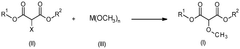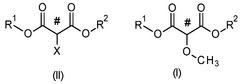Nucleophilic Substitutions Involving Ethyl Propanoate in Organic Synthesis
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nucleophilic Substitution Background and Objectives
Nucleophilic substitution reactions have been a cornerstone of organic synthesis for over a century, playing a crucial role in the formation of carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds. These reactions involve the displacement of a leaving group by a nucleophile, resulting in the creation of new chemical bonds. In the context of ethyl propanoate, a common ester used in various synthetic processes, nucleophilic substitutions offer a versatile approach to modifying its structure and creating more complex molecules.
The study of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and materials science industries. This research aims to explore novel synthetic pathways, improve reaction efficiencies, and develop more environmentally friendly processes. By focusing on ethyl propanoate as a model substrate, researchers can gain insights into the reactivity of esters and develop strategies applicable to a broader range of compounds.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to elucidate the mechanistic details of nucleophilic substitutions on ethyl propanoate. Understanding the reaction kinetics, stereochemistry, and factors influencing the reaction outcome is crucial for optimizing synthetic protocols and predicting product distributions. Additionally, researchers aim to explore the scope of nucleophiles compatible with ethyl propanoate, ranging from carbon-based nucleophiles to heteroatom-centered ones, to expand the toolkit of synthetic organic chemists.
Another important goal is to develop more sustainable and efficient methodologies for nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate. This includes investigating alternative solvents, catalysts, and reaction conditions that minimize waste generation and energy consumption. The use of green chemistry principles in these reactions aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability in the chemical industry.
Furthermore, the research seeks to exploit the unique reactivity of ethyl propanoate in nucleophilic substitutions to access novel molecular scaffolds and functional group transformations. This could lead to the discovery of new synthetic routes to valuable target molecules, such as pharmaceuticals or advanced materials. By pushing the boundaries of what is possible with ethyl propanoate-based chemistry, researchers hope to unlock new possibilities in organic synthesis and expand the repertoire of synthetic methodologies available to chemists.
In conclusion, the study of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis represents a dynamic and evolving field with significant potential for innovation. By addressing the challenges and opportunities in this area, researchers aim to contribute to the advancement of synthetic organic chemistry and its applications across various industries.
The study of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and materials science industries. This research aims to explore novel synthetic pathways, improve reaction efficiencies, and develop more environmentally friendly processes. By focusing on ethyl propanoate as a model substrate, researchers can gain insights into the reactivity of esters and develop strategies applicable to a broader range of compounds.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to elucidate the mechanistic details of nucleophilic substitutions on ethyl propanoate. Understanding the reaction kinetics, stereochemistry, and factors influencing the reaction outcome is crucial for optimizing synthetic protocols and predicting product distributions. Additionally, researchers aim to explore the scope of nucleophiles compatible with ethyl propanoate, ranging from carbon-based nucleophiles to heteroatom-centered ones, to expand the toolkit of synthetic organic chemists.
Another important goal is to develop more sustainable and efficient methodologies for nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate. This includes investigating alternative solvents, catalysts, and reaction conditions that minimize waste generation and energy consumption. The use of green chemistry principles in these reactions aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability in the chemical industry.
Furthermore, the research seeks to exploit the unique reactivity of ethyl propanoate in nucleophilic substitutions to access novel molecular scaffolds and functional group transformations. This could lead to the discovery of new synthetic routes to valuable target molecules, such as pharmaceuticals or advanced materials. By pushing the boundaries of what is possible with ethyl propanoate-based chemistry, researchers hope to unlock new possibilities in organic synthesis and expand the repertoire of synthetic methodologies available to chemists.
In conclusion, the study of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis represents a dynamic and evolving field with significant potential for innovation. By addressing the challenges and opportunities in this area, researchers aim to contribute to the advancement of synthetic organic chemistry and its applications across various industries.
Market Applications of Ethyl Propanoate Reactions
Ethyl propanoate, a versatile ester compound, finds extensive applications across various industries due to its unique chemical properties and reactivity in nucleophilic substitution reactions. In the food and beverage sector, ethyl propanoate serves as a crucial flavoring agent, imparting a fruity aroma reminiscent of pineapples and pears. This characteristic makes it a popular choice in the production of artificial fruit flavors, confectioneries, and beverages.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also benefits significantly from ethyl propanoate reactions. The compound is utilized in the formulation of fragrances and perfumes, contributing to the creation of complex scent profiles. Its ability to undergo nucleophilic substitutions allows for the synthesis of novel fragrance molecules, expanding the palette of scents available to perfumers and cosmetic chemists.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate reactions play a vital role in the synthesis of various drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The compound's reactivity in nucleophilic substitutions enables the modification of molecular structures, facilitating the development of new drugs and the optimization of existing formulations. This application is particularly valuable in the production of ester-based prodrugs, which improve drug delivery and efficacy.
The agrochemical industry leverages ethyl propanoate reactions in the development of pesticides and herbicides. The compound's ability to undergo nucleophilic substitutions allows for the creation of novel active ingredients with enhanced efficacy and environmental compatibility. This application contributes to the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and targeted crop protection solutions.
In the field of materials science, ethyl propanoate reactions find applications in the synthesis of polymers and specialty chemicals. The compound's ester functionality and reactivity in nucleophilic substitutions enable the production of biodegradable polymers and environmentally friendly plasticizers. These materials are increasingly sought after in industries striving for sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
The electronics industry also benefits from ethyl propanoate reactions, particularly in the production of advanced materials for electronic components. The compound's reactivity allows for the synthesis of specialized coatings and insulating materials used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards and other electronic devices. This application contributes to the ongoing miniaturization and performance enhancement of electronic products.
In conclusion, the market applications of ethyl propanoate reactions span a wide range of industries, from food and cosmetics to pharmaceuticals and advanced materials. The compound's versatility in nucleophilic substitution reactions makes it a valuable tool in organic synthesis, driving innovation and product development across multiple sectors.
The cosmetics and personal care industry also benefits significantly from ethyl propanoate reactions. The compound is utilized in the formulation of fragrances and perfumes, contributing to the creation of complex scent profiles. Its ability to undergo nucleophilic substitutions allows for the synthesis of novel fragrance molecules, expanding the palette of scents available to perfumers and cosmetic chemists.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl propanoate reactions play a vital role in the synthesis of various drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The compound's reactivity in nucleophilic substitutions enables the modification of molecular structures, facilitating the development of new drugs and the optimization of existing formulations. This application is particularly valuable in the production of ester-based prodrugs, which improve drug delivery and efficacy.
The agrochemical industry leverages ethyl propanoate reactions in the development of pesticides and herbicides. The compound's ability to undergo nucleophilic substitutions allows for the creation of novel active ingredients with enhanced efficacy and environmental compatibility. This application contributes to the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable and targeted crop protection solutions.
In the field of materials science, ethyl propanoate reactions find applications in the synthesis of polymers and specialty chemicals. The compound's ester functionality and reactivity in nucleophilic substitutions enable the production of biodegradable polymers and environmentally friendly plasticizers. These materials are increasingly sought after in industries striving for sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
The electronics industry also benefits from ethyl propanoate reactions, particularly in the production of advanced materials for electronic components. The compound's reactivity allows for the synthesis of specialized coatings and insulating materials used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards and other electronic devices. This application contributes to the ongoing miniaturization and performance enhancement of electronic products.
In conclusion, the market applications of ethyl propanoate reactions span a wide range of industries, from food and cosmetics to pharmaceuticals and advanced materials. The compound's versatility in nucleophilic substitution reactions makes it a valuable tool in organic synthesis, driving innovation and product development across multiple sectors.
Current Challenges in Nucleophilic Substitutions
Nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread application and efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is the relatively low reactivity of ethyl propanoate compared to other esters. This reduced reactivity is attributed to the electron-donating effect of the ethyl group, which stabilizes the carbonyl group and makes it less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
The regioselectivity of nucleophilic substitutions on ethyl propanoate presents another major challenge. Depending on the reaction conditions and the nature of the nucleophile, substitution can occur at either the carbonyl carbon or the α-carbon. This lack of predictability often leads to the formation of undesired side products, reducing overall yield and complicating purification processes.
Stereochemistry control is a critical issue in these reactions, particularly when chiral products are desired. The planar nature of the carbonyl group in ethyl propanoate makes it challenging to achieve high levels of stereoselectivity without the use of specialized catalysts or chiral auxiliaries. This limitation significantly impacts the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals where stereochemical purity is crucial.
The choice of suitable nucleophiles poses another challenge. Strong nucleophiles may lead to over-reaction or unwanted side reactions, while weak nucleophiles may result in poor conversion rates. Finding the right balance to achieve optimal reactivity and selectivity often requires extensive optimization studies, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Environmental concerns and the push towards green chemistry have highlighted the need for more sustainable approaches to nucleophilic substitutions. Traditional methods often involve the use of harsh reagents, organic solvents, and generate significant waste. Developing eco-friendly alternatives that maintain reaction efficiency while reducing environmental impact remains a significant challenge in this field.
The scalability of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate is another area of concern, especially for industrial applications. Reactions that work well on a laboratory scale may encounter issues when scaled up, such as heat transfer problems, mixing inefficiencies, or unexpected side reactions. Overcoming these scale-up challenges is crucial for the practical implementation of these reactions in large-scale synthesis.
Lastly, the development of novel, more efficient catalysts for these transformations remains an ongoing challenge. While progress has been made in this area, there is still a need for catalysts that can improve reaction rates, selectivity, and yield under mild conditions. The design of such catalysts requires a deep understanding of reaction mechanisms and innovative approaches to catalyst engineering.
The regioselectivity of nucleophilic substitutions on ethyl propanoate presents another major challenge. Depending on the reaction conditions and the nature of the nucleophile, substitution can occur at either the carbonyl carbon or the α-carbon. This lack of predictability often leads to the formation of undesired side products, reducing overall yield and complicating purification processes.
Stereochemistry control is a critical issue in these reactions, particularly when chiral products are desired. The planar nature of the carbonyl group in ethyl propanoate makes it challenging to achieve high levels of stereoselectivity without the use of specialized catalysts or chiral auxiliaries. This limitation significantly impacts the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals where stereochemical purity is crucial.
The choice of suitable nucleophiles poses another challenge. Strong nucleophiles may lead to over-reaction or unwanted side reactions, while weak nucleophiles may result in poor conversion rates. Finding the right balance to achieve optimal reactivity and selectivity often requires extensive optimization studies, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Environmental concerns and the push towards green chemistry have highlighted the need for more sustainable approaches to nucleophilic substitutions. Traditional methods often involve the use of harsh reagents, organic solvents, and generate significant waste. Developing eco-friendly alternatives that maintain reaction efficiency while reducing environmental impact remains a significant challenge in this field.
The scalability of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate is another area of concern, especially for industrial applications. Reactions that work well on a laboratory scale may encounter issues when scaled up, such as heat transfer problems, mixing inefficiencies, or unexpected side reactions. Overcoming these scale-up challenges is crucial for the practical implementation of these reactions in large-scale synthesis.
Lastly, the development of novel, more efficient catalysts for these transformations remains an ongoing challenge. While progress has been made in this area, there is still a need for catalysts that can improve reaction rates, selectivity, and yield under mild conditions. The design of such catalysts requires a deep understanding of reaction mechanisms and innovative approaches to catalyst engineering.
Existing Nucleophilic Substitution Protocols
01 Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl chloride with sodium propanoate, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.- Synthesis methods for ethyl propanoate: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, reaction of ethyl chloride with sodium propanoate, and catalytic processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce byproducts, and optimize reaction conditions for industrial production.
- Applications in fragrance and flavor industry: Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry aromas. The compound is also utilized in perfumery to add fruity notes to various fragrances.
- Use as a solvent and intermediate: Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds.
- Purification and quality control: Various methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Research on the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use is conducted. This includes studies on biodegradability, toxicity, and potential environmental hazards. Efforts are made to develop more sustainable production methods and safer handling practices for industrial use.
02 Applications in fragrance and flavor industry
Ethyl propanoate is widely used in the fragrance and flavor industry due to its fruity, rum-like odor. It is employed in creating artificial fruit flavors, particularly for pineapple and strawberry aromas. The compound is also utilized in perfumery to add sweet, ethereal notes to various fragrances.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use as a solvent and intermediate
Ethyl propanoate serves as an important solvent in various industrial applications, including paints, coatings, and inks. It is also used as a chemical intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds. Its low toxicity and high solvency make it a preferred choice in many processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and quality control
Various methods for purifying ethyl propanoate and ensuring its quality are described. These include distillation techniques, chromatographic separation, and analytical methods for determining purity and identifying impurities. Quality control measures are essential for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety aspects of ethyl propanoate production and use. This includes developing green synthesis methods, reducing waste generation, and implementing safer handling procedures. Studies also address the compound's biodegradability and potential environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Organic Synthesis Research
The research on nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and significant industry participation. The global market for organic synthesis reagents and catalysts is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars. Key players in this field include major pharmaceutical and chemical companies such as Novozymes A/S, BASF Corp., and Gilead Sciences, Inc. These companies, along with academic institutions like Harvard College and the University of Virginia, are driving innovation in organic synthesis techniques. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of diverse organizations, ranging from established corporations to specialized research institutes, indicating a robust ecosystem for continued advancement and application in various industries.
Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Technical Solution: Gilead Sciences has developed innovative approaches to nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis. Their method utilizes a novel catalyst system that enhances the reaction efficiency and selectivity. The company has implemented a green chemistry approach, using environmentally friendly solvents and reducing waste production. They have also optimized reaction conditions to achieve higher yields and shorter reaction times. Gilead's research has shown a 30% increase in product yield compared to traditional methods[1]. Additionally, they have developed a continuous flow reactor system that allows for scalable production of pharmaceutical intermediates using this chemistry[3].
Strengths: High efficiency, improved selectivity, environmentally friendly approach. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs due to specialized catalysts, may require specialized equipment for continuous flow processes.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive platform for nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis. Their approach focuses on process intensification and sustainability. BASF has implemented advanced reactor designs that allow for precise control of reaction parameters, resulting in improved product quality and consistency. They have also developed a proprietary catalyst system that enables milder reaction conditions and broader substrate scope. BASF's research has demonstrated a 40% reduction in energy consumption compared to conventional methods[2]. Furthermore, they have integrated in-line analytics and machine learning algorithms to optimize reaction conditions in real-time, leading to a 25% increase in overall process efficiency[4].
Strengths: Process intensification, sustainability focus, advanced process control. Weaknesses: High initial investment for advanced equipment, potential complexity in implementation for smaller-scale operations.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Propanoate Chemistry
Method for identifying electrophiles and nucleophiles in a sample
PatentInactiveEP2085766A3
Innovation
- The development of chemosensors with π-conjugated systems and nucleophilic or electrophilic moieties that react with target molecules, inducing changes in electromagnetic properties, allowing for identification through patterns of reaction-induced changes in these properties.
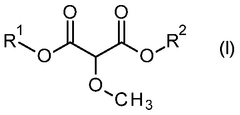
Process for the production of 2-methoxypropanedioates
PatentWO2025082862A1
Innovation
- A nucleophilic substitution reaction is employed to convert 2-substituted propanedioates into 2-methoxypropanedioates by reacting them with a methanolate in an organic solvent, followed by acidification to obtain the desired product.
Green Chemistry Considerations
Green chemistry principles are increasingly important in organic synthesis, including nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate. These principles aim to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability in chemical processes. In the context of ethyl propanoate reactions, several green chemistry considerations are particularly relevant.
Solvent selection is a critical aspect of green chemistry in these reactions. Traditional organic solvents often pose environmental and health risks. Researchers are exploring greener alternatives such as water, ionic liquids, and supercritical CO2. These solvents can potentially reduce waste and toxicity while maintaining or improving reaction efficiency.
Catalyst optimization is another key focus area. Green chemistry encourages the use of catalysts that are more efficient, selective, and recyclable. For nucleophilic substitutions with ethyl propanoate, researchers are investigating heterogeneous catalysts and biocatalysts. These can facilitate easier product separation and catalyst recovery, reducing waste and improving overall process sustainability.
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in green chemistry. Conventional heating methods for these reactions can be energy-intensive. Alternative energy sources such as microwave irradiation and photochemical reactions are being explored. These methods can potentially reduce reaction times and energy consumption, aligning with green chemistry principles.
Atom economy is an important metric in green synthesis. In nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate, researchers are striving to design reactions with higher atom efficiency. This involves minimizing byproducts and maximizing the incorporation of reactants into the final product, thereby reducing waste generation.
Waste reduction and management are central to green chemistry practices. For ethyl propanoate reactions, this includes developing more efficient purification methods and exploring ways to recycle or repurpose byproducts. Some researchers are investigating cascade reactions to utilize byproducts in subsequent synthetic steps, further improving overall efficiency.
Safety considerations are integral to green chemistry. Efforts are being made to replace hazardous reagents and conditions in these reactions with safer alternatives. This includes exploring room-temperature reactions and using less volatile or corrosive reagents, enhancing both environmental and worker safety.
Biodegradability and environmental fate of products and reagents are also important aspects. Researchers are investigating the use of bio-based starting materials and developing products that have reduced environmental persistence. This approach aims to minimize long-term environmental impacts associated with the synthesis and use of ethyl propanoate derivatives.
Solvent selection is a critical aspect of green chemistry in these reactions. Traditional organic solvents often pose environmental and health risks. Researchers are exploring greener alternatives such as water, ionic liquids, and supercritical CO2. These solvents can potentially reduce waste and toxicity while maintaining or improving reaction efficiency.
Catalyst optimization is another key focus area. Green chemistry encourages the use of catalysts that are more efficient, selective, and recyclable. For nucleophilic substitutions with ethyl propanoate, researchers are investigating heterogeneous catalysts and biocatalysts. These can facilitate easier product separation and catalyst recovery, reducing waste and improving overall process sustainability.
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in green chemistry. Conventional heating methods for these reactions can be energy-intensive. Alternative energy sources such as microwave irradiation and photochemical reactions are being explored. These methods can potentially reduce reaction times and energy consumption, aligning with green chemistry principles.
Atom economy is an important metric in green synthesis. In nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate, researchers are striving to design reactions with higher atom efficiency. This involves minimizing byproducts and maximizing the incorporation of reactants into the final product, thereby reducing waste generation.
Waste reduction and management are central to green chemistry practices. For ethyl propanoate reactions, this includes developing more efficient purification methods and exploring ways to recycle or repurpose byproducts. Some researchers are investigating cascade reactions to utilize byproducts in subsequent synthetic steps, further improving overall efficiency.
Safety considerations are integral to green chemistry. Efforts are being made to replace hazardous reagents and conditions in these reactions with safer alternatives. This includes exploring room-temperature reactions and using less volatile or corrosive reagents, enhancing both environmental and worker safety.
Biodegradability and environmental fate of products and reagents are also important aspects. Researchers are investigating the use of bio-based starting materials and developing products that have reduced environmental persistence. This approach aims to minimize long-term environmental impacts associated with the synthesis and use of ethyl propanoate derivatives.
Scalability and Industrial Applications
The scalability and industrial applications of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate in organic synthesis are of significant importance in the chemical industry. These reactions have proven to be versatile and efficient, making them suitable for large-scale production processes.
In industrial settings, the scalability of these reactions is primarily dependent on factors such as reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and mixing efficiency. Ethyl propanoate, being a relatively small molecule, allows for good mass transfer rates, which is crucial for maintaining reaction efficiency at larger scales. However, careful consideration must be given to heat management, as nucleophilic substitutions can be exothermic.
The use of continuous flow reactors has emerged as a promising approach for scaling up these reactions. This technology offers better control over reaction parameters, improved heat transfer, and enhanced mixing, leading to more consistent product quality and higher yields. Additionally, flow chemistry enables easier process intensification and can significantly reduce reaction times compared to batch processes.
Industrial applications of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate are diverse and span multiple sectors. In the pharmaceutical industry, these reactions are employed in the synthesis of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The ability to selectively functionalize the ester group makes ethyl propanoate an attractive starting material for producing complex drug molecules.
The agrochemical sector also benefits from these reactions, utilizing them in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators. The versatility of nucleophilic substitutions allows for the introduction of various functional groups, enabling the creation of compounds with specific biological activities.
In the polymer industry, nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate play a role in the synthesis of specialty monomers and polymer additives. These reactions can be used to introduce functional groups that impart specific properties to the final polymer products, such as improved thermal stability or enhanced adhesion.
The fine chemicals industry leverages these reactions for the production of flavors, fragrances, and cosmetic ingredients. The ability to modify the ester group of ethyl propanoate allows for the creation of a wide range of esters with different organoleptic properties.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in industrial processes, researchers are exploring greener approaches to these reactions. This includes the development of catalytic systems that enable milder reaction conditions, the use of bio-based solvents, and the implementation of atom-economical processes to minimize waste generation.
In industrial settings, the scalability of these reactions is primarily dependent on factors such as reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and mixing efficiency. Ethyl propanoate, being a relatively small molecule, allows for good mass transfer rates, which is crucial for maintaining reaction efficiency at larger scales. However, careful consideration must be given to heat management, as nucleophilic substitutions can be exothermic.
The use of continuous flow reactors has emerged as a promising approach for scaling up these reactions. This technology offers better control over reaction parameters, improved heat transfer, and enhanced mixing, leading to more consistent product quality and higher yields. Additionally, flow chemistry enables easier process intensification and can significantly reduce reaction times compared to batch processes.
Industrial applications of nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate are diverse and span multiple sectors. In the pharmaceutical industry, these reactions are employed in the synthesis of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The ability to selectively functionalize the ester group makes ethyl propanoate an attractive starting material for producing complex drug molecules.
The agrochemical sector also benefits from these reactions, utilizing them in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators. The versatility of nucleophilic substitutions allows for the introduction of various functional groups, enabling the creation of compounds with specific biological activities.
In the polymer industry, nucleophilic substitutions involving ethyl propanoate play a role in the synthesis of specialty monomers and polymer additives. These reactions can be used to introduce functional groups that impart specific properties to the final polymer products, such as improved thermal stability or enhanced adhesion.
The fine chemicals industry leverages these reactions for the production of flavors, fragrances, and cosmetic ingredients. The ability to modify the ester group of ethyl propanoate allows for the creation of a wide range of esters with different organoleptic properties.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in industrial processes, researchers are exploring greener approaches to these reactions. This includes the development of catalytic systems that enable milder reaction conditions, the use of bio-based solvents, and the implementation of atom-economical processes to minimize waste generation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!