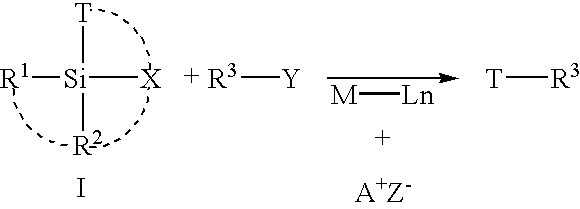Study of Ethyl Propanoate Reactivity in Cross-Coupling Reactions
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Background and Objectives
Cross-coupling reactions have emerged as a powerful tool in organic synthesis, enabling the formation of carbon-carbon bonds between diverse molecular fragments. Among the various substrates explored in these reactions, ethyl propanoate has garnered significant attention due to its potential as a versatile building block. The study of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions aims to expand the scope of synthetic methodologies and provide new avenues for the construction of complex molecules.
The development of cross-coupling reactions has revolutionized the field of organic synthesis, with pioneering work by Nobel laureates Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki paving the way for numerous applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and materials science industries. As the field continues to evolve, researchers are constantly seeking new substrates and reaction conditions to broaden the utility of these transformations.
Ethyl propanoate, a simple ester, presents an intriguing substrate for cross-coupling reactions due to its readily available nature and potential for functionalization. The presence of both an ester group and an alkyl chain offers multiple sites for reactivity, making it an attractive candidate for the development of novel synthetic methodologies. Understanding the reactivity patterns of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions could unlock new possibilities for the synthesis of valuable compounds.
The primary objective of this study is to comprehensively investigate the reactivity of ethyl propanoate in various cross-coupling reactions. This includes exploring its behavior as both an electrophilic and nucleophilic partner, examining different metal catalysts and ligand systems, and identifying optimal reaction conditions for selective transformations. By elucidating the factors that influence the reactivity of ethyl propanoate, researchers aim to develop efficient and selective methods for its incorporation into more complex molecular structures.
Furthermore, this study seeks to address the challenges associated with using ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions, such as potential side reactions, regioselectivity issues, and compatibility with different functional groups. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for expanding the synthetic utility of ethyl propanoate and enabling its application in the preparation of diverse molecular scaffolds.
The technological evolution in this field is expected to lead to the development of more efficient catalytic systems, novel reaction conditions, and innovative approaches to controlling selectivity. As the understanding of ethyl propanoate reactivity deepens, it is anticipated that new synthetic strategies will emerge, potentially revolutionizing the way certain classes of compounds are synthesized.
The development of cross-coupling reactions has revolutionized the field of organic synthesis, with pioneering work by Nobel laureates Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki paving the way for numerous applications in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and materials science industries. As the field continues to evolve, researchers are constantly seeking new substrates and reaction conditions to broaden the utility of these transformations.
Ethyl propanoate, a simple ester, presents an intriguing substrate for cross-coupling reactions due to its readily available nature and potential for functionalization. The presence of both an ester group and an alkyl chain offers multiple sites for reactivity, making it an attractive candidate for the development of novel synthetic methodologies. Understanding the reactivity patterns of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions could unlock new possibilities for the synthesis of valuable compounds.
The primary objective of this study is to comprehensively investigate the reactivity of ethyl propanoate in various cross-coupling reactions. This includes exploring its behavior as both an electrophilic and nucleophilic partner, examining different metal catalysts and ligand systems, and identifying optimal reaction conditions for selective transformations. By elucidating the factors that influence the reactivity of ethyl propanoate, researchers aim to develop efficient and selective methods for its incorporation into more complex molecular structures.
Furthermore, this study seeks to address the challenges associated with using ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions, such as potential side reactions, regioselectivity issues, and compatibility with different functional groups. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for expanding the synthetic utility of ethyl propanoate and enabling its application in the preparation of diverse molecular scaffolds.
The technological evolution in this field is expected to lead to the development of more efficient catalytic systems, novel reaction conditions, and innovative approaches to controlling selectivity. As the understanding of ethyl propanoate reactivity deepens, it is anticipated that new synthetic strategies will emerge, potentially revolutionizing the way certain classes of compounds are synthesized.
Market Analysis
The market for cross-coupling reactions, particularly those involving ethyl propanoate, has shown significant growth in recent years. This expansion is driven by the increasing demand for efficient and sustainable synthetic methods in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The versatility of cross-coupling reactions in forming carbon-carbon bonds has made them indispensable tools in organic synthesis, with applications ranging from drug discovery to the production of advanced materials.
In the pharmaceutical sector, cross-coupling reactions play a crucial role in the synthesis of complex drug molecules. The ability to selectively form carbon-carbon bonds under mild conditions has revolutionized the drug discovery process, enabling the rapid generation of diverse compound libraries. This has led to a surge in demand for novel and efficient cross-coupling methodologies, including those involving ethyl propanoate as a coupling partner.
The agrochemical industry has also embraced cross-coupling reactions for the development of new crop protection agents and fertilizers. The need for more environmentally friendly and targeted agricultural products has driven research into innovative synthetic routes, where ethyl propanoate-based cross-couplings could offer advantages in terms of atom economy and reduced environmental impact.
Materials science represents another growing market for cross-coupling reactions. The development of advanced polymers, organic electronics, and functional materials often relies on precise control over molecular structure, which can be achieved through carefully designed cross-coupling reactions. Ethyl propanoate, as a potential building block in these reactions, could contribute to the creation of materials with tailored properties for applications in renewable energy, electronics, and smart materials.
The global market for cross-coupling reactions is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a particular focus on developing more sustainable and cost-effective methodologies. This trend aligns well with the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions, as it represents a relatively inexpensive and readily available starting material.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for cross-coupling technologies, owing to their strong pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in research and development, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and India.
The market demand for cross-coupling reactions is also influenced by regulatory pressures and sustainability goals. As industries strive to reduce their environmental footprint, there is a growing emphasis on developing greener synthetic methods. This trend could potentially benefit ethyl propanoate-based cross-couplings if they can be demonstrated to offer environmental advantages over existing methodologies.
In conclusion, the market analysis reveals a robust and expanding demand for cross-coupling reactions across multiple industries. The potential integration of ethyl propanoate into these reactions aligns well with current market trends towards efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. As research in this area progresses, it is likely to open up new market opportunities and applications, further driving the growth of this technology sector.
In the pharmaceutical sector, cross-coupling reactions play a crucial role in the synthesis of complex drug molecules. The ability to selectively form carbon-carbon bonds under mild conditions has revolutionized the drug discovery process, enabling the rapid generation of diverse compound libraries. This has led to a surge in demand for novel and efficient cross-coupling methodologies, including those involving ethyl propanoate as a coupling partner.
The agrochemical industry has also embraced cross-coupling reactions for the development of new crop protection agents and fertilizers. The need for more environmentally friendly and targeted agricultural products has driven research into innovative synthetic routes, where ethyl propanoate-based cross-couplings could offer advantages in terms of atom economy and reduced environmental impact.
Materials science represents another growing market for cross-coupling reactions. The development of advanced polymers, organic electronics, and functional materials often relies on precise control over molecular structure, which can be achieved through carefully designed cross-coupling reactions. Ethyl propanoate, as a potential building block in these reactions, could contribute to the creation of materials with tailored properties for applications in renewable energy, electronics, and smart materials.
The global market for cross-coupling reactions is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a particular focus on developing more sustainable and cost-effective methodologies. This trend aligns well with the potential applications of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions, as it represents a relatively inexpensive and readily available starting material.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for cross-coupling technologies, owing to their strong pharmaceutical and chemical industries. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing investments in research and development, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and India.
The market demand for cross-coupling reactions is also influenced by regulatory pressures and sustainability goals. As industries strive to reduce their environmental footprint, there is a growing emphasis on developing greener synthetic methods. This trend could potentially benefit ethyl propanoate-based cross-couplings if they can be demonstrated to offer environmental advantages over existing methodologies.
In conclusion, the market analysis reveals a robust and expanding demand for cross-coupling reactions across multiple industries. The potential integration of ethyl propanoate into these reactions aligns well with current market trends towards efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. As research in this area progresses, it is likely to open up new market opportunities and applications, further driving the growth of this technology sector.
Current Challenges
The study of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread application and understanding. One of the primary obstacles is the relatively low reactivity of ethyl propanoate compared to other commonly used substrates in cross-coupling reactions. This reduced reactivity often necessitates harsher reaction conditions, which can lead to unwanted side reactions and decreased selectivity.
Another major challenge lies in the activation of the C-O bond in ethyl propanoate. Unlike C-X bonds (where X is a halogen) that are typically employed in cross-coupling reactions, the C-O bond is significantly stronger and less polarized. This makes it more difficult to cleave and activate, requiring the development of specialized catalysts and reaction conditions to overcome this energy barrier.
The presence of multiple reactive sites in ethyl propanoate also presents a challenge in terms of regioselectivity. The molecule contains both an ester group and an alkyl chain, each of which can potentially participate in the cross-coupling reaction. Achieving selective activation of the desired site while leaving other functional groups intact remains a significant hurdle for researchers in this field.
Furthermore, the potential for side reactions, such as transesterification or hydrolysis of the ester group under the reaction conditions typically employed in cross-coupling reactions, adds another layer of complexity to the study. These side reactions can compete with the desired cross-coupling pathway, leading to reduced yields and the formation of unwanted byproducts.
The development of efficient and selective catalysts for ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions is an ongoing challenge. While significant progress has been made in catalyst design for traditional cross-coupling substrates, the unique electronic and steric properties of ethyl propanoate require tailored catalytic systems. This necessitates extensive research into ligand design, metal selection, and reaction optimization to achieve high catalytic activity and selectivity.
Another current challenge is the limited scope of coupling partners that have been successfully employed with ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions. Expanding the range of viable coupling partners, including both organometallic reagents and organic electrophiles, is crucial for broadening the synthetic utility of these reactions.
Lastly, the mechanistic understanding of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions remains incomplete. Elucidating the detailed reaction pathways, including the nature of key intermediates and transition states, is essential for rational reaction design and optimization. This challenge is compounded by the difficulty in isolating and characterizing reactive intermediates under the often harsh reaction conditions required for ethyl propanoate activation.
Another major challenge lies in the activation of the C-O bond in ethyl propanoate. Unlike C-X bonds (where X is a halogen) that are typically employed in cross-coupling reactions, the C-O bond is significantly stronger and less polarized. This makes it more difficult to cleave and activate, requiring the development of specialized catalysts and reaction conditions to overcome this energy barrier.
The presence of multiple reactive sites in ethyl propanoate also presents a challenge in terms of regioselectivity. The molecule contains both an ester group and an alkyl chain, each of which can potentially participate in the cross-coupling reaction. Achieving selective activation of the desired site while leaving other functional groups intact remains a significant hurdle for researchers in this field.
Furthermore, the potential for side reactions, such as transesterification or hydrolysis of the ester group under the reaction conditions typically employed in cross-coupling reactions, adds another layer of complexity to the study. These side reactions can compete with the desired cross-coupling pathway, leading to reduced yields and the formation of unwanted byproducts.
The development of efficient and selective catalysts for ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions is an ongoing challenge. While significant progress has been made in catalyst design for traditional cross-coupling substrates, the unique electronic and steric properties of ethyl propanoate require tailored catalytic systems. This necessitates extensive research into ligand design, metal selection, and reaction optimization to achieve high catalytic activity and selectivity.
Another current challenge is the limited scope of coupling partners that have been successfully employed with ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions. Expanding the range of viable coupling partners, including both organometallic reagents and organic electrophiles, is crucial for broadening the synthetic utility of these reactions.
Lastly, the mechanistic understanding of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions remains incomplete. Elucidating the detailed reaction pathways, including the nature of key intermediates and transition states, is essential for rational reaction design and optimization. This challenge is compounded by the difficulty in isolating and characterizing reactive intermediates under the often harsh reaction conditions required for ethyl propanoate activation.
Existing Methodologies
01 Synthesis and preparation methods
Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions between propionic acid and ethanol, as well as catalytic processes. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and purification techniques to optimize yield and purity.- Synthesis and preparation methods: Various methods for synthesizing ethyl propanoate are described, including esterification reactions between propionic acid and ethanol, as well as catalytic processes. These methods often involve the use of specific catalysts, reaction conditions, and purification techniques to optimize yield and purity.
- Chemical properties and reactivity: Ethyl propanoate exhibits characteristic reactivity as an ester, including hydrolysis, transesterification, and reduction reactions. Its reactivity is influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of catalysts. Understanding these properties is crucial for its application in various chemical processes.
- Industrial applications: Ethyl propanoate finds applications in various industries, including flavors and fragrances, solvents, and as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Its use in these applications is based on its specific chemical properties and reactivity profile.
- Analytical methods and characterization: Various analytical techniques are employed to characterize ethyl propanoate and monitor its reactions. These may include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and other instrumental analyses. Such methods are crucial for quality control and understanding the compound's behavior in different reaction environments.
- Safety and environmental considerations: The handling, storage, and disposal of ethyl propanoate require specific safety measures due to its flammability and potential environmental impact. Proper risk assessment and management strategies are necessary when working with this compound in industrial or laboratory settings.
02 Applications in chemical industry
Ethyl propanoate finds applications in various industrial processes, such as solvent production, flavor and fragrance manufacturing, and as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. Its reactivity and properties make it suitable for use in diverse chemical reactions and formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reactivity in organic transformations
The reactivity of ethyl propanoate is explored in various organic transformations, including hydrolysis, transesterification, and reduction reactions. Its behavior as an ester in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions is also discussed, highlighting its versatility in organic synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions04 Physical and chemical properties
The physical and chemical properties of ethyl propanoate are described, including its boiling point, solubility, and stability under different conditions. These properties influence its reactivity and handling in various applications and chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and environmental considerations
Safety measures and environmental considerations related to the use and handling of ethyl propanoate are discussed. This includes information on its flammability, toxicity, and potential environmental impact, as well as recommended storage and disposal practices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The study of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions is currently in an emerging phase, with growing interest from both academia and industry. The market for this research area is relatively small but expanding, driven by the potential applications in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical development. The technology is still in its early stages of maturity, with ongoing research efforts focused on improving reaction efficiency and expanding substrate scope. Key players in this field include academic institutions like Yale University and the University of Strasbourg, as well as chemical companies such as BASF Corp. and Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. These organizations are actively contributing to the advancement of cross-coupling methodologies involving ethyl propanoate, with a focus on developing more sustainable and economically viable processes for chemical synthesis.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed innovative catalytic systems for cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate. Their approach utilizes palladium-based catalysts with tailored ligands to enhance reactivity and selectivity. The company has implemented a continuous flow reactor system that allows for precise control of reaction conditions, resulting in improved yields and reduced side products[1]. Sinopec's research has also focused on developing greener methodologies, incorporating bio-based solvents and recyclable catalysts to minimize environmental impact[2]. Their latest advancements include the use of dual catalysis, combining transition metal catalysis with photoredox catalysis to enable previously challenging transformations of ethyl propanoate derivatives[3].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, extensive R&D resources, and integration with petrochemical feedstocks. Weaknesses: Potential environmental concerns and dependence on fossil fuel-based raw materials.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has made significant strides in the study of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions. Their approach focuses on developing highly efficient and selective catalytic systems. BASF has pioneered the use of bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts, which exhibit synergistic effects, leading to enhanced activity and selectivity in cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate[4]. The company has also developed novel ligand architectures that stabilize reactive intermediates and promote challenging C-C bond formations. BASF's research extends to the application of flow chemistry techniques, enabling precise control over reaction parameters and facilitating rapid optimization of reaction conditions[5]. Additionally, they have explored the use of sustainable alternatives, such as bio-derived ethyl propanoate, in their cross-coupling methodologies[6].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in catalyst design and process optimization, strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: High research and development costs, potential regulatory challenges for new chemical processes.
Core Innovations
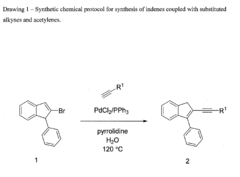
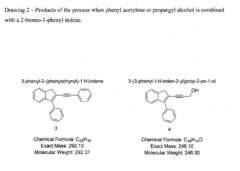
The cross coupling of 2-bromo-1-phenyl indenes with phenyl acetylenes and other substituted acetylenes in water
PatentActiveUS20150291492A1
Innovation
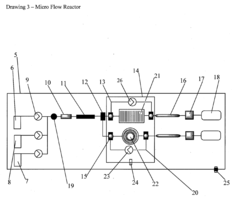
- A chemical process utilizing a palladium salt blend with triphenyl phosphine and pyrrolidine or piperidine in water at 120°C, allowing for the synthesis of alkyne and acetylene cross-coupled products without additives, compatible with both batch and micro flow reactor methods, thereby reducing waste and costs.
Cross-coupling reaction of organosilicon nucleophiles
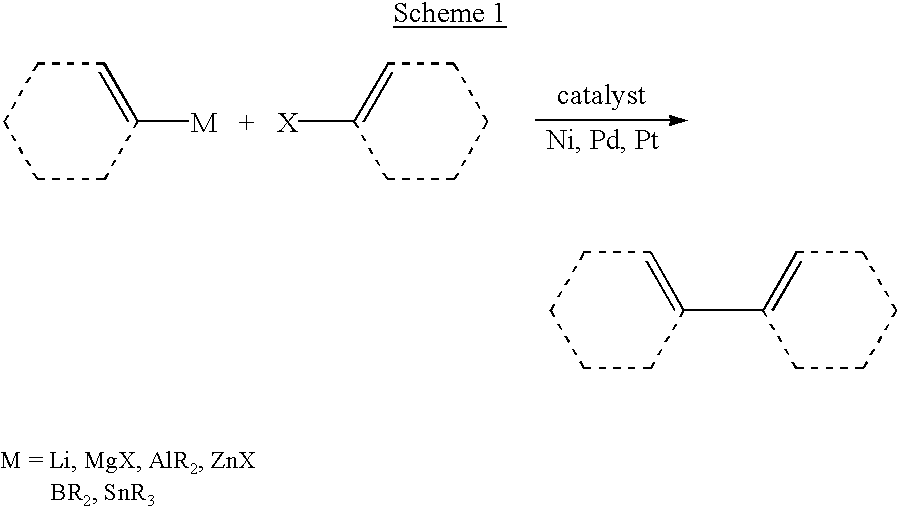
PatentInactiveUS6867323B2
Innovation
- The use of Group 10 transition metal complexes, particularly palladium complexes, with improved organosilicon nucleophiles that are readily prepared and exhibit high stereospecificity, activated by anions such as halide, hydroxide, or hydride ions, to facilitate cross-coupling reactions with organic electrophiles, reducing side-product formation and enhancing reaction efficiency.
Green Chemistry Aspects
Green chemistry principles have become increasingly important in the study of ethyl propanoate reactivity in cross-coupling reactions. This approach aims to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and sustainability in chemical processes. In the context of ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions, several green chemistry aspects have been explored and implemented.
One key focus has been on the development of more environmentally friendly catalysts. Traditional cross-coupling reactions often rely on precious metal catalysts, which can be expensive and pose environmental concerns. Researchers have made significant progress in designing catalytic systems that utilize earth-abundant metals, such as iron or nickel, as alternatives to palladium or platinum. These catalysts not only reduce the environmental footprint but also offer potential cost savings in large-scale applications.
Solvent selection is another critical aspect of green chemistry in ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions. Conventional organic solvents are often toxic, flammable, and difficult to dispose of safely. To address this issue, scientists have investigated the use of greener solvents, including water, ionic liquids, and supercritical carbon dioxide. These alternative solvents can provide a more environmentally benign reaction medium while maintaining or even enhancing reaction efficiency.
Energy efficiency has also been a focus of green chemistry efforts in this field. Researchers have explored various methods to reduce energy consumption during cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate. This includes the development of room-temperature protocols, microwave-assisted reactions, and flow chemistry techniques. These approaches not only minimize energy use but can also lead to faster reaction times and improved yields.
The principles of atom economy and waste reduction have been applied to optimize the reactivity of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions. Scientists have worked on developing more selective and efficient reaction pathways that maximize the incorporation of reactants into the final product while minimizing byproduct formation. This not only improves the overall sustainability of the process but can also simplify purification steps and reduce the need for extensive waste treatment.
Lastly, the use of renewable feedstocks has been explored as a means to enhance the green chemistry profile of ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions. Researchers have investigated the potential of bio-based starting materials and reagents derived from sustainable sources. This approach aligns with the broader goals of reducing dependence on fossil fuel-derived chemicals and moving towards a more circular economy in the chemical industry.
One key focus has been on the development of more environmentally friendly catalysts. Traditional cross-coupling reactions often rely on precious metal catalysts, which can be expensive and pose environmental concerns. Researchers have made significant progress in designing catalytic systems that utilize earth-abundant metals, such as iron or nickel, as alternatives to palladium or platinum. These catalysts not only reduce the environmental footprint but also offer potential cost savings in large-scale applications.
Solvent selection is another critical aspect of green chemistry in ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions. Conventional organic solvents are often toxic, flammable, and difficult to dispose of safely. To address this issue, scientists have investigated the use of greener solvents, including water, ionic liquids, and supercritical carbon dioxide. These alternative solvents can provide a more environmentally benign reaction medium while maintaining or even enhancing reaction efficiency.
Energy efficiency has also been a focus of green chemistry efforts in this field. Researchers have explored various methods to reduce energy consumption during cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate. This includes the development of room-temperature protocols, microwave-assisted reactions, and flow chemistry techniques. These approaches not only minimize energy use but can also lead to faster reaction times and improved yields.
The principles of atom economy and waste reduction have been applied to optimize the reactivity of ethyl propanoate in cross-coupling reactions. Scientists have worked on developing more selective and efficient reaction pathways that maximize the incorporation of reactants into the final product while minimizing byproduct formation. This not only improves the overall sustainability of the process but can also simplify purification steps and reduce the need for extensive waste treatment.
Lastly, the use of renewable feedstocks has been explored as a means to enhance the green chemistry profile of ethyl propanoate cross-coupling reactions. Researchers have investigated the potential of bio-based starting materials and reagents derived from sustainable sources. This approach aligns with the broader goals of reducing dependence on fossil fuel-derived chemicals and moving towards a more circular economy in the chemical industry.
Scalability Considerations
When considering the scalability of cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate, several key factors come into play. The transition from laboratory-scale experiments to industrial-scale production presents both challenges and opportunities. One of the primary considerations is the reaction kinetics and how they may be affected by increased volumes and concentrations. As the scale increases, heat transfer and mixing efficiency become critical parameters that need to be carefully managed to maintain reaction performance and yield.
The choice of catalyst and ligand systems also plays a crucial role in scalability. While certain catalysts may perform exceptionally well at small scales, their effectiveness and stability may be compromised in larger reactors. It is essential to evaluate the robustness of the catalytic system under prolonged reaction times and higher temperatures that are often associated with scaled-up processes. Additionally, the cost and availability of catalysts at industrial scales must be factored into the overall economic viability of the process.
Solvent selection is another vital aspect of scalability. The ideal solvent for a laboratory-scale reaction may not be suitable for large-scale production due to safety concerns, cost, or environmental regulations. Exploring alternative solvents or even solvent-free conditions could be beneficial for improving the scalability and sustainability of the process. Furthermore, the potential for solvent recycling and recovery should be assessed to minimize waste and reduce operational costs.
Process safety is paramount when scaling up cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate. The flammability and volatility of the compound necessitate stringent safety measures, including proper ventilation, temperature control, and pressure management. Risk assessments must be conducted to identify potential hazards associated with larger quantities of reagents and products, and appropriate mitigation strategies should be implemented.
Purification and isolation of the final product present additional scalability challenges. Techniques that are effective at small scales, such as column chromatography, may not be practical or economically feasible at industrial scales. Developing efficient and cost-effective purification methods, such as crystallization or distillation, is crucial for successful scale-up. The potential for continuous flow processes should also be explored, as they can offer advantages in terms of heat transfer, mixing, and overall process control.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of the scaled-up process must be carefully evaluated. This includes assessing the atom economy, reducing waste generation, and optimizing energy consumption. Implementing green chemistry principles and exploring bio-based alternatives for reagents or catalysts could enhance the overall sustainability and scalability of cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate.
The choice of catalyst and ligand systems also plays a crucial role in scalability. While certain catalysts may perform exceptionally well at small scales, their effectiveness and stability may be compromised in larger reactors. It is essential to evaluate the robustness of the catalytic system under prolonged reaction times and higher temperatures that are often associated with scaled-up processes. Additionally, the cost and availability of catalysts at industrial scales must be factored into the overall economic viability of the process.
Solvent selection is another vital aspect of scalability. The ideal solvent for a laboratory-scale reaction may not be suitable for large-scale production due to safety concerns, cost, or environmental regulations. Exploring alternative solvents or even solvent-free conditions could be beneficial for improving the scalability and sustainability of the process. Furthermore, the potential for solvent recycling and recovery should be assessed to minimize waste and reduce operational costs.
Process safety is paramount when scaling up cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate. The flammability and volatility of the compound necessitate stringent safety measures, including proper ventilation, temperature control, and pressure management. Risk assessments must be conducted to identify potential hazards associated with larger quantities of reagents and products, and appropriate mitigation strategies should be implemented.
Purification and isolation of the final product present additional scalability challenges. Techniques that are effective at small scales, such as column chromatography, may not be practical or economically feasible at industrial scales. Developing efficient and cost-effective purification methods, such as crystallization or distillation, is crucial for successful scale-up. The potential for continuous flow processes should also be explored, as they can offer advantages in terms of heat transfer, mixing, and overall process control.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of the scaled-up process must be carefully evaluated. This includes assessing the atom economy, reducing waste generation, and optimizing energy consumption. Implementing green chemistry principles and exploring bio-based alternatives for reagents or catalysts could enhance the overall sustainability and scalability of cross-coupling reactions involving ethyl propanoate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!