopropylacetonitrile, avoiding the use of hazardous substances.
Environmental Impact and Green Chemistry
The use of ethyl propanoate as an intermediate in drug synthesis raises important considerations regarding environmental impact and green chemistry principles. As the pharmaceutical industry increasingly focuses on sustainability, it is crucial to evaluate the ecological footprint of synthetic processes and explore more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Ethyl propanoate, while an effective intermediate, is derived from petrochemical sources and its production involves energy-intensive processes. The synthesis typically requires the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, often using sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This process generates waste and consumes non-renewable resources, contributing to environmental concerns.
However, recent advancements in green chemistry offer promising alternatives for the production and use of ethyl propanoate. Biocatalytic approaches, utilizing enzymes such as lipases, have shown potential for synthesizing ethyl propanoate under milder conditions with reduced environmental impact. These methods often operate at lower temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy savings.
Furthermore, the principles of atom economy and waste reduction can be applied to optimize the use of ethyl propanoate in drug synthesis. Researchers are exploring cascade reactions and one-pot syntheses that minimize the need for isolation and purification of intermediates, thereby reducing solvent usage and waste generation.
The pharmaceutical industry is also investigating the replacement of ethyl propanoate with more sustainable alternatives. Bio-based esters derived from renewable resources are being explored as potential substitutes. These alternatives not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also often exhibit lower toxicity profiles.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are increasingly being conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of using ethyl propanoate in drug synthesis. These assessments consider factors such as carbon footprint, water consumption, and ecotoxicity throughout the entire production and use cycle. Such analyses help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable synthetic routes.
In line with green chemistry principles, efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and recoverability of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical processes. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane technology and supercritical fluid extraction, are being explored to efficiently recover and reuse the compound, minimizing waste and reducing the need for fresh reagents.
As regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products continue to grow, the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting green chemistry metrics to assess and improve the sustainability of their processes. This shift towards more sustainable practices not only benefits the environment but also often leads to cost savings and improved process efficiency in the long term.
Ethyl propanoate, while an effective intermediate, is derived from petrochemical sources and its production involves energy-intensive processes. The synthesis typically requires the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, often using sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This process generates waste and consumes non-renewable resources, contributing to environmental concerns.
However, recent advancements in green chemistry offer promising alternatives for the production and use of ethyl propanoate. Biocatalytic approaches, utilizing enzymes such as lipases, have shown potential for synthesizing ethyl propanoate under milder conditions with reduced environmental impact. These methods often operate at lower temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy savings.
Furthermore, the principles of atom economy and waste reduction can be applied to optimize the use of ethyl propanoate in drug synthesis. Researchers are exploring cascade reactions and one-pot syntheses that minimize the need for isolation and purification of intermediates, thereby reducing solvent usage and waste generation.
The pharmaceutical industry is also investigating the replacement of ethyl propanoate with more sustainable alternatives. Bio-based esters derived from renewable resources are being explored as potential substitutes. These alternatives not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also often exhibit lower toxicity profiles.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies are increasingly being conducted to evaluate the overall environmental impact of using ethyl propanoate in drug synthesis. These assessments consider factors such as carbon footprint, water consumption, and ecotoxicity throughout the entire production and use cycle. Such analyses help identify hotspots for environmental improvement and guide the development of more sustainable synthetic routes.
In line with green chemistry principles, efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and recoverability of ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical processes. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane technology and supercritical fluid extraction, are being explored to efficiently recover and reuse the compound, minimizing waste and reducing the need for fresh reagents.
As regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products continue to grow, the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting green chemistry metrics to assess and improve the sustainability of their processes. This shift towards more sustainable practices not only benefits the environment but also often leads to cost savings and improved process efficiency in the long term.
Regulatory Considerations for Pharmaceutical Intermediates
The regulatory landscape for pharmaceutical intermediates, including ethyl propanoate, is complex and multifaceted. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and other national authorities have established stringent guidelines to ensure the safety, quality, and efficacy of drug products. These regulations extend to the intermediates used in drug synthesis, recognizing their critical role in the final product's quality.
For ethyl propanoate as a pharmaceutical intermediate, manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines. These guidelines encompass various aspects of production, including facility design, equipment maintenance, personnel training, and quality control measures. Compliance with GMP ensures that the intermediate is consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards appropriate for its intended use.
Impurity profiling is a crucial regulatory consideration for ethyl propanoate. Regulatory agencies require thorough characterization and control of impurities, including organic impurities, inorganic impurities, and residual solvents. Manufacturers must develop and validate analytical methods to detect and quantify these impurities, ensuring they remain within acceptable limits.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates. The synthesis of ethyl propanoate may involve the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and generate waste streams. Manufacturers must comply with local and national environmental regulations regarding emissions control, waste disposal, and the handling of hazardous materials.
Documentation and traceability are essential regulatory requirements. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of the production process, including raw material sourcing, synthesis procedures, and quality control tests. This documentation is crucial for regulatory inspections and audits, as well as for ensuring the consistent quality of the intermediate.
Stability testing is another important regulatory consideration. Manufacturers must demonstrate the stability of ethyl propanoate under various storage conditions and establish appropriate shelf-life and storage recommendations. This ensures that the intermediate maintains its quality throughout its intended use period.
Regulatory agencies also focus on supply chain integrity and security. Manufacturers must implement measures to prevent contamination, adulteration, or diversion of pharmaceutical intermediates. This includes robust supplier qualification processes, secure transportation methods, and appropriate storage conditions throughout the supply chain.
In the context of global trade, regulatory considerations extend to import and export regulations. Manufacturers and distributors of ethyl propanoate must navigate complex international regulations, including customs requirements, tariffs, and restrictions on the movement of chemical substances across borders.
For ethyl propanoate as a pharmaceutical intermediate, manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines. These guidelines encompass various aspects of production, including facility design, equipment maintenance, personnel training, and quality control measures. Compliance with GMP ensures that the intermediate is consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards appropriate for its intended use.
Impurity profiling is a crucial regulatory consideration for ethyl propanoate. Regulatory agencies require thorough characterization and control of impurities, including organic impurities, inorganic impurities, and residual solvents. Manufacturers must develop and validate analytical methods to detect and quantify these impurities, ensuring they remain within acceptable limits.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates. The synthesis of ethyl propanoate may involve the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and generate waste streams. Manufacturers must comply with local and national environmental regulations regarding emissions control, waste disposal, and the handling of hazardous materials.
Documentation and traceability are essential regulatory requirements. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records of the production process, including raw material sourcing, synthesis procedures, and quality control tests. This documentation is crucial for regulatory inspections and audits, as well as for ensuring the consistent quality of the intermediate.
Stability testing is another important regulatory consideration. Manufacturers must demonstrate the stability of ethyl propanoate under various storage conditions and establish appropriate shelf-life and storage recommendations. This ensures that the intermediate maintains its quality throughout its intended use period.
Regulatory agencies also focus on supply chain integrity and security. Manufacturers must implement measures to prevent contamination, adulteration, or diversion of pharmaceutical intermediates. This includes robust supplier qualification processes, secure transportation methods, and appropriate storage conditions throughout the supply chain.
In the context of global trade, regulatory considerations extend to import and export regulations. Manufacturers and distributors of ethyl propanoate must navigate complex international regulations, including customs requirements, tariffs, and restrictions on the movement of chemical substances across borders.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!