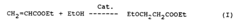Scaling Up Ethyl Propanoate Production: Industrial Challenges
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate Production Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, is a significant ester compound widely used in various industries, particularly in the production of fragrances, flavors, and solvents. The history of ethyl propanoate production dates back to the early 20th century when esterification processes were first developed on an industrial scale. Over the years, the demand for this versatile compound has steadily increased, driven by its applications in food additives, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate production technology has been marked by continuous improvements in reaction efficiency, yield optimization, and process safety. Initially, batch processes were the norm, but as demand grew, continuous flow reactors and more sophisticated catalytic systems were introduced. These advancements aimed to address the challenges of scalability, product purity, and environmental concerns associated with large-scale production.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods. This trend is driven by increasing environmental regulations and the growing consumer preference for green products. As a result, research efforts have been directed towards exploring bio-based feedstocks, enzymatic catalysis, and novel reactor designs that minimize waste and energy consumption.
The primary objective of scaling up ethyl propanoate production is to meet the rising global demand while addressing the industrial challenges associated with large-scale manufacturing. These challenges include maintaining product quality, ensuring process safety, optimizing energy efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing cost-effective production methods to remain competitive in the global market.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the flexibility of production facilities to adapt to fluctuating market demands and raw material availability. This requires the development of modular and adaptable production systems that can efficiently handle variations in production volume and feedstock composition. Furthermore, there is a need to integrate advanced process control and monitoring systems to ensure consistent product quality and optimize resource utilization.
As the industry moves towards Industry 4.0, there is an increasing focus on incorporating digital technologies and data analytics into ethyl propanoate production. This includes the implementation of predictive maintenance systems, real-time process optimization, and the use of artificial intelligence for quality control and production planning. These technological advancements aim to improve overall operational efficiency and reduce production costs.
The evolution of ethyl propanoate production technology has been marked by continuous improvements in reaction efficiency, yield optimization, and process safety. Initially, batch processes were the norm, but as demand grew, continuous flow reactors and more sophisticated catalytic systems were introduced. These advancements aimed to address the challenges of scalability, product purity, and environmental concerns associated with large-scale production.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards developing more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods. This trend is driven by increasing environmental regulations and the growing consumer preference for green products. As a result, research efforts have been directed towards exploring bio-based feedstocks, enzymatic catalysis, and novel reactor designs that minimize waste and energy consumption.
The primary objective of scaling up ethyl propanoate production is to meet the rising global demand while addressing the industrial challenges associated with large-scale manufacturing. These challenges include maintaining product quality, ensuring process safety, optimizing energy efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on developing cost-effective production methods to remain competitive in the global market.
Another crucial goal is to enhance the flexibility of production facilities to adapt to fluctuating market demands and raw material availability. This requires the development of modular and adaptable production systems that can efficiently handle variations in production volume and feedstock composition. Furthermore, there is a need to integrate advanced process control and monitoring systems to ensure consistent product quality and optimize resource utilization.
As the industry moves towards Industry 4.0, there is an increasing focus on incorporating digital technologies and data analytics into ethyl propanoate production. This includes the implementation of predictive maintenance systems, real-time process optimization, and the use of artificial intelligence for quality control and production planning. These technological advancements aim to improve overall operational efficiency and reduce production costs.
Market Analysis for Ethyl Propanoate
The global market for ethyl propanoate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. This ester compound, known for its fruity aroma reminiscent of pineapples, finds extensive use in the flavor and fragrance industry, serving as a key ingredient in food additives, perfumes, and cosmetics. The increasing consumer demand for natural and organic products has further boosted the market for ethyl propanoate, as it can be derived from both synthetic and natural sources.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl propanoate is widely used as a flavoring agent, particularly in confectionery, baked goods, and beverages. The growing popularity of flavored alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks has created a substantial demand for this compound. Additionally, the expanding processed food industry, especially in developing economies, has contributed significantly to the market growth.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another major consumer of ethyl propanoate. Its application as a solvent in drug formulations and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds has led to a consistent demand from this sector. The ongoing research and development activities in the pharmaceutical industry are expected to further drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in the coming years.
The paints and coatings industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate as a solvent, particularly in fast-drying formulations. The robust growth of the construction and automotive sectors in emerging economies has indirectly boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate in this application area.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest market for ethyl propanoate, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India have been key factors driving the demand in the Asia-Pacific region. The mature markets of North America and Europe continue to show steady growth, primarily driven by innovations in the flavor and fragrance industry.
The market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and small to medium-sized enterprises. Key players in the ethyl propanoate market have been focusing on expanding their production capacities and improving their distribution networks to meet the growing global demand. Strategic collaborations and partnerships with end-user industries have also been observed as common strategies among market players to strengthen their market position.
Looking ahead, the ethyl propanoate market is projected to maintain its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing adoption of natural flavors, the growing demand for processed foods, and the expansion of the cosmetics and personal care industry are expected to be the primary drivers of this growth. However, challenges such as stringent regulations regarding chemical usage in food products and the volatility in raw material prices may impact the market dynamics in the future.
In the food and beverage sector, ethyl propanoate is widely used as a flavoring agent, particularly in confectionery, baked goods, and beverages. The growing popularity of flavored alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks has created a substantial demand for this compound. Additionally, the expanding processed food industry, especially in developing economies, has contributed significantly to the market growth.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another major consumer of ethyl propanoate. Its application as a solvent in drug formulations and as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds has led to a consistent demand from this sector. The ongoing research and development activities in the pharmaceutical industry are expected to further drive the demand for ethyl propanoate in the coming years.
The paints and coatings industry also utilizes ethyl propanoate as a solvent, particularly in fast-drying formulations. The robust growth of the construction and automotive sectors in emerging economies has indirectly boosted the demand for ethyl propanoate in this application area.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest market for ethyl propanoate, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India have been key factors driving the demand in the Asia-Pacific region. The mature markets of North America and Europe continue to show steady growth, primarily driven by innovations in the flavor and fragrance industry.
The market is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and small to medium-sized enterprises. Key players in the ethyl propanoate market have been focusing on expanding their production capacities and improving their distribution networks to meet the growing global demand. Strategic collaborations and partnerships with end-user industries have also been observed as common strategies among market players to strengthen their market position.
Looking ahead, the ethyl propanoate market is projected to maintain its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing adoption of natural flavors, the growing demand for processed foods, and the expansion of the cosmetics and personal care industry are expected to be the primary drivers of this growth. However, challenges such as stringent regulations regarding chemical usage in food products and the volatility in raw material prices may impact the market dynamics in the future.
Current Industrial Challenges in Scaling Up
The scaling up of ethyl propanoate production faces several significant industrial challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and efficient large-scale manufacturing. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of raw materials, particularly ethanol and propionic acid. As the production scale increases, the demand for these precursors rises substantially, leading to potential supply chain bottlenecks and price fluctuations that can impact the overall economic viability of the process.
Another major challenge lies in the reactor design and process optimization for large-scale production. The esterification reaction between ethanol and propionic acid is equilibrium-limited, requiring careful control of reaction conditions to maximize yield and selectivity. As the reactor size increases, maintaining uniform temperature distribution and ensuring efficient mixing become increasingly difficult, potentially leading to reduced conversion rates and product quality issues.
Heat management presents a significant hurdle in scaling up ethyl propanoate production. The esterification reaction is exothermic, and as the production volume grows, the amount of heat generated increases substantially. Efficient heat removal systems are crucial to prevent runaway reactions and maintain optimal reaction conditions. However, designing and implementing such systems for large-scale reactors can be technically challenging and capital-intensive.
The separation and purification of ethyl propanoate from the reaction mixture pose additional challenges in industrial-scale production. Traditional distillation methods may become less efficient and more energy-intensive as the production volume increases. The presence of azeotropes in the system further complicates the separation process, necessitating the development of advanced separation techniques or the use of entrainers, which can add complexity and cost to the overall process.
Catalyst performance and longevity are critical factors in scaling up ethyl propanoate production. While homogeneous acid catalysts are commonly used in small-scale synthesis, they may not be suitable for large-scale operations due to corrosion issues and difficulties in catalyst recovery. Heterogeneous catalysts offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and reusability, but their activity and selectivity may decrease over time, requiring frequent regeneration or replacement.
Environmental and safety considerations also present challenges in scaling up production. The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and potential acid emissions necessitate robust emission control systems and safety measures. Implementing these safeguards at an industrial scale can be complex and costly, requiring significant investments in equipment and process modifications to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and maintain worker safety.
Another major challenge lies in the reactor design and process optimization for large-scale production. The esterification reaction between ethanol and propionic acid is equilibrium-limited, requiring careful control of reaction conditions to maximize yield and selectivity. As the reactor size increases, maintaining uniform temperature distribution and ensuring efficient mixing become increasingly difficult, potentially leading to reduced conversion rates and product quality issues.
Heat management presents a significant hurdle in scaling up ethyl propanoate production. The esterification reaction is exothermic, and as the production volume grows, the amount of heat generated increases substantially. Efficient heat removal systems are crucial to prevent runaway reactions and maintain optimal reaction conditions. However, designing and implementing such systems for large-scale reactors can be technically challenging and capital-intensive.
The separation and purification of ethyl propanoate from the reaction mixture pose additional challenges in industrial-scale production. Traditional distillation methods may become less efficient and more energy-intensive as the production volume increases. The presence of azeotropes in the system further complicates the separation process, necessitating the development of advanced separation techniques or the use of entrainers, which can add complexity and cost to the overall process.
Catalyst performance and longevity are critical factors in scaling up ethyl propanoate production. While homogeneous acid catalysts are commonly used in small-scale synthesis, they may not be suitable for large-scale operations due to corrosion issues and difficulties in catalyst recovery. Heterogeneous catalysts offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and reusability, but their activity and selectivity may decrease over time, requiring frequent regeneration or replacement.
Environmental and safety considerations also present challenges in scaling up production. The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and potential acid emissions necessitate robust emission control systems and safety measures. Implementing these safeguards at an industrial scale can be complex and costly, requiring significant investments in equipment and process modifications to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and maintain worker safety.
Existing Large-Scale Production Techniques
01 Large-scale production methods
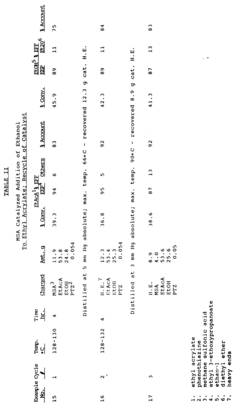
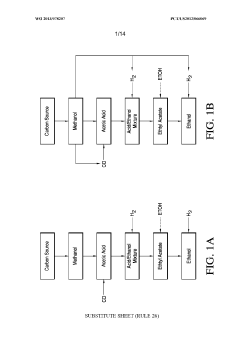
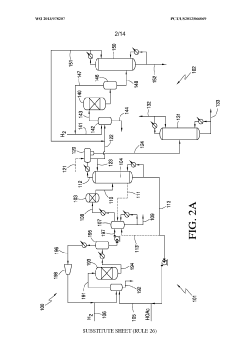
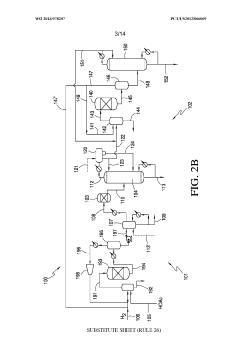
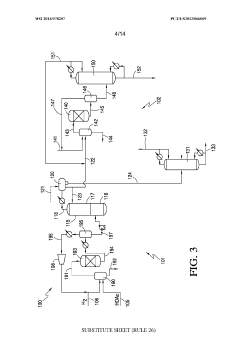
Various methods for large-scale production of ethyl propanoate have been developed. These include continuous flow processes, catalytic reactions, and optimized batch production techniques. These methods aim to increase yield, improve efficiency, and reduce production costs for industrial-scale manufacturing.- Large-scale production methods: Various methods for large-scale production of ethyl propanoate have been developed. These include continuous flow processes, catalytic reactions, and optimized batch production techniques. These methods aim to increase yield, improve efficiency, and reduce production costs for industrial-scale manufacturing.
- Catalytic synthesis processes: Catalytic processes play a crucial role in the production of ethyl propanoate. Different catalysts, such as heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts, are employed to facilitate the esterification reaction between propionic acid and ethanol. These catalysts help to increase reaction rates and selectivity, leading to improved production efficiency.
- Purification and separation techniques: Various purification and separation techniques are utilized in the production of ethyl propanoate to ensure high product quality. These may include distillation, extraction, and membrane separation processes. The choice of purification method depends on the specific production process and desired product purity.
- Continuous flow reactors: Continuous flow reactors have been developed for the production of ethyl propanoate, offering advantages such as improved heat and mass transfer, better control over reaction conditions, and increased productivity. These reactors are particularly suitable for large-scale production and can be integrated with in-line purification processes.
- Green chemistry approaches: Environmentally friendly approaches to ethyl propanoate production have been explored, focusing on the use of renewable feedstocks, bio-based catalysts, and sustainable solvents. These methods aim to reduce the environmental impact of the production process while maintaining or improving product quality and yield.
02 Catalytic synthesis processes
Catalytic processes play a crucial role in ethyl propanoate production. Different catalysts, such as heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts, are employed to facilitate the esterification reaction between propionic acid and ethanol. These catalysts enhance reaction rates, selectivity, and overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation techniques
Various purification and separation techniques are utilized to obtain high-purity ethyl propanoate. These include distillation, extraction, and membrane separation processes. Advanced separation methods help remove impurities and byproducts, ensuring the production of high-quality ethyl propanoate at industrial scales.Expand Specific Solutions04 Process optimization and control
Optimization of process parameters and implementation of advanced control systems are crucial for large-scale ethyl propanoate production. This includes temperature control, pressure regulation, and feed rate optimization. Process modeling and simulation tools are used to enhance production efficiency and maintain product quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Green chemistry approaches
Environmentally friendly approaches for ethyl propanoate production have gained attention. These include the use of bio-based feedstocks, enzymatic catalysis, and solvent-free reactions. Such methods aim to reduce environmental impact and improve sustainability in large-scale production processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Ester Production
The ethyl propanoate production industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in various sectors such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. The global market size for ethyl propanoate is expanding, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. Technologically, the production process is relatively mature, but challenges remain in scaling up for industrial production. Key players like Celanese International Corp., China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd. are investing in research and development to optimize production methods and improve efficiency. Other significant companies such as LG Chem Ltd., ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc., and BASF Corp. are also contributing to advancements in the field, focusing on sustainable production techniques and exploring new applications for ethyl propanoate.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed a proprietary process for large-scale ethyl propanoate production using advanced catalysts and reactor designs. Their method involves a two-step process: first, the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol using a heterogeneous acid catalyst, followed by a purification step utilizing innovative distillation techniques. This approach allows for continuous production with high yield and selectivity[1][3]. The company has also implemented process intensification strategies, such as reactive distillation, to combine reaction and separation steps, thereby improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption[2].
Strengths: High yield and selectivity, continuous production capability, energy-efficient process. Weaknesses: Potential high initial capital investment, reliance on specific catalyst technology.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has invested in a novel approach to ethyl propanoate production using a gas-phase catalytic process. Their method employs a fixed-bed reactor system with a proprietary zeolite-based catalyst, allowing for direct synthesis from ethanol and carbon monoxide[4]. This process operates at moderate temperatures and pressures, reducing energy requirements compared to traditional liquid-phase reactions. Sinopec has also integrated advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring to optimize reaction conditions and maintain product quality[5]. The company is exploring the use of renewable ethanol sources to enhance the sustainability of their production process[6].
Strengths: Direct synthesis from readily available feedstocks, energy-efficient process, potential for sustainable production. Weaknesses: Catalyst sensitivity to impurities, potential scale-up challenges.
Innovative Catalysts and Reaction Mechanisms
Production of ethyl 3-ethoxy propanoate by acid catalyzed addition of ethanol to ethyl acrylate
PatentInactiveEP0499731A1
Innovation
- EEP is produced through an acid-catalyzed addition of ethanol to ethyl acrylate using strong acid catalysts such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, or sulfonic acids, with reaction conditions optimized at temperatures between 75°C to 150°C and pressures of 30-50 psig, and the use of inhibitors to manage by-product formation.
Esterifying an ethanol and acetic acid mixture to produce an ester feed for hydrogenolysis
PatentWO2013078207A1
Innovation
- A method involving the hydrogenation of acetic acid to produce a mixture of ethanol and acetic acid, followed by esterification to create an ester feed stream that is then reduced to produce ethanol, using a catalyst system with active metals on a support and an acidic catalyst, optimizing the molar ratio of acetic acid to ethanol and controlling water content to enhance ethanol recovery and reduce costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The scaling up of ethyl propanoate production presents significant environmental challenges that must be addressed to ensure sustainable industrial practices. The primary environmental concerns revolve around the use of raw materials, energy consumption, waste generation, and emissions.
Ethyl propanoate production typically involves the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, often using sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This process requires careful consideration of resource efficiency and waste management. The sourcing of raw materials, particularly ethanol, can have substantial environmental implications. Ethanol derived from renewable sources, such as biomass fermentation, offers a more sustainable alternative to petrochemical-based ethanol, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the production process.
Energy consumption is a critical factor in the environmental impact of large-scale ethyl propanoate production. The reaction and subsequent purification steps, including distillation, require significant thermal energy. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as heat integration systems and advanced process control, can substantially reduce energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste management is another crucial aspect of sustainable production. The esterification process generates wastewater containing residual acids, alcohols, and other organic compounds. Proper treatment and recycling of this wastewater are essential to minimize environmental pollution and conserve water resources. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and biological treatment systems, can effectively remove contaminants and allow for water reuse within the production facility.
Emissions control is vital in mitigating the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate production. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the process can contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Implementing robust emission control systems, such as thermal oxidizers or carbon adsorption units, is crucial for compliance with environmental regulations and reducing the overall ecological footprint of the production facility.
Sustainability considerations extend beyond the immediate production process to encompass the entire life cycle of ethyl propanoate. This includes the environmental impact of transportation, packaging, and end-use applications. Adopting green chemistry principles in process design and optimization can lead to more sustainable production methods, such as developing catalysts that enable lower reaction temperatures or exploring alternative synthesis routes with reduced environmental impact.
Furthermore, implementing circular economy principles in ethyl propanoate production can significantly enhance sustainability. This may involve recovering and recycling unreacted raw materials, utilizing by-products in other industrial processes, and exploring opportunities for industrial symbiosis with neighboring facilities to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation.
Ethyl propanoate production typically involves the esterification of propionic acid with ethanol, often using sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This process requires careful consideration of resource efficiency and waste management. The sourcing of raw materials, particularly ethanol, can have substantial environmental implications. Ethanol derived from renewable sources, such as biomass fermentation, offers a more sustainable alternative to petrochemical-based ethanol, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the production process.
Energy consumption is a critical factor in the environmental impact of large-scale ethyl propanoate production. The reaction and subsequent purification steps, including distillation, require significant thermal energy. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as heat integration systems and advanced process control, can substantially reduce energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste management is another crucial aspect of sustainable production. The esterification process generates wastewater containing residual acids, alcohols, and other organic compounds. Proper treatment and recycling of this wastewater are essential to minimize environmental pollution and conserve water resources. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and biological treatment systems, can effectively remove contaminants and allow for water reuse within the production facility.
Emissions control is vital in mitigating the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate production. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the process can contribute to air pollution and smog formation. Implementing robust emission control systems, such as thermal oxidizers or carbon adsorption units, is crucial for compliance with environmental regulations and reducing the overall ecological footprint of the production facility.
Sustainability considerations extend beyond the immediate production process to encompass the entire life cycle of ethyl propanoate. This includes the environmental impact of transportation, packaging, and end-use applications. Adopting green chemistry principles in process design and optimization can lead to more sustainable production methods, such as developing catalysts that enable lower reaction temperatures or exploring alternative synthesis routes with reduced environmental impact.
Furthermore, implementing circular economy principles in ethyl propanoate production can significantly enhance sustainability. This may involve recovering and recycling unreacted raw materials, utilizing by-products in other industrial processes, and exploring opportunities for industrial symbiosis with neighboring facilities to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation.
Regulatory Compliance in Chemical Manufacturing
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of scaling up ethyl propanoate production in industrial settings. As manufacturers increase their production capacity, they must navigate a complex landscape of regulations governing chemical manufacturing processes, environmental impact, worker safety, and product quality.
One of the primary regulatory bodies overseeing chemical manufacturing in many countries is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA enforces regulations such as the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act, which set limits on emissions and effluents from industrial processes. For ethyl propanoate production, manufacturers must ensure that their facilities meet air quality standards for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and implement appropriate pollution control technologies.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a crucial role in ensuring worker safety in chemical manufacturing facilities. As production scales up, companies must adhere to OSHA's Process Safety Management (PSM) standards, which include requirements for hazard analysis, operating procedures, employee training, and emergency response planning. Specific to ethyl propanoate production, proper handling and storage of flammable materials and precursors like propionic acid and ethanol are essential compliance areas.
Product quality and safety regulations are enforced by agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for ethyl propanoate used in food applications. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures to ensure product purity and consistency. This includes maintaining detailed records of production processes, conducting regular quality tests, and implementing traceability systems.
International regulations also come into play for companies exporting ethyl propanoate. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers to register chemicals and provide safety data. Similarly, other countries have their own chemical control laws that must be adhered to for market access.
As production scales up, waste management becomes increasingly important. Regulations such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) govern the handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste generated during the manufacturing process. Proper classification, treatment, and documentation of waste streams are essential for compliance.
To successfully navigate these regulatory challenges, companies scaling up ethyl propanoate production must invest in robust compliance management systems. This includes dedicating resources to staying updated on changing regulations, conducting regular compliance audits, and implementing comprehensive training programs for employees. Proactive engagement with regulatory agencies and industry associations can also help manufacturers anticipate and prepare for upcoming regulatory changes that may impact their operations.
One of the primary regulatory bodies overseeing chemical manufacturing in many countries is the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA enforces regulations such as the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act, which set limits on emissions and effluents from industrial processes. For ethyl propanoate production, manufacturers must ensure that their facilities meet air quality standards for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and implement appropriate pollution control technologies.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a crucial role in ensuring worker safety in chemical manufacturing facilities. As production scales up, companies must adhere to OSHA's Process Safety Management (PSM) standards, which include requirements for hazard analysis, operating procedures, employee training, and emergency response planning. Specific to ethyl propanoate production, proper handling and storage of flammable materials and precursors like propionic acid and ethanol are essential compliance areas.
Product quality and safety regulations are enforced by agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for ethyl propanoate used in food applications. Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures to ensure product purity and consistency. This includes maintaining detailed records of production processes, conducting regular quality tests, and implementing traceability systems.
International regulations also come into play for companies exporting ethyl propanoate. The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires manufacturers to register chemicals and provide safety data. Similarly, other countries have their own chemical control laws that must be adhered to for market access.
As production scales up, waste management becomes increasingly important. Regulations such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) govern the handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste generated during the manufacturing process. Proper classification, treatment, and documentation of waste streams are essential for compliance.
To successfully navigate these regulatory challenges, companies scaling up ethyl propanoate production must invest in robust compliance management systems. This includes dedicating resources to staying updated on changing regulations, conducting regular compliance audits, and implementing comprehensive training programs for employees. Proactive engagement with regulatory agencies and industry associations can also help manufacturers anticipate and prepare for upcoming regulatory changes that may impact their operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!