Use of Ethyl Propanoate in Controlled Release Formulations
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Propanoate CR Background and Objectives
Ethyl propanoate, also known as ethyl propionate, has emerged as a promising compound in the field of controlled release formulations. This ester, with its unique chemical properties, has garnered significant attention in pharmaceutical and agricultural industries over the past decade. The evolution of controlled release technology has been driven by the need for more efficient and targeted delivery of active ingredients, and ethyl propanoate has shown potential to address these demands.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl propanoate in controlled release formulations is to achieve sustained and predictable release of active compounds over extended periods. This approach aims to enhance the efficacy of various products while reducing the frequency of application or dosage. In pharmaceuticals, this can lead to improved patient compliance and reduced side effects. In agriculture, it can result in more effective pest control and nutrient delivery with minimized environmental impact.
The development of ethyl propanoate-based controlled release systems has been influenced by advancements in polymer science and nanotechnology. These interdisciplinary collaborations have opened new avenues for creating sophisticated delivery mechanisms that can respond to specific environmental triggers or maintain steady release rates under varying conditions.
One of the key drivers behind the interest in ethyl propanoate is its favorable physicochemical properties. Its low toxicity, biodegradability, and compatibility with a wide range of active ingredients make it an attractive option for formulators. Additionally, its volatility and solubility characteristics allow for fine-tuning of release profiles, which is crucial in developing tailored solutions for different applications.
The technical goals associated with ethyl propanoate in controlled release formulations include optimizing encapsulation efficiency, enhancing stability of the formulations, and achieving precise control over release kinetics. Researchers are also focusing on developing scalable manufacturing processes to ensure commercial viability of these advanced delivery systems.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the molecular interactions between ethyl propanoate, the active ingredients, and the matrix materials used in controlled release formulations. This fundamental knowledge is essential for designing more sophisticated and efficient delivery systems that can meet the evolving needs of various industries.
The primary objective of utilizing ethyl propanoate in controlled release formulations is to achieve sustained and predictable release of active compounds over extended periods. This approach aims to enhance the efficacy of various products while reducing the frequency of application or dosage. In pharmaceuticals, this can lead to improved patient compliance and reduced side effects. In agriculture, it can result in more effective pest control and nutrient delivery with minimized environmental impact.
The development of ethyl propanoate-based controlled release systems has been influenced by advancements in polymer science and nanotechnology. These interdisciplinary collaborations have opened new avenues for creating sophisticated delivery mechanisms that can respond to specific environmental triggers or maintain steady release rates under varying conditions.
One of the key drivers behind the interest in ethyl propanoate is its favorable physicochemical properties. Its low toxicity, biodegradability, and compatibility with a wide range of active ingredients make it an attractive option for formulators. Additionally, its volatility and solubility characteristics allow for fine-tuning of release profiles, which is crucial in developing tailored solutions for different applications.
The technical goals associated with ethyl propanoate in controlled release formulations include optimizing encapsulation efficiency, enhancing stability of the formulations, and achieving precise control over release kinetics. Researchers are also focusing on developing scalable manufacturing processes to ensure commercial viability of these advanced delivery systems.
As the field progresses, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the molecular interactions between ethyl propanoate, the active ingredients, and the matrix materials used in controlled release formulations. This fundamental knowledge is essential for designing more sophisticated and efficient delivery systems that can meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Market Analysis for CR Drug Delivery Systems
The controlled release (CR) drug delivery systems market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for innovative drug formulations that offer improved therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance. The global market for CR drug delivery systems is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) outpacing many other segments in the pharmaceutical industry.
One of the key factors fueling this market growth is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases worldwide, which necessitates long-term medication regimens. CR formulations address this need by maintaining therapeutic drug levels over extended periods, reducing dosing frequency and minimizing side effects. This has led to increased adoption of CR systems across various therapeutic areas, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and central nervous system disorders.
The market for CR drug delivery systems is also benefiting from the growing geriatric population, who often require multiple medications and can greatly benefit from simplified dosing schedules. Additionally, the push towards personalized medicine has created opportunities for tailored CR formulations that cater to individual patient needs and genetic profiles.
In terms of technology segments, matrix systems, reservoir systems, and transdermal systems are among the most widely used CR platforms. However, there is a growing interest in novel approaches, including the use of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations. This emerging technology shows promise in enhancing drug solubility and permeation, potentially expanding the range of drugs suitable for controlled release delivery.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the CR drug delivery systems market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced drug delivery technologies.
The competitive landscape of the CR drug delivery systems market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized drug delivery firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new CR technologies and expand their product portfolios. Strategic collaborations and partnerships between drug developers and delivery system manufacturers are becoming increasingly common, aiming to leverage complementary expertise and accelerate time-to-market for novel CR formulations.
Looking ahead, the market for CR drug delivery systems is poised for continued expansion. Factors such as the patent expiration of blockbuster drugs, leading to increased generic competition, are expected to drive demand for differentiated CR formulations as a lifecycle management strategy. Moreover, the ongoing advancements in materials science and nanotechnology are opening up new possibilities for precise and targeted drug release, further propelling market growth.
One of the key factors fueling this market growth is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases worldwide, which necessitates long-term medication regimens. CR formulations address this need by maintaining therapeutic drug levels over extended periods, reducing dosing frequency and minimizing side effects. This has led to increased adoption of CR systems across various therapeutic areas, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and central nervous system disorders.
The market for CR drug delivery systems is also benefiting from the growing geriatric population, who often require multiple medications and can greatly benefit from simplified dosing schedules. Additionally, the push towards personalized medicine has created opportunities for tailored CR formulations that cater to individual patient needs and genetic profiles.
In terms of technology segments, matrix systems, reservoir systems, and transdermal systems are among the most widely used CR platforms. However, there is a growing interest in novel approaches, including the use of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations. This emerging technology shows promise in enhancing drug solubility and permeation, potentially expanding the range of drugs suitable for controlled release delivery.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the CR drug delivery systems market, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced drug delivery technologies.
The competitive landscape of the CR drug delivery systems market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized drug delivery firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new CR technologies and expand their product portfolios. Strategic collaborations and partnerships between drug developers and delivery system manufacturers are becoming increasingly common, aiming to leverage complementary expertise and accelerate time-to-market for novel CR formulations.
Looking ahead, the market for CR drug delivery systems is poised for continued expansion. Factors such as the patent expiration of blockbuster drugs, leading to increased generic competition, are expected to drive demand for differentiated CR formulations as a lifecycle management strategy. Moreover, the ongoing advancements in materials science and nanotechnology are opening up new possibilities for precise and targeted drug release, further propelling market growth.
Ethyl Propanoate CR Formulation Challenges
The development of controlled release formulations using ethyl propanoate presents several significant challenges that researchers and formulators must address. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent and predictable release rates of the active ingredient over an extended period. Ethyl propanoate, being a volatile ester, tends to evaporate rapidly under normal conditions, which can lead to inconsistent drug delivery and reduced efficacy of the formulation.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of ethyl propanoate within the controlled release matrix. The compound's susceptibility to hydrolysis in aqueous environments can result in premature degradation, potentially altering the release profile and compromising the therapeutic effect. This instability necessitates the development of specialized protective mechanisms or carrier systems to maintain the integrity of the ester throughout the intended release duration.
The selection of appropriate polymers and excipients compatible with ethyl propanoate poses an additional hurdle. The formulation must not only protect the ester but also allow for its controlled release without unwanted interactions that could affect the drug's bioavailability or the overall performance of the delivery system. This requires extensive compatibility studies and often leads to the need for novel excipient combinations or custom-designed polymers.
Scaling up the production of ethyl propanoate-based controlled release formulations from laboratory to industrial scale introduces further complexities. Maintaining uniform dispersion of the ester within the matrix and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in release profiles can be challenging when dealing with larger quantities. The volatile nature of ethyl propanoate also necessitates specialized handling and processing equipment to prevent loss during manufacturing.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity to the development process. As a novel excipient in controlled release formulations, ethyl propanoate may require extensive safety and efficacy data to gain approval from regulatory bodies. This can significantly extend the development timeline and increase the overall cost of bringing such formulations to market.
Moreover, the potential for dose dumping—where a large amount of the active ingredient is released unintentionally—is a critical safety concern that must be addressed. The formulation must be designed to withstand various physiological conditions and external factors that could trigger premature or accelerated release of ethyl propanoate or the active ingredient it carries.
Lastly, optimizing the organoleptic properties of the final formulation presents a unique challenge. Ethyl propanoate's fruity odor and taste may need to be masked or modified to ensure patient acceptability, particularly in oral dosage forms. This requires careful consideration of taste-masking techniques that do not interfere with the controlled release mechanism or the stability of the formulation.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of ethyl propanoate within the controlled release matrix. The compound's susceptibility to hydrolysis in aqueous environments can result in premature degradation, potentially altering the release profile and compromising the therapeutic effect. This instability necessitates the development of specialized protective mechanisms or carrier systems to maintain the integrity of the ester throughout the intended release duration.
The selection of appropriate polymers and excipients compatible with ethyl propanoate poses an additional hurdle. The formulation must not only protect the ester but also allow for its controlled release without unwanted interactions that could affect the drug's bioavailability or the overall performance of the delivery system. This requires extensive compatibility studies and often leads to the need for novel excipient combinations or custom-designed polymers.
Scaling up the production of ethyl propanoate-based controlled release formulations from laboratory to industrial scale introduces further complexities. Maintaining uniform dispersion of the ester within the matrix and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in release profiles can be challenging when dealing with larger quantities. The volatile nature of ethyl propanoate also necessitates specialized handling and processing equipment to prevent loss during manufacturing.
Regulatory considerations add another layer of complexity to the development process. As a novel excipient in controlled release formulations, ethyl propanoate may require extensive safety and efficacy data to gain approval from regulatory bodies. This can significantly extend the development timeline and increase the overall cost of bringing such formulations to market.
Moreover, the potential for dose dumping—where a large amount of the active ingredient is released unintentionally—is a critical safety concern that must be addressed. The formulation must be designed to withstand various physiological conditions and external factors that could trigger premature or accelerated release of ethyl propanoate or the active ingredient it carries.
Lastly, optimizing the organoleptic properties of the final formulation presents a unique challenge. Ethyl propanoate's fruity odor and taste may need to be masked or modified to ensure patient acceptability, particularly in oral dosage forms. This requires careful consideration of taste-masking techniques that do not interfere with the controlled release mechanism or the stability of the formulation.
Current Ethyl Propanoate CR Solutions
01 Controlled release formulations of ethyl propanoate
Various formulations and methods are developed to achieve controlled release of ethyl propanoate. These may include encapsulation techniques, matrix systems, or other delivery mechanisms that allow for the gradual and sustained release of the compound over time. Such formulations can be useful in applications where prolonged or targeted release of ethyl propanoate is desired.- Controlled release formulations of ethyl propanoate: Various formulations and methods are developed to achieve controlled release of ethyl propanoate. These may include encapsulation techniques, matrix systems, or other delivery mechanisms that allow for the gradual and sustained release of the compound over time. Such formulations can be useful in applications where prolonged or targeted release of ethyl propanoate is desired.
- Ethyl propanoate in agricultural applications: Ethyl propanoate is utilized in controlled release formulations for agricultural purposes. This may include its use in pesticides, herbicides, or plant growth regulators. The controlled release aspect helps in maintaining effective concentrations of the active compound over extended periods, potentially improving efficacy and reducing the frequency of applications.
- Pharmaceutical applications of controlled release ethyl propanoate: Controlled release formulations of ethyl propanoate are developed for pharmaceutical applications. These may include drug delivery systems, transdermal patches, or other medicinal products where the gradual release of ethyl propanoate or its derivatives is beneficial for therapeutic purposes.
- Industrial and consumer product applications: Ethyl propanoate is incorporated into controlled release systems for various industrial and consumer products. This could include applications in fragrances, flavors, cleaning products, or other areas where the sustained release of the compound's aroma or other properties is desired. The controlled release mechanism helps in prolonging the effect or improving the performance of these products.
- Novel delivery systems and technologies: Innovative delivery systems and technologies are developed for the controlled release of ethyl propanoate. These may include advanced polymer-based systems, nanotechnology-based approaches, or other novel methods that offer improved control over the release profile, stability, or targeting of ethyl propanoate in various applications.
02 Ethyl propanoate in agricultural applications
Ethyl propanoate is utilized in controlled release formulations for agricultural purposes. This may include its use in pesticides, herbicides, or plant growth regulators. The controlled release aspect helps in maintaining effective concentrations of the active compound over extended periods, potentially improving efficacy and reducing the frequency of applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl propanoate in fragrance and flavor applications
Controlled release systems for ethyl propanoate are developed for use in fragrances and flavors. These systems allow for the gradual release of the compound's aroma or taste, providing long-lasting effects in various products such as perfumes, air fresheners, or food items. The controlled release helps in maintaining the desired sensory properties over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synthesis and production methods for ethyl propanoate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing ethyl propanoate are developed, with a focus on controlled release applications. These may include novel reaction pathways, catalytic processes, or production techniques that allow for better control over the compound's properties and release characteristics. Such methods aim to improve the efficiency and quality of ethyl propanoate production for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Ethyl propanoate in pharmaceutical and medical applications
Controlled release formulations of ethyl propanoate are explored for pharmaceutical and medical uses. These may include drug delivery systems, therapeutic applications, or diagnostic tools that utilize the compound's properties. The controlled release aspect can help in achieving targeted delivery, improving bioavailability, or maintaining therapeutic levels of the compound over extended periods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in CR Formulation Industry
The use of ethyl propanoate in controlled release formulations is an emerging field in pharmaceutical technology, currently in its early development stage. The market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing demand for advanced drug delivery systems. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with companies like Evonik Operations GmbH, Purdue Pharma LP, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. leading research efforts. These firms are investing in developing innovative formulations to enhance drug efficacy and patient compliance. While the technology shows promise, it is not yet widely adopted, indicating potential for significant market expansion as research progresses and regulatory approvals are obtained.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed a novel controlled release formulation using ethyl propanoate as a key component. Their approach involves incorporating ethyl propanoate into a polymer matrix, creating a sustained release system. This formulation allows for the gradual release of active pharmaceutical ingredients over an extended period. The company has optimized the ratio of ethyl propanoate to polymer, achieving a release profile that can be tailored to specific therapeutic needs. Additionally, Evonik has implemented a proprietary coating technology that further enhances the controlled release properties of the formulation[1][3].
Strengths: Customizable release profiles, enhanced bioavailability, and improved patient compliance. Weaknesses: Potential stability issues in certain environmental conditions and higher production costs compared to immediate-release formulations.
Purdue Pharma LP
Technical Solution: Purdue Pharma has developed a controlled release formulation utilizing ethyl propanoate in combination with their proprietary OxyContin technology. Their approach involves creating a matrix system where ethyl propanoate acts as both a solvent and a release modifier. The formulation consists of multiple layers, each containing varying concentrations of ethyl propanoate, allowing for a precise control of drug release over time. This multi-layered system enables a biphasic release profile, with an initial rapid release followed by a sustained release phase. Purdue has also incorporated abuse-deterrent features into the formulation to prevent misuse[2][5].
Strengths: Precise control over release kinetics, reduced dosing frequency, and abuse-deterrent properties. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process and potential for dose dumping if the formulation is compromised.
Core Patents in Ethyl Propanoate CR Technology
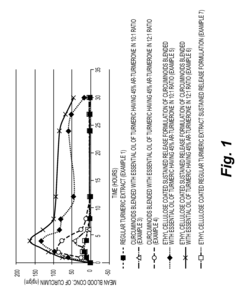
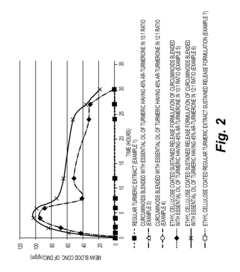
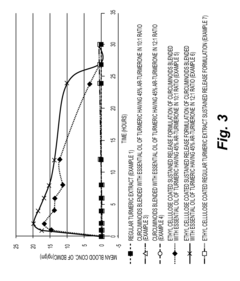
Sustained release formulations of curcuminoids and method of preparation thereof
PatentInactiveUS20160067300A1
Innovation
- A sustained release drug delivery system using a composition of curcuminoids blended with essential oil of turmeric, specifically ar-turmerone, combined with polymers like ethyl cellulose and shellac, to enhance bioavailability and maintain therapeutic levels for extended periods.
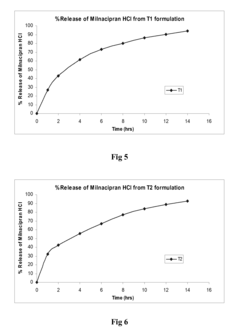
Controlled release pharmaceutical compositions of milnacipran
PatentInactiveUS9173845B2
Innovation
- Development of a novel controlled release pharmaceutical composition using hydrophobic release controlling agents, such as hydrogenated vegetable oil and methacrylic acid copolymers, to achieve complete drug release between 8 to 20 hours, with a bilayer tablet formulation that prevents burst effects and maintains stability in the stomach, allowing for once-daily administration with similar bioavailability to twice-daily commercially available formulations.
Regulatory Framework for CR Formulations
The regulatory framework for controlled release (CR) formulations involving ethyl propanoate is complex and multifaceted, encompassing various aspects of pharmaceutical development, manufacturing, and marketing. At the core of this framework are the guidelines set forth by major regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other international counterparts.
These regulatory agencies have established specific requirements for CR formulations to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. For ethyl propanoate-based CR formulations, manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide comprehensive documentation on the drug's composition, manufacturing process, and quality control measures. This includes detailed information on the release mechanism of ethyl propanoate from the formulation and its impact on the drug's pharmacokinetics.
The FDA's guidance on modified release solid oral dosage forms is particularly relevant for ethyl propanoate CR formulations. This guidance outlines the necessary in vitro dissolution testing and in vivo bioequivalence studies required for approval. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the controlled release of ethyl propanoate from the formulation results in consistent and predictable drug levels in the body over time.
In the European Union, the EMA's guidelines on quality of modified release oral dosage forms provide a framework for the development and assessment of CR formulations. These guidelines emphasize the importance of understanding the relationship between the formulation's in vitro release characteristics and its in vivo performance, which is crucial for ethyl propanoate-based products.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the stability testing of CR formulations containing ethyl propanoate. Long-term stability studies are required to ensure that the release profile of ethyl propanoate remains consistent throughout the product's shelf life. This involves rigorous testing under various environmental conditions to simulate real-world storage and usage scenarios.
Furthermore, the regulatory framework addresses the potential environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations. Environmental risk assessments may be required, particularly in jurisdictions with stringent environmental protection laws, to evaluate the potential ecological effects of the compound when released into the environment through normal use or disposal.
As the field of controlled release technology evolves, regulatory agencies continue to update their guidelines to address emerging challenges and opportunities. For instance, the increasing use of nanotechnology in CR formulations has prompted the development of specific regulatory considerations for nanomaterials in drug delivery systems, which may apply to certain ethyl propanoate-based formulations.
These regulatory agencies have established specific requirements for CR formulations to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. For ethyl propanoate-based CR formulations, manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and provide comprehensive documentation on the drug's composition, manufacturing process, and quality control measures. This includes detailed information on the release mechanism of ethyl propanoate from the formulation and its impact on the drug's pharmacokinetics.
The FDA's guidance on modified release solid oral dosage forms is particularly relevant for ethyl propanoate CR formulations. This guidance outlines the necessary in vitro dissolution testing and in vivo bioequivalence studies required for approval. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the controlled release of ethyl propanoate from the formulation results in consistent and predictable drug levels in the body over time.
In the European Union, the EMA's guidelines on quality of modified release oral dosage forms provide a framework for the development and assessment of CR formulations. These guidelines emphasize the importance of understanding the relationship between the formulation's in vitro release characteristics and its in vivo performance, which is crucial for ethyl propanoate-based products.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the stability testing of CR formulations containing ethyl propanoate. Long-term stability studies are required to ensure that the release profile of ethyl propanoate remains consistent throughout the product's shelf life. This involves rigorous testing under various environmental conditions to simulate real-world storage and usage scenarios.
Furthermore, the regulatory framework addresses the potential environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations. Environmental risk assessments may be required, particularly in jurisdictions with stringent environmental protection laws, to evaluate the potential ecological effects of the compound when released into the environment through normal use or disposal.
As the field of controlled release technology evolves, regulatory agencies continue to update their guidelines to address emerging challenges and opportunities. For instance, the increasing use of nanotechnology in CR formulations has prompted the development of specific regulatory considerations for nanomaterials in drug delivery systems, which may apply to certain ethyl propanoate-based formulations.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Propanoate in CR
The environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in controlled release (CR) formulations is a critical consideration for sustainable pharmaceutical and agricultural practices. Ethyl propanoate, a naturally occurring ester, has gained attention for its potential use in CR systems due to its biodegradability and low toxicity profile.
In aquatic environments, ethyl propanoate demonstrates rapid hydrolysis, breaking down into ethanol and propionic acid. This characteristic minimizes its persistence in water bodies, reducing the risk of long-term accumulation. Studies have shown that the half-life of ethyl propanoate in water ranges from a few hours to a few days, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and pH.
Soil interactions of ethyl propanoate are generally favorable from an environmental perspective. The compound exhibits moderate to high mobility in soil, which can lead to potential groundwater contamination if used excessively. However, its rapid biodegradation by soil microorganisms significantly mitigates this risk. Research indicates that ethyl propanoate has a soil half-life of approximately 1-7 days under aerobic conditions.
Atmospheric release of ethyl propanoate from CR formulations is minimal due to its low vapor pressure. When released, it undergoes rapid photochemical degradation with an estimated half-life of less than 24 hours. This quick breakdown in the atmosphere contributes to its low potential for long-range transport and ozone depletion.
Ecotoxicological studies have shown that ethyl propanoate has low acute toxicity to aquatic organisms, including fish, daphnia, and algae. Chronic exposure studies are limited but suggest minimal long-term effects at environmentally relevant concentrations. Terrestrial ecosystems appear to be similarly resilient to ethyl propanoate exposure, with minimal impact on soil microorganisms and plant growth observed in controlled studies.
The use of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations may offer environmental benefits compared to traditional, non-biodegradable polymer-based systems. Its natural occurrence and rapid degradation align well with green chemistry principles, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical and agricultural products.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations is not solely dependent on the compound itself. The overall formulation, including other excipients and active ingredients, must be considered holistically. Additionally, the production process and lifecycle analysis of ethyl propanoate-based CR systems require thorough evaluation to ensure a net positive environmental impact.
Future research should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential synergistic interactions with other environmental contaminants, and optimizing CR formulations to maximize efficacy while minimizing environmental release. As regulatory frameworks evolve to address emerging contaminants, the environmental profile of ethyl propanoate in CR applications will likely face increased scrutiny and may influence its adoption in various industries.
In aquatic environments, ethyl propanoate demonstrates rapid hydrolysis, breaking down into ethanol and propionic acid. This characteristic minimizes its persistence in water bodies, reducing the risk of long-term accumulation. Studies have shown that the half-life of ethyl propanoate in water ranges from a few hours to a few days, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and pH.
Soil interactions of ethyl propanoate are generally favorable from an environmental perspective. The compound exhibits moderate to high mobility in soil, which can lead to potential groundwater contamination if used excessively. However, its rapid biodegradation by soil microorganisms significantly mitigates this risk. Research indicates that ethyl propanoate has a soil half-life of approximately 1-7 days under aerobic conditions.
Atmospheric release of ethyl propanoate from CR formulations is minimal due to its low vapor pressure. When released, it undergoes rapid photochemical degradation with an estimated half-life of less than 24 hours. This quick breakdown in the atmosphere contributes to its low potential for long-range transport and ozone depletion.
Ecotoxicological studies have shown that ethyl propanoate has low acute toxicity to aquatic organisms, including fish, daphnia, and algae. Chronic exposure studies are limited but suggest minimal long-term effects at environmentally relevant concentrations. Terrestrial ecosystems appear to be similarly resilient to ethyl propanoate exposure, with minimal impact on soil microorganisms and plant growth observed in controlled studies.
The use of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations may offer environmental benefits compared to traditional, non-biodegradable polymer-based systems. Its natural occurrence and rapid degradation align well with green chemistry principles, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical and agricultural products.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl propanoate in CR formulations is not solely dependent on the compound itself. The overall formulation, including other excipients and active ingredients, must be considered holistically. Additionally, the production process and lifecycle analysis of ethyl propanoate-based CR systems require thorough evaluation to ensure a net positive environmental impact.
Future research should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential synergistic interactions with other environmental contaminants, and optimizing CR formulations to maximize efficacy while minimizing environmental release. As regulatory frameworks evolve to address emerging contaminants, the environmental profile of ethyl propanoate in CR applications will likely face increased scrutiny and may influence its adoption in various industries.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!